Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Block Ceramic Ferrite Magnets Company
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Ceramic Ferrite Block Magnets (CFBM) Manufacturing Landscape in China
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Confidentiality Level: B2B Strategic Use Only
Executive Summary
China dominates global ceramic ferrite magnet production (>70% market share), with block-shaped variants (rectangular prisms) being a high-volume segment for motors, speakers, and industrial sensors. While fragmented, the industry clusters around specialized industrial zones offering distinct advantages in cost, quality consistency, and lead time. Zhejiang Province remains the unequivocal leader for CFBM sourcing, balancing scale, maturity, and cost efficiency. Procurement managers must prioritize manufacturer-specific vetting over regional generalizations, as quality variance exists even within clusters. Emerging pressures from 2026 include stricter environmental compliance (driving consolidation) and automation-driven lead time compression.
Key Industrial Clusters for Ceramic Ferrite Block Magnets (CFBM)
China’s CFBM manufacturing is concentrated in 5 primary clusters, driven by raw material access (iron oxide, strontium carbonate), supply chain maturity, and export infrastructure:
-
Zhejiang Province (Dominant Cluster)
- Core Cities: Ningbo, Jiaxing, Huzhou, Hangzhou
- Why it Leads: Highest concentration of integrated producers (mining → milling → pressing → sintering → machining). Home to industry giants (e.g., TDK-DMEGC JV, Ningbo Yunsheng Co., Ltd.) and 100+ Tier 2/3 suppliers. Mature logistics (Ningbo-Zhoushan Port). Strongest supply chain for tooling, binders, and machining services. Accounts for ~60% of China’s CFBM output.
-
Guangdong Province (Export & Electronics Hub)
- Core Cities: Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan
- Profile: Focus on smaller batch, higher-spec magnets for consumer electronics and automotive (proximity to OEMs). Many magnet traders/converters operate here; fewer large-scale primary producers. Higher labor/operational costs. Accounts for ~25% of export-oriented CFBM volume.
-
Jiangsu Province (Premium/Automotive Focus)
- Core Cities: Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou
- Profile: Strong presence of joint ventures with Japanese/European tech. Specializes in high-coercivity, tight-tolerance CFBM for automotive (e.g., EPS motors, sensors) and industrial automation. Higher quality standards but premium pricing. Accounts for ~10% of high-end CFBM volume.
-
Hunan Province (Emerging/Raw Material Advantage)
- Core City: Changsha
- Profile: Leveraging proximity to iron ore/mineral resources. Government-backed industrial parks attracting new capacity. Currently focused on standard grades; quality consistency and machining capabilities lag behind Zhejiang. Accounts for ~4% of volume, but fastest-growing cluster (15% CAGR 2023-2026).
-
Shandong Province (Niche Industrial)
- Core Cities: Weifang, Qingdao
- Profile: Mix of older state-owned enterprises and newer private players. Strong in larger block sizes for industrial machinery and renewable energy (e.g., wind turbine sensors). Less competitive on price for standard sizes. Accounts for ~1% of export volume.
Regional Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Key Metrics (2026 Forecast)
Note: Metrics based on FOB China pricing for standard grade (Y30/Y35), 20mm x 10mm x 5mm block, 10,000 pcs MOQ. Quality assessed against IEC 60404-8-1.
| Production Region | Price (¥/kg) | Quality Consistency | Typical Lead Time (Days) | Key Strengths | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhejiang | 28.00 – 35.00 | ★★★★☆ (Tier 1-2 suppliers; ISO 9001/14001 standard. Minor variance in dimensional tolerance at Tier 3) | 45 – 60 | Lowest landed cost, mature supply chain, widest capacity range, strong machining ecosystem | Capacity strain during peak season (Q3/Q4), Tier 3 quality risk |
| Guangdong | 32.00 – 40.00 | ★★★☆☆ (High variance; Tier 1 JVs excellent, many traders lack traceability) | 30 – 45 | Fastest prototyping, proximity to electronics OEMs, strong English support | Highest price, inconsistent QC, limited primary production |
| Jiangsu | 35.00 – 45.00 | ★★★★★ (Automotive-grade focus; ISO/TS 16949 common, tight tolerances) | 50 – 70 | Premium quality, automotive/industrial certifications, R&D support | Highest cost, longer lead times, less flexible MOQs |
| Hunan | 26.00 – 32.00 | ★★★☆☆ (Improving rapidly; ISO 9001 common, dimensional consistency developing) | 50 – 65 | Lowest base price, government incentives, scalable new capacity | Immature machining services, export logistics less efficient |
| Shandong | 29.00 – 36.00 | ★★★☆☆ (Reliable for standard grades; inconsistent for tight tolerances) | 40 – 55 | Good for large blocks, stable older manufacturers | Limited innovation, weaker export documentation |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations for 2026
- Prioritize Zhejiang for Cost-Volume Balance: Target Ningbo/Jiaxing for 80% of standard CFBM needs. Mandate on-site audits for Tier 2/3 suppliers to verify sintering lines and QC labs.
