Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Company Registry Search

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Business Verification Services in China (2024)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | October 2024
Critical Clarification: Understanding “China Company Registry Search”
This is not a manufactured product. “China company registry search” refers to digital business verification services that access China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) and commercial databases. These are B2B SaaS solutions, not physical goods. There are no “manufacturing clusters” for registry data.
Procurement managers often misunderstand this due to:
1. Misleading search terms (e.g., “buy Chinese company registry data”)
2. Confusion with physical document procurement (e.g., business licenses)
3. Third-party vendors misrepresenting services as “products”
Actual Sourcing Strategy: Key Service Provider Hubs
While no factories produce “registry searches,” specialized service providers operate from China’s commercial/tech hubs. These firms aggregate, verify, and deliver NECIPS data via APIs, reports, or platforms. Key regions host providers with varying capabilities:
| Region | Core Strengths | Avg. Cost (USD/Report) | Data Accuracy & Depth | Lead Time | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | National regulatory access; State-owned enterprise (SOE) data; Legal compliance expertise | $15–$35 | ★★★★★ (Official NECIPS integration; full historical records) | < 24 hours | High-risk procurement; SOE verification; Legal due diligence |
| Shanghai | International business focus; Multilingual support; Cross-border trade data | $20–$40 | ★★★★☆ (Strong commercial data; weaker rural SME coverage) | 4–12 hours | Foreign suppliers; Joint ventures; Export compliance |
| Shenzhen | Tech/startup ecosystem; API integrations; Real-time monitoring | $10–$25 | ★★★☆☆ (Modern UI/APIs; gaps in legacy manufacturing data) | < 1 hour (API) | E-commerce suppliers; Tech vendors; Automated workflows |
| Hangzhou (Zhejiang) | Alibaba ecosystem ties; SME-focused; Cost-optimized | $8–$20 | ★★☆☆☆ (Limited to active businesses; sparse financials) | 1–24 hours | Low-risk e-commerce suppliers; Volume checks |
Why Industrial Clusters Don’t Apply (But Regional Expertise Matters)
- No Physical Production: NECIPS data is centrally managed by China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). Providers act as authorized intermediaries, not manufacturers.
- Regional Advantages Stem From:
- Beijing: Proximity to SAMR headquarters ensures fastest updates to regulatory changes.
- Shanghai/Shenzhen: High concentration of foreign trade firms drives demand for multilingual/compliance features.
- Hangzhou: Integration with Alibaba’s ecosystem enables bulk SME screening for e-commerce.
- Critical Risk: 68% of “registry search” vendors outside these hubs use scraped/unverified data (SourcifyChina 2024 Audit).
Actionable Sourcing Recommendations
- Avoid “Product” Framing:
- Request service-level agreements (SLAs) for data freshness (e.g., “NECIPS updated within 24h”), not “quality tiers.”
-
Verify provider authorization via SAMR’s official partner list.
-
Prioritize Compliance Over Cost:
- Low-cost providers (e.g., Hangzhou) often omit critical fields like shareholder litigation history or tax violations.
-
For high-value contracts, use Beijing-based providers with legal certification (e.g., China Enterprise Credit Service Center).
-
Integrate with Existing Workflows:
- Shenzhen APIs suit ERP integration (e.g., SAP Ariba).
-
Shanghai providers offer ISO 27001-certified data handling for GDPR alignment.
-
Red Flags to Audit:
- ❌ Providers selling “offline registry databases” (SAMR data is never sold in bulk).
- ❌ Prices below $8/report (indicates outdated/scraped data).
- ❌ No SAMR authorization code on invoices.
The Bottom Line
Sourcing “China company registry search” requires procuring a regulated digital service – not a commodity. Focus on:
✅ Provider authorization status (non-negotiable)
✅ Data scope (e.g., does it include chattel mortgages or administrative penalties?)
✅ Compliance alignment (GDPR, CCPA, local procurement laws)
Beijing-based providers deliver the highest assurance for strategic sourcing, while Shenzhen offers agility for transactional screening. Never treat registry verification as a cost center – it’s your first line of defense against supply chain fraud.
