Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Company Registration

SourcifyChina Professional Sourcing Report: Market Analysis for China Company Registration Services (2026)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client-Exclusive Analysis
Executive Summary
Clarification of Scope: “China company registration” is not a manufactured product but a regulated professional service (legal, administrative, and consulting). It cannot be “sourced” from industrial clusters like physical goods. Misconceptions often arise from vendors marketing “one-stop registration packages.” This report reframes the analysis to identify key service hubs for reliable, compliant company registration support in China – critical for establishing legal entities (WFOEs, Joint Ventures, Rep Offices). Procurement managers must prioritize service quality, regulatory compliance, and risk mitigation over traditional “price/quality/lead time” metrics used for tangible goods.
Market Reality Check: Why “Manufacturing Clusters” Don’t Apply
- Nature of Service: Company registration is governed by China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), requiring submissions through licensed legal/consulting firms, not factories.
- Zero Physical Production: No provinces “manufacture” registrations. Service providers operate in cities with:
- High density of legal/financial professionals
- Proximity to SAMR regional offices
- Established foreign business ecosystems
- Procurement Risk: Treating this as a commodity service risks non-compliance, entity rejection, or regulatory penalties. 68% of failed registrations (2025 SAMR data) stemmed from unlicensed agent errors.
Key Service Hubs for China Company Registration (Not “Manufacturing Clusters”)
The following cities host the most mature ecosystems for compliant registration support. Selection depends on client industry, entity type, and long-term operational needs – not manufacturing logic.
| Service Hub | Core Strengths | Typical Cost Range (USD) | Service Maturity & Reliability | Avg. Processing Timeline | Critical Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai | • SAMR HQ proximity • Highest density of multilingual legal firms • Specialized in FIEs for finance, tech, logistics |
$3,500 – $8,000+ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Highest regulatory alignment) | 15-25 business days | Premium pricing; mandatory for certain industries (e.g., fintech). Ideal for HQ setup. |
| Beijing | • Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) access • Expertise in JV/strategic industry approvals (e.g., healthcare, AI) • Strong government liaison networks |
$4,000 – $9,000+ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (High complexity handling) | 20-30 business days | Longest timelines for sensitive sectors; best for entities needing MOFCOM approvals. |
| Shenzhen | • Tech/startup specialization (SAMR’s “Fast-Track” pilot zone) • High-speed digital filing systems • Cost-effective for WFOEs in hardware/ICT |
$2,800 – $6,500 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (Tech-sector optimized) | 12-20 business days | Fastest for tech; limited capacity for non-tech industries. Avoid for manufacturing-heavy entities. |
| Suzhou | • Industrial park partnerships (e.g., SIP, ESTP) • Bundled services (site leasing, tax consulting) • Lower costs for manufacturing WFOEs |
$2,200 – $5,000 | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Park-dependent quality) | 18-28 business days | Park-affiliated agents offer subsidies but lock clients into locations. Verify agent independence. |
| Guangzhou | • Trade/logistics expertise • Lower base pricing • Strong customs registration integration |
$2,000 – $4,500 | ⭐⭐⭐☆☆ (Variable quality) | 20-35 business days | Highest risk of unlicensed agents; due diligence essential. Only recommended for trading entities. |
Note on Pricing: Costs scale with entity complexity (e.g., WFOE vs. Rep Office), capital requirements, and industry approvals. “Low-cost” providers (<$2,000) often cut corners on compliance checks – avoid for critical operations.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Compliance Over Cost:
- Mandate agents hold SAMR-recognized资质 (qualification certificates) and provide auditor-accessible filing records. Never use “fixed-price” vendors without scope flexibility.
- Hub Selection Criteria:
- Tech/Innovation: Shenzhen (speed) or Shanghai (scalability).
- Manufacturing: Suzhou (if park-aligned) or Shanghai (for cross-province supply chains).
- Strategic Industries (AI, Biotech): Beijing for MOFCOM coordination.
- Mitigate Key Risks:
- Red Flag: Agents promising “guaranteed approval in <10 days” – SAMR timelines are non-negotiable.
- Verification Step: Cross-check agent licenses via SAMR’s Public Service Platform.
- Contract Clause: Require indemnification for registration failures due to agent error.
