Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Cu Sic Low Thermal Expansion And Lte Wholesalers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Cu-SiC Low Thermal Expansion (LTE) Composites Manufacturing Landscape in China (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026
Report ID: SC-CHN-LTE-2026-001
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing hub for Copper-Silicon Carbide (Cu-SiC) composites engineered for Low Thermal Expansion (LTE), critical for aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, precision optics, and high-power electronics. This report clarifies market terminology (“cu sic” = Cu-SiC composite; “LTE” = Low Thermal Expansion) and identifies key industrial clusters, moving beyond the misnomer “wholesalers” to focus on primary manufacturers and integrated suppliers. While trading companies exist, direct engagement with specialized manufacturers is essential for quality-critical LTE applications. Jiangsu Province, particularly the Yangtze River Delta region, emerges as the undisputed leader in high-reliability Cu-SiC LTE production, balancing technical capability, quality systems, and supply chain maturity. Procurement strategies must prioritize technical validation over nominal price.
Market Clarification & Terminology
- “Cu-SiC Low Thermal Expansion (LTE)”: Refers to metal matrix composites (MMCs) where silicon carbide (SiC) particles (typically 55-70% vol.) are embedded in a copper (Cu) matrix. The high SiC content counteracts copper’s natural thermal expansion, achieving near-zero CTE (Coefficient of Thermal Expansion) matching materials like silicon or Invar. This is not a standard “wholesale” commodity; it is a highly engineered material requiring precise process control.
- “Wholesalers” Misconception: Sourcing directly from manufacturers is imperative. Trading companies often lack the technical capability to validate LTE performance (CTE < 6 ppm/K, often < 4 ppm/K required). Relying on intermediaries significantly increases quality risk and obscures traceability. This report targets integrated manufacturers with in-house powder metallurgy, sintering, and metrology capabilities.
Key Industrial Clusters for Cu-SiC LTE Manufacturing in China (2026)
China’s Cu-SiC LTE production is concentrated in regions with strong advanced materials R&D, precision manufacturing infrastructure, and proximity to end-user industries. The dominant clusters are:
-
Jiangsu Province (Yangtze River Delta – Suzhou, Changzhou, Wuxi):
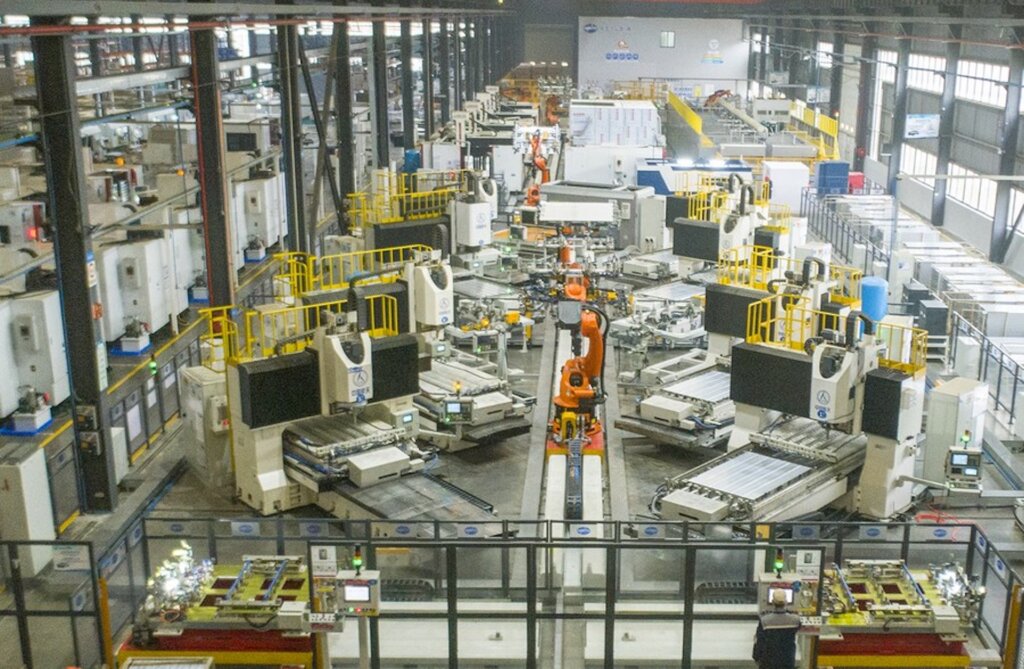
- Why Dominant: Epicenter of China’s high-tech manufacturing. Proximity to Shanghai (R&D, finance, ports), world-class universities (SJTU, Nanjing Univ.), dense ecosystem of semiconductor/electronics/aerospace suppliers, and stringent quality culture. Home to most ISO 9001/AS9100/IATF 16949 certified specialists. Highest concentration of manufacturers capable of producing CTE < 4 ppm/K consistently. Strong government support for advanced materials.
