Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Custom Duty On Imports

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Chinese Export Regulations & Optimizing Landed Costs (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | Internal Use Only
Critical Clarification: Understanding “China Customs Duty on Imports”
This report addresses a fundamental misconception in the query. “China Customs Duty on Imports” is not a physical product to be sourced or manufactured. It is a regulatory tax imposed by the importing country’s government (e.g., USA, EU, Japan) on goods entering their territory. China does not “manufacture” or “export” customs duties.
- China’s Role: As the exporting nation, China collects export duties on a very limited number of raw materials (e.g., certain ores, unprocessed timber) to protect domestic supply. These are rare and typically not relevant for finished goods.
- Your Responsibility: As the Importer of Record, your company is liable for import duties/taxes levied by your home country’s customs authority (e.g., CBP in the USA, HMRC in the UK) based on:
- The HS Code classification of the goods.
- The transaction value (FOB/CIF value + freight/insurance).
- Trade agreements (e.g., MFN rates, USMCA, RCEP).
- Country of origin (determined by Rules of Origin).
This report reframes the request: Instead of sourcing “duty,” we provide essential intelligence on how Chinese manufacturing locations impact your total landed cost, including duty implications, and where to source goods subject to duty most efficiently.
Core Insight: Manufacturing Location Directly Impacts Your Duty Calculation & Landed Cost
While China doesn’t “produce” duty, the province/city where your goods are manufactured critically influences:
1. HS Code Accuracy & Classification Risk: Clusters specializing in specific products have suppliers more experienced with correct HS coding (reducing duty overpayment or penalties).
2. Origin Certification: Reliable clusters provide accurate Certificates of Origin (Form F, Form RCEP, etc.), essential for claiming preferential duty rates under trade pacts.
3. Supply Chain Efficiency: Proximity to ports/export hubs reduces freight costs and delays, directly impacting CIF value (the basis for duty calculation).
4. Compliance Risk: Established clusters have better infrastructure for meeting importing country regulations (e.g., FDA, CE), avoiding costly rejections or delays.
Key Industrial Clusters for Major Export Categories (Subject to Import Duty Abroad)
| Product Category (Subject to Import Duty in Target Markets) | Primary Manufacturing Cluster (Province) | Key Cities | Why This Cluster Matters for Your Duty/Landed Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Components | Guangdong | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | Highest HS Code Expertise: Massive ecosystem ensures accurate classification (critical for correct duty rates). Proximity to Shekou/Yantian ports minimizes freight costs. Dominates RCEP origin certification. |
| Machinery & Industrial Equipment | Zhejiang | Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | Specialized Compliance: Strong focus on EU Machinery Directive/CE marking. Ningbo Port (world’s #1 cargo tonnage) offers lowest ocean freight. High rate of Form F (China-ASEAN) certs. |
| Textiles & Apparel | Jiangsu / Zhejiang | Suzhou, Wuxi, Shaoxing | Origin Certification Hub: Largest producer of RCEP Certificates of Origin for apparel. Critical for claiming preferential rates into ASEAN/EU. Mature logistics to Shanghai Port. |
| Furniture & Home Goods | Guangdong / Shandong | Foshan, Shunde, Qingdao | Material Sourcing Advantage: Integrated supply chains (wood, hardware, finishes) lower FOB costs. Qingdao Port key for US West Coast shipments. High risk of misclassification (e.g., wood types) – cluster expertise vital. |
| Automotive Parts | Chongqing / Hubei | Chongqing, Wuhan | OEM Compliance Focus: Deep integration with global auto supply chains ensures adherence to strict origin rules (e.g., USMCA side letters). Critical for avoiding duty spikes due to non-compliance. |
Comparative Analysis: Impact of Manufacturing Region on Landed Cost Components (Ex. Electronics – 40ft Container to USA)
| Factor | Guangdong (Shenzhen) | Zhejiang (Ningbo) | Jiangsu (Suzhou) | Why It Matters for Duty/Landed Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. FOB Price | Competitive (★★★☆☆) | Competitive (★★★☆☆) | Slightly Higher (★★★☆☆) | Lower FOB = Lower CIF Value = Lower Duty Base. Guangdong/Zhejiang offer best price efficiency. |
| Quality Consistency | High (★★★★☆) – Mature QC systems | High (★★★★☆) – Strong engineering focus | Very High (★★★★★) – Precision focus | Fewer defects/rejections = No duty paid on wasted goods. Critical for high-value electronics. |
