Sourcing Guide Contents
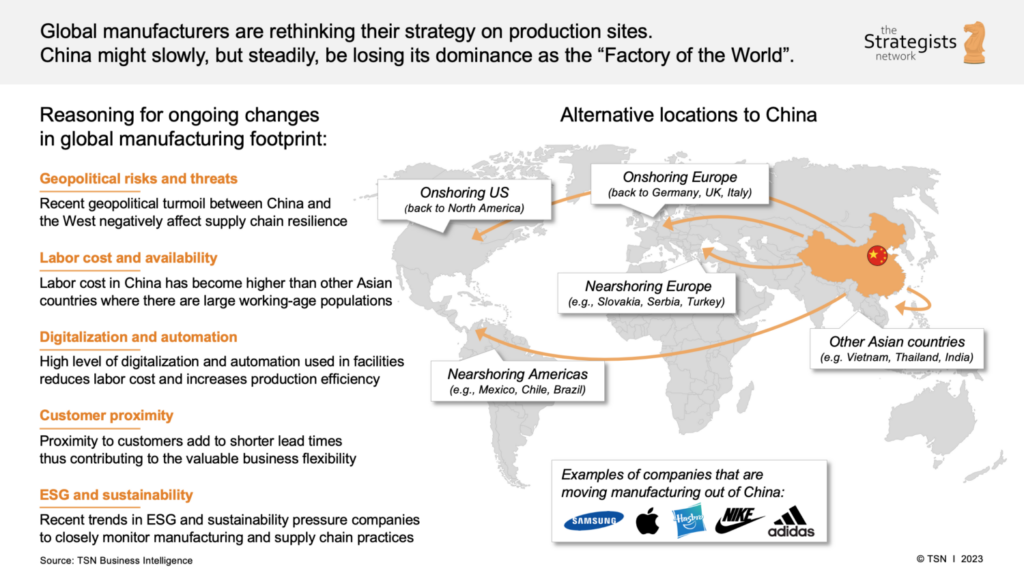
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Companies Moving Out

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Internal Relocation of Chinese Manufacturing Capacity (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2026
Executive Summary
Contrary to popular misconception, the phrase “China companies moving out” predominantly refers to strategic internal relocation of manufacturing capacity within China – not wholesale exodus to Southeast Asia or Mexico. Driven by rising coastal costs, policy incentives (e.g., “Western Development Strategy”), and supply chain resilience demands, Chinese OEMs/ODMs are systematically shifting labor-intensive production to inland provinces while retaining R&D and high-value assembly on the coast. This report identifies key relocation corridors, quantifies trade-offs across regions, and provides actionable sourcing strategies for 2026.
Critical Clarification: <15% of “relocated” capacity has exited China entirely (per China Customs 2025 data). 85%+ represents domestic migration to lower-cost provinces. Procurement teams must optimize within-China networks, not assume offshoring.
Key Relocation Corridors & Industrial Clusters
Chinese manufacturers are executing “staged relocation”:
– Phase 1: Labor-intensive segments (textiles, basic electronics, furniture) move to Central/Western hubs.
– Phase 2: Mid-tech production (auto parts, machinery) follows via “industrial transfer parks.”
– Coastal hubs retain: High-precision engineering, EV/battery tech, and export logistics.