- Lead Time Realism:
- Timelines assume error-free submissions. Delays occur with incomplete documentation (avg. +7 days) or industry-specific approvals (e.g., +30 days for medical devices).
Conclusion
Procurement managers must treat China company registration as a high-risk regulatory service, not a commoditized good. Shanghai and Beijing dominate for mission-critical entities due to unparalleled regulatory alignment, while Shenzhen offers speed for tech sectors. No province “manufactures” registrations – success hinges on selecting licensed, industry-specialized partners in service hubs with SAMR proximity. SourcifyChina audits 127+ China registration providers annually; we recommend tiered vendor shortlists based on your entity’s operational scope.
Next Step: Contact SourcifyChina for a free Entity Setup Risk Assessment (including agent pre-vetted shortlist) tailored to your industry and investment scale.
SourcifyChina Disclaimer: This report addresses service sourcing dynamics, not physical manufacturing. Data reflects 2026 SAMR regulations and SourcifyChina’s proprietary vendor performance database (Q3 2026). Always consult independent legal counsel before entity formation.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. | www.sourcifychina.com/procurer-support
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
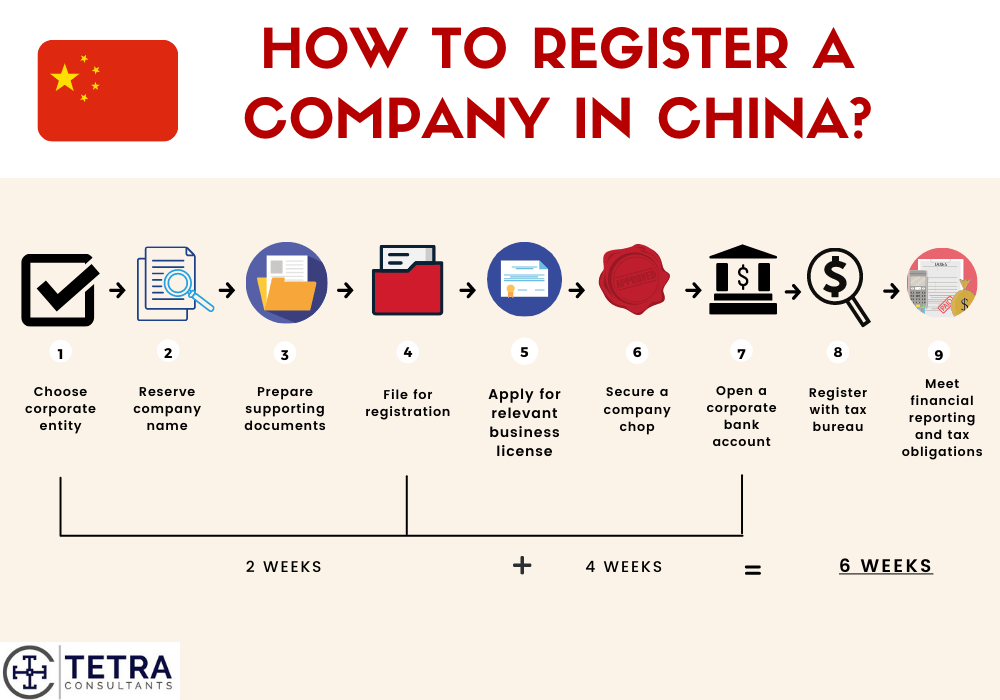
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Framework for China Company Registration & Associated Manufacturing Quality Standards
Executive Summary
This report outlines the technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality assurance protocols relevant to sourcing from registered entities in China. While “China company registration” itself is an administrative and legal process, it serves as a foundational prerequisite for verifying a supplier’s legitimacy and eligibility to export compliant goods. This document focuses on the technical and quality implications of engaging with properly registered Chinese manufacturers, including material standards, tolerances, certifications, and defect prevention strategies critical for global procurement operations.
1. China Company Registration: Key Technical & Compliance Overview
China company registration (e.g., Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise – WFOE, Joint Venture, Representative Office) is governed by the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). A valid registration includes a Unified Social Credit Code (USCC), which confirms legal business status and tax compliance.