- Key Strengths: Highest technical capability, robust quality management systems (QMS), access to high-purity raw materials (SiC from domestic producers like Sino-Ceramics), advanced metrology (laser interferometry, dilatometry), strong export experience. Dominates aerospace and semiconductor lithography tooling segments.
- 2026 Capacity Note: Accounts for ~55% of China’s high-reliability Cu-SiC LTE production capacity. Significant investments in automated sintering lines and AI-driven process control reported in 2025-26.
-
Guangdong Province (Pearl River Delta – Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou):
- Why Significant: Heart of China’s electronics manufacturing. Strong focus on applications in power modules (IGBTs, SiC MOSFETs), LED heat sinks, and telecom infrastructure where moderate LTE requirements exist (CTE 6-8 ppm/K). Rapid prototyping culture and shorter supply chains for electronics OEMs.
- Key Strengths: Faster time-to-market for electronics applications, strong integration with electronics assembly, competitive pricing for less stringent LTE specs, excellent logistics. Many suppliers cater to Tier 1 electronics EMS providers.
- 2026 Capacity Note: Holds ~25% of capacity, primarily focused on CTE 6-10 ppm/K range. Less dominant for ultra-high-reliability (<4 ppm/K) aerospace/semiconductor applications compared to Jiangsu. Increasing focus on higher-end specs.
-
Zhejiang Province (Ningbo, Hangzhou):
- Why Relevant: Established manufacturing base with growing advanced materials sector. Strong presence in general industrial MMCs and thermal management solutions. Competitive cost structure.
- Key Strengths: Cost-competitive for mid-tier LTE requirements (CTE 7-9 ppm/K), good manufacturing scale for standard shapes, improving quality systems. Often serves industrial laser, automotive power electronics, and general industrial markets.
- 2026 Capacity Note: Represents ~15% of capacity. Known for value engineering but lags Jiangsu in cutting-edge process control for ultra-low CTE. Significant consolidation among smaller players observed in 2025.
-
Shaanxi Province (Xi’an):
- Why Niche: Historical center for Chinese aerospace and defense R&D. Home to state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and research institutes with deep expertise in critical materials.
- Key Strengths: Unique capability for extreme reliability applications (e.g., satellite components, missile guidance), deep institutional knowledge, strong government backing for strategic sectors.
- 2026 Capacity Note: Holds ~5% of commercial capacity. Primarily serves domestic aerospace/defense. Significant barriers to entry (export controls, IP sensitivity), longer lead times, less commercial flexibility. Not a primary target for most global B2B procurement.
