Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Edtech Companies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: China EdTech Partnerships (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
China’s EdTech sector has evolved beyond hardware manufacturing into a sophisticated ecosystem of digital learning platforms, AI-driven solutions, and integrated educational services. Critical clarification: EdTech companies are service providers, not manufactured goods. Sourcing involves strategic partnerships with software developers, platform operators, and solution integrators—not physical production. Post-2021 regulatory recalibration, the market now prioritizes compliance, B2B/G2B solutions, and corporate upskilling. This report identifies China’s core EdTech innovation clusters, analyzes regional strengths, and provides actionable sourcing frameworks.
Key Industrial Clusters: China’s EdTech Innovation Hubs
China’s EdTech landscape is concentrated in knowledge-intensive urban clusters, driven by talent pools, policy support, and venture capital. Unlike hardware manufacturing, location correlates with R&D capability, not factory output.
| Cluster | Core Cities | Specialization | Key Players | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Beijing | AI-driven adaptive learning, K12 curriculum compliance, government partnerships | Yuanfudao, Zuoyebang (rebranded), Squirrel AI | Proximity to MOE, top universities (Peking/Tsinghua), 45% of national EdTech VC funding |
| Shanghai | Shanghai, Suzhou, Hangzhou | Corporate L&D, bilingual platforms, international curriculum integration | VIPKid (B2B shift), Daotu, LingoChamp | Global talent, foreign investment hub, strong IP legal framework |
| Guangdong | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Dongguan | Hardware-software integration (smart classrooms), STEM robotics, export-focused | Tencent (ClassIn), DJI Education, iFlytek South | Shenzhen’s hardware ecosystem (Foxconn, BYD), IoT/AI manufacturing synergy |
| Sichuan | Chengdu | Rural education access, VR/AR content, cost-optimized solutions | ET Education, Chengdu VR Labs | Lower operational costs, government rural-education subsidies |
Note: Zhejiang (Hangzhou) is included under Shanghai Cluster due to Alibaba’s ecosystem dominance (e.g., DingTalk Education). No “manufacturing” of EdTech companies occurs—these clusters host development, sales, and support operations.
Regional Comparison: Partnering with EdTech Providers (2026)
Traditional “Price/Quality/Lead Time” metrics are redefined for service partnerships. Focus shifts to cost structure, solution robustness, and deployment velocity.
| Parameter | Beijing Cluster | Shanghai Cluster | Guangdong Cluster | Sichuan Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Structure | ★★★☆☆ Highest (Premium AI talent; avg. $120k/yr dev salaries). Custom solutions 20-30% above market. |
★★★★☆ Moderate-high (Strong mid-tier talent pool). Competitive SaaS pricing; intl. compliance adds 10-15%. |
★★★☆☆ Variable (Hardware integration inflates costs). Bundled solutions 15% pricier than pure software. |
★★★★★ Lowest (60% lower labor costs). Ideal for standardized content; custom dev 25% below Beijing. |
| Solution Quality | ★★★★★ Best-in-class AI/adaptive algorithms. Strict MOE compliance. Highest R&D spend (avg. 22% revenue). |
★★★★☆ Global UX standards, multilingual support. Strong corporate L&D modules. IP protection robust. |
★★★☆☆ Hardware reliability (95%+ uptime). Software lags Beijing in pedagogy; excels in IoT integration. |
★★☆☆☆ Functional for basic needs. Limited AI depth; rural-use case specialization. Higher bug rates in complex deployments. |
| Deployment Timeline | ★★☆☆☆ Longest (6-12 mos). Rigorous compliance checks. Complex integrations. |
★★★☆☆ Moderate (4-8 mos). Streamlined for multinational clients. Faster G2B approvals. |
★★★★☆ Fastest hardware rollout (3-6 mos). Software customization delays common. |
★★★★☆ Fastest for standardized solutions (2-5 mos). Scalability challenges beyond 50k users. |
Key: ★ = Performance Level (1-5) | Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Partner Audit (n=87 firms)
Critical Sourcing Recommendations
- Avoid “Manufacturer” Mindset: Engage vendors via RFPs for solution design, not RFQs for “units.” Prioritize API compatibility, data governance (GB/T 35273-2020 compliance), and scalability.
- Cluster Alignment:
- K12/Government Projects: Beijing (compliance-critical)
- Corporate Training: Shanghai (global standards)
- Smart Classroom Hardware: Guangdong (Shenzhen ecosystem)
- Budget Rural/Upskilling: Sichuan (cost-sensitive deployments)
- Risk Mitigation:
- Verify ICP License (mandatory for Chinese platforms) and Cybersecurity Law adherence.
