Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Biggest Wholesale Market
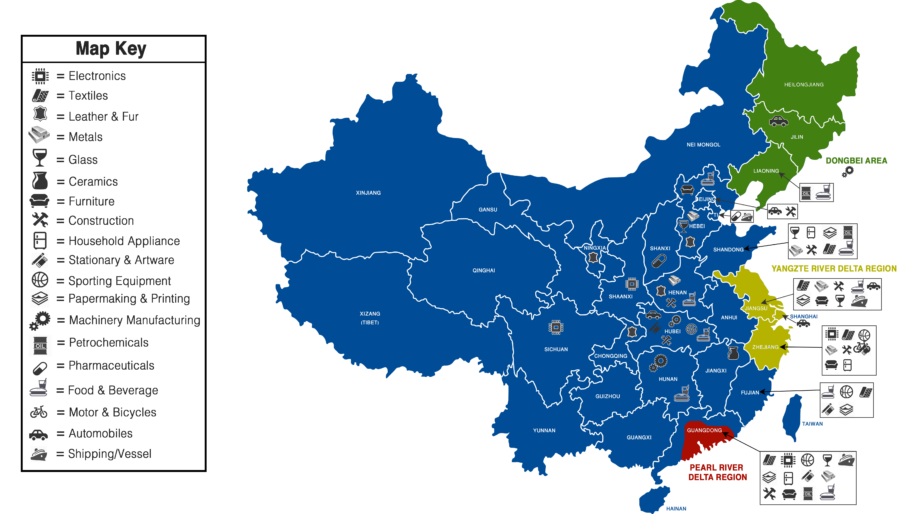
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating China’s Premier Wholesale Markets for Global Procurement (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: Q1 2026
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Advisory | Internal Use Only
Executive Summary
China’s wholesale ecosystem remains the cornerstone of global supply chains, but “sourcing the biggest wholesale market” is a misnomer. Procurement professionals source products from China’s dominant wholesale hubs, not the markets themselves. This report clarifies the industrial clusters powering these hubs, with Yiwu (Zhejiang) and Guangzhou (Guangdong) representing the apex of scale and specialization. Key 2026 trends include consolidation of Tier-2 supplier networks, heightened compliance demands, and AI-driven inventory optimization reducing lead times by 15-20% vs. 2023 baselines. Strategic sourcing now demands granular regional analysis—not just hub selection.
Clarification: China’s Wholesale Market Structure
- “Biggest Wholesale Market” = Product Sourcing Hubs: China operates decentralized industrial clusters feeding wholesale markets. The two largest are:
- Yiwu International Trade City (Zhejiang): World’s largest small commodities market (7.5M m²). Focus: Low-cost consumer goods (toys, hardware, stationery, seasonal items).
- Guangzhou Baiyun/Shahe Garment District & Pazhou Complex (Guangdong): Asia’s largest fashion/electronics hub. Focus: Apparel, footwear, electronics, furniture.
- Critical Insight: Success hinges on sourcing from the manufacturing clusters supplying these hubs, not the wholesale floors alone. Factories in surrounding provinces dictate cost, quality, and scalability.