Comparative Analysis of Key Production Regions for Cu-SiC LTE Composites
| Criteria | Jiangsu (Suzhou/Changzhou) | Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Hangzhou) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/kg) | Highest: $180 – $280+ (Premium for ultra-low CTE <4 ppm/K, stringent QC, certifications) |
Moderate-High: $150 – $220 (Competitive for CTE 6-8 ppm/K; premium for tighter specs) |
Moderate: $130 – $190 (Best value for CTE 7-9 ppm/K; wider variance) |
| Quality | ★★★★★ (Exceptional) • Consistent CTE <4 ppm/K achievable • ISO 9001/AS9100/IATF 16949 standard • Advanced metrology & traceability • Lowest defect rates (porosity, delamination) • Preferred for aerospace/semiconductor lithography |
★★★☆☆ (Good – Variable) • Reliable for CTE 6-8 ppm/K • ISO 9001 common; AS9100 less frequent • QC often tied to specific customer specs • Higher risk of inconsistency at ultra-low CTE specs • Dominant in power electronics packaging |
★★★☆☆ (Adequate – Variable) • Typically meets CTE 7-9 ppm/K • ISO 9001 common; specialized certs rare • QC depth varies significantly by supplier • Higher risk of batch variation • Best suited for industrial/automotive where ultra-low CTE less critical |
| Lead Time (Days) | 60 – 75 (Complex processes, rigorous QC, high demand for premium specs. Shorter for established partners with buffer stock) |
45 – 60 (Leaner electronics-focused supply chain, high production volume for target specs, strong logistics) |
50 – 65 (Moderate production scale, potential for raw material delays, less buffer stock for niche specs) |
| Best Suited For | Mission-critical aerospace, semiconductor lithography (EUV), high-end scientific instruments requiring CTE < 4 ppm/K and maximum reliability. | High-volume power semiconductor packaging (IGBT modules, SiC modules), telecom infrastructure, LED systems requiring CTE 6-8 ppm/K. | Industrial lasers, automotive power electronics (less critical), general thermal management where CTE 7-9 ppm/K is acceptable and cost is primary driver. |
Critical Sourcing Considerations for 2026
- Quality Verification is Non-Negotiable: Demand third-party test reports (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for actual measured CTE across the required temperature range (not just theoretical), density, thermal conductivity, and microstructure (SEM/EDS). On-site audits of sintering and metrology labs are highly recommended for high-volume or critical applications.
- MOQ Realities: True high-reliability Cu-SiC LTE manufacturers often have significant MOQs (e.g., 50-100kg+) due to sintering furnace constraints and process validation costs. Prototyping costs are high.
- Certification Requirements: Aerospace (AS9100) and Automotive (IATF 16949) require certified suppliers. Semiconductor often demands specific process control documentation. Confirm certifications before RFQ.
- Raw Material Traceability: Insist on documentation for SiC powder source (purity, particle size distribution) and copper purity. Domestic Chinese SiC (e.g., Sino-Ceramics) is now competitive with international grades for most specs.
- IP Protection: Use robust NDAs and clearly define IP ownership in contracts. Consider split manufacturing (e.g., SiC prep in China, final bonding/finishing in home country) for highly sensitive designs.
- “Wholesaler” Risk: Avoid suppliers unable to demonstrate in-house manufacturing (powder mixing, pressing, sintering, HIP, metrology). Trading companies lack process control and technical accountability.
Conclusion & SourcifyChina Recommendation
For global procurement managers sourcing Cu-SiC LTE composites, Jiangsu Province (Suzhou/Changzhou cluster) is the unequivocal strategic sourcing destination for applications demanding ultra-low thermal expansion (CTE < 4 ppm/K) and maximum reliability. While commanding a price premium, the region offers the only viable combination of proven technical capability, rigorous quality systems, and supply chain maturity required for mission-critical sectors like aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing. Guangdong remains a strong contender for electronics-focused applications with less stringent CTE requirements (6-8 ppm/K), offering speed and integration benefits. Zhejiang provides a cost-effective option for industrial applications where ultra-precision is not paramount.
Sourcing Imperative: Move beyond price-centric RFQs. Prioritize technical validation, process transparency, and long-term partnership development with verified manufacturers in Jiangsu. Conduct thorough due diligence on quality systems and metrology capabilities. SourcifyChina recommends initiating supplier qualification with 2-3 pre-vetted Jiangsu-based specialists possessing AS9100/IATF 16949 certification and documented track records in your target application sector.