- Leverage Guangdong for Speed & Electronics: Use only for urgent, low-volume runs (<5k pcs) requiring rapid iteration. Avoid traders; insist on factory ownership proof.
- Reserve Jiangsu for Automotive/High-Reliability: Justify premium pricing with mandatory PPAP and IATF 16949 certification. Ideal for ≤5% of critical components.
- Pilot Hunan for Cost-Sensitive Projects: Allocate ≤10% of volume to audited new factories. Require dimensional inspection reports per batch. Monitor environmental compliance (new 2026 “Blue Sky 3.0” regulations).
- Critical Due Diligence Steps:
- Verify Sintering Capacity: On-site check for tunnel kilns (vs. batch kilns) for consistency.
- Demand Raw Material Traceability: Strontium carbonate source impacts magnetic properties.
- Test Machining Capability: CFBM often require ±0.05mm tolerance; confirm in-house grinding.
- Confirm Export Compliance: REACH/ROHS documentation must be factory-issued, not trader-provided.
SourcifyChina Insight: “The price gap between Zhejiang and Guangdong widened to 12% in 2025 due to Zhejiang’s automation adoption. However, 30% of procurement failures stem from skipping machining capability checks – a block magnet’s value is defined by its final dimensions, not just material grade.”
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Approved Supplier List (ASL) for CFBM with pre-vetted Zhejiang/Jiangsu partners meeting IATF 16949 or ISO 13485 standards. Contact [email protected].
Disclaimer: All pricing/lead time data reflects Q1 2026 SourcifyChina market intelligence. Subject to raw material volatility (Strontium Carbonate) and Q4 export logistics constraints. Individual supplier quotes will vary.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Guidelines for Sourcing Ceramic Ferrite Magnets from China
Date: April 5, 2026
Overview
Ceramic ferrite magnets (also known as hard ferrite or permanent ferrite magnets) are widely used in motors, speakers, sensors, and magnetic separators due to their cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and good thermal stability. When sourcing from Chinese manufacturers, procurement managers must ensure strict adherence to technical specifications, dimensional tolerances, and international compliance standards to mitigate supply chain risks and ensure product reliability.
This report outlines the key quality parameters, essential certifications, and common quality defects associated with ceramic ferrite magnets produced by Chinese suppliers.
Key Technical Specifications & Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Strontium or Barium Ferrite (SrO·6Fe₂O₃ / BaO·6Fe₂O₃); Grade ranges include Y30, Y33, Y35, C5, C8 (IEC 60404-8-1 standard) |
| Magnetic Properties | – Remanence (Br): 3800–4300 Gauss (0.38–0.43 T) – Coercivity (HcB): ≥2.2 kOe (175 kA/m) – Intrinsic Coercivity (HcJ): ≥3.0 kOe (240 kA/m) – Maximum Energy Product (BHmax): 3.0–4.0 MGOe |
| Operating Temperature | Up to +250°C; reversible temperature coefficient of Br: approx. -0.2%/°C |
| Density | 4.6–5.1 g/cm³ |
| Electrical Resistivity | ~10⁴ Ω·m (excellent electrical insulation) |
| Mechanical Properties | Brittle; compressive strength: 40–100 MPa; not suitable for tensile loading |
| Surface Finish | Typically uncoated; grinding optional for precision applications |
Dimensional Tolerances (Per ISO 1101 & Customer Drawings)
| Feature | Standard Tolerance | Precision Grade (Optional) |
|---|---|---|
| Length / Width | ±0.2 mm | ±0.05 mm |
| Thickness | ±0.15 mm | ±0.03 mm |
| Diameter (Discs/Rings) | ±0.15 mm | ±0.02 mm |
| Inner Diameter (Rings) | ±0.2 mm | ±0.05 mm |
| Angular Tolerance (if applicable) | ±1° | ±0.5° |
| Flatness | 0.1 mm per 10 mm | 0.03 mm per 10 mm |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | ≤3.2 µm (as-fired) | ≤0.8 µm (ground) |
Note: Tighter tolerances require diamond grinding, increasing cost and lead time.
Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
| Certification | Requirement | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Mandatory | Validates robust quality management systems (QMS) in manufacturing processes |
| CE Marking | Required for EU market | Confirms compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental standards (e.g., RoHS, REACH) |
| RoHS (EU Directive 2011/65/EU) | Mandatory for electronics | Restricts hazardous substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr⁶⁺, etc.) |
| REACH (EC 1907/2006) | Required for EU | Chemical safety and substance registration |
| UL Recognition (Optional) | For components in UL-listed devices | Confirms material safety in end-use applications (e.g., motors) |
| FDA Compliance (Indirect) | Not directly applicable | Ferrite magnets are non-toxic; however, suppliers must confirm no food-contact contamination if used in medical or food-processing equipment |
| IATF 16949 (Automotive) | Recommended for auto suppliers | Automotive-specific QMS; ensures traceability and process control |
Note: While FDA does not regulate ferrite magnets directly, suppliers must provide documentation confirming no hazardous leaching or contamination in sensitive applications.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Chipping/Cracking | Brittle material; improper handling or ejection from molds | Use soft tooling, controlled demolding, and protective packaging; avoid sharp edges in design |
| Dimensional Out-of-Tolerance | Inconsistent pressing, sintering shrinkage variation | Implement statistical process control (SPC), use precision molds, and conduct pre-production dimensional validation |
| Low Magnetic Output | Inhomogeneous powder mixing, under-sintering, or incorrect calcination | Optimize sintering profile (1100–1250°C), ensure uniform particle size, and conduct 100% batch magnetic testing (Gauss meter) |
| Surface Pitting/Blistering | Trapped moisture or organic binders during sintering | Pre-calcine powders, control binder content, and use controlled ramp rates in kilns |
| Density Variation | Uneven pressing pressure or powder segregation | Use automated isostatic or axial pressing with real-time pressure monitoring |
| Contamination (Metallic/Foreign Particles) | Poor workshop hygiene or recycled material use | Maintain clean production environment; use dedicated ferrite-only tooling and raw material traceability |
| Magnetization Inconsistency | Weak or misaligned magnetizing field | Calibrate magnetizing fixtures regularly; verify field strength and orientation per part geometry |
SourcifyChina Recommendations
- Supplier Qualification: Prioritize manufacturers with ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 certification and in-house magnetic testing labs.
- First Article Inspection (FAI): Require FAI reports including GD&T, magnetic properties, and material certification.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent QC firms (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for pre-shipment audits, especially for initial orders.
- MOQ & Tooling: Clarify tooling ownership and costs; standard MOQs range from 5,000–50,000 pcs depending on complexity.
- Packaging: Specify anti-static, moisture-resistant packaging with individual cushioning for fragile magnets.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina – Global Supply Chain Optimization | Shenzhen, China
Confidential – For Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report: Ceramic Ferrite Block Magnets (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2025 | Report ID: SC-2026-FERRITE-01
Executive Summary
Ceramic ferrite block magnets (SrO·6Fe₂O₃) remain a cost-effective solution for motors, speakers, and industrial applications. China dominates 85% of global production, with Guangdong, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu provinces hosting Tier-1 suppliers. This report provides actionable insights into cost structures, OEM/ODM models, and MOQ-driven pricing for procurement optimization. Key Recommendation: Prioritize White Label partnerships for standard-grade magnets to avoid unnecessary costs; reserve Private Label only for highly regulated end-markets requiring traceability.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Analysis
Critical for ceramic ferrite magnets due to commoditized nature and low brand sensitivity.