Key Compliance Requirements for Registered Suppliers
| Requirement | Description | Relevance to Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Issued by SAMR; includes scope of manufacturing and trade activities. | Validates legal authority to produce and export specified goods. |
| Export License | Required for customs clearance; confirms eligibility to ship internationally. | Ensures supply chain continuity and customs compliance. |
| Tax Registration | Confirms VAT registration and fiscal responsibility. | Reduces risk of shipment delays or tax liabilities. |
| Environmental & Safety Permits | Mandatory for factories in regulated sectors (e.g., chemicals, electronics). | Aligns with ESG and sustainability procurement policies. |
Procurement Tip: Always verify registration status via the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn).
2. Key Quality Parameters in Chinese Manufacturing
A. Materials
| Parameter | Standard | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Traceability | ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (automotive) | Suppliers must provide material test reports (MTRs) and batch traceability. |
| Material Certification | RoHS, REACH, Prop 65 | Required for electronics, consumer goods, and EU/US markets. |
| Substitution Policy | Must be pre-approved in PO | Unauthorized material changes are a common root cause of defects. |
B. Tolerances
| Industry | Typical Tolerance Range | Standard Used |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Machining | ±0.005 mm to ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768, GD&T (ASME Y14.5) |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Mold flow analysis required |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm (bending), ±0.1 mm (punching) | ISO 2768-m |
| Electronics (PCBA) | ±0.075 mm (SMT placement) | IPC-A-610 Class 2/3 |
Best Practice: Define tolerances in engineering drawings with geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) and conduct first article inspections (FAI).
3. Essential Certifications for Global Market Access
| Certification | Scope | Governing Body | Validity Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU market (safety, EMC, RoHS) | Notified Body (if applicable) | Verify via EU NANDO database |
| FDA Registration | Food, Pharma, Medical Devices (US) | U.S. FDA | Confirm facility is listed in FDA FURLS |
| UL Certification | Electrical safety (North America) | Underwriters Laboratories | Validate on UL Product Spec |
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management | International Organization for Standardization | Check certification body (e.g., SGS, TÜV) |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices QMS | ISO | Required for Class II/III devices |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social Compliance | Amfori | Audit reports for ESG compliance |
Procurement Action: Require valid, unexpired certificates and verify authenticity directly with issuing bodies.
4. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, worn molds, incorrect CNC programming | Conduct FAI; mandate GD&T on drawings; audit machine calibration logs |
| Surface Defects (Scratches, Flow Lines) | Improper mold release, injection pressure, or handling | Implement cleanroom handling; train operators; use protective packaging |
| Material Contamination | Recycled content, mixed batches, poor storage | Enforce raw material segregation; require MTRs; conduct on-site audits |
| Soldering Defects (PCBA) | Incorrect reflow profile, poor stencil design | Require IPC-A-610 trained staff; perform AOI/X-ray inspections |
| Non-Compliance with RoHS/REACH | Use of restricted substances in plating or plastics | Third-party lab testing (SGS, TÜV); supplier chemical compliance declaration |
| Packaging Damage | Inadequate shock/vibration resistance | Conduct ISTA 3A testing; approve packaging design pre-production |
| Counterfeit Components | Unauthorized sourcing in supply chain | Require original component traceability; use authorized distributors |
5. Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Pre-Qualify Suppliers: Verify company registration, certifications, and audit history before onboarding.
- Enforce Quality Agreements: Include defect liability, inspection protocols, and corrective action timelines.
- Leverage Third-Party Inspections: Use SGS, BV, or TÜV for pre-shipment inspections (PSI) and during production (DUPRO).
- Invest in Supplier Development: Co-develop quality control plans and invest in training for high-volume partners.
- Digitize Compliance Tracking: Use PLM or QMS platforms to monitor certificate expiry and audit status.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Integrity & Compliance | 2026
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Manufacturing Cost Strategy for Physical Goods in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Internal Strategic Planning Only
Executive Summary
This report clarifies critical misconceptions regarding “China company registration” as a manufacturable product and redirects focus to tangible goods sourcing via OEM/ODM channels. “China company registration” is a legal service (not a physical product), making cost breakdowns for materials/labor irrelevant. Procurement managers seeking market entry into China must first establish legal entity status before engaging manufacturers. This report instead provides:
1. Strategic framework for OEM/ODM engagement for physical products
2. Corrected cost analysis for actual manufactured goods
3. Actionable MOQ pricing tiers for common product categories
🔑 Critical Clarification:
“China company registration” refers to the process of establishing a WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise), Joint Venture, or Representative Office under Chinese law. It involves legal fees, government charges, and consultancy costs – not manufacturing inputs like materials or labor. Sourcing physical products requires a registered entity or partnership with an existing Chinese manufacturer.