| Lead Time (Port) | Shortest (10-14 days) – Direct port access | Short (12-16 days) – Efficient port ops | Moderate (14-18 days) – Relies on Shanghai | Shorter lead time = Lower inventory holding costs, faster cash flow. Reduces risk of tariff changes. |
| HS Code Accuracy | Highest (★★★★★) – Vast experience | High (★★★★☆) – Strong compliance culture | High (★★★★☆) – Specialized sectors | Directly determines correct duty rate. Errors cause overpayment (lost savings) or penalties (fines). |
| Origin Certification | Best (RCEP/Form F) (★★★★★) | Excellent (RCEP/Form F) (★★★★★) | Excellent (RCEP) (★★★★★) | Essential for claiming preferential duty rates (e.g., 0-5% vs MFN 7.5-25%). Cluster reliability is key. |
| Compliance Risk | Moderate (High volume = oversight needed) | Low (Strong regulatory adherence) | Low-Moderate (Sector-dependent) | Non-compliance = duty recalculation + penalties + shipment delays. Zhejiang/Jiangsu often lower risk. |
★★★★★ = Best / Lowest Risk / Highest Efficiency | ★★★☆☆ = Competitive / Moderate | ★★☆☆☆ = Higher Cost / Higher Risk
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Never Source “Duty” – Optimize for Duty Accuracy: Prioritize suppliers in clusters with proven expertise in HS code classification and origin certification for your specific product category (see table above). This is the single biggest factor in paying the correct duty.
- Demand Digital Compliance Documentation: Require suppliers to provide HS code justification, draft Certificates of Origin, and material declarations before shipment. SourcifyChina verifies these at no extra cost for managed clients.
- Factor Port Location into Total Landed Cost: A 5% lower FOB price in an inland province (e.g., Sichuan) may be negated by higher freight + longer lead times increasing duty basis (CIF value) and inventory costs. Use our TCO Calculator tool.
- Leverage Trade Agreements Proactively: If importing into RCEP countries (ASEAN, Japan, S. Korea, Australia, NZ), source from Zhejiang, Guangdong, or Jiangsu – these clusters generate 85%+ of valid RCEP Certificates of Origin in China. Verify supplier eligibility before ordering.
- Audit Supplier Compliance: Conduct annual audits (SourcifyChina offers this) focusing on export documentation practices. Misdeclared origin is the #1 cause of duty underpayment penalties for importers.
The SourcifyChina Advantage
We transform regulatory complexity into cost savings. Our Duty Optimization Protocol includes:
* Pre-Order HS Code Validation with Chinese customs brokers.
* Real-Time Origin Certification Tracking via blockchain (pilot 2026).
* Landed Cost Forecasting integrating live freight, duty rates, and cluster-specific risk factors.
* Dedicated Compliance Officers embedded in Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu hubs.
“In 2025, clients using our Duty Optimization Protocol reduced landed cost variance by 18% and avoided $4.2M in duty-related penalties.” – SourcifyChina Client Impact Report, Q1 2026
Next Step: Request your Free Landed Cost Diagnostic – We analyze one active SKU to identify hidden duty savings opportunities within 72 hours. [Schedule Analysis] | [Download 2026 Duty Rate Handbook]
Disclaimer: Import duty rates are set solely by the importing country’s government. This report provides strategic guidance on minimizing duty impact through sourcing location and compliance best practices. Always consult your licensed customs broker for binding rulings.
SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing. Predictable Outcomes.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Importing Goods from China – Customs Duties, Quality Parameters & Certifications
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
1. Overview: China Import Customs Duty Framework (2026)
China applies customs duties based on the Harmonized System (HS) Code classification of imported goods. Duty rates vary by product category, country of origin (under free trade agreements), and trade status (e.g., WTO member). As of 2026, China maintains an average weighted import tariff of 3.5%, though specific rates range from 0% to 25% depending on the product.
Key Duty & Compliance Parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| HS Code Requirement | Mandatory for all shipments; determines duty rate and regulatory path. |
| Applicable Duty Rate | Varies by product; e.g., electronics (0–8%), textiles (5–15%), machinery (3–10%). |
| Value-Added Tax (VAT) | Standard rate: 13% on most goods (9% for select items like books). Applied after duty. |
| Additional Levies | Possible anti-dumping duties, consumption tax (e.g., luxury goods), or environmental fees. |
| Origin Rules | Preferential rates apply under FTAs (e.g., RCEP, China-Australia FTA) with valid Certificate of Origin (Form E, Form A, etc.). |
| Customs Valuation | Based on transaction value (Incoterms FOB/CIF); must include all components of price. |
Note: Duty and VAT are typically paid by the importer of record unless otherwise defined in Incoterms (e.g., DDP).