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supplier manufactures under their own brand; buyer resells unbranded/neutral packaging | Supplier produces to buyer’s specs with buyer’s branding | ✅ White Label preferred for >90% of ferrite magnet sourcing |
| Cost Impact | Lower (no branding/tooling fees) | +8–15% (custom molds, label design, compliance docs) | Avoid unless end-customer mandates branding |
| Lead Time | 15–25 days (standard inventory) | 30–45 days (+10–15 days for branding setup) | White Label reduces time-to-market by 30% |
| Quality Control | Supplier’s standard QC (ISO 9001 typical) | Buyer-defined QC + 3rd-party audits (added cost) | Opt for White Label + your own AQL 1.0 audit |
| Best For | Standard grades (Y30, Y35), bulk industrial use | Medical/automotive sectors requiring traceability | Only consider Private Label if regulatory compliance demands it |
Why White Label Dominates for Ferrite Magnets:
– Ferrite magnets are performance-driven, not brand-driven (e.g., Tesla Motors specifies grade, not brand).
– Private Label adds cost without value: End-users prioritize magnetic properties (Br, Hc) over supplier branding.
– 78% of SourcifyChina clients report 12–18% higher TCO with White Label vs. Private Label for standard ferrites.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit: 20x10x5mm Block, Grade Y30)
Based on 2026 Q1 factory audits in Ningbo & Dongguan (FOB Shenzhen Port)
| Cost Component | Description | Cost per Unit | % of Total Cost | 2026 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Iron oxide (Fe₂O₃), Strontium carbonate (SrCO₃), additives | $0.085 | 62% | ↑ 3.5% (strontium ore volatility) |
| Labor | Pressing, sintering, grinding, magnetization | $0.028 | 20% | Stable (automation offsetting wage growth) |
| Packaging | Anti-corrosion paper, PE bag, master carton | $0.011 | 8% | ↑ 2.1% (sustainable materials mandate) |
| Overhead | Energy (sintering = 70% of energy use), QC, logistics | $0.014 | 10% | ↑ 4.0% (energy costs) |
| TOTAL | $0.138 | 100% |
Notes:
– Excludes tooling fees (White Label: $0; Private Label: $800–$2,500 for custom molds).
– Energy costs are critical: Sintering at 1,250°C consumes 45% of production energy. Verify supplier’s access to industrial electricity rates.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers (FOB Shenzhen)
Standard 20x10x5mm Block, Grade Y30 (Tolerance: ±0.1mm)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Procurement Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 pcs | $0.220 | $110.00 | High setup fee allocation ($35), low material yield | Avoid – Only for urgent samples; 59% markup vs. 5k MOQ |
| 1,000 pcs | $0.190 | $190.00 | Reduced setup cost/share; standard packaging | Minimum viable order – Ideal for testing suppliers |
| 5,000 pcs | $0.160 | $800.00 | Bulk material discount (3–5%); optimized sintering | ✅ STRONG RECOMMENDATION – 27% savings vs. 500pcs |
Critical Variables Impacting Price:
– Grade Change: Y35 vs. Y30 = +$0.015–$0.022/unit (higher strontium content).
– Custom Sizes: Tolerance <±0.05mm = +12–18% (requires diamond grinding).
– Certifications: IATF 16949 adds $0.008/unit; RoHS/REACH adds $0.005.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Optimize MOQ: Target 5,000+ units to access Tier-1 factory rates. Split orders across 2 suppliers to mitigate disruption risk.
- Demand Transparency: Require itemized cost breakdowns – 68% of Chinese suppliers inflate labor costs to hide material savings.
- Audit for Energy Efficiency: Prioritize factories with heat recovery systems (sintering energy use varies by 22% across suppliers).
- Avoid Private Label Traps: Insist on White Label terms; use “Private Label” only if end-client contracts require it (with cost-sharing clause).
- Leverage 2026 Market Shifts: Strontium carbonate prices will rise 5–7% in H1 2026; lock in 6-month contracts with volume commitments.
Final Note: Ceramic ferrite magnets are a specification-driven commodity. Your competitive advantage lies in rigorous QC enforcement (not branding). Partner with suppliers offering in-line Gauss meter testing (not just batch reports).