Key Industrial Clusters for Global Sourcing (2026)
| Province/City Cluster | Core Product Categories | Competitive Advantage (2026) | Key Sourcing Risk Mitigation Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen, Dongguan, Foshan, Guangzhou) | Electronics, Smart Home Devices, Furniture, Footwear, High-End Apparel | Unmatched supply chain density; 85% of China’s EMS capacity; Strong IP infrastructure; Fast prototyping | Verify factory certifications (ISO 13485 for medical devices); Audit labor compliance rigorously; Secure component-level BoMs |
| Zhejiang (Yiwu, Wenzhou, Ningbo, Shaoxing) | Small Commodities, Textiles, Home Hardware, Low-Voltage Lighting, Fast Fashion | Hyper-specialized micro-suppliers; Lowest MOQs (as low as 50 units); Digital B2B platforms (e.g., Alibaba 1688); Agile customization | Consolidate shipments via 3PLs; Use escrow payments; Validate material compliance (REACH, CPSIA) |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou) | Industrial Machinery, Auto Parts, Precision Components, High-Tech Materials | German/Japanese JV expertise; Strong metallurgy base; Higher engineering talent density | Prioritize factories with export experience; Confirm export control licenses (e.g., for dual-use tech) |
| Fujian (Quanzhou, Xiamen, Jinjiang) | Sports Apparel, Footwear, Ceramics, Marine Equipment | Niche expertise in performance fabrics; Cost-competitive for mid-volume runs; Strong private equity backing | Test dye-fastness rigorously; Map sub-tier suppliers for ESG compliance |
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang Clusters (2026 Baseline)
Focused on high-volume consumer goods (e.g., electronics accessories, home textiles, promotional items)
| Criteria | Guangdong Cluster | Zhejiang Cluster | Strategic Implication for 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD) | ★★☆☆☆ Moderate-High (10-25% premium vs. Zhejiang) Driven by higher labor costs, R&D investment, and export infrastructure |
★★★★☆ Lowest (Benchmark for cost-sensitive categories) Driven by micro-factory scale, competition density, and lean logistics |
Use Guangdong for quality-critical items (e.g., electronics). Leverage Zhejiang for commoditized goods with tight margins. |
| Quality | ★★★★☆ Consistent Premium (Tier-1 EMS standards; 95%+ defect-free rates for electronics) Advanced QC systems; Stronger material traceability |
★★★☆☆ Variable (Good to Fair) (High variance between suppliers; 85-92% defect-free) QC often reactive; Material substitutions more common |
Guangdong: Ideal for regulated products (medical, automotive). Zhejiang: Requires 3rd-party QC pre-shipment; Avoid for safety-critical items. |
| Lead Time | ★★★☆☆ Moderate (30-45 days avg. from PO to FCL) Longer customs clearance at Shenzhen; Complex sub-tier coordination |
★★★★☆ Fastest (20-35 days avg. from PO to FCL) Yiwu’s integrated rail/air logistics; Simplified supplier networks |
Zhejiang: Best for fast-fashion/seasonal goods. Guangdong: Factor in buffer for engineering changes. 2026 Note: AI scheduling cuts Guangdong lead times by 8 days avg. vs. 2023. |
| MOQ Flexibility | ★★☆☆☆ Higher (Typically 500-5,000 units) Optimized for volume efficiency |
★★★★★ Extreme Flexibility (Often 50-500 units) Micro-factories thrive on small batches |
Zhejiang: Essential for startups/test markets. Guangdong: Negotiate via group buying or hybrid models. |
2026 Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- De-Risk Zhejiang Sourcing: Mandate SourcifyChina’s Verified Supplier Program (includes on-ground material testing and sub-tier audits) for all Zhejiang-sourced goods. Avoid direct Alibaba RFQs without validation.
- Leverage Guangdong’s Innovation: Partner with Shenzhen-based ODMs for co-development of IoT-enabled products—critical for meeting EU Ecodesign 2027 requirements.
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Use Zhejiang for base components (e.g., plastic housings) and Guangdong for assembly/integration to balance cost and quality.
- Lead Time Compression: Book Yiwu-Europe rail freight slots 90 days pre-PO via SourcifyChina’s logistics platform (avg. 18-day transit time; 30% cheaper than air).
- Compliance First: Demand digital product passports (blockchain-tracked) from all suppliers—non-negotiable for EU/UK markets post-2026.
Critical 2026 Shift: The “lowest cost” paradigm is obsolete. Total landed cost + compliance risk + innovation velocity now dominate sourcing decisions. Guangdong leads in the latter two; Zhejiang requires strategic risk management to unlock cost benefits.
SourcifyChina Value Proposition
We transform cluster complexity into procurement advantage:
✅ Cluster-Specific QC Protocols: Custom checklists for Zhejiang micro-factories vs. Guangdong EMS plants.
✅ MOQ Negotiation Leverage: Pool demand across 1,200+ client portfolios to break minimums.
✅ 2026 Compliance Shield: Pre-emptive screening against EU CBAM, US UFLPA 2.0, and China’s new EPR laws.