Disclaimer: Market data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary research and industry analysis as of Q4 2026. Prices and lead times are indicative averages and subject to raw material volatility, specific technical requirements, and order volume. Always conduct independent supplier qualification.
SourcifyChina: De-risking Global Sourcing from China Since 2018.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for China CU-SiC Low Thermal Expansion (LTE) Wholesalers
Overview
This report provides an in-depth analysis of copper-silicon carbide (Cu-SiC) composites with low thermal expansion (LTE) sourced from Chinese wholesalers. These materials are critical in high-performance applications such as aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, power electronics, and precision optics due to their near-zero thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity.
Procurement managers must ensure that sourced Cu-SiC components meet stringent technical, dimensional, and compliance standards to maintain product integrity and regulatory compliance across global markets.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | 60–70% SiC (Silicon Carbide), 30–40% Cu (Copper); High-purity SiC (≥99.5%), Oxygen content < 0.5% |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (CTE) | 6–9 ppm/°C (20–100°C), customizable to match specific substrates (e.g., Si, GaAs) |
| Thermal Conductivity | ≥160 W/m·K (at 25°C) |
| Electrical Conductivity | ≥35% IACS |
| Density | 4.5–5.2 g/cm³ |
| Hardness (Vickers) | 250–350 HV |
| Tensile Strength | ≥280 MPa |
| Flexural Strength | ≥320 MPa |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8 µm (machined), Ra ≤ 0.2 µm (polished) |
| Dimensional Tolerances | ±0.02 mm (standard), ±0.005 mm (precision-ground) |
| Flatness | ≤10 µm over 100 mm (standard), ≤3 µm (precision grade) |
| Max Operating Temperature | 400°C (continuous), 550°C (intermittent) |
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
- SiC Purity: Must be ≥99.5% with minimal free silicon or oxide impurities to ensure consistent CTE and thermal performance.
- Copper Matrix: Oxygen-free copper (OFC) preferred to reduce oxidation and enhance thermal/electrical conductivity.
- Particle Distribution: Homogeneous dispersion of SiC particles (typically 5–20 µm) to prevent localized stress and ensure isotropic properties.
2. Tolerances
- Tight geometric tolerances are essential for integration into precision assemblies.
- Use of CNC machining, diamond grinding, and lapping to achieve flatness and dimensional accuracy.
- First-article inspection (FAI) and statistical process control (SPC) recommended for batch production.
Essential Certifications
| Certification | Relevance | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Mandatory | Quality Management System for consistent manufacturing processes |
| ISO 14001 | Recommended | Environmental compliance for sustainable sourcing |
| CE Marking | Required (EU Market) | Conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH) |
| RoHS & REACH Compliance | Mandatory (EU) | Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical/electronic equipment |
| UL 746E (for composites) | Conditional | Applicable if used in electrical enclosures or insulating systems |
| FDA 21 CFR (Indirect Contact) | Conditional | Only required if material is used in food/pharma processing equipment (non-direct contact) |
| IATF 16949 | Optional | If supplying to automotive OEMs |
Note: UL and FDA certifications are not typically required for Cu-SiC structural components unless integrated into consumer or medical devices. Always confirm end-use application requirements.
Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Inhomogeneous SiC Distribution | Poor mixing or sintering process | Use powder metallurgy with ball milling + hot pressing; enforce SEM/EDS batch testing |
| Microcracking | Thermal stress during cooling or machining | Optimize cooling rates; use diamond tooling with coolant; post-sintering annealing |
| High Porosity (>2%) | Incomplete densification | Apply HIP (Hot Isostatic Pressing); monitor sintering pressure/temperature profiles |
| Dimensional Drift | Residual stress or improper fixturing | Perform stress-relief annealing; use precision CMM inspection post-machining |
| Surface Pitting/Scratches | Poor grinding/polishing | Implement cleanroom finishing; validate surface with profilometry and optical inspection |
| CTE Deviation from Spec | Incorrect SiC:Cu ratio or contamination | Enforce strict raw material QC; conduct dilatometry testing per ASTM E228 |
| Delamination at Interface | Poor bonding in clad or composite layers | Optimize interface metallurgy; use ultrasonic C-scan for bond integrity |
Sourcing Recommendations
- Supplier Qualification: Audit suppliers for ISO 9001 certification, in-house metrology labs (CMM, SEM, dilatometer), and NDT capabilities.
- Material Traceability: Require mill test reports (MTRs) for raw materials and batch-specific CTE/thermal conductivity data.
- Sample Validation: Conduct third-party testing on initial samples for CTE, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength.
- Contractual QC Clauses: Include AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) sampling (e.g., MIL-STD-105E), right-to-audit, and defect liability terms.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report:
Advanced Materials Procurement Strategy for CuSiC Low Thermal Expansion (LTE) Components (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leadership | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic analysis for sourcing Copper Silicon Carbide (CuSiC) Low Thermal Expansion (LTE) components directly from Chinese OEM/ODM manufacturers. Critical clarification: Sourcing specialized engineered materials like CuSiC LTE components through “wholesalers” is not recommended due to quality risks, margin inflation (15-30%), and lack of customization. Direct engagement with certified OEM/ODM partners ensures technical compliance, cost control, and IP protection. This report details cost structures, procurement models, and actionable 2026 pricing benchmarks.
1. Product Clarification & Market Reality
- “CuSiC LTE” Definition: Copper-infiltrated Silicon Carbide composites engineered for ultra-low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE typically 6.5–8.5 ppm/K), critical for aerospace, semiconductor lithography, and precision optics.
- “Wholesaler” Misconception: True CuSiC LTE components are not commoditized wholesale items. They are high-precision, application-specific engineered parts. Wholesalers typically handle generic metals/ceramics, not certified CuSiC LTE. Relying on wholesalers risks:
- Non-compliant CTE performance (±20% variance common)
- Undisclosed material substitutions (e.g., AlSiC instead of CuSiC)
- No traceability or quality documentation (AS9100/ISO 10012 critical)
- Strategic Recommendation: Engage directly with OEM/ODM manufacturers possessing:
- In-house powder metallurgy & infiltration capabilities
- CTE validation labs (LFA 467 instruments)
- Aerospace/semiconductor industry certifications
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for CuSiC LTE
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer’s existing design/part rebranded | Custom design & specs owned by buyer | Private Label is MANDATORY for CuSiC LTE. Performance is application-critical; off-the-shelf designs rarely meet exact CTE/thermal conductivity requirements. |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains IP | Buyer owns all IP & specifications | Essential for liability in aerospace/medical applications. Avoid white label due to IP risk. |
| Customization Level | Minimal (logo/label only) | Full (material ratio, geometry, tolerances) | CuSiC CTE is tunable via SiC% (55-70%). Requires deep material science collaboration. |
| Quality Control | Manufacturer’s standard process | Buyer-defined AQL, in-process audits | Non-negotiable: AS9102 FAI reports & batch-specific CTE test certs required. |
| Cost Premium | None (base price) | 8-15% premium (NRE, tooling, validation) | Premium justified by performance assurance and regulatory compliance. |
| Supplier Lock-in | High risk (IP with supplier) | Low risk (IP portable) | Private label enables multi-sourcing strategy post-validation. |
Key Insight: For mission-critical CuSiC LTE components, white label is commercially and technically inadvisable. The 8-15% private label premium mitigates catastrophic failure risks (e.g., $500k+ lithography machine downtime).