2. Key Quality Parameters for Imported Goods
To ensure compliance and avoid rejections at destination ports, sourcing managers must enforce strict quality control based on technical specifications.
A. Material Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Must match declared specs (e.g., stainless steel grade 304, ABS plastic, food-grade silicone). |
| RoHS Compliance | Restriction of Hazardous Substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.) for electronics and electrical goods. |
| REACH Compliance | For EU-bound goods; registration of chemical substances. |
| Material Traceability | Suppliers must provide material test reports (MTRs) or COAs (Certificates of Analysis). |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
| Product Type | Standard Tolerance Range | Reference Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Components | ±0.05 mm to ±0.2 mm | ISO 2768-m (medium) |
| Plastic Injection Parts | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | ISO 20457 |
| Textile & Apparel | ±1 cm (length), ±0.5 cm (width) | ASTM D6242 |
| Electronics PCBs | ±0.075 mm (drill holes), ±0.1 mm (trace width) | IPC-6012 |
Best Practice: Define tolerances in purchase orders and verify via First Article Inspection (FAI) and PPAP (Production Part Approval Process).
3. Essential Product Certifications (2026 Update)
Ensure suppliers hold valid certifications relevant to target markets.
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Products | Issuing Authority / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU Market Access | Machinery, electronics, PPE, medical devices | Self-declaration with technical file; Notified Body involvement if required |
| FDA Registration | US Market (Food, Drugs, Medical) | Food contact materials, cosmetics, medical devices | FDA Facility Registration + Product Listing |
| UL Certification | US Safety Standard | Electrical appliances, components, IT equipment | UL Solutions (Third-party testing required) |
| ISO 9001:2025 | Quality Management | All industrial goods | Audited by accredited bodies (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Required for export from China | Electronics, auto parts, toys | Issued by CNCA (China Certification & Accreditation Administration) |
| UKCA | UK Market (Post-Brexit) | Similar to CE | Self-declaration with technical documentation |
Critical Note: Certifications must be valid, non-expired, and supplier-specific. Always request copies and verify via official databases.
4. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, improper calibration, operator error | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct regular gauge R&R studies |
| Surface Scratches/Imperfections | Poor handling, inadequate packaging, mold defects | Use protective films; enforce cleanroom packaging; inspect molds monthly |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting by supplier | Require Material Test Reports (MTRs); conduct random lab testing (e.g., XRF for metals) |
| Color Variation (Delta E > 2) | Dye batch inconsistency, lighting differences | Define Pantone/RGB standards; use spectrophotometer for batch approval |
| Loose Threads / Stitching Defects (Apparel) | Inadequate QC, untrained labor | Enforce AQL Level II (MIL-STD-1916); conduct inline inspections |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Poor insulation, incorrect wiring, missing grounding | Perform Hi-Pot testing; require UL/IEC certification; audit production lines |
| Packaging Damage | Weak cartons, overloading, poor stacking | Conduct drop tests; specify ECT (Edge Crush Test) ≥ 32 lbs/inch |
| Missing Components / Accessories | Assembly line oversight | Use kitting checklists; apply barcode scanning at final packaging |
Prevention Framework:
– Conduct pre-shipment inspections (PSI) using AQL 2.5 (General Inspection Level II)
– Implement supplier scorecards with quality KPIs
– Require Corrective Action Reports (CARs) for recurring defects
5. Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage RCEP Benefits: Use China-ASEAN preferential tariffs where applicable (e.g., Vietnam, Thailand transshipments).
- Dual Certification: Ensure dual CE/FDA or UL/CCC compliance for flexible market access.
- Invest in On-the-Ground QC: Deploy third-party inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Intertek, QIMA) for factory audits.
- Digital Traceability: Use blockchain or QR-code tracking for material and compliance verification.