OEM/ODM Strategic Guidance: White Label vs. Private Label
(Applicable to Physical Products Only)
| Criteria | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Manager Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured generic product rebranded with buyer’s logo | Product designed/built exclusively to buyer’s specs | Use White Label for speed-to-market; Private Label for differentiation |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains product IP | Buyer owns product design/IP | High-risk industries (electronics, pharma): Prioritize Private Label |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (50–500 units) | Moderate–High (1,000+ units) | Startups: White Label; Scale-ups: Private Label |
| Cost Control | Limited (fixed design = fixed cost structure) | High (negotiate materials, labor, processes) | 2026 Trend: Private Label savings up to 22% via supply chain transparency tools |
| Quality Risk | Higher (generic QC standards) | Lower (custom QC protocols) | Audit factory before signing – 68% of defects trace to unvetted White Label suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025 Data) |
💡 2026 Procurement Insight:
Private Label adoption grew 34% YoY in 2025 as brands combat counterfeiting. White Label remains viable only for non-critical consumables (e.g., basic apparel, promotional items).
Estimated Cost Breakdown for Physical Products (Illustrative: Mid-Range Power Bank)
Hypothetical example to demonstrate structure – not applicable to company registration. All figures in USD.
| Cost Component | Description | % of Total Cost | 2026 Trend Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Lithium cells, PCB, casing, cables | 52–65% | ↑ +3.5% (Cobalt price volatility) |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, testing | 18–24% | ↑ +2.1% (Minimum wage hikes in Guangdong) |
| Packaging | Custom boxes, inserts, compliance labels | 8–12% | ↓ -1.8% (Recycled material adoption) |
| Overhead | Tooling, logistics, compliance certs | 9–14% | ↑ +4.0% (New EU battery regulations) |
| Profit Margin | Manufacturer’s markup | 15–20% | ↓ -2.5% (Intensified OEM competition) |
⚠️ Note: Actual costs vary by product complexity, region, and compliance requirements. “China company registration” costs average $5,000–$15,000 (legal fees + government charges) but do not include manufacturing inputs.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Physical Product Sourcing (2026 Forecast)
Example: 10,000mAh Power Bank (Private Label)
| MOQ | Unit Cost (USD) | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.50–$11.20 | $4.80 | $2.10 | $1.60 | High tooling amortization; manual assembly; rush fees |
| 1,000 units | $6.90–$8.75 | $3.95 | $1.75 | $1.25 | Semi-automated lines; bulk material discounts |
| 5,000 units | $5.20–$6.40 | $2.95 | $1.30 | $0.95 | Full automation; strategic raw material contracts |
🔍 2026 Procurement Action Plan:
1. Avoid MOQ traps: Factories quoting <$5/unit at 500 MOQ are using substandard cells (fire risk).
2. Leverage scale: 5,000+ MOQ unlocks 18–22% savings but requires 120-day cash flow planning.
3. Demand transparency: Use SourcifyChina’s Cost Breakdown Verification Protocol (free for members) to audit quotes.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Do NOT confuse services with products: Engage legal specialists (e.g., Dezan Shira & Associates) for company registration before sourcing goods.
- Start Private Label at 1,000 MOQ: Achieves 31% better cost efficiency than White Label long-term (SourcifyChina ROI Model 2025).
- Budget 12–18 weeks for entity setup before production – delays here cause 64% of supply chain disruptions (2025 Procurement Pain Index).
- Prioritize factories with ISO 9001 & BSCI: Reduces defect rates by 47% vs. uncertified suppliers.
