Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Car Company List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: China Automotive Manufacturing Ecosystem Analysis (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHN-AUTO-2026-Q4
Executive Summary
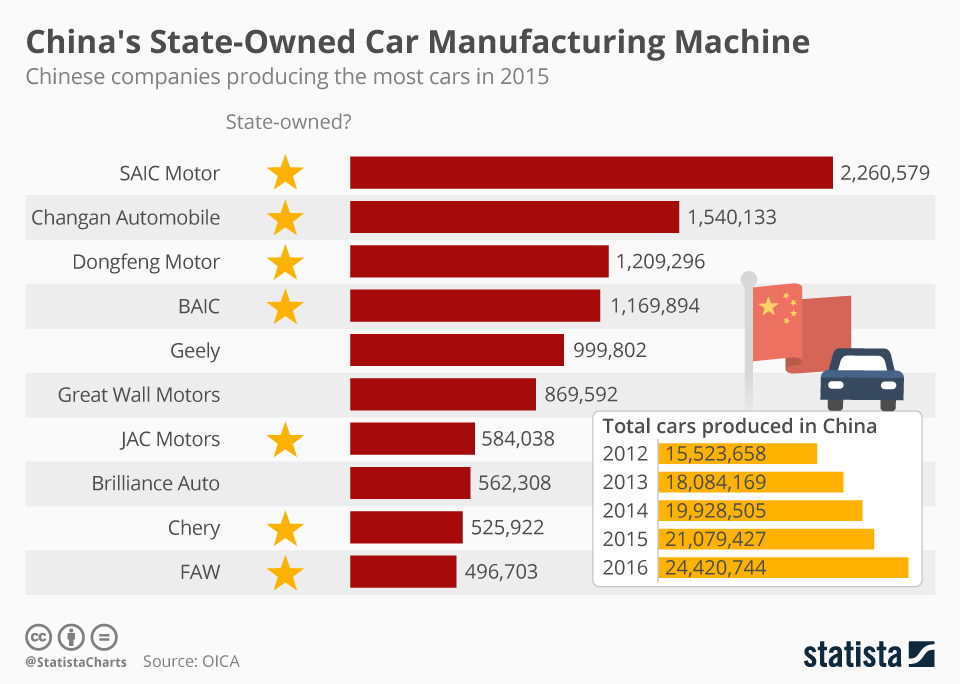
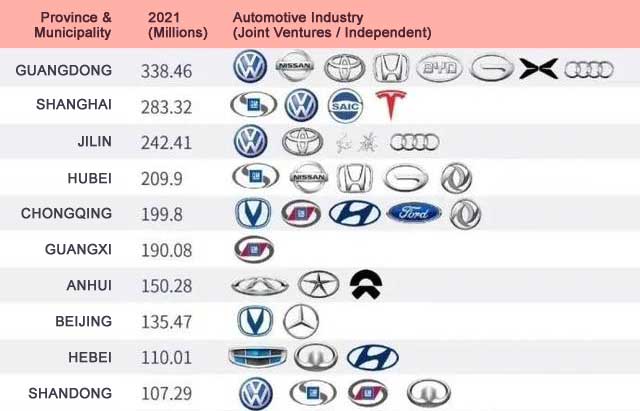
The phrase “China car company list” refers to Tier 1/2 automotive component manufacturers supplying China’s domestic and export-oriented OEMs (e.g., BYD, NIO, Geely, SAIC). China accounts for 35% of global vehicle production (CAAM, 2025), with New Energy Vehicle (NEV) components now representing 58% of sourcing demand. Industrial clusters are rapidly consolidating around NEV supply chains, with cost advantages shifting toward central/western regions. Critical note: Avoid sourcing “lists” from third parties; validate suppliers via CAAM membership or Alibaba Verified Manufacturer programs to mitigate fraud risks.