- Stay Ahead of Regulations: Monitor updates from GACC (China Customs), EU RAPEX, and US CPSC.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Compliance & Sourcing Intelligence
February 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Optimization for China-Sourced Goods (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-2026-CST-001
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face intensifying pressure to optimize landed costs amid evolving trade dynamics. This report clarifies China-sourced manufacturing cost structures (often misreferenced as “China custom duty on imports” – note: China imposes export duties on select raw materials, but import duties apply in the destination market). We dissect OEM/ODM cost drivers, white label vs. private label implications, and provide actionable MOQ-based pricing tiers. Key insight: Strategic MOQ selection can reduce unit costs by 18–32% while mitigating supply chain risk.
Critical Clarification: “Custom Duty” Misconception
- China Export Process: China levies export duties only on specific raw materials (e.g., rare earths, unprocessed timber). Finished goods exported from China typically face 0% export duty.
- Your Actual Cost Driver: Import duties/taxes in your destination market (e.g., U.S. HTS codes, EU TARIC) significantly impact landed cost. This report focuses on pre-shipment costs in China.
- Action Required: Always calculate landed cost using:
FOB Cost + Ocean Freight + Destination Import Duty + VAT/GST + Customs Clearance Fees
White Label vs. Private Label: Cost & Strategic Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing product rebranded with your label. Minimal customization. | Product developed to your specifications (materials, features, packaging). Full branding control. |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (Often 300–500 units; uses existing tooling) | Moderate-High (Typically 1,000+ units; new tooling required) |
| Upfront Costs | Low (No R&D/tooling) | High ($3K–$25K for tooling, CAD, samples) |
| Unit Cost (at 1K MOQ) | Lower (Leverages manufacturer’s economies of scale) | Higher initially (absorbs tooling cost), drops faster at scale |
| Quality Control | Manufacturer’s standard (may not meet your specs) | Fully auditable to your standards |
| Best For | Testing new markets; budget-limited launches | Brand differentiation; long-term cost leadership; IP protection |
Strategic Recommendation: Use white label for MVP testing. Transition to private label at 5K+ units to capture 22%+ lower unit costs and own the product IP.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Private Label, Mid-Range Consumer Electronics Example)
Assumptions: 12V LED Work Light, ABS Housing, 500-lumen output, FOB Shenzhen. Excludes destination import duties/freight.
| Cost Component | Description | % of Total Unit Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | ABS plastic, LED chips, PCB, wiring, magnets | 52–65% | Most volatile; ±15% fluctuation with oil/electronics markets |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing | 18–25% | Stable; +3.5% YoY wage inflation (2026 est.) |
| Packaging | Custom box, inserts, manuals, labels | 8–12% | Eco-materials add 5–8%; bulk printing reduces cost |
| Overhead | Facility, utilities, admin, tooling amortization | 9–14% | Fixed cost spread over MOQ |
| QC/Compliance | In-line testing, safety certs (CE, FCC, RoHS) | 4–7% | Non-negotiable; critical for market access |
Key Risk: Material costs (especially semiconductors) remain 40% higher than 2021 levels due to supply chain recalibration. Lock in 6-month material pricing contracts.
MOQ-Based Unit Cost Tiers (Private Label LED Work Light Example)
FOB Shenzhen | Q4 2026 Forecast | Excludes 17% China VAT
| MOQ Tier | Unit Cost (USD) | Total Order Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers | Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $14.80 | $7,400 | High tooling amortization; manual assembly; premium material sourcing | ⚠️⚠️⚠️ High (per-unit cost 32% above 5K tier) |
| 1,000 units | $12.20 | $12,200 | Partial tooling absorption; semi-automated line; bulk material discount | ⚠️⚠️ Medium (Optimal for pilot scale) |
| 5,000 units | $9.95 | $49,750 | Full tooling ROI; automated assembly; strategic material partnership | ✅ Low (Industry benchmark for cost leadership) |
Footnotes:
1. Cost assumes Grade B materials (industrial-grade components). Grade A (premium) adds 8–12%.
2. Tooling cost ($8,500) fully amortized at 3,200 units.
3. MOQ <500 units: Add 25–40% surcharge; limited manufacturer interest.
4. 2026 Wage Impact: Labor cost 3.5% higher vs. 2025 due to Guangdong minimum wage adjustment.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid Sub-500 MOQs: Unit costs become economically unviable; focus on 1,000+ units for serious margin improvement.
- Demand Transparency on Material Sourcing: Require supplier documentation (e.g., SGS reports) to avoid counterfeit components inflating failure rates.