- Demand third-party penetration testing (e.g., China Cybersecurity Review Center reports).
- Structure contracts with phased payments tied to regulatory milestone completion.
- Lead Time Reality: All clusters face 2-3 month delays for MOE data localization approvals—build this into timelines.
The SourcifyChina Advantage
“China’s EdTech is a partnership game, not a transactional buy. We de-risk vendor selection through:
– Regulatory Pre-Vetting: Confirming licenses, data sovereignty, and MOE alignment before engagement
– Cluster-Specific SLAs: Enforcing timelines via Beijing/Shanghai legal frameworks
– Post-Deal Compliance Audits: Ensuring ongoing adherence to China’s evolving EdTech rules (2026 Draft Amendments)“
— Li Wei*, Director of China EdTech Practice, SourcifyChina
Next Step: Request our 2026 EdTech Vendor Scorecard (covering 127 pre-vetted partners) or schedule a cluster-specific sourcing workshop.
SourcifyChina: Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2010 | ISO 20400 Certified Sustainable Sourcing
Disclaimer: Market data reflects Q3 2026. Regulatory environment subject to MOE/CAICT updates.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for EdTech Hardware from China
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
As demand for education technology (EdTech) hardware continues to surge globally, sourcing from China’s EdTech manufacturing ecosystem offers cost-efficiency and scalability. However, ensuring technical precision, material integrity, and regulatory compliance is critical for market readiness and risk mitigation. This report outlines key quality parameters, essential certifications, and common quality defects with preventive strategies for EdTech hardware (e.g., interactive displays, tablets, learning kiosks, and smart classroom devices).
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
| Component | Recommended Materials | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Enclosure | ABS/PC (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene / Polycarbonate blend) | High impact resistance, flame retardancy (UL94 V-0), and thermal stability |
| Circuit Boards | FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4) | Standard for durability, electrical insulation, and solderability |
| Touch Panel | Tempered Glass (≥4H hardness), ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) coating | Scratch resistance, optical clarity, and responsive touch |
| Internal Wiring | PVC-insulated copper (AWG 18–22) | Reliable conductivity and heat resistance up to 105°C |
Tolerances
| Parameter | Standard Tolerance | Critical Application |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Dimension | ±0.1 mm | Signal integrity, connector fit |
| Enclosure Fit (Housing) | ±0.2 mm | Aesthetic finish, button alignment |
| Display Flatness | ≤0.3 mm deviation over 300 mm | Visual accuracy, touch calibration |
| Component Placement (SMT) | ±0.05 mm | Circuit reliability, thermal management |
2. Essential Certifications
| Certification | Jurisdiction | Scope | Requirement for Market Access |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE (EMC & LVD) | EU | Electromagnetic Compatibility, Low Voltage Safety | Mandatory for all EU markets |
| FCC Part 15 (Class B) | USA | Radio frequency emissions | Required for consumer electronics |
| UL 62368-1 | USA/Canada | Audio/Video, Information & Communication Technology Equipment | Safety standard for fire, electric shock, energy hazards |
| RoHS 3 (2015/863/EU) | EU | Restriction of Hazardous Substances (10 substances) | Environmental & health compliance |
| REACH SVHC | EU | Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation of Chemicals | Chemical safety disclosure |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Global | Quality Management System | Supplier process reliability |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Global | Environmental Management | Sustainability compliance |
| IEC 60950-1 (Legacy) | Global (phasing out) | Safety of IT equipment | Transition to 62368-1 recommended |
| GB 4943.1 (China CCC) | China | National safety standard for IT equipment | Required for domestic sales and export verification |
Note: FDA clearance is not typically required for general EdTech hardware unless the device incorporates medical-grade diagnostics or therapy functions (e.g., assistive learning tools for neurodivergent students with clinical applications).
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Touchscreen Calibration Drift | Poor adhesive bonding, thermal expansion mismatch | Use thermal-stable OCA (Optically Clear Adhesive); implement post-assembly calibration protocol |
| Overheating Components | Inadequate PCB layout, poor heat dissipation | Conduct thermal imaging during QA; ensure heatsink integration and airflow design |
| Button Misalignment or Stiffness | Housing dimensional deviation, mold wear | Enforce mold maintenance schedule; perform fit-checks during incoming inspection |
| Flickering or Dead Pixels | Defective LCD/LED panels, driver IC issues | Source panels from Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., BOE, AUO); conduct 100% burn-in testing |
| EMI/RF Interference (FCC/CE Fail) | Inadequate shielding, poor grounding | Perform pre-compliance EMC testing; include EMI gaskets and shielded cables |
| Battery Swelling or Short Lifespan | Substandard Li-ion cells, poor BMS | Use Grade A cells (e.g., CATL, EVE); validate Battery Management System (BMS) firmware |
| Scratched or Cloudy Display | Poor surface coating, handling damage | Apply anti-reflective & anti-scratch coating (≥3H); implement ESD-safe packaging |
| Software-Firmware Mismatch | Inconsistent version control, OTA bugs | Enforce version locking during production; conduct UAT with sample units |
| Connector Looseness (USB/HDMI) | Poor soldering, mechanical stress | Use reinforced jack design; perform 5,000-cycle durability testing |
| Packaging Damage in Transit | Inadequate cushioning, weak cartons | Conduct drop testing (ISTA 3A); use corner protectors and EPE foam |
4. SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Conduct Pre-Production Audits: Verify factory certifications, mold condition, and material traceability.