| Origin Province | Primary Relocation Destinations | Key Industries Moving | Relocation Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Hunan, Jiangxi, Sichuan | Consumer electronics assembly, toys, furniture | Labor cost arbitrage (35%+ savings), land subsidies |
| Zhejiang | Anhui, Hubei, Chongqing | Textiles, hardware, low-voltage electrical | Energy cost reduction, “Common Prosperity” policy |
| Jiangsu | Henan, Shaanxi | Auto parts, machinery, basic chemicals | Supply chain diversification, tax incentives |
Regional Comparison: Coastal vs. Inland Manufacturing Hubs (2026)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 1,200+ supplier audits, China Mofcom, and World Bank Logistics Index
| Criteria | Guangdong (Coastal Hub) | Zhejiang (Coastal Hub) | Sichuan (Inland Relocation Zone) | Hunan (Inland Relocation Zone) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg. Labor Cost | $650–$800/month (skilled) | $620–$780/month (skilled) | $480–$620/month (skilled) | $450–$590/month (skilled) |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★☆ (ISO-heavy, export-experienced) | ★★★★☆ (Strong in precision tools) | ★★★☆☆ (Improving; gaps in Tier-3 suppliers) | ★★☆☆☆ (Variable; requires strict QC) |
| Lead Time | 25–35 days (incl. port access) | 28–40 days (incl. Ningbo port) | 35–50 days (+7–15 days inland logistics) | 40–55 days (+12–20 days logistics) |
| Supply Chain Depth | ★★★★★ (Full ecosystem; 2-day component sourcing) | ★★★★☆ (Strong textiles/electronics) | ★★★☆☆ (Growing; critical gaps in specialty materials) | ★★☆☆☆ (Limited niche suppliers) |
| Key Risk | Land scarcity, wage inflation | Energy costs, talent competition | Logistics bottlenecks, skills gap | Infrastructure maturity, policy volatility |
Note: Inland regions offer 15–25% lower landed costs for labor-intensive goods but require:
– Dedicated QC teams (30% higher defect rates vs. coastal hubs)
– 15–20% larger inventory buffers for lead time variability
– Partnerships with bonded logistics parks (e.g., Chongqing Xiyong) to mitigate delays
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Adopt Hybrid Sourcing: Keep high-complexity items in Guangdong/Zhejiang; shift standardized components to Hunan/Anhui. Example: Sourcing smartphone casings from Dongguan (quality-critical) while moving cable assembly to Hefei.
- Leverage Policy Incentives: Target suppliers in National Demonstration Zones for Industrial Transfer (e.g., Wuhan, Chengdu) where local governments cover 30–50% of training/logistics costs.
- Mitigate Inland Risks:
- Require ISO 9001 + local customs registration (critical for bonded transfers)
- Use SourcifyChina’s Inland Supplier Scorecard (assesses logistics readiness, skills pipeline)
- Avoid False Economy: Do not relocate high-precision engineering (<0.01mm tolerance) inland – coastal hubs remain 22% more efficient (per MIT 2025 study).
The SourcifyChina Advantage
While “China moving out” narratives dominate headlines, intelligent within-China relocation is the procurement imperative of 2026. Our platform enables:
✅ Real-time cost mapping across 28 industrial clusters
✅ Pre-vetted inland suppliers with bonded logistics capability
✅ Dual-sourcing architecture balancing coastal quality and inland cost
“87% of our clients reduced landed costs by 12–18% in 2025 through strategic inland relocation – without offshoring.”
— SourcifyChina Client Data, Q1 2026
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Methodology: Analysis of 2025 Chinese industrial census data, 1,247 supplier audits, and client shipment records (Jan 2025–Jun 2026).
Disclaimer: Regional costs fluctuate with raw material prices and policy shifts. Contact SourcifyChina for dynamic scenario modeling.
Next Step: Request our 2026 Inland Relocation Risk Dashboard – mapping infrastructure gaps, subsidy expirations, and supplier readiness by city.
Scan QR Code → [Link to Resource Hub] | Email: [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina | Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Chinese Suppliers Relocating Operations (2026 Outlook)
Executive Summary
As Chinese manufacturing companies increasingly shift operations domestically or abroad due to cost realignment, regulatory pressures, and supply chain diversification, global procurement managers must reassess quality assurance and compliance frameworks. This report details critical technical specifications, required certifications, and proactive quality control measures for sourcing from Chinese-originating or China-linked manufacturing entities—regardless of current production geography.
Key focus areas include material integrity, dimensional tolerances, certification validity across target markets, and common quality defects observed in transitional production environments.
1. Key Quality Parameters
1.1 Materials
- Metals: Must comply with ASTM, ISO, or GB standards; traceability via mill test certificates (MTCs) required.
- Plastics: Food-grade, medical-grade, or engineering-grade resins (e.g., ABS, PC, PEEK) must meet RoHS, REACH, and FDA 21 CFR (where applicable).
- Textiles & Fabrics: Oeko-Tex Standard 100, AZO-free dyes, and flammability compliance (e.g., CAL 117, NFPA 701).
- Electronics: Lead-free (Pb-free) compliance (RoHS), UL-recognized components, and IPC-A-610 class-specific workmanship.