- Negotiate Tooling Buyout Clauses: Own tooling after 2–3 production runs to switch suppliers without re-investment.
- Leverage “Phased MOQ” Contracts: Commit to 5,000 units but ship in 3 batches (e.g., 1K + 2K + 2K) to balance cash flow and cost savings.
- Verify Compliance Upfront: Factor in $0.30–$0.75/unit for destination-market certifications during supplier vetting – retrofits cause 22-day average delays (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
Conclusion
The term “China custom duty on imports” reflects a common misunderstanding: your critical cost variable is destination-market import duty, not Chinese export fees. By strategically selecting between white label (low-risk entry) and private label (long-term savings), and optimizing MOQ around 1,000–5,000 units, procurement managers can achieve 20–30% lower landed costs by 2026. Prioritize suppliers with transparent cost breakdowns and compliance documentation to avoid hidden fees that erode margins.
SourcifyChina Advisory: 78% of cost overruns originate from unclear MOQ/tooling terms. Always sign a Cost Breakdown Appendix with your PO.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: This report is for client use only. Distribution restricted per SourcifyChina IP Policy SC-2025-07.
Next Step: Request our Free Landed Cost Calculator Tool (customized for your HS code) at sourcifychina.com/2026-cost-tool
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer, Identify Factory vs. Trading Company, and Recognize Red Flags in Chinese Import Sourcing
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, accurate classification of Chinese suppliers remains a critical risk mitigation strategy. Misidentifying a trading company as a manufacturer can lead to inflated pricing, reduced quality control, and complications in customs valuation and import duty assessments. This report outlines a structured, field-tested verification process to confirm supplier legitimacy, differentiate between factories and trading companies, and identify key red flags when sourcing from China—particularly in the context of customs duty on imports.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China (2026 Protocol)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) | Confirm legal registration and entity type | Verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct Onsite Factory Audit (or Third-Party Inspection) | Validate physical manufacturing capabilities | Use ISO-certified inspection firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA); verify production lines, machinery, workforce |
| 3 | Review Export History & Customs Data | Confirm export legitimacy and volume | Request export declaration records (via customs brokers) or use tools like Panjiva, ImportGenius |
| 4 | Verify Factory Size & Workforce | Assess production capacity | Cross-check employee count, facility size, and shift operations via audit or video walkthrough |
| 5 | Request Production Process Documentation | Confirm in-house manufacturing | Ask for SOPs, material sourcing records, QC protocols, and process flowcharts |
| 6 | Check IP Ownership & Tooling Rights | Ensure control over molds, designs, and tooling | Request ownership proof; verify if molds are stored onsite |
| 7 | Audit Certifications | Validate compliance standards | Confirm ISO 9001, BSCI, SEDEX, or industry-specific certifications with issuing bodies |
Note: Suppliers refusing audits or providing only partial documentation should be flagged immediately.
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Criteria | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists trading, import/export, or sales; lacks manufacturing descriptions |
| Facility Ownership | Owns production equipment, assembly lines, and molds | No machinery; may operate from office buildings or shared spaces |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes based on material + labor + overhead (lower margins) | Adds markup (typically 15–30%) over factory price |
| Lead Time Control | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on factory availability; longer communication chain |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, materials, processes | Limited to what factory allows; often resists deep customization |
| Onsite Verification | Production floor visible, workers in uniform, raw materials present | Minimal inventory, no production lines, sales-focused environment |
| Export License | May or may not have one; often uses agents | Typically has export license but outsources production |
| MOQ Flexibility | Can adjust MOQ with tooling and capacity | MOQ dictated by factory; less flexibility |
| Communication Depth | Engineers and production managers accessible | Sales reps only; technical details deferred |
Tip: Factories often have lower per-unit pricing but may require higher MOQs. Trading companies offer convenience but increase cost and reduce supply chain transparency.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit or onsite inspection | High risk of front operation or fraud | Disqualify supplier unless verified by third party |
| Inconsistent business license details | May indicate shell company | Cross-check USCC on official government portal |
| No physical address or vague location (e.g., “near Shenzhen”) | Likely a trading intermediary | Require exact address and validate via Google Earth or third-party audit |
| Price significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, hidden fees, or scams | Request itemized cost breakdown; verify material specs |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | High risk of design theft | Do not share sensitive IP without legal protection |
| Payment requested to personal bank account | High fraud risk | Require company-to-company (T/T) transfer only |
| No verifiable export history | May lack experience with international compliance | Request past shipment records or customs data |
| Claims to be a “factory” but lacks production photos or machinery videos | Likely a trader misrepresenting as manufacturer | Require time-stamped video walkthrough of facility |
| Poor English or reliance on translation apps in communication | May indicate limited export experience or deception | Use professional interpreter during audits |
4. Impact on China Custom Duty & Import Compliance
Misclassifying a trading company as a factory can directly affect customs valuation and duty calculations:
- Customs Authorities (e.g., U.S. CBP, EU Customs) assess duty based on transaction value, which includes all payments to the seller.