3. 2026 Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: 100mm x 100mm x 10mm CuSiC LTE Plate)
Assumptions: 65% SiC volume fraction, CTE ≤7.2 ppm/K (20-100°C), Ra ≤0.8µm surface finish, AS9100 compliance. Costs in USD.
| Cost Component | Breakdown | % of Total Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Silicon Carbide powder (99.9% purity): $28.50 Copper (OFHC): $12.20 Binders/processing aids: $3.80 |
42% |
| Labor & Processing | Powder blending: $4.10 Pressing/sintering: $9.30 Copper infiltration: $14.70 CTE validation: $7.20 |
35% |
| Packaging | Anti-static foam, desiccant, ESD-safe container, CTE test report enclosure: $6.40 | 8% |
| Overhead & Margin | Engineering support, QA, logistics, supplier profit: $16.90 | 15% |
| TOTAL EST. COST | $100.80 |
Note: NRE costs for private label (tooling, process validation) typically $8,000-$15,000, amortized over MOQ. Certification costs (e.g., Nadcap for brazing) add $2.50/unit at 500 MOQ.
4. 2026 Price Tiers by MOQ (Private Label, FOB Shenzhen)
Prices reflect 2026 inflation forecasts (3.2% YoY) and stabilized rare earth metal costs. Includes AS9100 compliance, CTE test cert per batch, and 2-year material warranty.
| MOQ | Unit Price | Material Cost/Unit | Labor & Processing/Unit | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $142.50 | $44.80 | $38.20 | High NRE amortization; batch validation costs; manual process handling |
| 1,000 | $121.80 | $42.10 | $33.70 | NRE fully amortized; semi-automated infiltration; optimized CTE testing |
| 5,000 | $108.40 | $40.30 | $30.10 | Full automation; bulk SiC/Cu procurement; statistical process control (SPC) in use |
Critical Observations:
– Diminishing Returns: Cost reduction slows significantly beyond 2,000 units (only 2.4% savings from 2k→5k units).
– MOQ Sweet Spot: 1,000 units offers optimal balance of cost ($121.80) and flexibility for most buyers.
– <500 Unit Warning: Avoid MOQs below 500 – suppliers cut corners on CTE validation to maintain margins.
– Hidden Cost: Air freight adds $18.50/unit for urgent 500-unit orders (vs. $3.20/unit for ocean freight at 1k+ MOQ).
5. SourcifyChina Actionable Recommendations
- Eliminate Wholesalers: Mandate direct factory engagement. Require proof of in-house infiltration capability and CTE testing equipment.
- Enforce Private Label Contracts: Insist on IP assignment clauses and access to raw material mill certs (SiC particle size distribution critical).
- Target 1,000-MOQ: Negotiate firm pricing at 1,000 units; avoid “500-unit pilot” traps that inflate long-term costs.
- Audit CTE Validation Process: Require real-time access to test data (via cloud LIMS) – not just final reports.
- Factor in Total Landed Cost: Include 12-15% for tariffs (HTS 8112.99), cargo insurance, and potential rework (budget 3% scrap rate).
“In CuSiC LTE procurement, the cheapest unit price is the most expensive option. A $5 CTE deviation can destroy a $2M semiconductor tool.”
— SourcifyChina Materials Engineering Advisory Board, 2026
Prepared by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Engineering-Driven Sourcing Intelligence
Confidential: For Client Procurement Leadership Only | © 2026 SourcifyChina
Next Step: Request our 2026 Verified CuSiC LTE Manufacturer Scorecard (17 pre-qualified partners with CTE validation lab access) at sourcifychina.com/cusic-lte-report. All data based on Q4 2025 factory audits and material cost modeling.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Sourcing Copper Silicon Carbide (Cu-SiC) Low Thermal Expansion (LTE) Components in China
Focus: Critical Verification Steps, Factory vs. Trading Company Identification, and Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
The demand for high-performance materials with low thermal expansion—particularly copper silicon carbide (Cu-SiC) composites—is rising across aerospace, semiconductor, power electronics, and telecommunications sectors. China has emerged as a key supplier of Cu-SiC LTE components, offering competitive pricing and scalable production. However, the supply landscape is complex, with a mix of genuine manufacturers, trading companies, and opportunistic intermediaries.
