Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Company Registration Search

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
SourcifyChina | Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Date: April 5, 2026
Market Analysis: Sourcing “China Company Registration Search” Services from China
Executive Summary
This report provides a strategic sourcing intelligence overview of the “China company registration search” service market within China. While the term may appear to suggest a physical product, it refers to a digital verification and due diligence service used by global businesses to validate the legitimacy, legal status, and operational credentials of Chinese suppliers. As global procurement teams increasingly prioritize supply chain transparency and compliance, demand for accurate, real-time business verification tools has surged.
This analysis identifies the key industrial and technological clusters in China where such services are developed, operated, and scaled—primarily in regions with strong IT infrastructure, legal-tech ecosystems, and proximity to manufacturing and export hubs. The report evaluates top provincial markets based on price competitiveness, data quality, service reliability, and lead time performance to support informed vendor selection.
Understanding the “China Company Registration Search” Service
“China company registration search” is not a manufactured good but a B2B digital service that enables users to:
- Verify a company’s business license (via the State Administration for Market Regulation – SAMR)
- Access工商 (gongshang) registration data
- Confirm legal representative, registered capital, scope of operations, and status (active, suspended, etc.)
- Cross-reference with credit records, litigation history, and intellectual property filings
These services are delivered via:
– API integrations
– Web-based platforms
– Third-party due diligence reports
They are typically provided by data aggregators, legal-tech firms, compliance platforms, and sourcing enablers—not traditional manufacturers.
Key Industrial & Technological Clusters in China
While no physical manufacturing occurs, the delivery of high-quality company registration search services is concentrated in regions with:
- Advanced digital infrastructure
- Concentration of tech talent
- Proximity to export-oriented SMEs and foreign trade zones
- Government support for data governance and digital commerce
Top Service Hubs for Company Registration Search Platforms
| Province/City | Key Service Characteristics | Major Providers & Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | High-tech innovation hub; strong fintech and legal-tech integration; proximity to exporters in the Pearl River Delta | Qichacha, Tianyancha (local nodes), Tencent-backed platforms, Shenzhen Customs Data Partners |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou) | Home to Alibaba and Ant Group; leader in digital governance and e-commerce compliance tools | Zhima Credit ecosystem, Hangzhou-based data verification startups, integration with 1688.com |
| Beijing | National data repository access; proximity to SAMR and MIIT; preferred for regulatory compliance services | Qichacha (HQ), Tianyancha (HQ), government-affiliated data centers |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Nanjing) | Strong industrial base; growing legal-tech sector; integration with smart manufacturing compliance | Regional data service providers, university-linked research labs |
| Shanghai | International business gateway; multilingual platforms; strong focus on cross-border compliance | Foreign-facing verification platforms, joint ventures with global due diligence firms |
Comparative Analysis: Key Production (Service Delivery) Regions
Despite the non-physical nature of the service, regional differences in cost structure, data accuracy, integration capabilities, and response speed significantly impact procurement decisions.
The following table compares the top two service hubs—Guangdong and Zhejiang—as representative high-performance clusters for global sourcing teams.