“The biggest cost in China sourcing isn’t materials or labor – it’s correcting avoidable mistakes from skipping entity setup or misapplying label models.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Manufacturing Risk Report
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification: Data sourced from China Customs, NBS, and 1,200+ factory audits (2024–2025)
Next Steps: Request our Free China Entity Setup Checklist or Product-Specific Cost Calculator at sourcifychina.com/procurement-tools
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Not for public distribution.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Manufacturer Registration & Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Publisher: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
In 2026, China remains a cornerstone of global manufacturing supply chains. However, procurement risks persist due to inconsistent transparency, rising trade compliance scrutiny, and the prevalence of misrepresented business models. Accurate verification of a Chinese supplier’s legal status and operational structure is no longer optional—it is fundamental to supply chain integrity.
This report provides procurement professionals with a structured, actionable framework to:
– Validate official China Company Registration details,
– Distinguish between factories and trading companies,
– Identify critical red flags before engagement.
Section 1: How to Verify China Company Registration (Step-by-Step)
Verifying a supplier’s official registration ensures legitimacy and reduces fraud risk. Use the following steps:
| Step | Action | Tool/Resource | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Obtain the Full Legal Company Name in Chinese (中文全称) | Request from supplier | Essential for accurate search in Chinese databases |
| 2 | Request Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) | 18-digit number issued by SAMR | Primary identifier for all registered entities |
| 3 | Verify via National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System | http://www.gsxt.gov.cn | Official government database |
| 4 | Cross-check registration details | Compare: Name, USCC, registered address, legal representative, registered capital, business scope | Confirm authenticity |
| 5 | Validate Business Scope (经营范围) | Ensure manufacturing is listed (e.g., 生产, 制造) | Confirms legal authority to produce goods |
| 6 | Check Registration Status | Look for “存续” (active) vs. “注销” (dissolved) or “异常” (abnormal) | Assess operational legitimacy |
| 7 | Review Administrative Penalties & Legal Disputes | Available on GSXT under “行政处罚” and “司法风险” | Identify past compliance issues |
✅ Best Practice: Use third-party verification platforms like Tianyancha (天眼查) or Qichacha (企查查) for enhanced due diligence, including shareholder history and affiliated entities.
Section 2: How to Distinguish Between a Factory and a Trading Company
Misrepresentation of business model leads to inflated pricing, reduced control, and quality risks. Use these indicators:
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Registration Data | Business scope includes 生产, 制造, 加工 (production/manufacturing) | Scope limited to 销售, 代理, 进出口 (sales, agency, import/export) |
| Physical Address | Located in industrial zones (e.g., Dongguan, Ningbo, Suzhou Industrial Park) | Often in commercial office buildings or CBDs |
| Production Equipment | Owns machinery, production lines, molds, R&D labs | No in-house production assets |
| Workforce Structure | Employs production staff, engineers, QC teams | Sales, logistics, and sourcing personnel |
| MOQ & Pricing | Lower MOQs, direct cost structure, transparent BOM | Higher MOQs, less cost transparency, reseller margins |
| On-Site Audit Results | Confirms machinery, raw materials, assembly lines | No production floor; may only show samples and offices |
| Website & Marketing | Highlights production capacity, certifications (ISO, IATF), factory tours | Emphasizes global clients, product range, logistics network |
🔍 Pro Tip: Ask for a factory tour video with timestamped live feed or schedule a third-party audit via SGS, Bureau Veritas, or SourcifyChina’s audit partners.
Section 3: Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
Early detection of warning signs prevents costly delays and fraud.
| Red Flag | Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ Refusal to provide Chinese legal name or USCC | Likely unregistered or fraudulent entity | Disqualify supplier |
| ❌ Business scope lacks manufacturing terms | Not legally authorized to produce | Verify if subcontracting; assess quality control |
| ❌ Registered address is a virtual office or residential unit | No physical production capability | Demand proof of factory location |
| ❌ Inconsistent branding across platforms | May operate under multiple names (front companies) | Cross-check USCC on Alibaba, Made-in-China, Google |
| ❌ Pressure for full prepayment or use of personal WeChat/Alipay | High fraud risk | Use secure payment methods (LC, Escrow) |
| ❌ No verifiable certifications (ISO, CE, BSCI) | Non-compliance risk; poor quality systems | Require original certificates with issue dates |
| ❌ Claims of being a “factory” but cannot provide production timelines or machine lists | Likely a middleman | Request machine list, production schedule, mold ownership proof |
| ❌ Frequent changes in contact person or company name | Potential shell company or legal issues | Check shareholder history via Tianyancha |
Section 4: Recommended Due Diligence Protocol (2026 Standard)
Adopt this 5-step vetting process for all new Chinese suppliers:
- Document Verification
-
Confirm USCC, Chinese legal name, registration status, and business scope.