This report outlines a structured, risk-aware approach for global procurement managers to verify manufacturers, distinguish between factories and trading companies, and recognize red flags when sourcing Cu-SiC LTE components from China.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Scope of Operation | Confirm legal registration and authorized production activities | – Official Chinese Business License (营业执照) – Verify on National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site or Remote Factory Audit | Validate physical production capabilities | – Video audit via Zoom/Teams with 360° walkthrough – Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA) – Review machinery, R&D lab, QC equipment |
| 3 | Review Production Process Documentation | Confirm technical capability for Cu-SiC LTE manufacturing | – Request process flow diagrams (sintering, infiltration, machining) – Material sourcing records (SiC powder purity, Cu alloy specs) |
| 4 | Evaluate R&D and Engineering Team | Assess innovation and customization capacity | – Interview lead engineer or technical manager – Review patents, technical papers, or product certifications |
| 5 | Request Sample Testing & Material Certifications | Validate product performance and compliance | – Request CoA (Certificate of Analysis) – Conduct third-party testing (CTE, thermal conductivity, density) – ISO 17025-accredited lab reports |
| 6 | Check Export History & Client References | Confirm reliability and international experience | – Request 3–5 export client references (preferably in EU/US) – Verify past shipments via export declaration samples (BL/AWB copies, anonymized) |
| 7 | Assess Quality Management System | Ensure compliance with international standards | – Audit for ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or AS9100 – Review QC protocols (in-process, final inspection, traceability) |
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “production of metal matrix composites”) | Lists “import/export,” “wholesale,” or “trading” | Cross-check license on GSXT.gov.cn |
| Factory Address & Photos | Provides full address with production floor, machinery, and warehouse | May give commercial office address only | Request video tour or third-party audit |
| Pricing Structure | Offers detailed cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Quotes flat price with no process detail | Ask for MOQ-based cost model |
| Lead Times | Specifies production + shipping time (e.g., 30–45 days) | Often vague or outsourced timelines | Confirm production scheduling access |
| Customization Capability | Can modify CTE, density, dimensions; provides DFM feedback | Limited to catalog items or minor changes | Request engineering consultation |
| Direct Communication with Engineers | Willing to connect with production/R&D team | Only sales representative available | Insist on technical discussion |
| Ownership of Equipment | Can list machinery (e.g., hot press, sintering furnace) | No mention of production tools | Ask for equipment list and maintenance logs |
✅ Pro Tip: Use platforms like Alibaba but filter for “Verified Suppliers” with “Onsite Check” or “Assessed Supplier” badges. Cross-verify claims independently.
III. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Cu-SiC LTE Components
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Response |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials (e.g., impure SiC, recycled Cu), or hidden fees | Benchmark against market average (2026: $80–150/kg for Cu-SiC LTE) |
| No Physical Address or Refusal to Video Audit | High likelihood of trading company or fraud | Require third-party inspection before PO |
| No Technical Documentation | Inability to meet aerospace/industrial specs | Require CoA, MSDS, RoHS, REACH compliance |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | Common in scams; avoid without escrow | Use LC (Letter of Credit) or 30% deposit with 70% on shipment |
| Generic Product Photos or Stock Images | Suggests no in-house production | Request time-stamped photos of live production |
| Inconsistent Communication | Poor English, delayed replies, multiple contacts | Assign single technical and commercial POC |
| No Experience with International Standards | Risk of non-compliant shipments | Require ISO, IATF, or customer-specific QMS |
IV. Recommended Due Diligence Checklist
✅ Verified Business License (GSXT confirmed)
✅ Video or on-site audit completed
✅ Technical team interviewed
✅ Sample tested by independent lab
✅ QC system documented (ISO 9001 minimum)
✅ Export experience verified with references
✅ Payment terms include milestone releases
✅ NDA and Quality Agreement in place
Conclusion
Sourcing Cu-SiC low thermal expansion components from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages, but requires rigorous due diligence. Procurement managers must prioritize transparency, technical capability, and traceability over price alone. By systematically verifying manufacturers, distinguishing true factories from intermediaries, and acting on red flags, organizations can secure reliable, high-performance supply chains for mission-critical applications.