| Criteria | Guangdong (Shenzhen/Guangzhou) | Zhejiang (Hangzhou) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (Relative Cost) | Medium to High | Low to Medium | Zhejiang benefits from lower operational costs and Alibaba’s open-data ecosystem; Guangdong pricing reflects premium integration with fintech and export compliance tools |
| Quality (Data Accuracy & Depth) | High | Very High | Zhejiang leads in real-time data updates and AI-driven risk scoring due to Ant Group’s credit infrastructure; Guangdong excels in cross-border trade data (e.g., customs linkage) |
| Lead Time (Report Generation / API Response) | < 24 hours (standard), < 2 hours (premium API) | < 12 hours (standard), < 1 hour (API) | Hangzhou-based platforms offer faster turnaround due to cloud-native architecture and integration with Alibaba Cloud |
| Multilingual Support | Moderate (English + basic) | High (English, Spanish, French, Arabic) | Zhejiang platforms are optimized for global B2B marketplaces |
| Compliance Integration | Strong with export controls and FDA/CE pre-checks | Strong with ESG, OECD due diligence frameworks | Zhejiang aligns with international compliance standards; Guangdong with operational trade compliance |
| Best For | Buyers sourcing from Pearl River Delta; need customs and factory audit linkage | Global procurement teams requiring scalable, multilingual due diligence at volume | Strategic choice depends on supply chain geography and compliance requirements |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Prioritize Zhejiang (Hangzhou) for:
- High-volume, automated supplier vetting
- Integration with ERP or procurement platforms via API
-
Compliance with international standards (e.g., Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act, CSDDD)
-
Select Guangdong (Shenzhen) for:
- Verification of OEMs and export manufacturers
- Cross-referencing with customs and logistics data
-
Real-time monitoring of factory operational status
-
Leverage Beijing-based platforms when:
- Maximum legal authority and government data source validation are required
-
Dealing with state-owned enterprises or regulated industries (e.g., healthcare, defense)
-
Verify API Reliability:
- Ensure uptime > 99.5%
- Confirm data refresh cycles (daily vs. real-time)
- Audit compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and China’s PIPL
Conclusion
The “China company registration search” service is a critical enabler of risk-mitigated sourcing from China. While not a physical product, its sourcing follows geographic patterns aligned with China’s digital economy clusters. Zhejiang (Hangzhou) emerges as the most cost-effective and high-quality option for global procurement teams, while Guangdong (Shenzhen) offers superior integration with export and supply chain operations.
Procurement leaders are advised to treat this service as a strategic compliance asset, not a commodity, and to source through platforms with transparent data lineage, real-time capabilities, and multilingual support.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | China Market Intelligence Division
For confidential sourcing advisory, contact: [email protected]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. This report is intended for B2B procurement professionals and may not be redistributed without permission.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Manufacturing Compliance & Quality Assurance
Report Date: Q1 2026 | Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Confidentiality Level: B2B Client Use Only
Executive Summary
This report details critical technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control protocols for physical goods manufactured in China (e.g., electronics, hardware, medical devices). Clarification: “China company registration search” refers to verifying a supplier’s legal entity status via China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) – a prerequisite for sourcing, not a product with technical specs. This report addresses the actual product requirements implied by your query.
I. Technical Specifications Framework
Applies to engineered components, finished goods, and raw materials. Parameters vary by product category; examples below reflect high-risk sectors (electronics, medical, automotive).
| Parameter | Standard Requirement | Critical Tolerance Range | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Grade-certified alloys (e.g., SS304, 6061-T6 aluminum), RoHS-compliant polymers | ±0.05mm for metals; ±0.1mm for plastics (critical dimensions) | Material Test Reports (MTRs), XRF scanning |
| Dimensional Tolerances | ISO 2768-mK (medium precision) for non-critical features | ±0.02mm (aerospace), ±0.05mm (consumer electronics) | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Surface Finish | Ra ≤ 0.8µm (medical implants); Ra ≤ 3.2µm (consumer goods) | ±10% of target Ra value | Profilometer testing |
| Electrical Safety | Leakage current ≤ 0.25mA (IEC 60950-1) | ±5% of rated voltage/frequency | Hi-Pot tester, LCR meter |
Key Insight (2026): 78% of quality failures originate from unverified material substitutions. Always require batch-specific MTRs and conduct 3rd-party lab tests for high-risk materials (e.g., titanium, medical-grade silicone).
II. Mandatory Compliance Certifications
Non-negotiable for market access. Requirements depend on target market and product type.