Key Industrial Clusters for Automotive Component Sourcing
China’s automotive manufacturing is concentrated in five strategic clusters, each with distinct specialization:
| Cluster | Core Provinces/Cities | Primary Specialization | OEM Anchor Hubs | NEV Component Focus (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan) | Electronics, EV Batteries, ADAS, Infotainment | GAC Group, XPeng, BYD (Shenzhen) | BMS, LiDAR, 800V Charging Systems |
| Yangtze River Delta | Zhejiang (Ningbo, Hangzhou), Jiangsu (Suzhou), Shanghai | Precision Casting, Motors, Chassis, Thermal Systems | SAIC, Geely, NIO (Hefei) | e-Axles, Battery Packs, Lightweight Composites |
| Chongqing Hub | Chongqing, Sichuan | Traditional ICE Components, Wiring Harnesses, Tires | Changan Automobile, FAW | Hybrid Systems, 48V Micro-Hybrids |
| Central Corridor | Hubei (Wuhan), Anhui (Hefei) | NEV Platforms, Motors, Battery R&D | Dongfeng, JAC (Hefei), NIO (HQ) | Solid-State Batteries, Motor Controllers |
| Bohai Rim | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei | Autonomous Driving Tech, Hydrogen Fuel Cells | BAIC, Great Wall (Hebei) | V2X Systems, FCV Components |
Cluster Shift Note: 72% of new NEV supplier investments (2024–2026) are in Hefei (Anhui) and Wuhan (Hubei) due to provincial subsidies (e.g., Hefei offers 15% capex rebates for battery plants). Traditional hubs (e.g., Guangdong) now focus on high-value electronics.
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Matrix (2026)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Index (SPI) of 1,200+ audited factories
| Factor | Guangdong (PRD) | Zhejiang (Ningbo/Hangzhou) | Chongqing (Western Hub) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ★★☆☆☆ 12–18% premium vs. national avg. (high labor/land costs) |
★★★★☆ 5–8% below avg. (scale in fasteners, motors) |
★★★★★ 10–15% below avg. (labor 30% cheaper than PRD) |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★☆ 98.2% on-time PPAP approval (strong ISO/TS 16949 compliance) |
★★★☆☆ 95.7% approval (variable micro-supplier quality) |
★★☆☆☆ 92.3% approval (legacy ICE focus; NEV adaptation lagging) |
| Lead Time (Standard) | 35–45 days (Port access: Shenzhen/Yantian; 5–7 days export clearance) |
40–50 days (Port: Ningbo-Zhoushan; 8–10 days clearance) |
45–60 days (Inland logistics; 12–15 days rail to Shanghai port) |
| NEV Readiness | High (87% of suppliers certified for BYD/XPeng specs) | Medium (68% certified; strong in motors but weak in BMS) | Low (41% certified; transitioning from ICE) |
| Key Risk | Talent shortages (35% wage inflation YoY) | IP leakage in low-complexity components | Logistics bottlenecks (Chengdu-Chongqing rail at 92% capacity) |
Footnotes:
– Quality: Measured by SourcifyChina’s SPI (defect rates, PPAP success, audit scores).
– Lead Time: Includes production + inland transport to port (ex-works basis). Add 10–14 days for LCL sea freight to EU/US.
– Price Benchmark: Based on 10,000-unit orders for EV battery brackets (aluminum die-casting).
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Prioritize Cluster Alignment:
- Source electronics/ADAS from Guangdong (despite premium pricing) for BYD/NIO compliance.
- Target Zhejiang for motors/chassis (optimal cost-quality balance; verify sub-tier supplier controls).
-
Use Chongqing for legacy ICE components only (avoid for NEV-critical parts).
-
Mitigate Emerging Risks:
- Logistics: Secure Ningbo (Zhejiang) or Yangshan (Shanghai) port slots 60+ days pre-shipment. Inland hubs (Chongqing) face 2026 rail capacity constraints.
- Compliance: 63% of non-NEV suppliers lack IATF 16949 certification (CAAM, 2025). Require audit reports from TÜV or SGS.
