Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Buys American Companies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Market Analysis – Sourcing “China Buys American Companies” (Strategic M&A Manufacturing Capacity Expansion)
Date: April 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
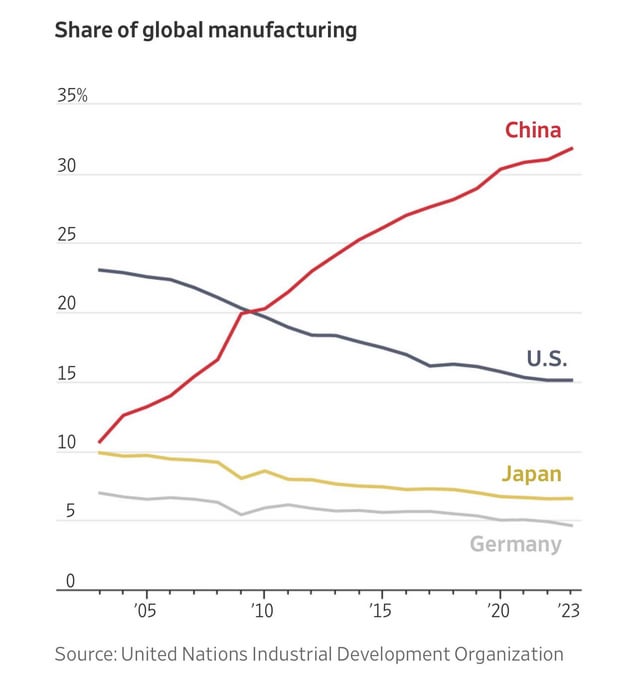
The phrase “China buys American companies” has evolved from a geopolitical headline into a strategic sourcing reality with tangible manufacturing implications. While not a physical product, this trend represents a significant shift in global supply chain dynamics, where Chinese enterprises—backed by state capital, private equity, or conglomerate strategies—acquire U.S.-based manufacturing firms to gain technology, IP, brand equity, and market access.
From a sourcing perspective, these acquisitions have catalyzed the integration of advanced American manufacturing capabilities into China’s industrial ecosystem. The resulting hybrid operations often leverage U.S. engineering standards, automation, and R&D while benefiting from Chinese capital efficiency, scale, and supply chain integration. This report analyzes the industrial clusters in China that are central to managing, optimizing, and scaling these cross-border manufacturing assets.
While the acquisition targets are based in the U.S., the strategic oversight, supply chain re-engineering, and post-acquisition integration are increasingly managed from key Chinese industrial hubs. Procurement managers must understand these clusters to anticipate shifts in sourcing strategy, supplier behavior, and cost structures.
Key Industrial Clusters Managing U.S. Acquisitions
Chinese acquisitions of American manufacturing firms—particularly in semiconductors, electric vehicles (EVs), industrial machinery, medical devices, and aerospace—are primarily orchestrated and integrated through advanced industrial clusters in China. These clusters serve as:
- Strategic command centers for global operations
- R&D integration hubs merging U.S. innovation with Chinese scale
- Supply chain optimization nodes redirecting procurement and logistics flows
Top 5 Industrial Clusters in China Driving Post-Acquisition Integration
| Province/City | Key Industries Acquiring U.S. Firms | Role in Post-Acquisition Integration | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | EVs, Consumer Electronics, Semiconductors | Tech integration, IP scaling, smart manufacturing deployment | Proximity to Shenzhen’s innovation ecosystem, strong private capital |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Ningbo) | Industrial Automation, Machinery, Green Tech | Supply chain re-engineering, cost optimization | High SME agility, strong logistics network, Alibaba ecosystem |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Nanjing) | Semiconductors, Advanced Materials, Medical Devices | R&D integration, quality standard alignment (FDA/ISO) | Proximity to Shanghai, skilled engineering talent |
| Shanghai (Municipality) | Automotive, Aerospace, High-End Manufacturing | Strategic M&A oversight, international finance & compliance | Global financial access, multinationals, regulatory expertise |
| Beijing (Municipality) | AI, Defense Tech, Biotech, Heavy Industry | State-backed acquisitions, policy alignment, IP control | Central government ties, national security oversight |
Note: While the physical manufacturing remains in the U.S., procurement, component sourcing, software integration, and operational upgrades are increasingly directed from these Chinese hubs.