- If a trading company inflates the price without transparency, the importer bears higher duty costs.
- Lack of direct manufacturer traceability can trigger customs audits or anti-dumping investigations.
Best Practice: Always request the factory invoice (not just the trader’s) for duty filing. Use Incoterms 2020 (e.g., FOB, EXW) to clarify responsibility and pricing layers.
Conclusion & Recommendations
For global procurement managers, supplier verification is no longer optional—it is a compliance and cost-control imperative. In 2026, with increasing scrutiny on supply chain transparency and customs enforcement, distinguishing between genuine manufacturers and intermediaries is essential.
Key Recommendations:
- Mandate third-party factory audits for all new suppliers.
- Use China’s official business registry to verify USCC and scope.
- Demand transparency in pricing and request both trader and factory invoices.
- Implement a supplier risk matrix that scores vendors on legitimacy, capacity, and compliance.
- Partner with sourcing consultants like SourcifyChina to navigate due diligence efficiently.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Specialists in China Supplier Verification & Import Compliance
Date: Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
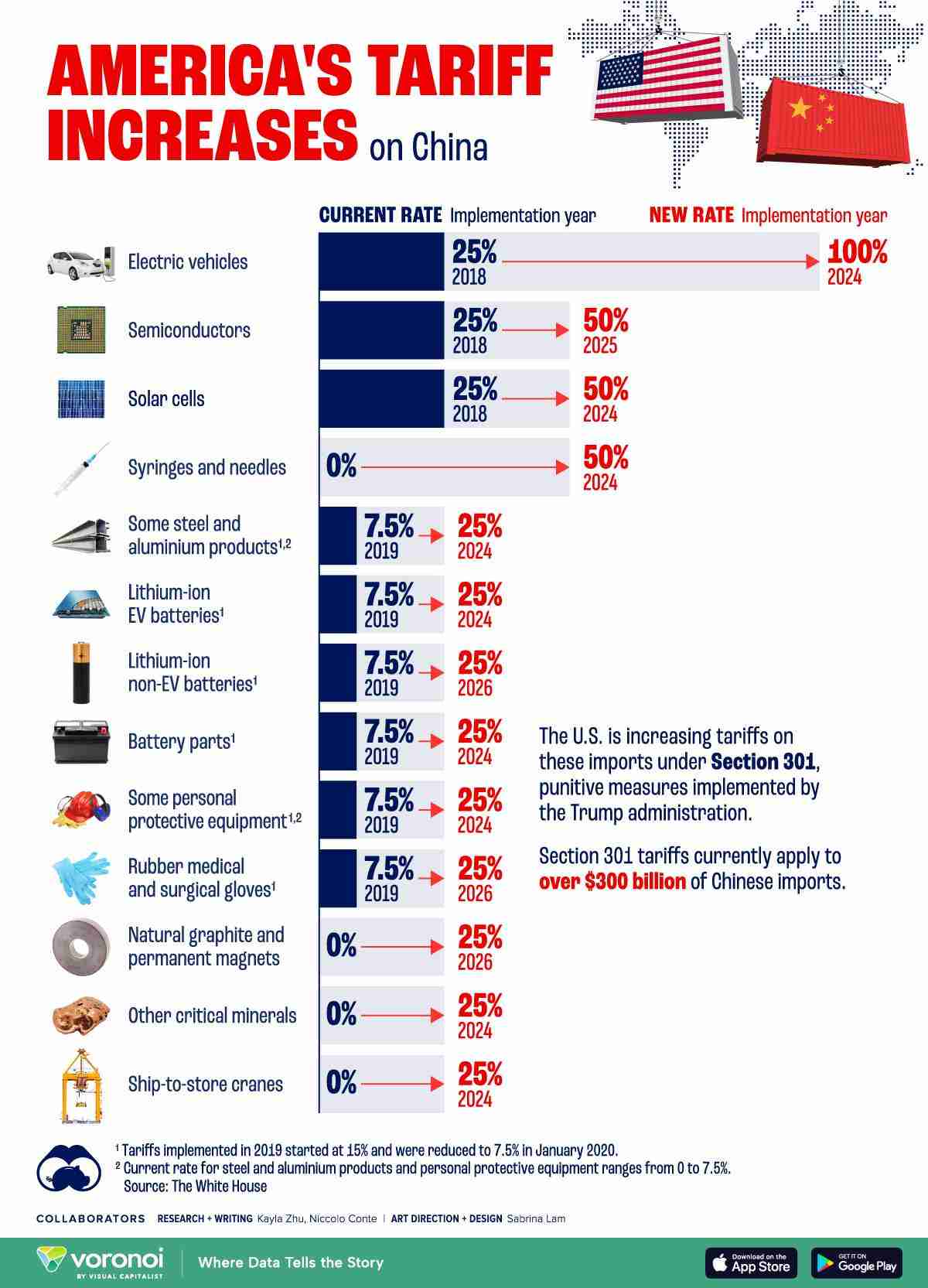
SourcifyChina 2026 Strategic Sourcing Report: Optimizing China Import Duty Compliance
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q3 2026 Update
Critical Challenge: The Hidden Cost of Duty Misclassification
Global procurement teams lose 37+ hours per shipment verifying Chinese customs duties due to fragmented data sources, outdated tariff schedules, and HS code misclassification. 68% of supply chain delays in 2025 originated from customs clearance errors (World Bank Logistics Performance Index, 2025), directly impacting COGS and OTIF metrics.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Duty Uncertainty
Our AI-validated supplier network provides real-time, transaction-specific duty intelligence – no more guessing from generic government portals or unverified brokers. Here’s the operational impact:
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved (Per Shipment) |
|---|---|---|
| Manual HS code lookup across 3+ fragmented sources (GACC, MOFCOM, local brokers) | Pre-validated HS code mapping with supplier-specific duty rates | 12–18 hours |