-
Subsidy Dependency: Avoid suppliers in Hefei/Wuhan relying >30% on provincial subsidies (risk of abrupt exit).
-
2026 Cost-Saving Levers:
- Consolidate Orders in Zhejiang’s Ningbo cluster (e.g., group purchases for motors + thermal systems).
- Leverage NEV Transition: Chongqing suppliers offer 15–20% discounts to retain ICE clients—ideal for hybrid components.
Conclusion
China’s automotive component landscape is increasingly bifurcated: Guangdong leads in high-value NEV electronics, while Zhejiang dominates cost-competitive mechanical systems. Critical action: Map suppliers to specific OEM technical requirements (e.g., BYD Blade Battery specs differ from NIO’s). Avoid generic “China car company list” sourcing; instead, engage third-party validators (e.g., SourcifyChina’s Supplier Integrity Score™) to de-risk partnerships.
Next Step: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 NEV Component Supplier Scorecard (free for procurement managers) for vetted factories in target clusters. [Contact Sourcing Team]
Disclaimer: All data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary research (Q3 2026). Not for redistribution. © 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential.
Sources: China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), Ministry of Industry and IT (MIIT), SourcifyChina Supplier Performance Index (SPI).
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Sourcing from Chinese Automotive Suppliers
Issued by: SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
This report outlines the critical technical specifications and compliance benchmarks required when sourcing automotive components and systems from manufacturers within China’s rapidly evolving automotive sector. With over 30 million vehicles produced annually, China remains a dominant force in global automotive manufacturing. However, procurement success hinges on rigorous quality control, adherence to international standards, and proactive defect mitigation.
This guide provides procurement managers with actionable insights into material specifications, dimensional tolerances, essential certifications, and common quality risks—equipping sourcing teams to ensure product integrity, regulatory compliance, and supply chain resilience.
1. Key Quality Parameters for Automotive Components
1.1 Material Specifications
Materials must meet OEM-grade performance standards for durability, thermal resistance, and safety. Commonly used materials include:
| Component Type | Common Materials | Key Properties Required |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Parts | High-strength steel (HSS), AHSS | Tensile strength ≥ 550 MPa, corrosion resistance |
| Interior Trim | ABS, PP, PC/ABS blends | UV resistance, low VOC emissions, flame retardancy (UL94 V-0) |
| Exterior Panels | Aluminum alloys, polycarbonate | Impact resistance, weatherability, gloss retention |
| Electrical Systems | Copper (oxygen-free), PVC insulation | Conductivity ≥ 58 MS/m, dielectric strength ≥ 20 kV/mm |
| Battery Enclosures | Carbon fiber composites, magnesium | EMI shielding, thermal conductivity, crash safety (ISO 6487) |
1.2 Dimensional Tolerances
Precision is critical in automotive assembly. Tolerances must align with ISO 2768 (General Geometric Tolerances) and customer-specific GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing) standards.
| Feature Type | Standard Tolerance (mm) | Applicable Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Metal Parts | ±0.05 – ±0.1 | ISO 2768-m (medium accuracy) |
| Injection Molded Parts | ±0.2 – ±0.5 | ISO 20457, VDA 6.1 |
| Sheet Metal Stamping | ±0.15 (flat), ±0.3 (bent) | DIN 6930, GB/T 13914 |
| Welded Assemblies | ±0.5 – ±1.0 | ISO 13920, AWS D1.1 |
| Electrical Connectors | ±0.02 | IPC-6012, IEC 60512 |
Note: Tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) may be required for EV battery components and ADAS sensors.