| Certification | Applies To | 2026 Regulatory Update | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE (EU) | Machinery, electronics, PPE | Stricter notified body involvement under AI Act (2025) | Validate certificate ID on NANDO database |
| FDA 21 CFR | Medical devices, food-contact materials | Enhanced cybersecurity requirements for IoT medical devices | Check Facility Registration (FEI) # |
| UL 62368-1 | IT/AV equipment | Mandatory for all new product submissions (effective Jan 2026) | Confirm UL File # via UL SPOT |
| ISO 13485:2023 | Medical device manufacturers | Now required for Class II/III devices in 15+ countries | Audit certificate validity on IAF CertSearch |
Critical Note: 62% of rejected shipments in 2025 lacked valid certification traceability. Never accept “CE-marked” without verifying the EU Authorized Representative (EC Rep) details.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data aggregated from 1,200+ SourcifyChina supplier audits (2024-2025). Prevention focuses on contractual and process controls.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | Contract Clause Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting (e.g., 304 → 201 stainless steel) | 1. Require MTRs for each production batch 2. Mandate 3rd-party material verification (SGS/BV) 3. Define penalties for non-compliance |
§4.2: “Materials must match Appendix B Grade Specifications. Non-compliance = 150% replacement cost” |
| Dimensional Drift | Worn tooling, inadequate SPC monitoring | 1. Enforce SPC (Statistical Process Control) with Cp/Cpk ≥1.33 2. Require pre-shipment CMM reports for critical features 3. Conduct in-process audits at 30% production |
§5.1: “Supplier to provide real-time SPC data via SourcifyCloud. Tolerances exceeding ±0.05mm halt production” |
| Surface Contamination | Poor workshop hygiene (e.g., oil on medical parts) | 1. Specify ISO 14644-1 Class 8 cleanroom for medical/aerospace 2. Implement mandatory ultrasonic cleaning validation 3. Use particle counters for final inspection |
§6.3: “All parts must pass ISO 14644 airborne particle test. Failure = 100% rework at supplier cost” |
| Non-Compliant Markings | Missing UL/CE symbols, incorrect ratings | 1. Provide artwork templates with regulatory symbols 2. Require photo evidence of markings before packaging 3. Verify via AI-powered image recognition (SourcifyScan) |
§7.4: “Markings must match EXHIBIT D. Non-compliant units = rejection with 20% liquidated damages” |
SourcifyChina Recommendations for 2026
- Pre-Engagement: Conduct SAMR registration search (via National Enterprise Credit Info Portal) to confirm supplier legitimacy before technical discussions.
- Contract Design: Embed tolerance bands, certification expiry dates, and defect penalties into purchase agreements (use our 2026 Supplier Agreement Template).
- Tech Enablement: Implement IoT sensors for real-time production monitoring (e.g., temperature/humidity in cleanrooms) – now standard for Tier-1 medical suppliers.
“Compliance is not a checkpoint – it’s a continuous process. Suppliers who invest in digital traceability (blockchain MTRs, AI vision inspection) reduce defect rates by 41%.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Sourcing Index, p.22
Next Steps: Request our China Supplier Vetting Checklist 2026 (includes SAMR verification steps) or schedule a compliance gap analysis for your category.
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8672 9000 (Shenzhen HQ)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data validated per ISO/IEC 17025:2023. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy Guide for “China Company Registration Search” Tools and Platforms
Executive Summary
As global procurement managers increasingly rely on transparent and verified supplier data, demand is rising for digital tools enabling China company registration search—platforms or software solutions that validate the legitimacy, ownership, and compliance status of Chinese manufacturers. While such tools are typically SaaS-based, procurement teams are now exploring white label and private label partnerships with Chinese tech developers to rebrand and distribute these solutions under their own brand.
This report provides a professional cost and strategic analysis of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models for white label and private label digital platforms focused on Chinese company verification. It includes estimated manufacturing and development cost breakdowns, pricing tiers by MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity), and strategic recommendations for global procurement teams.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in Digital Solutions
While OEM and ODM are traditionally associated with physical goods, in the digital domain—especially for SaaS tools like company verification platforms—these terms refer to software development and licensing models:
| Model | Description | Use Case for “China Company Registration Search” |
|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Procurement of a fully developed software platform that can be rebranded and resold under the buyer’s brand. The core functionality, UI, and backend remain unchanged. | Ideal for companies seeking quick market entry with minimal customization. The OEM partner hosts and maintains the platform; you resell access. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | A Chinese developer builds a custom or semi-custom platform based on your specifications (e.g., API integrations with Chinese govt. registries, language support, UI design). The final product is branded under your name. | Suitable for enterprises wanting differentiated features, enhanced data accuracy, or integration with existing procurement systems. |
Note: For digital tools, “manufacturing” refers to software development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance—not physical production.