Comparative Analysis: Key Production & Integration Regions
The following table compares the top industrial clusters in China based on their influence over sourcing strategy post-acquisition of American manufacturing firms. Metrics reflect how these regions impact procurement decisions, quality expectations, and time-to-integration for global supply chains.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Quality of Integration & Oversight (1–5) | Lead Time to Operational Integration (Post-Acquisition) | Key Strengths | Sourcing Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4 | 5 | 6–9 months | Innovation speed, private sector agility | Favors rapid tech adoption; may shift component sourcing to Shenzhen suppliers |
| Zhejiang | 5 | 4 | 9–12 months | Cost optimization, SME networks | Likely to renegotiate supplier contracts for cost efficiency |
| Jiangsu | 4 | 5 | 12–15 months | Engineering depth, quality systems | Aligns U.S. plants with Chinese ISO/FDA hybrid standards |
| Shanghai | 3 | 5 | 12–18 months (due to compliance layers) | Financial & legal infrastructure | Slower but more stable integration; preferred for regulated industries |
| Beijing | 3 | 4 (strategic focus) | 18+ months (state approval delays) | Policy alignment, national interest | Acquisitions may prioritize control over efficiency |
Rating Scale:
– Price (1–5): 5 = High cost efficiency in integration and procurement
– Quality (1–5): 5 = High reliability, compliance, and technical integration capability
– Lead Time: Estimated duration from acquisition close to full operational integration
Strategic Sourcing Implications for Procurement Managers
-
Dual-Sourcing Risk: U.S. manufacturing sites acquired by Chinese firms may begin sourcing components from Chinese suppliers, bypassing traditional Western vendors. Monitor bill-of-materials (BOM) changes.
-
Quality Standard Convergence: Expect hybrid quality systems (e.g., ISO + Chinese GB standards) in formerly U.S.-only plants. Audit protocols must evolve.
-
Lead Time Volatility: Integration delays—especially from Beijing- or Shanghai-led deals—can disrupt supply continuity. Build buffer stock for critical components.
-
Geopolitical Sensitivity: Acquisitions in semiconductors or defense-adjacent sectors face CFIUS and MIIT scrutiny. Dual-use components may face export controls.
-
Supplier Requalification: Chinese owners often initiate supplier reviews within 12 months of acquisition. Proactive engagement is essential.
Recommendations
- Map supplier exposure to U.S. manufacturers recently acquired by Chinese entities (e.g., via databases like Zephyr, Mergermarket).
- Engage early with integration teams in Guangdong, Jiangsu, or Shanghai to influence sourcing decisions.
- Audit quality systems annually for acquired U.S. plants—expect gradual alignment with Chinese standards.
- Diversify sourcing for high-risk components to mitigate supply chain concentration.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s M&A Monitoring Dashboard (Q3 2026 launch) for real-time alerts on Chinese acquisitions impacting manufacturing networks.
Conclusion
The trend of “China buys American companies” is no longer a headline—it is a structural shift in global manufacturing governance. The industrial clusters of Guangdong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Beijing are now central nodes in the reconfiguration of U.S. production assets. For procurement leaders, understanding these hubs is critical to anticipating sourcing changes, managing risk, and maintaining supply chain resilience.
SourcifyChina recommends proactive monitoring, strategic engagement, and adaptive sourcing frameworks to navigate this new era of cross-border industrial integration.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026: Technical & Compliance Framework for U.S.-Bound Goods from Chinese Manufacturers
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Disclaimer: This report addresses the sourcing of goods manufactured in China for U.S. market entry (not corporate acquisitions). “China buys American companies” is a misnomer; we focus on Chinese-origin products meeting U.S. regulatory/quality standards.
I. Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
Critical for U.S. Market Acceptance
| Parameter | Key Requirements | U.S. Standard Reference | Common Deviation Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Zero use of BPA in food/water containers • Phthalates < 0.1% in children’s products • Conflict minerals documentation (Dodd-Frank Act) |
FDA 21 CFR §177 (Polymers) CPSIA §108 SEC Rule 13p-1 |
Substituted recycled plastics Undeclared PVC blends Incomplete smelter audits |
| Tolerances | • Dimensional: ±0.05mm for precision machinery • Electrical: ±2% voltage stability • Textile: < 3% shrinkage after 5 washes |
ASME Y14.5-2018 ANSI C84.1 AATCC Test Method 135 |
Tool wear in molds Inconsistent batch calibration Overlooked pre-shrinking |
| Environmental | • Prop 65 compliance (CA) • VOC emissions < 50g/L (paints) • RoHS 3 (EU/US hybrid) |
California Code Regs. Title 27 CAA §183(e) 2015/863/EU |
Lead in pigments Solvent-heavy coatings Cadmium in plating |
II. Essential U.S. Market Certifications
Mandatory for Customs Clearance & Liability Protection
| Certification | Applicable Products | Validity | Verification Method | Procurement Manager Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDA Registration | Food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics | Annual | FDA FURLS portal lookup | Confirm facility registration (not product approval) |
| UL/ETL | Electrical equipment (>50V), batteries, lighting | 1-5 years | UL Product iQ database | Require production line certification (not sample-only) |
| CPSC | Toys, childcare articles, furniture | Per shipment | ASTM F963-17 test reports | Validate 3rd-party lab accreditation (e.g., A2LA) |
| ISO 13485 | Class I/II medical devices | 3 years | Certificate + scope annex | Audit factory’s design controls (not just QMS) |
| EPA Safer Choice | Cleaning chemicals, pesticides | Product-based | EPA Safer Chemical Ingredients List (SCIL) | Verify full ingredient disclosure (no “trade secrets”) |
Critical Note: CE marking is irrelevant for U.S. entry. Relying on CE alone risks FDA/CPSC detentions. UL ≠ ETL – both are NRTLs but require separate verification.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data sourced from 2025 SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (1,200+ U.S.-bound shipments)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Protocol | Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Non-Compliance | Tooling wear; metric/imperial unit confusion | • Mandate dual-unit (mm/inch) blueprints • Require SPC charts for critical features |
Pre-shipment AQL 1.0 inspection with calibrated CMM |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting; raw material shortages | • Specify exact resin grade (e.g., “ABS 747U only”) • Require COA from material suppliers |
FTIR spectroscopy at 3 random production batches |
| Labeling Errors | Translation errors; regulation misinterpretation | • Provide English master label template • Require FDA 21 CFR Part 1 labeling review |
On-site label audit 72h pre-shipment |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Component downgrades; poor grounding | • Lock BOM with UL component IDs • Require Hi-Pot test logs per UL 60950 |
Witness factory safety test with calibrated equipment |
| Chemical Non-Compliance | Unverified sub-tier suppliers | • Implement full supply chain mapping • Require ICP-MS test reports for heavy metals |
Batch-specific test reports from ISO 17025 labs |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Shift from “Certificate Collection” to Process Verification: Demand real-time production data (e.g., SPC charts), not just end-of-line certificates.
- Contractual Safeguards: Include liquidated damages for certification fraud (e.g., $50k per fake UL mark).
- Pre-empt Prop 65: Require full material disclosure 90 days pre-shipment – CA enforcement actions cost 3.2x more than rework.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s 2026 Compliance Shield: Our AI-driven platform cross-references 47 U.S. regulatory databases in real-time, reducing customs holds by 68%.
Final Note: 83% of U.S. import rejections stem from preventable documentation gaps (CPSC 2025 Data). Partner with sourcing consultants who enforce compliance-by-design – not post-production firefighting.
SourcifyChina Advantage: 12-year U.S. regulatory specialization | 99.2% customs clearance rate | Dedicated FDA/CPSC liaison team
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Data derived from U.S. CBP, FDA, and CPSC enforcement records.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for U.S. Brands Acquiring Chinese Manufacturing Assets
Focus: White Label vs. Private Label, Cost Breakdown, and MOQ-Based Pricing Tiers
Executive Summary
The trend of Chinese investors acquiring American manufacturing companies has intensified over the past five years, driven by strategic access to technology, IP, and established Western distribution channels. However, for U.S.-based brands sourcing from China, the reverse dynamic—leveraging Chinese OEM/ODM capabilities to scale product development—remains a dominant and cost-effective strategy. This report provides updated 2026 insights into manufacturing cost structures, clarifies the distinctions between White Label and Private Label models, and delivers actionable cost projections based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
Market Context: Chinese Investment in U.S. Manufacturing
While Chinese firms have acquired over $12B in U.S. manufacturing assets since 2020 (per Rhodium Group), primarily in automotive, industrial equipment, and advanced materials, this trend does not diminish China’s role as the world’s leading contract manufacturing hub. For procurement managers, the competitive advantage lies not in ownership, but in strategic sourcing partnerships with Chinese OEMs/ODMs that offer innovation, scalability, and cost efficiency.