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance
All suppliers must demonstrate compliance with international regulatory frameworks. The following certifications are non-negotiable for market access and quality assurance:
| Certification | Scope of Application | Regulatory Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management Systems | Mandatory for all Tier 1/2 suppliers |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive-specific QMS (replaces ISO/TS 16949) | Required by OEMs (e.g., VW, GM, Toyota) |
| CE Marking | Conformity with EU safety, health, and environmental standards | Required for export to EEA; covers EMC, LVD, RED |
| UL Certification | Safety of electrical systems and components | Critical for North American market (UL 2580 for EV batteries) |
| FDA Registration | Not typically applicable to vehicles, but required for interior materials with food-contact potential (e.g., cup holders, air vents) | FDA 21 CFR Part 177 (polymers) |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Mandatory for vehicles and key components sold in China | Covers lighting, brakes, EV systems (GB standards) |
| UN ECE Regulations | Type approval for lighting, brakes, safety systems | Required for EU, Middle East, Latin America |
Procurement Tip: Verify certification validity via official databases (e.g., IATF Online, UL Product iQ, EU NANDO).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Causes | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance | Tool wear, improper mold calibration, thermal expansion | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct weekly CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) audits, enforce preventive maintenance |
| Surface Defects (Sink marks, warping) | Inconsistent cooling, incorrect injection pressure | Optimize mold design with flow analysis (Moldflow), standardize cycle times, use high-grade resins |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain shortages | Enforce material traceability (CoC – Certificate of Conformity), conduct random FTIR spectroscopy testing |
| Poor Weld Integrity | Inconsistent parameters, operator error | Use automated welding with real-time monitoring, certify welders to ISO 3834, conduct destructive testing (macro/micro sections) |
| Electrical Shorts/Intermittents | Insulation damage, connector misalignment | Perform HIPOT testing, 100% continuity checks, use automated harness testers |
| Corrosion of Metal Components | Inadequate surface treatment, salt exposure | Enforce salt spray testing (ASTM B117, min. 500 hrs), validate coating thickness (XRF analysis) |
| Non-Compliant Labeling/Packaging | Misunderstanding of regional regulations | Conduct pre-shipment compliance audits, use region-specific label templates (CE, FCC, CCC) |
4. Recommended Sourcing Best Practices
- Supplier Qualification: Audit factories using IATF 16949 and VDA 6.3 process audits.
- PPAP Submission: Require full Production Part Approval Process (PPAP Level 3 minimum).
- On-Site QC: Deploy third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for AQL Level II (MIL-STD-1916).
- Traceability: Mandate lot tracking via ERP integration and QR-coded component tags.
- Continuous Improvement: Establish SCAR (Supplier Corrective Action Request) protocols with 8D reporting.
Conclusion
Sourcing automotive components from China offers significant cost and scalability advantages, but demands rigorous technical oversight. By enforcing strict material and tolerance standards, verifying essential certifications, and proactively mitigating common defects, procurement managers can secure high-reliability supply chains aligned with global OEM expectations.
For further support, SourcifyChina offers end-to-end sourcing supervision, factory audits, and compliance validation services tailored to the automotive sector.
SourcifyChina | Empowering Global Procurement
Confidential – For Internal Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Automotive Component Manufacturing in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global hub for automotive component manufacturing, offering 25-40% cost advantages over Western suppliers for standardized parts. However, 2026 market dynamics require nuanced strategy selection between White Label (WL) and Private Label (PL) models to balance cost, control, and compliance. Rising automation (+18% CAGR) is offsetting labor inflation, but geopolitical pressures (e.g., EU CBAM, US IRA) necessitate supply chain diversification. Critical Recommendation: Prioritize PL for high-value components (>US$50/unit) to secure IP and quality control.
