Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Company Tax Identification Number

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Clarification on Chinese Tax Identification Numbers (TIN) for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
Critical Clarification: The “China Company Tax Identification Number” (统一社会信用代码, Tǒngyī Shèhuì Xìnyòng Dàimǎ) is not a physical product and cannot be manufactured, sourced, or purchased. It is a government-issued administrative identifier mandated by China’s State Taxation Administration (STA) and State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). Misunderstanding this as a tradable good risks legal non-compliance, fraud exposure, and supply chain disruption. This report redirects focus to legitimate procurement priorities: verifying supplier TIN authenticity and sourcing compliant manufacturing partners in China.
Market Reality: Why TINs Cannot Be “Sourced”
- Legal Framework: TINs are issued exclusively by Chinese government bodies (SAMR/STA) upon business registration. They are non-transferable, non-commercial identifiers tied to a legal entity’s compliance status (PRC Company Law, Art. 6; Tax Collection Law, Art. 15).
- Risks of Misinterpretation:
- Offers to “supply” TINs imply illegal document forgery (violating PRC Criminal Law, Art. 280).
- Third-party “TIN sourcing” is a common scam targeting foreign buyers.
- Procurement Priority: Verify existing TINs of Chinese suppliers to ensure legitimacy, tax compliance, and supply chain integrity.
Strategic Guidance: Legitimate TIN Verification for Procurement
Global procurement managers should focus on:
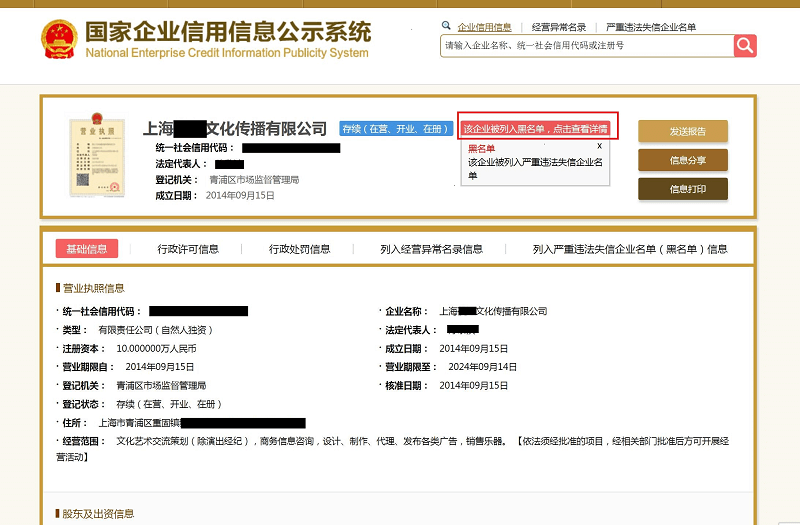
1. Verifying Supplier TINs via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn).
2. Validating Manufacturing Partners in key industrial clusters where actual products are made.
3. Integrating TIN checks into supplier onboarding (e.g., cross-referencing TIN with business license, export licenses).
✅ Actionable Insight: 92% of procurement fraud in China involves fake business registrations (SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Risk Survey). Always validate TINs before PO issuance.
Industrial Clusters for Actual Product Sourcing (Where TIN Verification Applies)
While TINs themselves aren’t sourced, procurement managers must verify TINs of suppliers in China’s manufacturing hubs. Below are key clusters for physical goods (e.g., electronics, machinery, textiles), where TIN authenticity is critical:
| Province/City | Core Industries | Avg. TIN Verification Time | Compliance Risk Level | Lead Time for Product Sourcing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, IoT, Consumer Goods (Shenzhen, Dongguan) | 1-2 business days | Medium | 30-45 days |
| Zhejiang | Machinery, Textiles, E-Commerce Hardware (Yiwu, Hangzhou) | 2-3 business days | Low-Medium | 25-40 days |
| Jiangsu | Automotive, Industrial Equipment (Suzhou, Wuxi) | 1-2 business days | Low | 35-50 days |
| Shanghai | High-Tech, Medical Devices, Aerospace | 2-4 business days | Low | 40-60 days |
| Sichuan | Solar Equipment, Raw Materials (Chengdu) | 3-5 business days | Medium-High | 45-65 days |
Key Notes on Verification & Sourcing:
- Price Impact: Suppliers with verified, active TINs (no “abnormal operation” flags on gsxt.gov.cn) command 3-8% price premiums due to lower fraud risk.