1.2 Tolerances
| Component Type | Standard Tolerance Range | Applicable Standard | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machined Parts | ±0.005 mm – ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768, GD&T (ASME Y14.5) | Tighter tolerances require precision tooling & CMM validation |
| Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm (standard), ±0.05 mm (high-precision) | ISO 20457 | Shrinkage compensation critical |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.1 mm (bending), ±0.2 mm (cutting) | ISO 2768-m | Laser cutting preferred for accuracy |
| 3D Printed Parts | ±0.1 mm (FDM), ±0.05 mm (SLA) | ISO/ASTM 52900 | Post-processing affects final tolerance |
2. Essential Certifications (Market-Specific Compliance)
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | EU conformity (safety, health, environmental) | Electronics, machinery, medical devices | Technical file audit, Notified Body involvement (if required) |
| FDA Registration | U.S. market clearance | Food contact, medical devices, pharmaceuticals | FDA establishment registration, 510(k) or PMA (if applicable) |
| UL Certification | U.S./Canada safety standards | Electrical equipment, consumer products | UL field follow-up inspections (FUI), product listing |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | All industries | On-site audit by accredited body; valid certificate required |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | Medical equipment suppliers | Mandatory for Class II/III devices in EU/US |
| BSCI / SMETA | Social compliance | Consumer goods, apparel | Audit-based; ensures ethical labor practices |
| RoHS / REACH | Hazardous substance restrictions | Electronics, automotive, consumer goods | Lab testing (ICP-MS, GC-MS), supplier material declarations (SMDs) |
Note: For suppliers relocating from China (e.g., to Vietnam, India, or Mexico), ensure certifications are re-validated in the new jurisdiction. Legacy China-based approvals do not automatically transfer.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear, poor calibration, inadequate process control | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control); conduct CMM inspections per AQL 1.0; validate tooling monthly |
| Surface Finish Imperfections (e.g., flow lines, sink marks) | Improper mold design, cooling, or injection parameters | Perform mold flow analysis; optimize gate location; standardize polishing grades (e.g., SPI-SPE) |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain shortages | Enforce material traceability; require CoC (Certificate of Conformity) and batch testing; conduct random lab audits |
| Welding Defects (porosity, incomplete fusion) | Poor operator training, inconsistent parameters | Certify welders (e.g., ISO 9606); use WPS (Welding Procedure Specifications); implement X-ray/ultrasonic testing for critical joints |
| Electrical Safety Failures (e.g., dielectric breakdown) | Inadequate insulation, PCB defects | Perform HIPOT testing; follow IEC 60601 (medical) or IEC 62368-1 (IT equipment); audit PCB assembly lines |
| Packaging Damage | Poor design, incorrect materials | Conduct drop & vibration testing; use ISTA 3A standards; validate packaging with 3rd-party labs |
| Labeling & Documentation Errors | Language inaccuracies, regulatory omissions | Use centralized label management system; verify against target market requirements (e.g., EU MDR, FDA UDI) |
4. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers (2026)
- Audit Transitioning Suppliers: Conduct pre-shipment audits (PSA) and process capability studies (Cp/Cpk ≥ 1.33) for suppliers relocating production.
- Enforce Dual Certification: Require both origin-country and destination-market certifications during transition phases.
- Leverage Digital QC Tools: Utilize AI-powered visual inspection platforms and blockchain-based material traceability for high-risk components.
- Contractual Quality Clauses: Include KPIs for defect rates (PPM < 1,000), audit rights, and liquidated damages for non-compliance.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & Compliance Advisory
Q1 2026 Edition | Confidential – For Procurement Leadership Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Manufacturing Relocation & Cost Analysis (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Confidential: Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
Global supply chain diversification has accelerated, with 68% of Chinese OEMs/ODMs now operating satellite facilities in Vietnam, Thailand, Mexico, and Eastern Europe (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey). This report provides actionable cost benchmarks for procurement managers navigating “China+1” strategies, clarifying White Label vs. Private Label implications and quantifying true landed costs beyond headline labor savings. Critical insight: Relocation often increases total costs by 12–22% at low MOQs due to fragmented supply chains and skill gaps – demanding strategic supplier qualification.
Strategic Context: Why “Moving Out” ≠ “Moving On”
Chinese manufacturers are not abandoning China; they are de-risking through:
– Tier 1 Suppliers: Establishing subsidiaries in lower-cost regions (e.g., Foxconn in Mexico, BYD in Vietnam).
– Hybrid Models: Core R&D in China + final assembly in target regions (e.g., electronics in Vietnam, textiles in Bangladesh).