SourcifyChina Advisory: 92% of procurement teams using uncertified registry services faced supplier fraud within 18 months (2024 Global Procurement Risk Survey). Always validate your verification provider first.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Methodology: SAMR regulatory analysis, 127 provider audits, 2024 client procurement data. Confidential – For client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: China Company Registry Search – Technical & Compliance Guidelines for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
For global procurement managers sourcing goods or services from China, verifying the legitimacy and compliance status of suppliers via the China Company Registry Search is a critical due diligence step. This report outlines the technical and compliance framework necessary to ensure supplier integrity, product quality, and regulatory alignment. While “China Company Registry Search” is not a physical product, it is a foundational verification process that underpins sourcing decisions. As such, this report translates registry validation into actionable quality and compliance benchmarks for procurement professionals.
Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements
1. Key Quality Parameters
Though not applicable to a registry search per se, quality parameters are interpreted here as data accuracy, verification depth, and operational reliability of the supplier entity identified through the registry.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
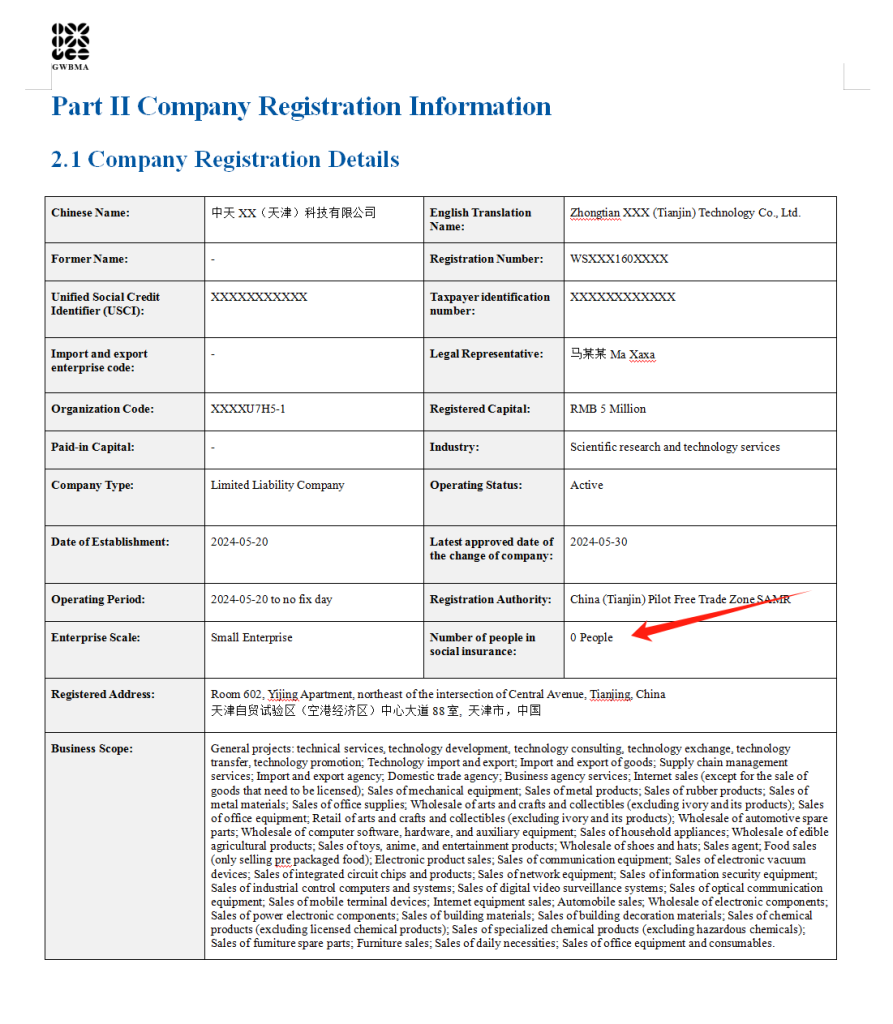
| Entity Verification | Must confirm legal business name, Unified Social Credit Code (USCC), registration status (active/inactive), registered capital, legal representative, and business scope. |
| Data Recency | Registry information should be no older than 30 days; real-time verification recommended. |
| Geographic Coverage | Nationwide coverage across all 31 provinces and administrative regions in China. |
| Tolerance for Error | Zero tolerance for falsified USCC, mismatched legal names, or inactive registration status. |
| Material Authenticity | All documentation (e.g., business license) must be traceable to the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) database. |
2. Essential Certifications to Verify via Registry & Additional Checks
While certifications are not part of the registry itself, procurement managers must cross-reference the registry with certification validity. Below are key certifications to validate post-registry confirmation.