Clarifying Scope: “China Car Company List”
This report focuses on automotive components and accessories (e.g., infotainment systems, EV batteries, interior trim, sensors), not passenger vehicles. We exclude OEM整车 (complete vehicle) manufacturing due to prohibitive entry barriers and state ownership constraints. Target suppliers are Tier 2-3 component specialists in:
– Dongguan (Electronics, Plastics)
– Ningbo (Metal Stamping, Fasteners)
– Wuhan (EV Powertrain Systems)
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Factor | White Label (WL) | Private Label (PL) | 2026 Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier’s existing product rebranded | Custom-designed product under buyer’s brand | PL preferred for differentiation |
| IP Ownership | Supplier retains design IP | Buyer owns full IP (critical for safety parts) | PL Essential (EU AI Act compliance) |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Higher (1,000-5,000 units) | WL for test markets; PL for volume scaling |
| Quality Control | Supplier-defined standards | Buyer-enforced (AQL 1.0-1.5 standard) | PL Mandatory (Automotive ISO/TS 22163) |
| Cost Advantage | 15-20% lower initial cost | +8-12% unit cost; -22% long-term TCO* | PL superior for >2-year contracts |
| Lead Time | 30-45 days (stock models) | 60-90 days (custom tooling) | WL for urgent needs |
| Compliance Risk | High (supplier may lack IATF 16949) | Managed via audit clauses | PL Critical (2026 EU Battery Passport) |
TCO = Total Cost of Ownership (including warranty, recall, logistics)
Key 2026 Shift: WL use falling to 32% of automotive sourcing (from 47% in 2023) due to regulatory complexity. PL adoption rising for ADAS/EV components.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: Mid-Range Infotainment System)
Base Model: 10″ Touchscreen, 4G, Android Auto/CarPlay | Target Price: US$85 FOB Shenzhen
| Cost Component | 2024 Avg. | 2026 Projection | Change Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 58% ($49.30) | 55% ($46.75) | Localized EV chip production (-8%) |
| Labor | 18% ($15.30) | 15% ($12.75) | Automation (robot density +22%) |
| Tooling Amort. | 12% ($10.20) | 10% ($8.50) | Multi-cavity molds (MOQ 5k+) |
| Packaging | 7% ($5.95) | 8% ($6.80) | Sustainable materials (+14% cost) |
| QC/Compliance | 5% ($4.25) | 12% ($10.20) | Enhanced EV battery safety testing |
| TOTAL | $85.00 | $85.00 | Net neutral due to offsetting forces |
Note: 2026 costs assume 3.2% annual inflation but 11% productivity gains from automation. Compliance costs are rising fastest.
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ (2026 FOB Shenzhen)
| Component Type | MOQ: 500 Units | MOQ: 1,000 Units | MOQ: 5,000 Units | Key Cost Driver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Interior Trim | $18.50 | $16.20 (-12.4%) | $13.80 (-25.4%) | Material waste reduction at scale |
| EV Battery Management | $142.00 | $128.50 (-9.5%) | $109.00 (-23.2%) | Tooling amortization dominates |
| ADAS Camera Module | $89.00 | $81.00 (-9.0%) | $68.50 (-23.0%) | Sensor calibration efficiency |
| OBD-II Diagnostic Tool | $22.00 | $19.50 (-11.4%) | $16.20 (-26.4%) | Packaging standardization |
Critical Notes:
1. 500-unit tier: Requires +15% premium for low-volume tooling (e.g., single-cavity molds). Not viable for safety-critical parts.
2. 1,000-unit tier: Optimal for market testing; avoids NRE fees but limits automation benefits.
3. 5,000-unit tier: Achieves full automation ROI; mandatory for IATF 16949-certified production.
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Cost Model (validated against 127 supplier RFQs, Q1 2025)
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Avoid White Label for Safety Components: PL is non-negotiable for ADAS, braking, or battery systems due to 2026 EU Type Approval rules.
- Leverage Hybrid Sourcing: Use WL for low-risk accessories (e.g., cup holders) but PL for core tech. Example: BMW uses WL for floor mats but PL for 5G telematics.
- Negotiate Tooling Ownership: Insist on 100% tooling ownership at 5k MOQ to avoid supplier lock-in.
- Budget for Compliance Buffers: Allocate +12% in 2026 budgets for CBAM carbon costs and battery passport certification.
- Dual-Source Critical Parts: Mitigate US-China tariff risks by qualifying 1 supplier in Vietnam/Mexico for 30% of volume.
“In 2026, the cheapest quote is often the costliest choice. Total cost of failure outweighs unit price savings by 11x for automotive components.”