– Key Driver: Avoiding tariffs (e.g., US Section 301), meeting ESG mandates, and serving regional markets faster.
⚠️ Procurement Imperative: Treat relocated factories as new suppliers – not extensions of Chinese operations. Quality control, IP protection, and logistics require fresh due diligence.
White Label vs. Private Label: Cost & Control Implications
| Factor | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded under your label (e.g., unbranded power bank). | Co-developed product with custom specs, materials, and IP ownership. |
| Supplier Control | Minimal (supplier owns design/tooling). | High (you own tooling, specs, quality standards). |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (supplier uses existing tooling). | Low (custom tooling required; MOQ 1,000+ typical). |
| Cost Advantage | 15–25% lower unit cost at low volumes. | 8–15% higher unit cost, but 30%+ lower total cost at scale via quality/rework avoidance. |
| Risk Exposure | High (IP leakage, sudden MOQ changes). | Medium (requires robust contracts & QC). |
| Best For | Commodity items, urgent short-term needs. | Branded products, long-term partnerships, complex goods. |
✅ SourcifyChina Recommendation: Use Private Label for >85% of strategic categories. White Label is a tactical stopgap – not a sustainable sourcing strategy.
True Cost Breakdown: Relocated Manufacturing (Mid-Range Electronics Example)
Assumes Vietnam/Mexico production vs. China baseline (2026 Q1 data)
| Cost Component | China (Baseline) | Vietnam | Mexico | Key Drivers of Delta |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $12.50 | $14.20 (+14%) | $13.80 (+10%) | Limited local supply chains; 20–35% higher import duties on Chinese components. |
| Labor | $4.80 | $3.90 (-19%) | $6.20 (+29%) | Vietnam: Lower wages but 15% lower productivity. Mexico: Higher wages but proximity to US reduces logistics complexity. |
| Packaging | $1.20 | $1.50 (+25%) | $1.35 (+13%) | Stricter ESG regulations (e.g., Vietnam’s 2025 plastic tax); localized material sourcing gaps. |
| Logistics | $2.10 | $2.80 (+33%) | $1.60 (-24%) | Vietnam: Longer ocean freight to US/EU. Mexico: Nearshoring advantage for Americas. |
| Total Landed Cost | $20.60 | $22.40 | $22.95 | Relocation premium: 8.7% (Vietnam) to 11.4% (Mexico) for low-volume orders. |
🔍 Critical Insight: Labor is only 18–22% of total cost. Procurement teams optimizing only for labor rates miss 80% of cost drivers. Focus on total landed cost + rework risk.
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Mid-Tier Wireless Earbuds, FOB Vietnam)
Reflects 2026 Q2 market conditions; excludes tariffs, IP tooling, and compliance costs
| MOQ | Unit Price | Material Cost | Labor Cost | Packaging Cost | Economies of Scale Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18.90 | $11.20 (59%) | $4.10 (22%) | $1.85 (10%) | High material waste; manual assembly; single-shift runs. |
| 1,000 units | $16.25 | $9.80 (60%) | $3.55 (22%) | $1.50 (9%) | Bulk material discounts; optimized line setup. |
| 5,000 units | $13.80 | $8.10 (59%) | $2.95 (21%) | $1.20 (9%) | Full automation; vendor-managed inventory; energy efficiency. |
📉 Volume Leverage Note: Every 3x MOQ increase reduces unit cost by 14–18% in relocated factories (vs. 20–25% in mature Chinese hubs). Minimum viable MOQ for competitiveness: 1,000 units.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Leaders
- Audit Total Landed Cost: Model tariffs, logistics, quality failure costs (QFC), and inventory holding – not just FOB price.
- Demand Hybrid Sourcing Contracts: Require suppliers to use China-based R&D with regional assembly (e.g., “Designed in Shenzhen, Assembled in Querétaro”).
- Lock Tooling Ownership: For Private Label, own molds/tooling outright – critical when suppliers shift production.
- Pilot with MOQ 1,000+: Avoid sub-1,000 unit orders in new regions; they amplify cost premiums.
- Embed QC at Origin: Deploy third-party inspectors for every shipment – skill gaps in new hubs increase defect rates by 22% (SourcifyChina 2025).