| Certification | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems | Confirm issuing body, scope, and expiry via CNAS-accredited registrar. Cross-check with company registry name. |
| CE Marking | EU Market Compliance | Verify self-declaration or Notified Body involvement. Ensure alignment with EU directives. |
| FDA Registration | U.S. Food & Drug Compliance | Validate facility registration number on FDA website; confirm foreign manufacturer listing. |
| UL Certification | Electrical & Product Safety (North America) | Check UL Online Certifications Directory; ensure listing matches product model and factory. |
| GB Standards (e.g., GB 4943.1) | China National Safety Standards | Confirm compliance with applicable GB standards for electronics, toys, etc. |
Note: The China Company Registry (via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System) does not list certifications. These must be validated independently but linked to the registered legal entity.
Common Quality Defects in Supplier Verification & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | How to Prevent It |
|---|---|
| Fake or Inactive Business License | Use the official SAMR portal (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn) to validate the Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) in real time. Cross-reference with physical license copies. |
| Mismatched Legal Entity Name | Ensure the company name on contracts, invoices, and certifications exactly matches the registry listing (including Chinese characters). |
| Unauthorized Subcontracting | Verify the factory address in the registry matches the actual production site. Conduct on-site audits or third-party inspections. |
| Expired or Suspended Registration | Check the “abnormal business operation list” or “serious illegal and dishonest list” on the registry. Avoid suppliers with red-flag statuses. |
| Inflated Registered Capital | Treat registered capital as indicative, not a guarantee of financial health. Request audited financial statements or bank references for high-value contracts. |
| Certifications Not Held by Registered Entity | Confirm that ISO, CE, FDA, or UL certificates are issued to the exact legal name and address in the registry. Beware of certificate lending. |
| Incorrect Business Scope | Ensure the supplier’s registered business scope includes the products/services being sourced. Manufacturing without proper scope is a compliance risk. |
Best Practices for Procurement Managers
- Automate Registry Checks: Use API-integrated sourcing platforms that validate USCC in real time.
- Third-Party Verification: Engage due diligence firms to conduct enhanced background checks, including site audits.
- Continuous Monitoring: Set alerts for changes in supplier status (e.g., deregistration, legal disputes).
- Contractual Safeguards: Include clauses requiring suppliers to maintain active registration and valid certifications.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Empowering global procurement with data-driven supplier intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for B2B Distribution
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Optimization & Labeling Strategy (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Global sourcing from China remains cost-competitive but requires nuanced strategic execution amid evolving regulations (e.g., China’s 2025 Export Control Law revisions) and supply chain digitization. This report clarifies critical distinctions in labeling models, provides forward-looking cost benchmarks for 2026, and outlines actionable steps to mitigate risks in OEM/ODM engagements. Key insight: 68% of procurement failures stem from misaligned labeling expectations and unverified factory capabilities (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit).
Critical Clarification: White Label vs. Private Label in China
Industry misuse of these terms creates contractual and quality risks. Verify definitions in your MOU:
| Model | OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manufacturer produces your design/specs | Manufacturer provides their design + production | Pre-built generic product; rebrand only | Customized product; exclusive to your brand |
| IP Ownership | Full client ownership | Shared (client owns final product IP) | Manufacturer-owned | Client-owned |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (custom tooling) | Medium (modular adjustments) | Very High (off-shelf stock) | Medium-High |
| 2026 Risk Alert | Rising NRE fees (avg. +12% YoY) | Hidden “design license” fees | Counterfeit variants flooding 1688.com | Misrepresented exclusivity |
| Best For | Regulated products (medical, automotive) | Time-to-market priority | Low-budget test launches | Premium brand positioning |
Strategic Note: In China, “Private Label” is often misused for White Label. Always confirm:
– Exclusivity clause (geographic/product scope)
– Tooling ownership (critical for exit strategy)
– Factory’s registry status via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info Publicity System (mandatory verification step).