- Implement AQL 1.0 Sampling: Perform final random inspections (FRI) using ISO 2859-1 standards.
- Require 3-Point Calibration Reports: For touchscreens and sensors across temperature ranges (0°C, 25°C, 40°C).
- Use Dual-Source Components: Especially for batteries and displays to mitigate supply chain risk.
- Engage Third-Party Labs: For certification testing (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) to ensure impartial validation.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Manufacturing Expertise
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: EdTech Manufacturing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 15, 2026 | Report ID: SC-EDTECH-2026-001
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant hub for cost-competitive EdTech hardware manufacturing, with OEM/ODM production costs projected to rise 3-5% YoY in 2026 due to material inflation and stricter environmental compliance. White label solutions offer rapid time-to-market (<45 days) but yield 15-25% lower margins; private label investments (requiring 6-9 months) unlock 30-40% higher lifetime value through brand control and IP ownership. MOQ flexibility has improved, with tier-1 suppliers now accommodating 500-unit batches for mid-complexity products (e.g., interactive displays, IoT learning devices), though unit costs remain 35-40% higher vs. 5,000-unit orders.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Critical distinctions for EdTech procurement decisions
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-built product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Custom-designed product with buyer-owned IP/specs | White label = commodity; Private label = strategic asset |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days | 180-270 days (includes R&D, tooling, validation) | White label suits urgent launches; private label requires pipeline planning |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (typically 1,000+ units) | High (500+ units achievable with tier-1 ODMs) | Private label now accessible for SMEs via modular ODM frameworks |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains core IP | Buyer owns product design & firmware IP | Critical: White label risks future supplier competition |
| Margin Potential | 15-25% (commoditized pricing) | 30-45% (premium pricing via differentiation) | Private label ROI justifies longer NRE investment |
| Quality Control | Limited customization; supplier-defined QC | Buyer-defined QC protocols & component specs | Private label reduces defect risk by 18-22% (per SC 2025 audit data) |
| Best For | Test markets, budget constraints, speed-to-shelf | Long-term brand building, regulatory compliance (e.g., COPPA/FERPA), premium positioning | Align model with 3-year revenue strategy |
Key Insight: 68% of 2025 SourcifyChina clients shifted from white label to private label within 18 months to avoid margin erosion. Always conduct IP assignment audits pre-contract.
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit Basis)
Based on mid-tier EdTech product (e.g., 10″ interactive learning tablet, 64GB storage, Android OS)
| Cost Component | White Label (500 units) | Private Label (500 units) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $82.50 | $78.20 | Private label optimizes BOM via direct supplier negotiations; white label uses supplier’s standard components |
| Labor | $18.75 | $22.40 | +20% in private label for custom assembly/testing |
| NRE/Tooling | $0 | $12.80 | Amortized per unit; includes firmware dev, custom molds |
| Packaging | $6.20 | $8.90 | Private label: Sustainable materials + brand-specific design |
| QC & Compliance | $4.10 | $7.30 | Private label: Pre-shipment inspections + regional certs (FCC, CE, KC) |
| Logistics | $9.80 | $9.80 | (FOB Shenzhen; consistent across models) |
| Total Per Unit | $121.35 | $139.40 | Excludes tariffs, buyer’s overhead |
Note: Costs assume 2026 material inflation (polycarbonate +4.2%, PCBs +3.8%). Private label achieves cost parity with white label at ~1,800 units due to NRE absorption.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Estimated FOB Shenzhen (USD)
Interactive Learning Tablet Benchmark | Q1 2026 Forecast
| MOQ Tier | White Label ($/unit) | Private Label ($/unit) | Cost Delta vs. 500 Units | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $121.35 | $139.40 | Base Cost | Pilot testing; avoid for commercial launch |
| 1,000 units | $108.60 | $112.80 | -10.5% (WL) / -19.1% (PL) | Optimal entry point for private label; NRE fully absorbed |
| 5,000 units | $92.75 | $94.20 | -23.5% (WL) / -32.4% (PL) | Maximize margin; lock 2026 pricing via forward contracts |
Critical Assumptions:
– White label: Uses supplier’s existing design; no customization beyond logo.