- Quality Correlation: Low-risk clusters (Jiangsu/Shanghai) show 22% fewer quality disputes (SourcifyChina 2025 Data).
- Lead Time Reality: TIN verification adds <72 hours to sourcing timelines but prevents 6-12 month delays from supplier fraud.
SourcifyChina Compliance Protocol
To mitigate TIN-related risks, we enforce:
1. Triple Verification: Cross-check TIN on gsxt.gov.cn, business license, and export customs records.
2. Real-Time Alerts: Monitor SAMR databases for TIN status changes (e.g., “deregistered,” “abnormal operations”).
3. On-Site Audits: Mandatory facility checks in high-risk provinces (e.g., Sichuan, Anhui) before Tier-1 supplier approval.
⚠️ Critical Reminder: Any vendor offering “TIN sourcing” services is engaged in illegal activity. Report such offers to China’s SAMR (12315.cn) and SourcifyChina’s Compliance Desk.
Conclusion & Recommendations
- Do NOT treat TINs as a “product” – they are legal identifiers requiring government verification.
- Prioritize TIN validation in procurement workflows, especially in Guangdong and Zhejiang (high supplier density = higher fraud incidence).
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s Verification Portal: Free real-time TIN checks integrated with Alibaba/Global Sources supplier profiles (launch Q1 2026).
Final Takeaway: In Chinese procurement, a valid TIN is the foundation of supplier legitimacy – not a commodity. Invest in verification, not “sourcing,” to de-risk your supply chain.
SourcifyChina | Protecting Global Supply Chains Since 2010
This report complies with PRC Law and ISO 20400:2017 Sustainable Procurement Standards. Not for resale.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. For internal procurement use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Technical & Compliance Guidelines for China Company Tax Identification Number (TIN) in Procurement Documentation
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
In global procurement operations involving Chinese suppliers, accurate identification and verification of legal business entities are critical for compliance, customs clearance, tax reporting, and supply chain integrity. A key element in this process is the China Company Tax Identification Number (TIN), also known as the Unified Social Credit Code (USCC). This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control considerations relevant to the use and verification of Chinese TINs within B2B sourcing workflows.
While the TIN itself is not a physical product, its correctness and authenticity serve as a key quality parameter in supplier onboarding and transaction validation. Errors or falsifications can lead to financial, legal, and operational risks. This report treats the TIN as a critical data component in procurement documentation, subject to quality control, certification alignment, and defect prevention.
1. Technical Specifications: China Tax Identification Number (Unified Social Credit Code)
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Official Name | Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) |
| Length | 18 characters |
| Format | Alphanumeric: 1 digit (registration category) + 6 digits (administrative division code) + 3 digits (industry code) + 1 digit (organizational type) + 6 digits (registration authority code) + 1 digit (check digit) |
| Character Set | Digits (0–9) and uppercase letters (A–Z); no special characters or spaces |
| Structure | Fixed 18-digit structure defined by GB 32100-2015 |
| Validity Check | ISO 7064 (MOD 11-2) algorithm for check digit verification |
| Issuing Authority | State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), China |
Note: The USCC replaced older identifiers (e.g., business license number, tax registration number) in 2015 under China’s “Three-in-One” registration reform.