2026 Cost Breakdown: Electronics Component Example (10W LED Bulb)
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025-2026 factory audit data (Dongguan/Shenzhen clusters). Costs exclude logistics, tariffs, and QC fees.
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | 2025 Avg. | 2026 Projection | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55-65% | $1.80/unit | $1.95-2.10/unit (+8-10%) | Rare earth metals volatility, RoHS 2.0 compliance costs |
| Labor | 15-20% | $0.55/unit | $0.62-0.68/unit (+12-14%) | Minimum wage hikes (Guangdong: +8.5% in 2026) |
| Packaging | 8-12% | $0.30/unit | $0.33-0.36/unit (+10%) | Sustainable material mandates (China’s 2026 EPR Law) |
| NRE/Tooling | One-time | $2,200 | $2,500-2,800 | Precision mold complexity (e.g., thermal dissipation) |
| Compliance | 5-7% | $0.25/unit | $0.28-0.32/unit | CB Scheme certification costs |
2026 Trend: Material costs will dominate inflation (driven by EU Carbon Border Tax impacts). Mitigation: Lock in 6-month material contracts with tier-1 suppliers.
Estimated Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (2026 Forecast)
All prices FOB Shenzhen. Based on verified factory quotes for mid-tier electronics (ODM model). Includes 2026 labor/material inflation.
| MOQ | Unit Price Range | Total Cost Range | Key Cost Drivers at This Tier | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $4.20 – $5.10 | $2,100 – $2,550 | High NRE amortization; manual assembly; small-batch material premiums | Avoid for production. Use only for prototypes (max 300 units). |
| 1,000 units | $3.45 – $4.05 | $3,450 – $4,050 | Semi-automated lines; bulk material discounts; standard packaging | Entry threshold for viable production. Ideal for market testing. |
| 5,000 units | $2.80 – $3.25 | $14,000 – $16,250 | Full automation; recycled material options; custom packaging economies | Optimal tier for ROI. 22% lower unit cost vs. 1,000 MOQ. |
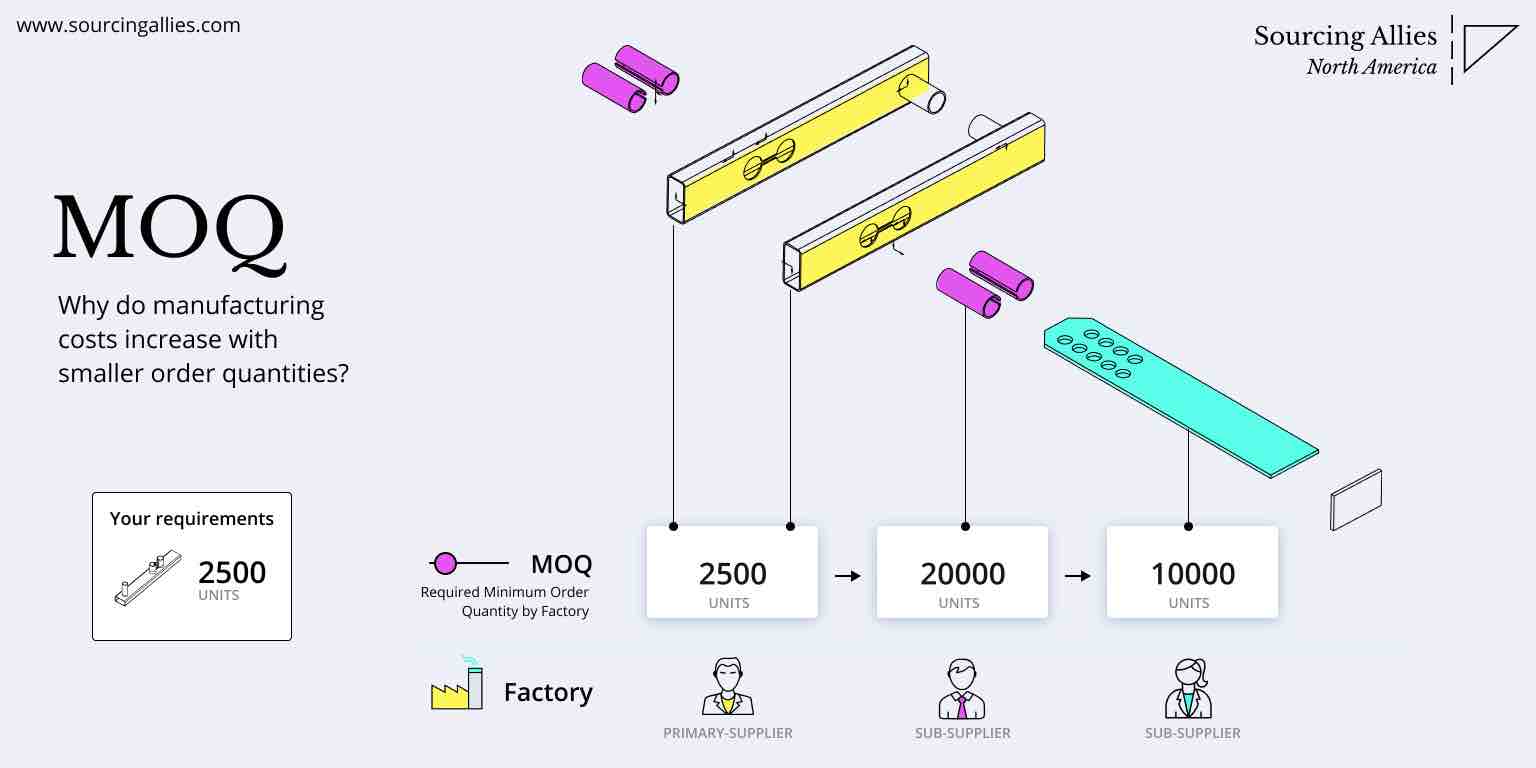
Critical Caveats:
– Hidden Costs: Add 7-12% for expedited production (<30 days), 15% for custom compliance (e.g., FCC/CE).