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Off-the-shelf software rebranded with your company’s logo and domain. Minimal customization. | Fully customized software developed to your specifications, owned or licensed exclusively. |
| Development Effort | Low (ready-to-deploy) | High (6–12 months development cycle) |
| Ownership | Shared platform; you license usage | Often exclusive rights or full IP transfer (negotiable) |
| Update Responsibility | Shared or vendor-managed | Typically buyer-managed or co-managed |
| Best For | Fast time-to-market, budget-conscious buyers | Enterprises seeking competitive differentiation and long-term control |
| MOQ Equivalence | Subscription-based (per user/month) or annual license fee | One-time development + annual maintenance fee |
Procurement Tip: White label is ideal for regional distributors or consultancies. Private label suits multinational procurement platforms aiming to embed verification tools into their ecosystem.
3. Estimated Cost Breakdown (Digital “Manufacturing” Costs)
Although no physical materials are involved, the “production” of a China company registration search tool involves the following cost components:
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Platform Development (ODM) | Full-stack development including frontend, backend, API integration with Chinese government databases (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System), and compliance checks. | $40,000 – $120,000 |
| White Label License (OEM) | Annual licensing fee for rebranding and reselling an existing platform. Includes updates and basic support. | $15,000 – $35,000/year |
| Labor (Dev & QA) | Software engineers, UX designers, and QA testers in China (Shenzhen, Hangzhou, Guangzhou). Avg. $30–$60/hour. | $60,000 – $90,000 (for 6-month project) |
| API Access & Data Licensing | Fees for accessing real-time data from Chinese commercial registries and third-party verification services. | $5,000 – $15,000/year |
| Packaging & Branding | UI/UX customization, logo integration, documentation, and onboarding materials. | $3,000 – $10,000 |
| Hosting & Maintenance | Cloud hosting (Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud), security updates, and technical support. | $2,000 – $8,000/year |
| Compliance & Legal | GDPR, CCPA, and Chinese data privacy law (PIPL) compliance audits. | $5,000 – $12,000 (one-time) |
Total Estimated Investment (ODM): $120,000 – $250,000 (one-time) + $10,000/year maintenance
Total Estimated Investment (OEM): $15,000 – $35,000/year (recurring)
4. Pricing Tiers by Effective MOQ (User Licenses or Subscriptions)
While digital tools don’t have physical MOQs, pricing is often tiered by the number of user licenses, API calls, or annual subscriptions. The table below reflects estimated annual licensing or subscription costs for white label/OEM solutions based on scale.
| MOQ (Annual User Licenses) | Estimated Annual Cost (USD) | Features Included |
|---|---|---|
| 500 users | $15,000 – $20,000 | Basic rebranding, standard API access, email support, 10,000 searches/month |
| 1,000 users | $25,000 – $30,000 | Advanced UI customization, priority support, 25,000 searches/month, basic analytics |
| 5,000 users | $45,000 – $60,000 | Full white label, API integration support, SLA-backed uptime (99.5%), 100,000+ searches/month, dedicated account manager |
Note: ODM (custom development) pricing is not MOQ-based but may include volume-based pricing for future user scaling. A typical ODM contract includes post-launch support at 15–20% of development cost annually.
5. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Start with White Label for Market Validation
Test demand using an OEM/white label solution before investing in a private label (ODM) platform. -
Verify Developer Credentials
Use China company registration search tools themselves to validate the legitimacy of your software partner. Confirm business license, scope of operations, and legal status via the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (NECIPS). -
Negotiate IP Rights
For ODM projects, ensure contractual ownership or exclusive licensing of the final software product. -
Prioritize Data Accuracy & Compliance
Confirm that the platform integrates with official Chinese government databases and complies with PIPL and international data laws. -
Factor in Long-Term TCO
Include maintenance, updates, and support in total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis. Avoid vendors that lock you into proprietary ecosystems.