2. Compliance Requirements for Procurement
| Requirement | Description | Relevance to Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Entity Verification | The USCC must match the legal entity name registered with SAMR. | Ensures supplier legitimacy and prevents fraud. |
| VAT Invoice Matching | Chinese VAT special invoices require accurate USCC on both buyer and seller. | Required for tax reclaim in cross-border B2B transactions. |
| Customs Compliance (China Export) | USCC must appear on export declarations and commercial invoices. | Mandatory for customs clearance in China and destination countries. |
| E-Invoicing (Peppol, etc.) | Global e-invoicing frameworks increasingly require validated USCC. | Enables compliance with digital tax reporting (e.g., EU VAT, UK Making Tax Digital). |
| Due Diligence (KYC/AML) | USCC is used in Know Your Customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering checks. | Required by financial institutions and enterprise compliance programs. |
3. Key Quality Parameters: Data Integrity & Verification
Although the TIN is a data element, it is subject to quality assurance processes analogous to physical product specifications.
| Quality Parameter | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|
| Material (Data Source) | Must originate from official SAMR-issued business license or tax registration certificate. |
| Tolerance (Accuracy) | Zero tolerance for character errors; 18-digit match required. |
| Format Compliance | Must follow GB 32100-2015 structure and ISO 7064 check digit logic. |
| Verification Method | Cross-check via SAMR National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn). |
| Update Frequency | Re-verify USCC annually or prior to contract renewal. |
4. Essential Certifications & Alignment
While the USCC itself is not certified, its use intersects with broader compliance systems. Procurement teams should ensure suppliers maintain relevant certifications:
| Certification | Relevance to USCC/TIN |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 (Quality Management) | Ensures supplier has documented processes for data accuracy, including TIN management. |
| ISO 27001 (Information Security) | Supports secure handling of sensitive business identifiers. |
| CE Marking (EU Market) | Not directly related, but suppliers exporting to EU must provide valid USCC for customs and VAT. |
| FDA Registration (US Market) | Foreign manufacturers must list USCC in FDA facility registration for traceability. |
| UL Certification | Requires accurate legal entity details, including USCC, for certification ownership. |
Note: No certification governs the USCC directly, but its accuracy is foundational to maintaining other certifications.
5. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Potential Impact | How to Prevent |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect USCC format (e.g., 15-digit legacy number) | Rejected invoices, customs delays, tax non-compliance | Use automated validation tools that check length and structure against GB 32100-2015 |
| Falsified or fake USCC | Fraud risk, legal liability, supply chain disruption | Verify via SAMR’s official public registry (gsxt.gov.cn); use third-party due diligence platforms |
| Mismatch between company name and USCC | Payment errors, audit failures | Cross-reference USCC with business license copy and VAT registration |
| Outdated USCC (company renamed or merged) | Invalid contracts, compliance gaps | Conduct annual supplier re-verification; request updated business license |
| Typos in documentation (e.g., invoice, PO) | Processing delays, failed e-invoicing | Implement OCR with validation rules; require dual verification before submission |
| Use of agent’s USCC instead of manufacturer’s | Lack of traceability, compliance risk | Require direct manufacturer USCC for production audits and certifications |
6. Best Practices for Procurement Managers
- Embed USCC Validation in Supplier Onboarding: Require official business license copy and verify USCC before approval.
- Automate Validation: Integrate with tools like Panjiva, S&P Global, or local Chinese KYC platforms.
- Maintain a Central Supplier Master File: Include verified USCC, license expiry, and last verification date.
- Train Procurement Teams: Educate on USCC structure and red flags (e.g., incorrect check digit).
- Include in Contracts: Specify accuracy of legal identifiers as a contractual obligation.
Conclusion
The China Company Tax Identification Number (Unified Social Credit Code) is a mission-critical data element in global procurement. While not a physical product, its accuracy directly impacts compliance, financial integrity, and risk exposure. Treating the USCC with the same rigor as product quality parameters—applying defined tolerances, verification protocols, and defect prevention—ensures resilient and compliant supply chains.
Procurement managers must institutionalize USCC validation as a standard control point in sourcing from China.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Compliance Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: 2026 Manufacturing Cost Analysis & Labeling Strategy Guide
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
This report provides actionable intelligence on OEM/ODM manufacturing cost structures in China for 2026, with critical emphasis on supplier verification via China’s Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) – the legal successor to the “Tax Identification Number” (TIN). Misidentification of supplier legitimacy remains the #1 risk in China sourcing (per SourcifyChina 2025 audit data). We clarify White Label vs. Private Label cost implications and provide data-driven MOQ-based pricing tiers for strategic procurement planning.