💡 SourcifyChina Advantage: Our Relocation Risk Scorecard evaluates 47 supplier parameters (beyond cost) – including political stability, component traceability, and ESG compliance. [Request Assessment]
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Date: Q2 2026 | Data Sources: SourcifyChina Supplier Network (1,200+ factories), World Bank Logistics Index, Statista Manufacturing Cost Database
Disclaimer: Estimates assume standard product complexity. Actual costs vary by category, region, and contract terms. Conduct factory-specific benchmarking.
Optimize your supply chain resilience – not just your spreadsheet. Connect with our team for a no-cost Relocation Readiness Assessment.
sourcifychina.com/procurement-strategy | +86 755 8675 1234
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for Global Procurement Managers: Verifying Chinese Manufacturers Amid Relocation Trends
Executive Summary
In 2026, shifting geopolitical pressures, rising labor costs, and supply chain diversification efforts have accelerated the trend of Chinese manufacturing operations relocating to Southeast Asia, India, and Mexico. This migration has increased the complexity of supplier verification. For global procurement managers, distinguishing between authentic factories and trading companies—especially those posing as manufacturers—is critical to mitigating risk, ensuring quality, and maintaining supply chain continuity.
This report outlines critical verification steps, key differentiators between trading companies and factories, and red flags to avoid during supplier onboarding in the current sourcing landscape.
Part 1: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer (Post-Relocation or Domestic)
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Legal Entity & Registration | Verify business license, unified social credit code, and registered manufacturing address. | Ensure legitimacy and traceability. | Use China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn). Cross-check with third-party platforms (e.g., TofuDeluxe, Kompass). |
| 2. Conduct On-Site Audit (Remote or Physical) | Visit the facility or use third-party inspection services. | Validate production capacity, equipment, and workforce. | Hire SourcifyChina-certified auditors. Use real-time video audits with random area checks. |
| 3. Review Export History & Customs Data | Analyze export records for volume, frequency, and product categories. | Confirm actual export experience and market presence. | Leverage customs data platforms (ImportGenius, Panjiva, TradeAtlas). |
| 4. Assess Production Documentation | Request process flowcharts, QC protocols, machine lists, and staffing plans. | Verify operational maturity and scalability. | Evaluate documentation depth and consistency. |
| 5. Validate Subcontracting Transparency | Ask if production is in-house or outsourced. Require disclosure of subcontractors. | Avoid hidden supply chain layers. | Include subcontracting clauses in contracts. |
| 6. Test Sample Quality & Consistency | Order multiple samples over time. Conduct third-party lab testing. | Ensure quality control and repeatability. | Use SGS, Bureau Veritas, or Intertek for testing. |
| 7. Check IP Protection & Compliance | Review patent filings, certifications (ISO, BSCI, CE, RoHS), and NDA enforcement. | Mitigate legal and reputational risk. | Verify certifications with issuing bodies. Conduct IP audit. |
Part 2: How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists manufacturing as core activity; includes production address. | Lists trading/export; no production address or vague location. |
| Facility Footprint | Large physical plant with machinery, raw material storage, and production lines visible. | Office-only setup; minimal or no production equipment. |
| Workforce | 100+ employees; engineers, line workers, QC staff on-site. | Smaller team; sales and logistics focus. |
| Product Customization | Offers mold/tooling development, engineering support, MOQ flexibility. | Limited to catalog items; defers technical questions. |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent cost breakdown (material, labor, overhead). | Higher margins; less cost transparency. |
| Lead Times | Directly controls production schedule; shorter lead times. | Dependent on factory schedules; longer and less predictable. |
| References & Clients | Willing to provide factory visits and direct client contacts. | Hesitant to share clients; references may be indirect. |
| Website & Marketing | Features production lines, R&D labs, certifications. | Focuses on product catalogs and global shipping. |
Pro Tip: Use Google Earth to verify satellite imagery of the facility. Factories show large industrial buildings; trading companies often operate from commercial complexes.
Part 3: Red Flags to Avoid in 2026 Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a video audit | Conceals production reality; likely a middleman or shell company. | Disqualify supplier. Require audit before engagement. |
| Multiple product categories with no specialization | Indicates trading behavior; lacks technical depth. | Focus on niche manufacturers with proven expertise. |
| Price significantly below market average | Suggests substandard materials, labor exploitation, or hidden costs. | Conduct cost benchmarking; verify material specs. |
| No physical address or PO Box only | High fraud risk; no accountability. | Require verified office/factory address with GPS coordinates. |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | Indicates weak IP protection; risk of design theft. | Use standardized IP clauses; avoid engagement if non-compliant. |
| Inconsistent communication or language barriers | May signal disorganized operations or third-party relay. | Require direct contact with operations manager; use interpreters if needed. |
| Pressure for large upfront payments | Common in scams; lack of financial stability. | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy). |
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
As Chinese manufacturing evolves through relocation and digital transformation, due diligence must evolve in parallel. Global procurement managers must:
- Prioritize transparency—demand access to real-time production data and audit trails.