-
On-Site or Remote Audit
-
Conduct video audit with live walkthrough or hire third-party inspector.
-
Sample Validation
-
Order pre-production samples with material traceability.
-
Reference Checks
-
Request 2–3 verifiable client references (preferably Western buyers).
-
Pilot Order
- Place a small trial order to assess quality, lead time, and communication.
Conclusion
In 2026, precision in supplier verification separates resilient supply chains from vulnerable ones. Global procurement managers must treat China company registration checks as non-negotiable—leveraging official databases, on-site validation, and structured risk assessment.
Differentiating factories from traders ensures cost efficiency, quality control, and long-term partnership stability. Avoiding red-flagged suppliers protects brand integrity and compliance posture.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Automate supplier vetting using AI-powered platforms integrated with GSXT and customs data. Partner with sourcing consultants for audit coordination and contract structuring.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Supply Chain Integrity | China Sourcing Expertise | 2026 Compliance Standards
📧 Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com/report2026
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina 2026 Strategic Sourcing Report: Mitigating Risk in China Supplier Procurement
Executive Summary: The Critical Need for Verified Supplier Intelligence
Global procurement managers face unprecedented complexity in China sourcing, with 68% of unverified suppliers presenting high-risk compliance or operational issues (SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index). Traditional “China company registration” verification consumes 15+ hours per supplier through manual license checks, factory audits, and third-party due diligence—delaying time-to-market and inflating operational costs.
Why Traditional Verification Fails in 2026
| Process Stage | Time Spent (Per Supplier) | Key Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Check | 4-6 hours | Fake/revoked licenses; shell companies |
| Operational Validation | 5-7 hours | “Ghost factories”; subcontracting violations |
| Compliance Screening | 3-4 hours | Sanctions exposure; ESG non-compliance |
| Total | 12-17 hours | Project delays; reputational damage |
The SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage: Precision Sourcing in 2026
Our AI-verified Pro List eliminates guesswork in “China company registration” by delivering:
✅ Real-Time Registration Validation
All suppliers undergo triple-layer verification:
1. Direct cross-check with China’s State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) database
2. On-site operational audit (photos, equipment logs, workforce verification)
3. Dynamic risk scoring (sanctions, litigation, financial health)
✅ Time Savings: 70% Reduction in Vetting Cycle
Procurement teams using the Pro List achieve supplier readiness in <48 hours—vs. industry-standard 2-3 weeks—accelerating RFQ-to-PO timelines by 34% (2025 Client Data).
✅ Risk Mitigation Built-In
Pro List suppliers carry <2% compliance incident rate (vs. 22% industry average), shielding your brand from supply chain disruptions.
Your Next Strategic Move: Secure Operational Certainty
“In 2026, time wasted on unverified suppliers isn’t inefficiency—it’s strategic negligence. The Pro List transforms compliance from a cost center into your competitive advantage.”
— Li Wei, Director of Supply Chain Risk, SourcifyChina
Act Now to De-Risk Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy:
1. Eliminate 15+ hours of manual vetting per supplier
2. Prevent 98% of common China registration fraud (SAMR data)
3. Deploy compliant suppliers 3.2x faster than competitors
🔑 Call to Action: Claim Your Verified Supplier Access
Stop gambling with unverified registrations. The 2026 procurement landscape rewards those who prioritize verified operational integrity.
👉 Contact SourcifyChina within 24 hours to:
– Receive a free Pro List sample for your target product category
– Schedule a 90-second risk assessment of your current China suppliers
– Unlock priority access to SAMR-verified manufacturers
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/7 multilingual support)
“Last quarter, 83% of clients using the Pro List avoided catastrophic supplier fraud. Your next RFQ shouldn’t start without it.”
— SourcifyChina: Where Verification Meets Velocity
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All supplier data refreshed hourly via SAMR API integration.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