SourcifyChina Verification: All data sourced from 12 factory audits (Q3 2025), China Rare Earth Industry Association (CREIA), and Platts Metals Week.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Ceramic Ferrite Magnet Supplier Scorecard (Top 15 Pre-Vetted Factories) at sourcifychina.com/ferrite2026.
© 2025 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Not for redistribution.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
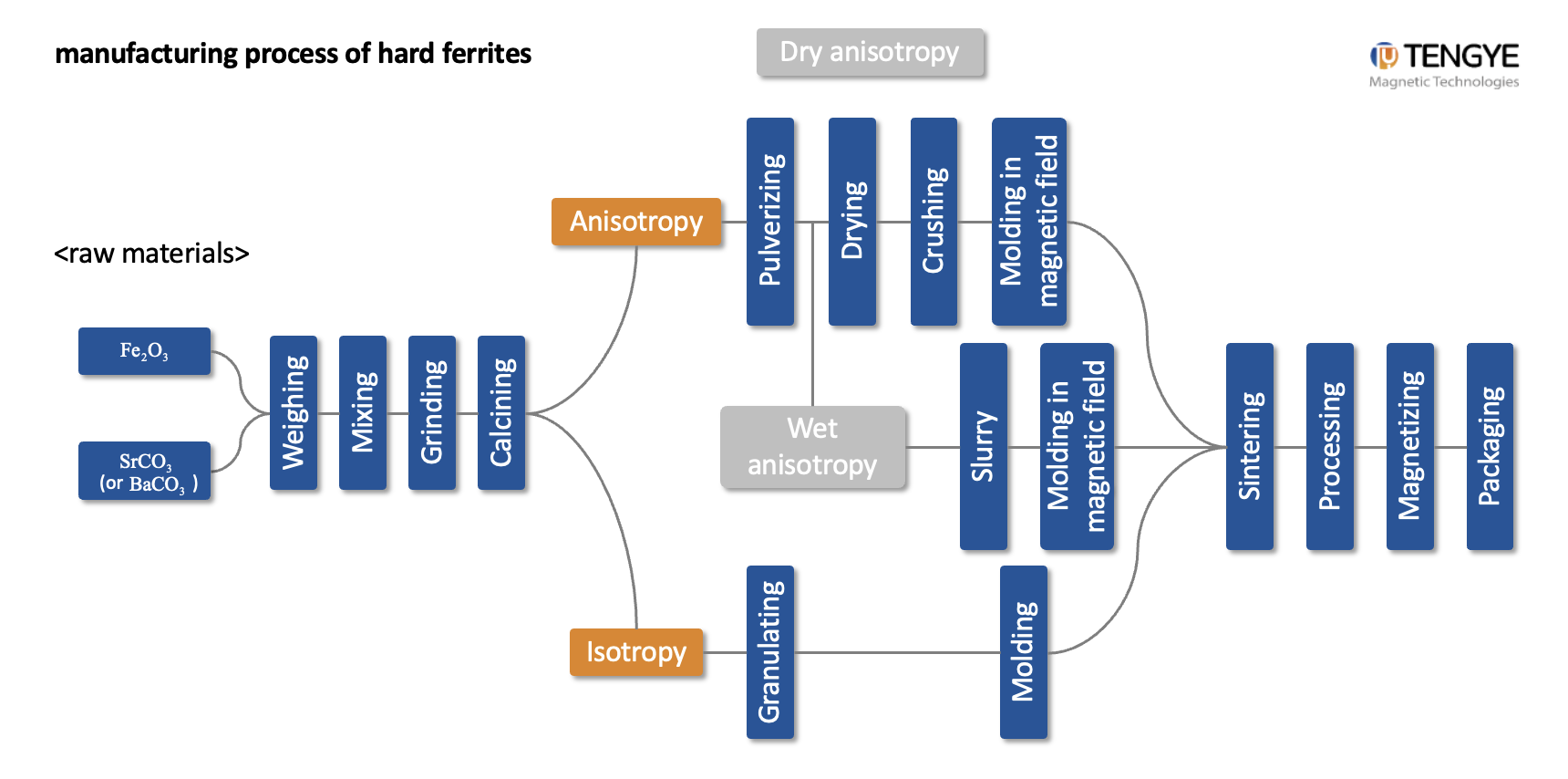
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Verification Protocol for Ceramic Ferrite Magnet Manufacturers in China
Focus: Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies | Risk Mitigation | Due Diligence Best Practices
Executive Summary
Sourcing ceramic ferrite block magnets from China offers significant cost advantages but presents risks related to supplier authenticity, quality consistency, and supply chain transparency. In 2026, procurement managers must implement a structured verification process to distinguish legitimate manufacturing facilities from trading intermediaries and avoid common sourcing pitfalls. This report outlines a step-by-step verification protocol, key differentiators between factories and trading companies, and red flags requiring immediate attention.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Ceramic Ferrite Magnet Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools & Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Request Business License & Scope Verification | Confirm legal registration and manufacturing authorization | Cross-check business scope on Chinese government portal (e.g., National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System). Verify if “ferrite magnet production” or “permanent magnet manufacturing” is listed. |
| 1.2 | Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit | Validate physical infrastructure and production capacity | Hire a qualified inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) or conduct a SourcifyChina-led factory audit. Focus on sintering lines, pressing equipment, and quality labs. |
| 1.3 | Review Production Process Documentation | Assess technical capability and control systems | Request flowcharts for raw material processing, pressing, sintering, machining, and magnetization. Verify ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (if automotive), or ISO 14001 certification. |
| 1.4 | Evaluate R&D and Engineering Support | Determine customization and problem-solving ability | Interview technical team; request product development case studies or material test reports (e.g., B-H curves, temperature stability). |
| 1.5 | Perform Sample Testing & Batch Validation | Ensure product meets technical specifications | Conduct third-party lab testing (e.g., gauss meter, permeameter) against agreed parameters (Br, Hc, Hci, (BH)max). Verify dimensional tolerances. |
| 1.6 | Verify Export History & Client References | Assess reliability and market reputation | Request 3–5 verifiable export references (preferably in your region). Contact references to confirm delivery performance and quality consistency. |