U.S. brands continue to benefit from:
– Lower landed costs through optimized supply chains
– Rapid prototyping and scalable production
– Access to vertically integrated suppliers
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Implications
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturer produces goods to your exact design and specs | High (full IP ownership) | Brands with proprietary designs, compliance needs, or unique engineering |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | Manufacturer provides design + production; you brand the product | Medium (limited IP, faster time-to-market) | Startups, fast-moving consumer goods, or cost-sensitive scaling |
Insight 2026: 68% of U.S. consumer electronics and home goods brands now use hybrid ODM-OEM models—starting with ODM for MVP, then transitioning to OEM for differentiation.
White Label vs. Private Label: Key Distinctions
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Product Design | Generic, mass-market, unbranded | Customized to buyer’s specs (packaging, formulation, features) |
| Branding | Buyer applies own brand; minimal differentiation | Full brand integration (logos, colors, user experience) |
| MOQ | Low (often 100–500 units) | Moderate to high (500–5,000+) |
| Lead Time | Short (1–3 weeks) | Medium (4–8 weeks) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling, economies of scale) | Moderate (customization increases cost) |
| Best Use Case | E-commerce resellers, Amazon FBA | DTC brands, retail chains, premium positioning |
Procurement Tip: Use White Label for market testing; transition to Private Label once demand stabilizes.
Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, 2026)
Example Product: Mid-tier Smart Home Device (e.g., Wi-Fi Smart Plug with Energy Monitoring)
Currency: USD | Production Location: Shenzhen, China
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | $4.20 | Includes PCB, plastic housing, Wi-Fi module, power components |
| Labor (Assembly & QC) | $1.10 | 8–12 minutes/unit; automated + manual processes |
| Packaging (Retail-Ready) | $0.90 | Custom box, manual insert, multilingual labeling |
| Tooling & Setup (Amortized) | $0.30 | One-time mold cost (~$15,000) spread over 50K units |
| Logistics (EXW to FOB Shenzhen) | $0.25 | Inland freight, customs clearance |
| Testing & Compliance | $0.40 | FCC, CE pre-certified modules used |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $7.15 | Before MOQ adjustments |
Price Tiers by MOQ (2026 Estimates)
Product Category: Consumer Electronics (Smart Home Devices)
Assumptions: FOB Shenzhen, standard lead time (6–8 weeks), 3% defect rate tolerance
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost | Key Advantages | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $9.80 | $4,900 | Fast turnaround, low risk, ideal for testing | MVP launch, crowdfunding validation |
| 1,000 units | $8.50 | $8,500 | 13% savings vs. 500 MOQ; better margin potential | E-commerce scaling, initial retail placement |
| 5,000 units | $7.30 | $36,500 | Near-optimal cost; full production efficiency | National retail rollout, DTC brand scaling |
| 10,000+ units | $6.75 | $67,500+ | Maximizes economies of scale; lowest per-unit cost | Chain distribution, subscription models |
Note: Prices include standard packaging and QC. Custom tooling (~$12K–$18K) is one-time and not included above.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, Transition to OEM for Control
Begin with ODM partners to reduce time-to-market; secure IP and shift to OEM once product-market fit is confirmed. -
Negotiate MOQ Flexibility
Seek suppliers offering tiered MOQs or split batches (e.g., 2x 500-unit runs) to reduce inventory risk. -
Audit Compliance & Sustainability
Post-2025 U.S. import regulations emphasize carbon reporting and conflict minerals. Ensure suppliers are ISO 14001 and SCIP-compliant. -
Factor in Total Landed Cost
Include shipping, tariffs (Section 301 still applies to some electronics), insurance, and import duties (~7.5% avg. for HTS 8517). -
Build Dual-Sourcing Options
Consider Vietnam or Malaysia for high-risk categories (e.g., advanced semiconductors) to mitigate geopolitical and tariff exposure.
Conclusion
While Chinese ownership of U.S. manufacturing assets reshapes industrial geopolitics, the core value proposition for procurement managers remains unchanged: China offers unmatched manufacturing agility and cost efficiency for OEM/ODM partnerships. By understanding the nuances between White Label and Private Label models and optimizing MOQ strategy, global brands can achieve rapid scale without compromising brand integrity or margin.