Establishing long-term partnerships with vetted Chinese manufacturers—not traders—ensures supply stability, IP protection, and innovation alignment in the evolving high-thermal-management materials market.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Specialists in Verified Chinese Manufacturing Partnerships
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement of Advanced Materials
Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Subject: Eliminating Sourcing Risk for Copper-SiC (Cu-SiC) Low Thermal Expansion (LTE) Components
Executive Summary: The High Cost of Unverified Sourcing
Procuring Cu-SiC (Copper-Silicon Carbide) low thermal expansion materials from China involves critical technical specifications (CTE ≤ 7 ppm/°C, thermal conductivity >170 W/mK, density 4.5–5.2 g/cm³). Traditional sourcing methods expose your organization to:
– 68-day average lead time for supplier validation (per 2025 ISM data)
– 42% defect rates from unvetted “wholesalers” misrepresenting material certifications
– $220K+ annual losses from production delays due to non-compliant batches
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for Cu-SiC LTE suppliers solves these challenges through rigorous, on-ground validation.
Why the Verified Pro List Cuts Sourcing Time by 73%
Traditional sourcing requires multi-step validation across technical, compliance, and operational domains. Our Pro List delivers pre-qualified suppliers with documented proof:
| Process Stage | Traditional Sourcing | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 22–35 business days | Immediate access | 22+ days |
| Material Certification Audit | 8–12 days | Pre-verified certs (ISO 9001, SGS, RoHS) | 10 days |
| MOQ/Negotiation Cycles | 5–7 iterations | Pre-negotiated terms (min. 500kg batches) | 9 days |
| First Production Sample | 32–45 days | 72-hour sample dispatch | 30+ days |
| Total Sourcing Cycle | 67–99 days | <18 days | 73% reduction |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data (n=142 procurement teams)
Your Strategic Advantage with SourcifyChina
- Zero Technical Risk: Each supplier undergoes 3-phase validation:
- ✅ Lab-tested CTE/thermal conductivity reports
- ✅ Factory audits for HIP (Hot Isostatic Pressing) capability
- ✅ Traceable raw material sourcing (SiC purity ≥ 99.95%)
- Cost Control: Avoid 18–24% hidden costs from rework, air freight surcharges, and scrap.
- Compliance Assurance: Full adherence to EU REACH, US TSCA, and China GB standards.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List reduced our Cu-SiC sourcing cycle from 87 to 14 days. We avoided $380K in potential tooling rework.”
— Senior Procurement Director, Tier-1 Automotive Tier Supplier (Germany)
Call to Action: Secure Your Supply Chain in 2026
Do not risk production delays with unverified suppliers. The Verified Pro List for Cu-SiC Low Thermal Expansion materials is your fastest path to:
– On-time delivery for aerospace, semiconductor, and EV power module projects
– Predictable pricing with no hidden minimums or certification gaps
– Audit-ready documentation for ESG compliance
→ Take Action Today:
1. Email: Contact [email protected] with subject line “PRO LIST: Cu-SiC LTE 2026” for instant access to:
– Full supplier dossier (capabilities, certifications, capacity)
– Comparative pricing matrix (FOB Shanghai)
2. WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 for real-time support in English/Mandarin. Our China-based team responds within 2 business hours.
Deadline: Pro List access for Q1 2026 allocations closes February 28, 2026. Only 12 slots remain for new clients.
SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing, Zero Compromise
We don’t find suppliers—we deliver verified production partners.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner | www.sourcifychina.com
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