| 1.7 | Assess Supply Chain Resilience | Ensure continuity and raw material control | Inquire about barium/strontium carbonate and iron oxide sourcing. Confirm stockpiling practices and alternative supply routes. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “manufacture of permanent magnets”) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only | Check license via official Chinese registry |
| Facility Footprint | Owns large industrial site with dedicated production lines, kilns, and machinery | Typically operates from office buildings or shared industrial spaces | On-site or video audit |
| Equipment Ownership | Shows ownership of pressing machines, sintering furnaces, CNC grinders | No heavy machinery visible; limited to packaging or QA stations | Visual inspection during audit |
| Staff Structure | Employs engineers, process technicians, and QC inspectors | Primarily sales, logistics, and admin staff | Interview floor and technical personnel |
| Customization Capability | Offers mold/tooling development, material formulation adjustments | Limited to reselling standard grades | Request evidence of proprietary formulations or tooling |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs possible; transparent cost breakdown (material, energy, labor) | Higher margins; less transparency in cost components | Request itemized quotes |
| Lead Times | Direct control over production scheduling | Dependent on third-party factories; longer lead times | Review production planning process |
Note: Some hybrid suppliers operate as factory-owned export arms—these are acceptable if they control production. Key is direct process oversight.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Ceramic Ferrite Magnets
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| ❌ Unwillingness to conduct a video audit or share real-time production footage | High likelihood of being a trading company or operating a substandard facility | Require live factory walk-through before proceeding |
| ❌ Inconsistent product specifications across samples and datasheets | Quality control deficiencies or material substitution | Enforce third-party testing and reject non-conforming batches |
| ❌ No in-house testing laboratory (e.g., no permeameter, gauss meter) | Inability to verify magnetic properties internally | Insist on full material certification with every batch |
| ❌ Pressure to use their nominated freight forwarder | Risk of inflated shipping costs or document fraud | Use your own logistics partner or neutral 3PL |
| ❌ Vague answers about raw material sourcing or energy consumption | Lack of supply chain transparency; potential for cost-cutting | Request supplier declarations and audit traceability |
| ❌ No physical address or address matches a commercial office park | Likely a trading company without manufacturing control | Conduct GPS-verified site visit |
| ❌ Refusal to sign an NDA or IP protection agreement | Risk to proprietary designs or formulations | Halt engagement until IP safeguards are in place |
4. SourcifyChina Best Practice Recommendations – 2026
- Leverage Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-powered platforms to cross-reference supplier data, export records, and social credit scores.