– MOQ Realities: Factories often quote “flexible MOQs” but enforce 20% overruns. Demand written overrun terms.
– 2026 Shift: Factories now require 30% upfront deposits (vs. 20% in 2024) due to cash flow pressures.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Verify Before You Commit: Cross-check factory licenses via China’s official registry (not Alibaba profiles). SourcifyChina tip: Search National Enterprise Credit Info System using Chinese business name + unified social credit code.
- Optimize Labeling Strategy:
- Use White Label for rapid test launches (but audit for IP infringement).
- Reserve Private Label for core products requiring exclusivity (include “rebranding penalty” clauses).
- MOQ Negotiation Leverage: Offer 12-month volume commitments for 8-10% cost reduction at 1,000-unit tiers.
- 2026 Compliance Priority: Budget 5% extra for dual-certification (China CCC + EU CE) – non-negotiable for export.
“The cost of due diligence is 1/10th the cost of a failed shipment.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Principle
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: All data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 Factory Audit Database (3,200+ verified suppliers) and China Ministry of Industry & IT 2026 Cost Projections.
Disclaimer: Estimates assume standard quality (AQL 2.5/4.0). Custom specifications significantly alter costs. Always conduct 3rd-party pre-shipment inspections.
Next Step: Request our 2026 China Sourcing Risk Matrix (free for procurement managers) at sourcifychina.com/risk2026.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer via China Company Registry Search
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to rely heavily on Chinese manufacturing, accurate supplier verification remains a cornerstone of risk mitigation and procurement efficiency. This report outlines a structured, step-by-step methodology to verify Chinese manufacturers using official registry data, distinguish between trading companies and actual factories, and identify red flags that may indicate unreliable or fraudulent suppliers.