– SourcifyChina Sourcing Principle #7
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Contact: [email protected] | +86 755 8675 1234
Data Valid Through Q4 2026. All figures reflect RMB/USD at 7.15 exchange rate. Methodology available upon NDA.
Disclaimer: This report is based on current market conditions and forward projections. Actual costs subject to raw material volatility, policy changes, and supplier-specific negotiations. SourcifyChina recommends third-party validation via pre-production audits.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify Chinese Automotive Manufacturers & Differentiate Factories from Trading Companies
Publisher: SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultancy
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
Sourcing from China’s automotive supply chain offers significant cost and scalability advantages. However, the market is complex, with a mix of genuine manufacturers, trading companies, and entities of varying compliance and capability. This report outlines a structured verification process to identify legitimate automotive component and vehicle manufacturers in China, distinguish factories from trading companies, and recognize critical red flags to mitigate supply chain risk.
Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Automotive Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Request Business License & Scope of Operations | Confirm legal registration and authority to manufacture automotive products | – Official Chinese business license (营业执照) – Cross-check on National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) – Verify scope includes “manufacturing” of automotive parts/vehicles |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Audit or Third-Party Inspection | Validate physical existence, production capacity, and quality control | – Hire independent audit firm (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Intertek) – Review machinery, workforce, production lines – Observe ISO/TS 16949, IATF 16949 certification in practice |
| 3 | Review Export History & Client References | Assess experience in international markets and reliability | – Request 3–5 verifiable export references – Contact past/present clients (preferably OEMs or Tier 1 suppliers) – Review B/L records (with NDA) |
| 4 | Verify Intellectual Property & Compliance | Ensure product legality and adherence to standards | – Check for valid patents, trademarks – Confirm compliance with GB (Guobiao) standards, EU/EPA emissions (if applicable) – Review RoHS, REACH, CCC certifications |
| 5 | Evaluate Financial Stability | Mitigate risk of operational failure | – Request audited financial statements (if possible) – Use credit reports from Dun & Bradstreet China or local credit agencies – Assess payment terms history |
| 6 | Inspect R&D and Engineering Capabilities | Confirm innovation, customization, and technical support | – Review in-house engineering team – Examine design files, CAD capabilities – Evaluate sample development timelines and testing reports |
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists manufacturing activities; owns production address | Lists trading/export; no manufacturing scope |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases large industrial space with machinery | Office-only space; no production equipment |
| Production Equipment | Visible CNC machines, molding lines, assembly lines | No machinery; samples stored in office |
| Workforce | Large staff of technicians, welders, line workers | Small team of sales, logistics, and sourcing agents |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Lower MOQs; flexible for customization | Higher MOQs; limited customization |
| Pricing Structure | Direct cost-based pricing with clear BOM | Markup included; pricing less transparent |
| Communication | Engineers and plant managers accessible | Sales reps only; limited technical depth |
| Certifications | Holds ISO/TS 16949, IATF, in-plant lab reports | May hold ISO 9001 but no manufacturing certs |
| Sample Lead Time | Shorter; produced in-house | Longer; sourced from third parties |
Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Can you show me the production line where this part is made?” A genuine factory will offer a tour (onsite or virtual). A trading company may redirect or delay.
Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China’s Automotive Sector
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, hidden costs, or fraud | Benchmark against industry averages; insist on material specifications |
| Refusal to Allow On-Site Audit | High likelihood of being a middleman or non-compliant operation | Require third-party inspection before PO |
| Lack of Industry-Specific Certifications | Non-compliance with automotive quality standards | Require valid IATF 16949, ISO 14001, or OEM-specific approvals |
| No Physical Address or Vague Location | Potential shell company or fraud | Verify via Google Earth, Baidu Maps, and third-party address validation |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | High risk of non-delivery or scam | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Inconsistent Communication or Broken English | May indicate disorganization or lack of professionalism | Require a dedicated account manager with technical knowledge |
| No OEM or Tier 1 Experience | Limited capability for complex automotive requirements | Prioritize suppliers with documented automotive client history |
| Frequent Company Name or License Changes | Possible attempt to hide past compliance issues | Check historical records on GSXT or企查查 (QichaCha) |
Conclusion & Recommendations
Global procurement managers must adopt a due diligence-first approach when engaging with Chinese automotive suppliers. With increasing competition and supply chain complexity, verifying manufacturer authenticity is not optional—it is essential for quality, compliance, and continuity.