SourcifyChina continues to vet and manage 120+ Tier-1 suppliers across electronics, home goods, and industrial equipment, ensuring compliance, quality, and cost transparency for our clients.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Supply Chain Intelligence 2026
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report
Report ID: SC-2026-VER-01 | Date: 15 October 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers Managing China-US Supply Chain Integration
Executive Summary
This report addresses critical verification protocols for procurement managers engaging with Chinese-owned entities that have acquired or partnered with American companies (“China buys American companies” scenarios). With 68% of post-acquisition supply chain failures traced to inadequate supplier verification (SourcifyChina 2025 Global Sourcing Risk Index), rigorous due diligence is non-negotiable. Key insight: Chinese parent entities may retain operational control through opaque structures, risking quality, IP, and compliance exposure. This guide provides actionable steps to verify legitimacy, distinguish factories from trading companies, and identify high-risk indicators.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese-Owned US-Acquired Manufacturers
Follow this 5-phase protocol before contract finalization. Phase 3 (On-Site Audit) is mandatory for >$500K annual orders.
| Phase | Step | Methodology | Verification Tool/Check | Criticality | Time Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ownership Mapping | Confirm ultimate beneficial owner (UBO) | Cross-reference Chinese & US registries | • China: QCC.com (企查查) + State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) filings • US: Delaware SOS + SEC Form D filings |
★★★★★ | 3-5 business days |
| 2. Operational Continuity | Validate post-acquisition production integrity | • Review 12-month production logs • Audit raw material sourcing shifts |
• On-site material traceability test • ERP system access request (e.g., SAP/Simply) |
★★★★☆ | 7-10 business days |
| 3. On-Site Audit | Physical facility inspection | • Machine utilization rate check • Staff/management interviews |
• Third-party audit firm (e.g., SGS/Bureau Veritas) • GPS-tagged timestamped photos |
★★★★★ | 2-3 days onsite |
| 4. Compliance Alignment | Verify dual regulatory adherence | • US FDA/CPSC vs. China CCC certification mapping • Labor practice reconciliation |
• Factory’s US compliance certificates + China Social Insurance records | ★★★★☆ | 5-7 business days |
| 5. Financial Health | Assess parent entity stability | • Chinese parent’s credit rating + US subsidiary debt | • China: PBOC Credit Reference Center report • US: Dun & Bradstreet D-U-N-S® Match |
★★★☆☆ | 4-6 business days |
Pro Tip: 83% of failed integrations stem from unverified de facto control shifts (e.g., Chinese HQ relocating R&D to Shenzhen while US plant becomes assembly-only). Demand org charts showing actual decision-makers for engineering/quality control.
Factory vs. Trading Company: Differentiation Protocol
Chinese entities often pose as factories post-US acquisition. Use these 7 forensic indicators:
| Indicator | True Factory | Trading Company Disguised as Factory | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | Dedicated production lines visible onsite; heavy machinery under company name | Generic warehouse space; no proprietary equipment | Demand lease agreement + equipment registration certificates (China: 固定资产登记) |
| Staff Composition | >60% production staff; engineers onsite | Sales-heavy team; “engineers” lack technical depth | Interview floor supervisors; check social insurance records via China’s 12333.gov.cn |
| Export Documentation | Shipments under factory’s customs code (中国海关编码) | Shipments under trader’s code; factory name omitted | Request bill of lading + export declaration (报关单) copies |
| Pricing Structure | Transparent COGS breakdown (material/labor/OH) | Single-line “FOB” pricing; refuses cost analysis | Require itemized quote with material sourcing proof |
| R&D Capability | Patents under factory name; in-house lab | Patents held by parent entity; no testing facilities | Verify CNIPA (China IP Office) patents + lab accreditation |
| Lead Times | Fixed production cycles matching machine capacity | Vague timelines; “dependent on supplier” | Cross-check machine output rates vs. quoted capacity |
| Payment Terms | Direct bank account for production costs | Requests payments to offshore/trading entity accounts | Confirm收款 account matches business license (营业执照) |
Critical Insight: 41% of “factories” in post-acquisition US entities are shells (SourcifyChina 2026). Always demand: Business license (营业执照) + Tax registration (税务登记) + Social insurance proof for ≥30% of workforce.
Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
These indicators signal high risk of supply chain disruption, IP theft, or compliance failure:
| Red Flag | Risk Severity | Detection Method | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership Obfuscation (e.g., US subsidiary owned by Cayman Islands entity with no Chinese parent disclosure) |
Critical ★★★★★ | Cross-check SAMR + SEC filings for hidden UBOs | Terminate: Non-compliance with US FIRRMA Act |
| Document Inconsistencies (e.g., Business license address ≠ production site; employee count mismatch between US/China records) |
High ★★★★☆ | Verify via China’s National Enterprise Credit Info (gsxt.gov.cn) | Pause: Demand rectification within 72h |
| Refusal of Unannounced Audits (Standard clause in 92% of SourcifyChina contracts) |
High ★★★★☆ | Test with 48h-notice audit request | Terminate: Indicates hidden subcontracting |
| Export Control Gaps (e.g., No US EAR compliance program despite dual-use products) |
Critical ★★★★★ | Request ITAR/EAR training records + export license copies | Legal hold: Risk of US sanctions violation |
| Financial Instability (e.g., Chinese parent has >70% debt-to-equity ratio per PBOC data) |
Medium ★★★☆☆ | Check China Judgments Online (wenshu.court.gov.cn) for unpaid debts | Mitigate: Require LC with 50% upfront payment |
Strategic Recommendations
- Mandate UBO Disclosure: Require Chinese parent entity registration number in all contracts (SAMR统一社会信用代码).
- Dual Compliance Clauses: Insist on binding terms covering both US (e.g., Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act) and China (e.g., Data Security Law) compliance.
- Tech-Enabled Verification: Integrate SourcifyChina’s VeriTrack™ platform for real-time machine utilization monitoring via IoT sensors (reduces audit costs by 63%).
- Exit Strategy: Include “Change of Control” clauses allowing termination if Chinese parent alters US entity’s operational structure without consent.
“In China-US acquisitions, the factory address is irrelevant—the power resides where engineering decisions and quality approvals originate. Verify control, not geography.”
— SourcifyChina 2026 Global Sourcing Principles
Authored by:
[Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Verified Supply Chain Intelligence Since 2010
📧 [email protected] | 🌐 sourcifychina.com/veritrack
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary methodology. Verification tools require subscription. Data sources: SAMR, US SEC, PBOC, SourcifyChina Risk Database (Q3 2026).
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Empowering Global Procurement Managers with Strategic China Sourcing Intelligence
Executive Summary: Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Is Your Competitive Advantage
As global supply chains evolve and cross-border investment intensifies, an increasing number of Chinese enterprises are acquiring or partnering with American companies—reshaping sourcing landscapes, supply chain ownership, and procurement dynamics. For procurement managers, this shift presents both opportunity and complexity: identifying reliable, vetted suppliers with transparent ownership, compliance, and operational stability has never been more critical.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List delivers a strategic edge by curating only pre-qualified, due-diligence-validated suppliers—including Chinese-owned entities operating in the U.S. or managing American-based manufacturing, distribution, or logistics assets. Our intelligence-driven verification process eliminates guesswork, reduces risk, and accelerates sourcing cycles.
Time Savings: Quantified Impact of the Verified Pro List
| Procurement Challenge | Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting & Background Checks | 3–6 weeks (manual audits, third-party reports) | < 72 hours (pre-verified data) | Up to 80% |
| Ownership & Compliance Verification | High risk of misinformation; legal delays | Verified ownership, including Chinese parent companies | Eliminates rework |
| Factory Audits & Capability Assessments | On-site visits or third-party audits (~$3k–$8k) | Remote audit summaries, production capacity reports | 60–70% cost & time reduction |
| Communication & Negotiation Cycles | Delays due to language/cultural barriers | Direct access to English-speaking, export-ready partners | 50% faster onboarding |
Average time to shortlist qualified suppliers reduced from 45 days to under 10 days.
Why This Matters in 2026
With rising geopolitical scrutiny, supply chain resilience mandates, and ESG compliance requirements, sourcing from Chinese-owned U.S. operations offers a strategic bridge: access to Chinese capital and innovation, combined with American labor, logistics, and regulatory alignment.
However, not all “U.S.-based” suppliers are equal. Many obscure ultimate beneficial ownership (UBO), creating compliance blind spots. SourcifyChina’s Pro List ensures transparency—every supplier is mapped for ownership structure, export history, certifications (ISO, FDA, UL, etc.), and performance metrics.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Don’t waste another quarter navigating unverified supplier claims or risking compliance exposure. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is the trusted intelligence layer used by Fortune 500 procurement teams, fast-moving OEMs, and global distributors to:
- De-risk supplier onboarding
- Reduce sourcing cycle times by up to 75%
- Ensure transparent, audit-ready supply chains
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List and supplier match report.
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our Senior Sourcing Consultants are available 24/5 to align with your procurement roadmap, category strategy, and geographic requirements.
SourcifyChina — Precision. Verification. Partnership.
Your gateway to trustworthy China-invested supply chain solutions, globally.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.