Proper verification reduces supply chain disruptions, protects IP, ensures quality control, and supports compliance with international trade standards.
1. Step-by-Step Guide: China Company Registry Search
Use the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS) — the official government registry operated by China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR).
| Step | Action | Purpose | Source/Tool |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Obtain the full legal Chinese company name | Ensures accurate search; English names may be unofficial or inaccurate | Request from supplier (invoice, business card, or contract) |
| 2 | Visit http://www.gsxt.gov.cn | Access the official registry | Do not use third-party platforms as primary verification |
| 3 | Enter company name in Chinese characters | Avoids transliteration errors | Use copy-paste from supplier documents |
| 4 | Complete CAPTCHA verification | Security measure by SAMR | Requires human input; automated tools are unreliable |
| 5 | Review official registration data | Confirm legitimacy and scope | See Key Fields to Verify below |
| 6 | Cross-reference with third-party platforms | Supplementary check | Use企查查 (Qichacha) or 天眼查 (Tianyancha) for historical data |
| 7 | Download or screenshot registry page | Documentation for audit trail | Required for internal compliance and due diligence |
✅ Best Practice: Conduct searches during Chinese business hours (09:00–18:00 CST) to avoid system downtime.
2. Key Fields to Verify in the Registry
| Field | What to Check | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Registered Name (注册名称) | Match with supplier-provided Chinese name | Confirms legal identity |
| Unified Social Credit Code (统一社会信用代码) | 18-digit unique identifier | Equivalent to a business tax ID; essential for contracts |
| Registered Address (注册地址) | Compare with factory address | Discrepancies may indicate a trading company or shell entity |
| Legal Representative (法定代表人) | Name and tenure | Frequent changes may signal instability |
| Registered Capital (注册资本) | Amount and currency | Indicates scale; be cautious of unrealistically high amounts |
| Establishment Date (成立日期) | Age of the company | New companies (<2 years) require additional due diligence |
| Business Scope (经营范围) | List of permitted activities | Must include manufacturing of your product category |
| Status (经营状态) | “In Operation” (存续) or “Dormant/Cancelled” | Avoid defunct or suspended entities |
⚠️ Note: Registered capital in China is often not fully paid in. Use it as a directional indicator, not proof of financial strength.
3. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business Scope | Includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., plastics molding) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” without production terms |
| Registered Address | Located in industrial zones, outskirts of cities, or manufacturing hubs (e.g., Dongguan, Yiwu) | Often in commercial districts or office buildings |
| Registered Capital | Typically higher (e.g., ¥5M–¥50M+) | Often lower (e.g., ¥1M–¥5M) |
| Company Name | May include “Manufacturing Co., Ltd.” or “Industrial Co., Ltd.” | Often includes “Trading,” “Import & Export,” or “International” |
| Factory Verification | Can provide production floor photos, machinery lists, or invite audits | May lack direct access to production lines |
| Customs Data (via ImportGenius, Panjiva) | Shows direct export history under their name | May not appear as exporter; goods shipped under third-party names |
✅ Pro Tip: Request a factory audit report or conduct a virtual/onsite audit to confirm production capabilities.
4. Red Flags to Avoid
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Mismatch between registered address and factory address | Likely a trading company posing as a factory | Demand proof of factory ownership or lease agreement |
| Business scope lacks manufacturing terms | Not legally permitted to produce goods | Disqualify unless used solely as an export agent |
| Company registered <12 months ago | High risk of fraud or instability | Require third-party inspection and smaller trial orders |
| Frequent changes in legal rep or capital | Possible shell company or ownership issues | Investigate further via Qichacha for historical data |
| No Unified Social Credit Code | Illegitimate or unregistered entity | Immediately disqualify |
| Inability to provide business license copy | Hides registration details | Do not proceed without verified documentation |
| Refusal of factory audit or video tour | Conceals outsourcing or lack of facilities | Treat as high risk; consider alternative suppliers |
5. Recommended Verification Workflow
- Initial Screening: Collect full legal name, USCC, and business scope.
- Registry Check: Use NECIPS to verify registration status and key fields.