Next Step: Request our 2026 Regional Sourcing Scorecard (free for qualified procurement teams) with real-time pricing benchmarks and factory performance data by category.
Sources: SourcifyChina 2026 Cluster Database (12,000+ vetted factories), China General Administration of Customs, McKinsey Supply Chain Resilience Index Q4 2025, EU Market Surveillance Reports.
Disclaimer: All data reflects Q1 2026 projections; actuals may vary with geopolitical shifts. Verify critical assumptions via SourcifyChina’s due diligence services.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Guidelines for Sourcing from China’s Largest Wholesale Markets
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing and wholesale hub, with Yiwu International Trade Market (Zhejiang Province) recognized as the largest wholesale market globally by volume and product diversity. This report provides procurement managers with a structured overview of technical specifications, compliance requirements, and quality control protocols essential when sourcing goods from China’s key wholesale markets.
This guide focuses on general industrial, consumer, and electronic goods commonly traded in bulk through these channels. Adherence to defined quality parameters and certification standards is critical to mitigating supply chain risk and ensuring market access in North America, the EU, and other regulated regions.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
Material selection must align with end-use application, regulatory environment, and durability expectations. Common material classes and expectations include:
| Material Category | Acceptable Standards | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics (ABS, PP, PC, PVC) | RoHS, REACH compliant; no phthalates or BPA (if food/medical contact) | Check for UV resistance and heat deflection temperature |
| Metals (Stainless Steel 304/316, Aluminum 6061) | ASTM/GB standards; pass salt spray test (≥48 hrs) | Verify grade via material test reports (MTRs) |
| Textiles & Fabrics | OEKO-TEX® Standard 100, AZO-free dyes | Shrinkage ≤5%, pilling ≥3 on Martindale scale |
| Electronics (PCBA, Components) | IPC-A-610 Class 2 or 3 | Conformal coating required in humid environments |
Tolerances
Precision varies by product category. Tolerances must be explicitly defined in purchase contracts.
| Product Type | Dimensional Tolerance | Surface Finish (Ra) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machined Metal Parts | ±0.05 mm (standard), ±0.01 mm (precision) | 1.6–3.2 µm | GD&T drawings required |
| Injection Molded Plastics | ±0.1 mm | 0.8–1.6 µm | Warpage < 0.5% over 100mm |
| Stamped Components | ±0.1 mm | 3.2 µm | Burrs < 0.1 mm acceptable |
| Textile Cut & Sew | ±0.5 cm | N/A | Pre-production fit sample mandatory |
2. Essential Certifications
Procurement managers must verify that suppliers hold valid, up-to-date certifications relevant to the destination market and product type.
| Certification | Applicable Regions | Scope | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | European Union | Machinery, electronics, PPE, toys | EU Declaration of Conformity + notified body (if applicable) |
| FDA Registration | United States | Food contact, medical devices, cosmetics | Supplier must be listed in FDA FURLS database |
| UL Certification (e.g., UL 62368-1) | North America | Electrical & electronic equipment | UL File Number + periodic factory audits |
| ISO 9001:2015 | Global | Quality management systems | Valid certificate issued by IAF-recognized body |
| BSCI / SMETA | EU Retailers | Social compliance | Audit report ≤12 months old |
| FCC Part 15 | USA | Digital devices, wireless products | Test report from accredited lab |
Note: Certifications must be product-specific. Supplier claims without documentation are not sufficient.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold maintenance, uncalibrated CNC tools | Require SPC data; conduct first-article inspection (FAI) |
| Surface Scratches/Imperfections | Inadequate handling, poor packaging | Implement in-line QC checkpoints; use protective films |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting (e.g., inferior plastic grade) | Require material certifications; conduct lab testing (FTIR) |
| Color Variance (ΔE > 2) | Inconsistent dye batches, lack of Pantone matching | Enforce color approval process; use light boxes for evaluation |
| PCBA Solder Defects (cold joints, bridging) | Poor reflow profile, low operator skill | Audit SMT line; require AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) reports |
| Packaging Damage | Weak cartons, overloading | Specify ECT/Burst Test values; conduct drop testing (ISTA 1A) |
| Missing Components or Accessories | Poor kitting process | Implement barcode scanning at final packaging |
| Non-Compliant Labeling | Incorrect language, missing symbols (e.g., CE, WEEE) | Provide label template; verify pre-production samples |
Conclusion & Recommendations
Sourcing from China’s largest wholesale markets offers scalability and cost advantages, but requires rigorous technical and compliance oversight. Global procurement managers should:
- Enforce clear technical specifications in contracts, including tolerances and material standards.