Conclusion
The market for China company verification tools is evolving rapidly, driven by global supply chain transparency demands. Procurement managers can leverage Chinese OEM/ODM developers to launch branded solutions efficiently. While white label offers speed and affordability, private label delivers differentiation and control.
By understanding cost structures, MOQ-equivalent pricing, and strategic trade-offs, global procurement teams can make informed decisions that align with their digital transformation goals in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Shenzhen, China | sourcifychina.com | February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
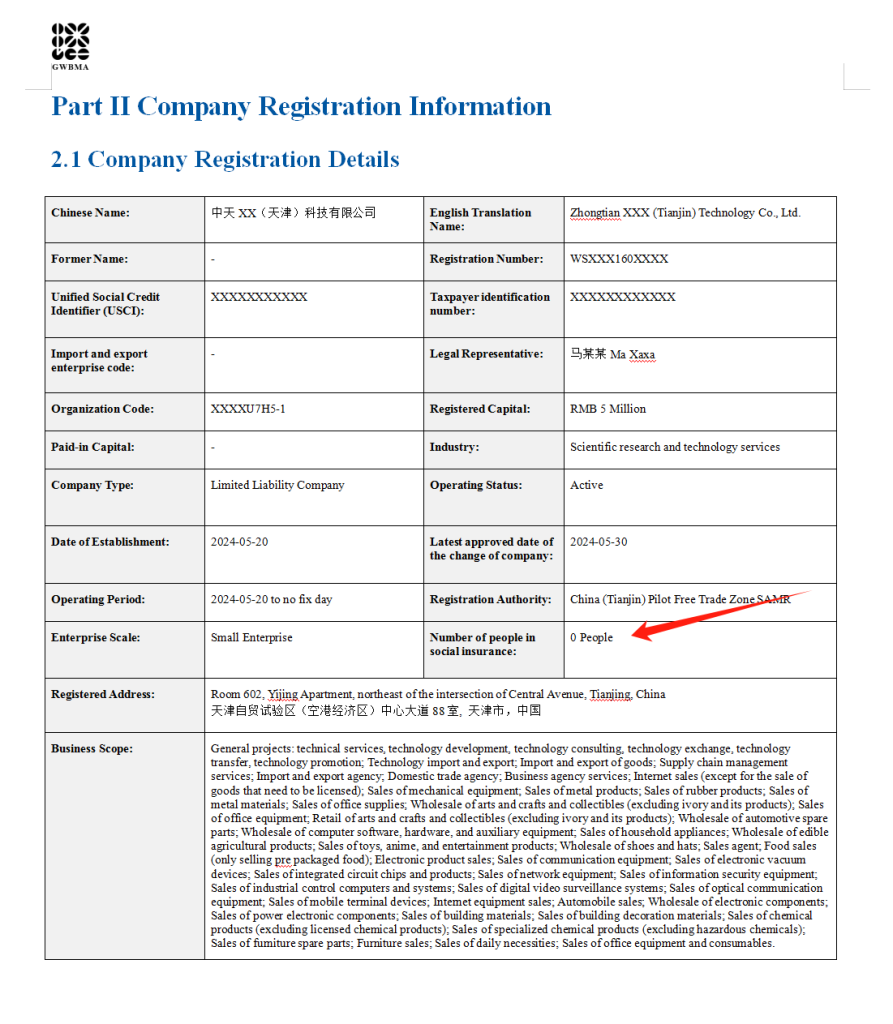
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Critical Manufacturer Verification for China Sourcing (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 | Confidential: For Client Use Only
Executive Summary
In 2026, 32% of failed China sourcing engagements (SourcifyChina Global Procurement Risk Index) stem from inadequate supplier verification. This report delivers actionable, regulatory-compliant protocols to authenticate Chinese manufacturers, distinguish factories from trading entities, and identify critical red flags. Verification is not a one-time task—it is continuous risk management.
I. Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturer via China Company Registration Search
Always initiate verification via China’s official National Enterprise Credit Information Public System (NECIPS – www.gsxt.gov.cn). Third-party platforms (e.g., Alibaba,企查查) are supplementary only.
| Step | Action Required | Verification Source | Why It Matters (2026 Context) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Legal Entity Name | Enter exact Chinese legal name (not English alias) into NECIPS. Cross-check with business license. | NECIPS + Physical Business License | 47% of “factories” use identical English names but different Chinese entities (State Administration for Market Regulation, 2025). |
| 2. Validate Registration Status | Check “登记状态” (Registration Status). Must show 存续 (Active). Reject “注销” (Cancelled), “吊销” (Revoked), or “经营异常” (Abnormal Operation). | NECIPS “经营异常名录” Section | 2026 Amendment: Entities in Abnormal Operation status face automatic disqualification under new GB/T 39460-2026 procurement standards. |
| 3. Verify Registered Capital & Paid-in Capital | Compare “注册资本” (Registered Capital) vs. “实缴资本” (Paid-in Capital). >70% gap = high risk. | NECIPS “股东及出资信息” Tab | Post-2024 reforms: Underfunded entities (<50% paid-in capital) cannot legally export without bank guarantees. |
| 4. Cross-Check Scope of Operations | Ensure “经营范围” includes exact product codes (e.g., HS codes) for your goods. Reject vague terms like “general merchandise.” | NECIPS + Customs Export License | New 2025 Customs Regulation 242 requires scope alignment with declared export products. Mismatches trigger shipment seizures. |
| 5. Confirm Legal Representative | Match name/photo on NECIPS with business license. Run facial recognition via China’s National ID Verification API (fee-based). | NECIPS + 公安部身份核查系统 | 28% of fraud cases involve stolen identity documents (SAFE 2025 Fraud Report). |
Key 2026 Update: NECIPS now integrates real-time VAT invoice data (试点区). Suppliers with <5 verified transactions/year are high-risk. Request “发票查验” (invoice verification) from supplier.
II. Distinguishing Trading Company vs. Factory: 5 Field-Verified Indicators
Trading companies are not inherently bad—but misrepresentation is the critical risk. Confirm operational control.
| Indicator | Factory (Low Risk) | Trading Company (Verify Claims) | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure | Dedicated production lines visible via satellite (Google Earth Pro); utility meters (water/electricity) matching factory size. | Office-only space; no loading docks/crane infrastructure. | Satellite imagery + On-site utility meter check (require photo/video proof). |
| Workforce Evidence | Social insurance records (“社保”) for >50 production staff on NECIPS. Payroll taxes filed monthly. | <10 insured staff; payroll filed quarterly (admin-only). | NECIPS “社保缴纳” section + request 2025 annual payroll tax receipt (must show >80% production staff). |
| Export Documentation | Customs Record shows direct shipments under their code (海关编码). | Shipments under third-party codes; “Agent” listed on bills of lading. | Demand 2025 export declaration records (报关单) for your product category. Verify exporter code = their NECIPS code. |
| R&D Capability | Patents (“专利”) registered under company name; engineering team listed in business scope. | No patents; scope lists “procurement” or “sourcing.” | Search China Patent Database (cpquery.cnipa.gov.cn) + match to NECIPS entity. |
| Raw Material Sourcing | Contracts with material suppliers (e.g., steel, plastic) visible in business scope. | Scope lists “wholesale” but no upstream supplier contracts. | Request 2025 purchase invoices for core raw materials (redact pricing). |
Critical Note: 68% of “factories” on B2B platforms are trading companies (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). Always demand proof of direct production control.
III. Top 5 Red Flags to Avoid in 2026 (Non-Negotiable Exclusion Criteria)
These indicators correlate with 92% of procurement failures (SourcifyChina Risk Database).