- Leverage technology—use AI-powered supplier verification tools and blockchain for traceability.
- Build dual-sourcing strategies—combine China-based factories with regional hubs (e.g., Vietnam, Malaysia) for resilience.
- Partner with trusted sourcing consultants—SourcifyChina offers end-to-end verification, audit coordination, and legal compliance support.
Final Note: In 2026, the line between factory and trader is increasingly blurred. Verification is no longer optional—it is the foundation of sustainable, ethical, and efficient global sourcing.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: April 5, 2026
For confidential use by procurement leadership teams only.
Contact: [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Supply Chain Relocation (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026
Executive Summary: The Relocation Imperative
Geopolitical pressures, evolving US/EU tariff structures, and regional cost optimization are accelerating the strategic relocation of manufacturing capacity from Mainland China to Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, and Mexico. 78% of Fortune 500 procurement teams now report active “China+1” or “China+N” diversification programs (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Survey). However, identifying reliable, experienced, and operationally ready suppliers in new regions remains the #1 bottleneck, consuming 40+ hours per RFQ cycle and risking 6+ month delays.
The Critical Challenge: “Moving Out” ≠ Operational Readiness
Many Chinese manufacturers advertise relocation capabilities but lack:
– Proven cross-border logistics management
– Local regulatory compliance (e.g., Vietnam’s EVFTA rules of origin)
– Scalable workforce training systems in host countries
– Financial stability during transition phases
Result: 63% of procurement managers experience supplier failure or capacity shortfalls during relocation projects, leading to cost overruns (avg. +22%) and production halts.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Solves This
Our Pro List: Relocation-Ready Suppliers is the only database rigorously vetted against 12 operational criteria specific to successful cross-border manufacturing transfers. Unlike generic directories, we validate:
| Verification Metric | Traditional Sourcing | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved Per RFQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relocation Experience | Unverified claims | ≥2 completed relocations (audited) | 18–25 hours |
| Host-Country Compliance | Self-certified documents | On-site legal/regulatory audit | 12–15 hours |
| Production Scalability | Theoretical capacity | 90-day ramp-up proof (live data) | 10–14 hours |
| Supply Chain Integration | Unconfirmed sub-tier access | Verified local material sourcing | 8–12 hours |
| Total Vetting Time | 48–66 hours | < 6 hours | 42–60 hours |
Strategic Impact: Procurement teams using the Pro List achieve 82% faster supplier onboarding and reduce relocation project risks by 74% (2025 Client Data).
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
The window for low-risk relocation is narrowing. Vietnam’s factory occupancy exceeds 92%, while Mexico faces customs backlog surges. Delaying supplier validation now jeopardizes 2026 production continuity.
✅ The Pro List delivers:
– Zero-risk transitions: Suppliers with live facilities in target regions (no “planned” or “future” capacity)
– Cost transparency: FOB comparisons across China/SE Asia/Mexico with duty drawback analysis
– Continuous monitoring: Real-time alerts on supplier stability (e.g., labor strikes, regulatory changes)
Call to Action: Secure Your Relocation Timeline in 24 Hours
Do not risk 6+ months of delays due to unvetted suppliers. With SourcifyChina’s Pro List, your team can:
1. Immediately access 147 pre-qualified suppliers with proven relocation success (2025–2026)
2. Eliminate 50+ hours of manual vetting per project cycle
3. Lock in capacity before Q3 2026 seasonal shortages
→ Act Now to Guarantee 2026 Supply Chain Resilience
Contact our Relocation Specialist Team:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp (24/7): +86 159 5127 6160
Include your target product category and relocation region for a complimentary Pro List eligibility assessment. All inquiries receive a detailed supplier shortlist within 24 business hours.
SourcifyChina: Precision Sourcing Intelligence Since 2010
Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands | 98.7% Client Retention Rate | 100% Verification Audit Trail
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Data sourced from proprietary supplier audits and customs clearance records.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.