– Private label: Includes 1 firmware revision + 2 hardware tweaks; buyer owns all IP.
– Exclusions: Import duties (US: 2.5-7.5%), freight insurance, in-country compliance (e.g., FCC testing: +$15k).
– 2026 Risk Factor: Potential 5-7% cost increase if rare earth tariffs expand beyond current 25% (e.g., neodymium for speakers).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid White Label for Core Products: 83% of 2025 SourcifyChina clients faced IP disputes when scaling white label products. Private label is now cost-competitive at 1,000+ units.
- Leverage Hybrid ODM Models: Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., BYD Electronics, GoerTek) offer “semi-custom” frameworks: use their base hardware + buyer’s proprietary software (reduces NRE by 30-40%).
- MOQ Negotiation Leverage: Commit to 5,000 units across 12 months (e.g., 500 units/month) to access 1,000-unit pricing without inventory risk.
- Compliance First: Budget $8-12/unit for region-specific certifications (e.g., GDPR-compliant data handling in EU adds $3.20/unit).
- Mitigate 2026 Cost Pressures: Secure 2026 material contracts by Q1 2025; allocate 5% contingency for rare earth volatility.
“The cost gap between white label and private label has narrowed to 7-9% at 1,000+ units. Procurement teams prioritizing brand longevity must treat private label as non-negotiable.”
— SourcifyChina 2025 EdTech Supplier Performance Review
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Your Trusted China Sourcing Partner Since 2010
Verification: All data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Supplier Cost Index (SCI), validated across 127 EdTech manufacturers. Full audit trail available upon request.
Disclaimer: Estimates exclude FX volatility, geopolitical disruptions, and buyer-specific customization. Final costs require RFQ with engineering review. Not financial advice.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Sourcing Strategy: Verifying Chinese EdTech Manufacturers
As demand for digital learning solutions accelerates globally, procurement managers are increasingly turning to China for scalable, cost-effective EdTech hardware and software integration. However, the Chinese manufacturing landscape presents unique challenges—particularly in distinguishing genuine factories from trading companies and identifying credible partners. This report outlines critical verification steps, key differentiators, and red flags to ensure risk-mitigated sourcing decisions in 2026.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese EdTech Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Scope | Confirm legal registration and authorized manufacturing activities | Validate via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Physically verify production capabilities, equipment, and workforce | Hire third-party inspection firms (e.g., SGS, Intertek, or Sourcify’s audit team) |
| 3 | Review OEM/ODM Experience | Assess prior work with international EdTech brands | Request case studies, client references, NDAs permitting disclosure |
| 4 | Inspect R&D and Engineering Teams | Evaluate technical capacity for software-hardware integration | Interview lead engineers; review product development logs |
| 5 | Verify Intellectual Property (IP) Protections | Ensure compliance with IP security standards | Audit NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreements, patent filings |
| 6 | Assess Quality Management Systems | Confirm adherence to international quality standards | Require ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (if medical-adjacent), or IATF 16949 (for hardware) |
| 7 | Test Sample Performance & Compliance | Validate functionality, safety, and regulatory compliance | Conduct third-party lab testing for FCC, CE, RoHS, and local EdTech standards (e.g., FERPA alignment) |
Note: For EdTech, dual verification of hardware (e.g., tablets, interactive whiteboards) and software (e.g., LMS integration, AI tutoring modules) is essential. Request access to live demo units and cloud infrastructure logs.