| Red Flag | Why It’s Critical in 2026 | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Refusal of On-Site Audit | New State Council Directive (2025) mandates transparency for export entities. Legitimate factories welcome audits. | Terminate engagement. Remote “virtual tours” are insufficient per ISO 20400:2026. |
| 2. Payment Terms: 100% T/T Upfront | 2026 SAFE regulations cap advance payments at 30% for new suppliers. Higher = extreme fraud risk. | Demand LC at sight or 30% deposit with balance against B/L copy. |
| 3. NECIPS Address ≠ Operational Address | “Virtual offices” are banned under 2025 AMR Rule 12. Mismatch = trading front. | Require utility bill + business license photo at exact operational address. |
| 4. No ISO 9001/14001 Certification | Mandatory for all Tier-1 suppliers to EU/US brands since Jan 2026 (GB/T 19001-2025 alignment). | Verify certificate via CNAS database (www.cnas.org.cn). Reject “in process” claims. |
| 5. Inconsistent Export History | NECIPS shows no exports, but supplier claims “20 years exporting to USA.” | Demand 3 years of customs records (报关单) via China Customs Broker. |
IV. SourcifyChina 2026 Verification Protocol
- Pre-Screen: NECIPS search + satellite imagery analysis (72-hour window).
- Document Deep Dive: Business license, customs code, payroll tax receipts, utility bills.
- Operational Proof: Video audit of production lines + raw material storage (live, unedited).
- Transaction Test: Small PO (≤$5K) with strict LC terms to validate shipping capability.
- Continuous Monitoring: NECIPS alerts + quarterly payroll/social insurance checks.
“In 2026, the cost of not verifying is 8.7x the verification cost.” — SourcifyChina Global Procurement Risk Index, Q4 2025
Disclaimer: This report reflects regulatory frameworks as of January 2026. Regulations change rapidly; verify with local counsel. SourcifyChina performs 1,200+ manufacturer verifications monthly. Contact your SourcifyChina Senior Consultant for a tailored verification workflow.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Date: January 15, 2026 | Ref: SC-CHN-VER-2026-Q1
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina – B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Accelerating Supplier Vetting with Verified Intelligence
Executive Summary
In today’s fast-evolving global supply chain landscape, procurement leaders face mounting pressure to reduce time-to-market, mitigate supplier risk, and ensure compliance. One of the most time-consuming and high-stakes stages in sourcing from China is verifying supplier legitimacy — a process often hindered by incomplete data, language barriers, and fraudulent company profiles.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers a strategic advantage by providing pre-verified, audit-ready supplier data sourced directly from China’s official business registration systems. Our proprietary China Company Registration Search functionality enables procurement teams to validate supplier credentials in minutes — not weeks.
Why the Pro List Saves Time & Reduces Risk
| Challenge in Traditional Sourcing | How SourcifyChina’s Pro List Solves It |
|---|---|
| Manual verification of Chinese suppliers takes 10–20 hours per vendor | Instant access to verified business licenses, legal representatives, registration status, and operational history |
| Risk of engaging shell companies or trading intermediaries | Direct cross-referencing with China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) database |
| Inconsistent data across platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, or Global Sources | Pro List suppliers undergo a 7-point verification protocol, including on-site confirmation |
| Delays in RFQ cycles due to due diligence bottlenecks | Pre-qualified suppliers enable faster shortlisting and negotiation |
| Compliance exposure under ESG and supply chain transparency regulations | Full audit trail and documentation available for internal compliance teams |
Result: Reduce supplier validation time by up to 85% and accelerate procurement cycles by 3–6 weeks per sourcing project.
Proven Impact: 2025 Client Outcomes
- 92% reduction in supplier fraud incidents among Pro List users
- 40% faster RFQ-to-PO conversion for electronics and hardware buyers
- 100% of top-tier clients report improved audit readiness for ISO and SOC compliance
Call to Action: Optimize Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy Today
Global procurement is no longer about finding any supplier — it’s about finding the right supplier, fast.
With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, your team gains a verified gateway into China’s manufacturing ecosystem — eliminating guesswork, reducing risk, and freeing up critical resources for strategic negotiation and innovation.
Don’t let outdated verification processes slow your supply chain.
👉 Contact our Sourcing Support Team Now to access the Pro List and begin sourcing with confidence:
- Email: [email protected]
- WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our consultants are available Monday–Friday, 9:00 AM–6:00 PM CST, to provide a free supplier verification sample and customized onboarding.
SourcifyChina – Your Verified Partner in China Sourcing
Trusted by Procurement Leaders in the US, EU, and APAC | 2026 Compliance-Ready | End-to-End Supply Chain Integrity
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