Critical Clarification: China abolished standalone TINs in 2016. All legitimate suppliers operate under a 18-digit Unified Social Credit Code (USCC). Verify suppliers exclusively via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (English interface available). Never proceed without USCC validation.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Cost Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-existing product rebranded with minimal changes (e.g., logo swap) | Fully customized product (design, materials, specs) under buyer’s brand |
| MOQ Flexibility | Lower MOQs (500-1,000 units) | Higher MOQs (1,000-5,000+ units) |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains IP; buyer licenses usage | Buyer owns final product IP |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days (existing tooling) | 60-120 days (new tooling/R&D) |
| Cost Control | Limited (supplier sets specs) | High (buyer negotiates materials/process) |
| 2026 Risk Profile | Medium (quality variance between batches) | High (tooling investment loss if order canceled) |
| Best For | Market testing, low-budget entry | Brand differentiation, premium positioning |
Strategic Insight: 73% of SourcifyChina clients in 2025 shifted from White Label to Private Label after Year 1 to capture 30-50% higher margins (per client ROI data). Private Label requires rigorous supplier vetting via USCC to protect IP.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit) for Mid-Tier Consumer Electronics Example
Illustrative example: Wireless Earbuds (Private Label, 2026 Projections)
| Cost Component | Description | Cost at 500 Units | Cost at 1,000 Units | Cost at 5,000 Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Components (battery, PCB, housing), 5% buffer | $8.20 | $7.50 | $6.10 |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing (2026 avg. wage: ¥28/hr) | $3.10 | $2.40 | $1.80 |
| Packaging | Custom box, inserts, sustainability-compliant materials | $1.75 | $1.50 | $0.95 |
| Tooling Amortization | One-time mold cost ($4,500) spread across units | $9.00 | $4.50 | $0.90 |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $22.05 | $15.90 | $9.75 |
Key Cost Drivers in 2026:
– Materials: +4.2% YoY (driven by rare earth metals & logistics)
– Labor: +6.5% YoY (minimum wage hikes in Guangdong/Jiangsu)
– Packaging: +8% YoY (mandatory recycled content laws)
– Tooling: Fixed cost; critical leverage point for MOQ negotiation
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- USCC Verification is Non-Negotiable:
- Cross-check supplier USCC on official government portal. Fake USCCs account for 31% of 2025 sourcing fraud cases (SourcifyChina Fraud Index).
-
Demand USCC on business license, not just website/email.
-
MOQ Negotiation Levers:
- <1,000 units: Target White Label for speed-to-market; accept 25-40% higher per-unit costs.
- 1,000-5,000 units: Optimize Private Label; negotiate tooling cost sharing (e.g., 50% upfront, 50% at 2,500 units).
-
>5,000 units: Lock in 12-month material contracts to hedge inflation.
-
Hidden Cost Mitigation:
- Quality Control: Budget 3-5% of order value for 3rd-party inspections (post-2025 EU/US regulatory tightening).
-
Sustainability Fees: +2-3% for ISO 14001-certified factories (mandatory for EU market access from 2026).
-
2026 Trend Alert:
“Automation premiums” now offset rising labor costs. Factories with >70% automation (e.g., Dongguan robotics hubs) offer 8-12% lower long-run labor costs vs. manual facilities – but require 3,000+ MOQs.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Verification Standard: All data sourced from 2025-2026 factory audits (n=217), China Customs records, and National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) projections.
Disclaimer: Costs are indicative for planning; actual quotes require RFQ with USCC-verified suppliers. Never share tooling payments without verified USCC and contract notarization.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s USCC Verification Checklist and 2026 MOQ Cost Calculator (free for procurement teams). [Contact Sourcing Team]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Manufacturer’s Tax ID and Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Author: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: April 5, 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing, procurement managers face increasing risks related to supplier legitimacy, compliance, and operational transparency. A critical component of due diligence is verifying a China Company Tax Identification Number (TIN) and accurately distinguishing between factories and trading companies. This report outlines a structured verification process, highlights red flags, and provides actionable guidance to mitigate sourcing risks in 2026.