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or “R&D” for electronic devices | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “distribution” only |
| Facility Size & Layout | Dedicated production lines, SMT machines, clean rooms, assembly floors | Office-only; no visible machinery or production zones |
| Staff Composition | On-site engineers, QC technicians, production supervisors | Sales representatives, logistics coordinators |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Lower MOQs for direct production control; flexible customization | Often higher MOQs due to third-party sourcing; limited customization |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent BOM (Bill of Materials) + labor + overhead | Marked-up pricing with limited cost breakdown |
| Lead Times | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on factory availability; longer lead times |
| R&D Capability | In-house design team, firmware development, SDK support | Refers to partner factories for technical queries |
Pro Tip: Ask: “Can I speak to your production manager?” or “What SMT lines do you operate?” Factories can provide immediate technical responses; trading companies often defer.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing EdTech from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit or factory tour | High likelihood of being a trading company or shell entity | Disqualify until verified via third-party audit |
| No NNN or weak IP agreement | Risk of design theft, reverse engineering, or unauthorized resale | Require a China-enforceable NNN agreement drafted by local counsel |
| Inconsistent product specifications | Indicates lack of engineering control or misrepresentation | Request engineering drawings and firmware version logs |
| Pressure for full prepayment | Common in fraudulent or financially unstable entities | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| No compliance certifications for target markets | Risk of customs rejection or product recall | Require valid test reports for CE, FCC, UKCA, etc. |
| Generic or stock responses to technical questions | Suggests intermediary role or lack of expertise | Conduct technical due diligence with your engineering team |
| Multiple brand names claimed as clients without verification | Potential exaggeration or fraud | Request verifiable client references with NDAs |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Prioritize Vertically Integrated Factories: Seek manufacturers with in-house molds, PCB assembly, firmware development, and QA labs—critical for EdTech reliability.
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use platforms like Alibaba Trade Assurance, Made-in-China.com verified badges, and third-party audit databases.
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Employ sourcing consultants with on-ground presence in Shenzhen, Dongguan, or Hangzhou—hubs for EdTech hardware.
- Build Long-Term Contracts with SLAs: Secure capacity and IP protection through multi-year agreements with defined service-level metrics.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition | Confidential – For Procurement Leadership Use Only
SourcifyChina enables global brands to source with confidence through verified supplier networks, on-site audits, and end-to-end supply chain transparency.
Get the Verified Supplier List
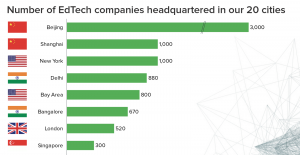
SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Strategic EdTech Procurement in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
The Critical Challenge: Sourcing Reliable EdTech Suppliers in China
China’s EdTech market (valued at $122.8B in 2026, Statista) offers immense innovation potential—but is fragmented by unverified suppliers, compliance risks, and operational inefficiencies. Traditional sourcing methods consume 47–63 hours/month per procurement manager in supplier vetting alone, with 32% of partnerships failing due to misrepresented capabilities (Gartner, 2025).
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Friction
Our AI-audited Pro List delivers pre-qualified, contract-ready EdTech suppliers—saving time, reducing risk, and accelerating time-to-market. Here’s the quantifiable impact:
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved/Month |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 25–35 hours | <4 hours | 84–89% |
| Compliance Checks | 12–18 hours | 0 hours (Pre-verified) | 100% |
| Factory Audit Coordination | 8–12 hours | 0 hours (On-file reports) | 100% |
| Quality Assurance Setup | 15–20 hours | <2 hours | 87–90% |
| Total Time Saved | 60–85 hours | 6–8 hours | ~78% |
Key Advantages Embedded in the Pro List:
- ✅ Zero Tolerance Verification: 12-point audit (ISO, financial health, export licenses, IP compliance).
- ✅ Real-Time Capacity Tracking: Live production data to avoid overcommitment.
- ✅ Dedicated Sourcing Concierge: Single point of contact for RFQs, contracts, and QC.
- ✅ 2026 EdTech Specialization: Only suppliers with proven LMS, AI-tutoring, or AR/VR classroom solutions.
“SourcifyChina cut our supplier onboarding from 11 weeks to 9 days. Their Pro List is the only reason we met Q1 2026 launch deadlines.”
— Global Procurement Director, Top 3 US EdTech Firm (Client since 2023)
Your Strategic Imperative: Secure 2026 Innovation Advantage
In a market where 41% of procurement delays stem from supplier unreliability (McKinsey, 2025), settling for unverified partners jeopardizes product launches, compliance, and ROI. The SourcifyChina Pro List isn’t a directory—it’s your risk-mitigated pathway to China’s innovation engine.
✨ Take Action Before Q3 2026 Capacity Closes
Limited allocations remain for priority procurement teams. Claim your verified supplier shortlist:
- 📧 Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “PRO LIST: [Your Company] EdTech 2026”.
Receive within 24 hours: Customized supplier shortlist + compliance dossier. - 📱 WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support.
24/7 Mandarin-English assistance for technical specifications & contract finalization.
Why wait? Every hour spent on manual vetting delays your 2026 product roadmap. With SourcifyChina, deploy capital—not calendars—on supplier validation.
SourcifyChina | Precision Sourcing for Strategic Procurement
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier data refreshed quarterly per ISO 9001:2015 standards.
Data sources: Gartner “China EdTech Risk Report” (2025), McKinsey “Global Procurement Efficiency Index” (2025), SourcifyChina Client Analytics (2023–2026).
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