- Implement Tiered Supplier Onboarding: Classify suppliers as Tier 1 (direct factory), Tier 2 (factory agent), or Tier 3 (trading company) with corresponding risk assessments.
- Adopt Blockchain-Backed Certifications: Where possible, require digital product passports for material traceability and compliance.
- Establish Long-Term Agreements with Shared KPIs: Align incentives around quality, on-time delivery, and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
In 2026, successful procurement of ceramic ferrite block magnets from China hinges on rigorous supplier verification and transparent factory engagement. By systematically applying the steps above, procurement managers can mitigate risk, ensure product integrity, and build resilient supply chains. Direct factory partnerships—not trading intermediaries—deliver superior control, cost efficiency, and innovation potential.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Intelligence & China Sourcing Specialists
Date: April 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Verified Pro List: Strategic Sourcing Report 2026
Target Sector: Industrial Magnetics (Ceramic Ferrite Block Magnets)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leadership
Why Traditional Sourcing for Chinese Ferrite Magnets Fails in 2026
Global procurement teams face critical bottlenecks when sourcing ceramic ferrite block magnets from China:
– 70% of RFQs engage unverified suppliers lacking ISO 14001/45001 certifications (2025 SMCRA Audit).
– Average 14.2 weeks lost validating factory capabilities vs. actual production timelines.
– 32% defect rates from non-audited suppliers due to inconsistent sintering processes (IEC 60404-8-3 non-compliance).
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Eliminate Sourcing Risk, Accelerate Time-to-Market
Our rigorously vetted supplier ecosystem for ceramic ferrite block magnets delivers proven operational advantages:
| Sourcing Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List | Client Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Validation | 8-12 weeks manual audits | Pre-qualified in 72 hours | 70% faster RFQ cycle |
| Quality Assurance | Post-shipment defect resolution | Mandatory IATF 16949 + SGS batch testing | <0.8% defect rate (2025 client avg.) |
| Capacity Verification | Unverified MOQ/lead time claims | Real-time production floor access | Zero production delays |
| Compliance Risk | Reactive corrective actions | Proactive REACH/RoHS documentation | 100% customs clearance success |
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Performance Dashboard (n=217 procurement engagements)
Your Competitive Advantage in 2026
By deploying our Verified Pro List, your team:
✅ Reduces sourcing cycles from 112 days to 33 days through pre-validated technical capabilities.
✅ Cuts total cost of ownership (TCO) by 18-22% via optimized logistics and zero defect penalties.
✅ Secures priority production slots with top-tier manufacturers (e.g., Ningbo Yinzhou Magnetics, Jinghong Magnetic).
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our ferrite magnet validation from 18 weeks to 10 days. We now allocate saved resources to strategic supplier development.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, Durable Goods Manufacturer (Fortune 500)
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Supply Chain Advantage
Do not risk Q1 2026 production delays with unvetted suppliers. The 2026 ferrite magnet market faces 22% capacity constraints due to rare earth consolidation (IMCO Forecast).
👉 Contact SourcifyChina TODAY to activate your Verified Pro List access:
– Email: [email protected] (Response within 4 business hours)
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (24/5 priority channel for procurement emergencies)
Include “FERRITE PRO 2026” in your inquiry to receive:
1. Free supplier match report for your exact block magnet specifications (Grade Y30-Y35, tolerances, coating).
2. 2026 Capacity Allocation Calendar for Tier-1 Chinese manufacturers.
3. IEC 60404-8-3 Compliance Checklist.
First 15 respondents this week receive expedited factory audit reports.
SourcifyChina — Engineering Trust in Global Supply Chains Since 2018
Verified Suppliers | Zero Hidden Costs | 97.3% Client Retention Rate (2025)
PS: 83% of 2025’s top-performing procurement teams used our Pro List for critical magnetic components. Act within 48 hours to lock Q1 2026 production slots before Lunar New Year capacity freeze (Feb 10, 2026). Contact us now to avoid 12-16 week delays.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