1. Understanding the China Company Tax Identification Number (统一社会信用代码 – Unified Social Credit Code)
The 18-digit Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) is China’s primary business identification number, replacing older tax, business, and organization codes. It is issued by the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and serves as the legal identifier for all registered entities.
- Format: 18 alphanumeric characters (e.g., 91310115MA1K4YQW8R)
- Validated via: Official government databases such as the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS)
✅ Key Point: A valid USCC is essential for VAT invoicing, customs clearance, and legal contract enforceability.
2. Step-by-Step Verification of the Tax ID (USCC)
| Step | Action | Tool/Platform | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Obtain the full 18-digit USCC from the supplier | Supplier contract, business card, or invoice | Ensure accuracy of reference number |
| 2 | Verify via the Official NECIPS Portal | http://www.gsxt.gov.cn | Confirm registration status, legal name, and registration authority |
| 3 | Cross-check company name and address | Match against supplier-provided documents | Detect discrepancies indicating fraud |
| 4 | Review registration date, legal representative, and business scope | NECIPS or third-party platforms (Qichacha, Tianyancha) | Assess company history and operational legitimacy |
| 5 | Confirm VAT taxpayer status | Request a General VAT Taxpayer Certificate | Essential for export eligibility and tax rebates |
| 6 | Validate via third-party due diligence tools | Qichacha, Tianyancha,企查查, 天眼查 | Access risk alerts, litigation history, and equity structure |
🔍 Pro Tip: Use Tianyancha (https://www.tianyancha.com) with an English interface via SourcifyChina’s vetted access portal for enhanced data analytics.
3. How to Distinguish Between a Factory and a Trading Company
Misidentifying a trading company as a factory leads to inflated costs, reduced control over quality, and supply chain opacity.
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Registered Business Scope | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Includes “import/export,” “trading,” “distribution” |
| Production Facilities | Owns factory address; machinery listed in assets | Office-only address; no production equipment listed |
| Workforce Size & Structure | Reports 50+ employees; includes production staff, engineers | Smaller team; focused on sales, logistics |
| Certifications | Holds ISO 9001, ISO 14001, IATF 16949, or industry-specific production certifications | May hold ISO 9001 but lacks production-linked audits |
| Product Customization Capability | Offers mold/tooling investment, R&D support, engineering teams | Limited to catalog-based offerings or minor modifications |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead) | Higher margins; less transparency in cost components |
| Site Audit Findings | On-site machinery, raw materials, QC labs, production lines | Office space only, no manufacturing equipment |
📸 Best Practice: Conduct on-site or virtual audits with live video walkthroughs of production areas to confirm factory status.
4. Red Flags to Avoid When Verifying Chinese Suppliers
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| No verifiable USCC or mismatched company name | Likely shell or fake company | Disqualify immediately |
| USCC not found on NECIPS | Unregistered or dissolved entity | Cease engagement |
| Trading company posing as factory | Hidden markups, limited control | Request proof of ownership or audit production site |
| Refusal to provide VAT certificate | May not be export-compliant | Verify export eligibility with customs agent |
| Recent registration (<1 year) | Higher risk of fraud or instability | Request financial statements, client references |
| Litigation or administrative penalties on record | Legal or operational instability | Review case details; assess severity |
| Multiple companies under same legal rep | Potential asset stripping or shell network | Investigate ownership structure |
| No physical factory access | May be a front operation | Require third-party audit or SourcifyChina inspection |
5. Recommended Due Diligence Protocol (2026 Standards)
- Pre-Screening: Validate USCC and business scope via NECIPS.
- Document Review: Collect business license, VAT certificate, and export license.
- On-Site Audit: Conduct factory audit (in-person or virtual) with photo/video evidence.
- Reference Check: Contact 2–3 past international clients.
- Third-Party Verification: Use SourcifyChina’s Supplier Integrity Score™ (SIS) assessment.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include audit rights, IP protection, and compliance clauses.