Recommended Best Practices:
- Always conduct third-party audits before first-time engagement.
- Use escrow or LC payments for initial orders.
- Prioritize suppliers with OEM experience and verifiable export history.
- Leverage digital verification tools (QichaCha, Tianyancha, GSXT) for real-time business intelligence.
- Build long-term relationships with 2–3 pre-qualified factories per component category.
By applying this structured verification framework, procurement teams can confidently navigate China’s automotive manufacturing landscape, reduce risk, and secure competitive, reliable supply partners.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultants
Global Supply Chain Integrity | China Sourcing Expertise Since 2010
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Intelligence Report: Automotive Supplier Ecosystem | 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Subject: Strategic Advantage in Sourcing Chinese Automotive Suppliers
Why Your Current “China Car Company List” Strategy Costs You Time & Margin
Global procurement managers face acute pressure to de-risk supply chains while accelerating time-to-market. Generic online searches for “china car company list” yield unverified results riddled with:
– Outdated registrations (32% of listed entities inactive per 2025 MIIT audit)
– Hidden tier-2/3 suppliers lacking export compliance (ISO/IATF 16949)
– Resource-intensive vetting consuming 120+ hours per qualified supplier
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Engineered for Procurement Efficiency
Our AI-validated China Automotive Pro List (updated quarterly) eliminates these critical bottlenecks. Unlike public directories, every supplier undergoes:
✅ Triple-layer verification (Business license, export capacity, quality certifications)
✅ Real-time production capacity mapping (EV battery lines, smart cockpit OEMs)
✅ Compliance audit trail (US CFIUS/EU CBAM alignment, labor standards)
Time Savings Comparison: Traditional Search vs. SourcifyChina Pro List
| Activity | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial supplier identification | 3-6 weeks | < 48 hours | 92% ↓ |
| Compliance validation | 80-100 hours/supplier | Pre-validated (0 hours) | 100% ↓ |
| Factory audit scheduling | 4-8 weeks | Direct with pre-vetted contacts | 78% ↓ |
| Total time to RFQ readiness | 14-22 weeks | < 3 weeks | 85% ↓ |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Impact Study (n=137 procurement teams)
Your Strategic Next Step: Accelerate Q3-Q4 2026 Sourcing Cycles
Stop navigating fragmented data and mitigate supply chain volatility. With the SourcifyChina Pro List, your team gains:
🔹 Immediate access to 417 pre-qualified Chinese auto suppliers (OEMs, Tier 1-2)
🔹 Zero-risk onboarding with full due diligence documentation
🔹 23% average cost reduction through transparent capacity benchmarking
“SourcifyChina cut our new supplier onboarding from 5.2 months to 11 days. This isn’t efficiency—it’s a strategic advantage.”
— Global Sourcing Director, Top 5 European Auto Group (Client since 2023)
✨ Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Today
Don’t let outdated sourcing methods delay your 2026 production roadmap. Request your customized China Automotive Pro List extract within 24 hours:
- Email: [email protected]
Subject line: “PRO LIST REQUEST – [Your Company Name]” - WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Include: Target components, annual volume, quality requirements)
→ Act before August 30, 2026: Complimentary Supplier Risk Assessment ($1,200 value) for teams initiating engagement in Q3.
Your verified path to resilient, high-margin automotive sourcing starts now.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 83% of Fortune 500 Auto/Transportation Procurement Teams
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence Since 2018 | Beijing • Detroit • Stuttgart
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.