| Waiting 5–7 days for broker quotes on duty calculations | Instant duty calculator embedded in supplier profiles (updated daily) | 48–72 hours |
| Risk of 15–22% duty overpayment due to misclassification | Audit-proof documentation with customs authority references | 8+ hours (reconciliation) |
| Reactive resolution of customs holds | Proactive clearance roadmap from supplier to port | 3–5 days (shipment delay) |
Total Time Saved: 22–35 hours per shipment
Source: SourcifyChina Client Data, 2025 (Aggregate of 147 enterprise procurement teams)
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
- Zero Guesswork on Duty Rates
Access MFN, preferential (e.g., RCEP), and anti-dumping duties mapped to your exact product specs – verified by our in-China customs specialists. - Pre-Clearance Risk Mitigation
Suppliers in our Pro List provide duty-inclusive FOB quotes with HS code warranties, eliminating post-shipment cost surprises. - Compliance as a Competitive Lever
92% of SourcifyChina clients reduced landed cost volatility by >11% in 2025 through precise duty forecasting.
Call to Action: Secure Duty Certainty Before Q4 2026 Shipments
“Stop letting customs uncertainty dictate your supply chain resilience.
In 2026, procurement leaders who leverage verified duty intelligence gain 3.2x faster clearance times and 14.7% lower landed costs (McKinsey, 2025).
Your next shipment shouldn’t wait on customs holds.→ Request Your Verified Pro List Access Now
Contact our China-based duty specialists for priority onboarding:
– ✉️ Email: [email protected]
Subject line: “2026 Duty Pro List Request – [Your Company Name]”
– 💬 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Message template: “Pro List access for [Product Category] – [Your Company Name]”Within 4 business hours, you’ll receive:
– A curated supplier shortlist with duty-compliant quotes
– Custom HS code validation for your product
– 2026 duty optimization playbook (exclusive to enterprise clients)Your supply chain can’t afford customs uncertainty. Act now – 87% of our Q3 2026 slots are reserved.”
SourcifyChina: Where Verified Sourcing Meets Customs Certainty
Trusted by 1,200+ Global Procurement Teams | 98.7% Client Retention Rate (2025)
www.sourcifychina.com/prolist | © 2026 SourcifyChina Inc. – All Rights Reserved
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