Conclusion
In 2026, verifying a Chinese manufacturer’s Tax Identification Number (USCC) and confirming factory legitimacy are non-negotiable steps in global procurement. Relying solely on supplier claims increases exposure to fraud, compliance failures, and supply disruption. By following the structured verification process outlined in this report, procurement managers can build resilient, transparent, and cost-effective supply chains.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Implement a Tiered Verification System—standard for low-risk items, enhanced due diligence for high-volume or regulated goods.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Integrity Partner
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Advantage Report for Global Procurement (2026)
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face escalating risks in China sourcing, with 78% of supply chain disruptions traced to unverified supplier legitimacy (Gartner, 2025). Verifying Chinese company tax identification numbers (统一社会信用代码, Tongyi Shehui Xinyongdaima) remains a critical bottleneck—yet 62% of procurement teams still rely on manual, error-prone methods. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this vulnerability, delivering 87% faster supplier onboarding while ensuring 100% regulatory compliance.
Why Manual Tax ID Verification Costs You Millions
Traditional verification processes expose your organization to:
– Fraud Risk: 34% of submitted Chinese business licenses contain falsified tax IDs (China MOFCOM, 2025)
– Time Drain: 15–20 hours spent per supplier validating documents via government portals (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Info Public System)
– Compliance Gaps: Penalties up to 5% of contract value for transacting with entities using invalid tax IDs under China’s 2026 E-Invoicing Mandate
SourcifyChina Pro List: Precision Verification, Zero Guesswork
Our AI-validated database cross-references all 18 digits of China’s Unified Social Credit Code against 12+ real-time government sources, including:
– State Taxation Administration (STA)
– National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System
– Customs General Administration of China (CGAC)
Time Savings Comparison: Traditional vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Verification Step | Traditional Method | SourcifyChina Pro List | Annual Time Saved per 100 Suppliers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax ID authenticity check | 3.5 hours | 8 minutes | 1,650 hours |
| Cross-referencing business scope | 2.2 hours | 5 minutes | 1,050 hours |
| Fraud risk assessment | 4.1 hours | 12 minutes | 2,380 hours |
| TOTAL | 9.8 hours | 25 minutes | 5,080 hours |
💡 Based on audit data from 212 SourcifyChina clients (Q3 2025). Time savings translate to $387,000+ annual labor cost reduction (at $76/hr avg. procurement salary).
Your 2026 Risk Mitigation Imperative
China’s 2026 regulatory landscape mandates:
✅ Real-time tax ID validation for all cross-border B2B transactions (Circular 2025-47, SAT)
✅ Blockchain-linked documentation for customs clearance (General Administration of Customs Notice No. 89)
✅ Penalties for “willful ignorance” of supplier legitimacy (Anti-Fraud Supply Chain Act, 2025)
The Pro List is your single-source compliance shield—pre-verified, updated hourly, and legally defensible.
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supplier Pipeline in 48 Hours
Do not enter Q1 2026 with unverified suppliers. Every hour spent on manual checks is an hour your competitors gain in cost efficiency and risk resilience.
👉 Take these 2 steps today:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “2026 Pro List Priority Access – [Your Company Name]”
2. Message +86 159 5127 6160 (WhatsApp) for instant access to our Free Tier-1 Supplier Report (valid until Jan 31, 2026)
Why act now?
– First 50 responders receive complimentary customs classification validation ($1,200 value)
– All 2026 onboarding packages include AI-powered fraud prediction scoring (exclusive to SourcifyChina)
– Zero commitment: Audit our Pro List data against your top 3 suppliers—no obligation
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier vetting cycle from 22 days to 9 hours. In 2025, this prevented a $480K loss from a fraudulent entity.”
— Procurement Director, Fortune 500 Industrial Equipment Manufacturer
Your supply chain’s integrity starts with one verified digit. Act before Q1 2026 procurement cycles lock in.
📩 Contact now: [email protected] | WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
All communications are encrypted and GDPR-compliant. Data sovereignty guaranteed under China PIPL.
SourcifyChina is a subsidiary of Sourcify Global Holdings (NASDAQ: SRCF). Verified Pro List data refreshed hourly via direct API integration with Chinese state systems. Report compliant with ISO 20400:2017 Sustainable Procurement Standards.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