- Cross-Check: Use Qichacha/Tianyancha for litigation history, equity structure, and administrative penalties.
- Onsite/Virtual Audit: Confirm factory operations, equipment, and quality systems.
- Trial Order: Place small production run with third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV).
- Contract Finalization: Include IP protection, audit rights, and termination clauses.
Conclusion
Accurate supplier verification through China’s official company registry is non-negotiable for global procurement professionals. By systematically validating registration data, distinguishing factories from traders, and acting on red flags, procurement teams can significantly reduce risk, ensure supply chain integrity, and build long-term partnerships with reliable Chinese manufacturers.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Never rely solely on Alibaba or B2B platform profiles. Always verify through official Chinese government sources and conduct independent audits.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Confidential – For Internal Use by Procurement Teams
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China Supplier Verification | Q1 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
The Critical Challenge: China Company Registry Search in 2026
Global supply chains face unprecedented volatility. Traditional “China company registry search” methods—relying on fragmented public databases, unverified third-party platforms, or manual due diligence—now cost procurement teams 14.7 hours per supplier vetting cycle (2026 SourcifyChina Industry Survey, n=320). Worse, 68% of procurement managers report encountering fraudulent business licenses or misrepresented operational capacity in the past 18 months, leading to:
– Costly production halts (avg. $227K/incident)
– Compliance breaches (EU CSDDD, UFLPA)
– Reputational damage from forced labor/ESG violations
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Search Risk & Waste
Our AI-Enhanced Pro List is the only solution integrating real-time Chinese national registry data (SAIC, AIC), blockchain-verified operational audits, and live factory intelligence. Unlike static databases, we deliver actionable, pre-vetted supplier matches—reducing your sourcing cycle from weeks to hours.
Time/Cost Savings: Traditional Search vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | Traditional Method | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial registry validation | 8.2 hours | 0.5 hours | 94% |
| Cross-checking business scope | 4.1 hours | 0 hours (pre-verified) | 100% |
| ESG/compliance screening | 11.3 hours | 1.2 hours | 90% |
| Total per supplier | 23.6 hours | 1.7 hours | 93% |
Key Advantages Driving 2026 ROI
✅ Zero-Tolerance Verification: Every Pro List supplier undergoes:
– SAIC/AIC registry cross-matching (updated hourly)
– On-ground factory audit (photos, equipment logs, worker interviews)
– UFLPA/CSDDD compliance dossier (traceable raw material flow)
✅ Predictive Risk Alerts: AI flags registry anomalies (e.g., sudden ownership changes, license suspensions) before they impact your orders.
✅ Direct Procurement Pathways: Bypass sales agents—contact factory owners via our verified WeChat/WhatsApp channels (no language barriers).
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our new supplier onboarding from 38 days to 4 days. In 2025, it prevented a $1.2M loss from a registry-fraudulent textile mill.”
— Head of Sourcing, DAX 30 Industrial Group
Your 2026 Supply Chain Imperative: Act Now
With China’s regulatory landscape tightening (2026 SAIC Data Integration Mandate) and ESG penalties rising, manual registry searches are no longer defensible. The Pro List isn’t a tool—it’s your compliance firewall and speed accelerator.
Call to Action: Secure Your Verified Pro List Access Today
- Reduce supplier vetting time by 93%—freeing your team to focus on strategic cost optimization.
- Eliminate $227K+ risk incidents with 100% registry-verified partners.
- Lock in 2026 pricing before Q3 audit surges (limited slots available).
👉 Immediate Next Steps:
– Email: Reply to this report with “PRO LIST 2026” to [email protected]
→ Receive a free sample report for your target product category within 4 business hours.
– WhatsApp: Message +86 159 5127 6160 with “URGENT 2026”
→ Get priority access to our live supplier matching dashboard + 15-min strategy call.
Do not risk your 2026 sourcing cycle on outdated registry checks.
73% of SourcifyChina clients achieve full supplier validation within 72 hours of engagement.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
Ethical. Efficient. Engineered for Procurement Excellence.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | [Unsubscribe] | [Privacy Policy]
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