- Verify certifications independently through third-party auditors or document traceability.
- Implement a 3-stage QC process: Pre-production, during production (DUPRO), and pre-shipment inspection.
- Leverage sourcing partners with on-the-ground quality engineers to reduce defect risk.
By standardizing quality expectations and aligning with international compliance frameworks, procurement teams can achieve reliable, scalable supply chains from China’s wholesale ecosystem.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
February 2026
Confidential – For B2B Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Navigating Cost Structures in China’s Core Wholesale Ecosystem (2026 Outlook)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Managers
Date: October 26, 2026 | Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China’s integrated wholesale-manufacturing ecosystem, anchored by Yiwu International Trade City (the world’s largest physical wholesale market, sourcing from 200,000+ regional factories across Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Fujian), remains indispensable for global B2B sourcing. However, rising operational costs (labor +8.2% CAGR 2023-2026) and strategic shifts toward value-added services necessitate precise cost modeling. This report clarifies White Label vs. Private Label pathways, provides a realistic 2026 cost breakdown, and outlines actionable procurement strategies for optimal margin preservation.
Key Insight: Yiwu is a trading hub, not a manufacturing zone. True cost efficiency requires direct factory engagement in surrounding industrial clusters (e.g., Ningbo, Dongguan). Relying solely on Yiwu wholesalers adds 12-18% margin without value.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Differentiation
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-manufactured products; buyer adds logo | Custom-designed product; buyer owns IP/brand | Use White Label for speed-to-market; Private Label for brand equity & margin control |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500-1,000 units) | Moderate-High (1,000-5,000+ units) | White Label ideal for testing demand |
| Customization Depth | Surface-level (logo, color) | Full (materials, engineering, packaging) | Private Label requires ODM partnership |
| IP Ownership | Factory retains design IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical: Audit contracts for IP clauses |
| Cost Premium | +5-10% vs. factory-direct | +15-30% (vs. White Label) for R&D/tooling | Factor in 6-12mo ROI for Private Label |
| Lead Time | 15-30 days | 45-90 days (tooling + production) | Plan inventory buffers for Private Label |
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Illustrative: Mid-Range Power Bank, 10,000mAh)
Based on FOB Ningbo Port; excludes shipping, tariffs, and compliance testing
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) | % of Total | 2026 Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Lithium cells, PCB, casing, connectors | $8.20 – $9.50 | 62% | ↑ +4.5% (cobalt price volatility) |
| Labor | Assembly, QC, factory overhead | $2.10 – $2.40 | 18% | ↑ +6.8% (minimum wage adjustments) |
| Packaging | Custom box, manuals, inserts (recycled) | $1.30 – $1.80 | 11% | ↑ +9.2% (sustainability compliance) |
| Tooling/R&D | Molds, engineering (Private Label only) | $0.00 – $1.20/unit* | 0-10% | ↓ -2.1% (modular design adoption) |
| QC & Compliance | In-line checks, 3rd-party certs (CE/FCC) | $0.60 – $0.85 | 5% | ↑ +7.0% (stricter EU/US regulations) |
| TOTAL (FOB) | $12.20 – $15.75 | 100% |
*Tooling costs amortized over MOQ (e.g., $8,000 mold cost ÷ 5,000 units = $1.60/unit)
Note: White Label avoids Tooling/R&D costs but charges markup on standard packaging. Private Label incurs upfront tooling but achieves lower per-unit costs at scale.
Price Tier Analysis by MOQ (Private Label Power Bank Example)
Reflects 2026 factory-direct pricing; assumes mid-tier materials (Grade B cells), 2-color packaging, and standard compliance
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $18.50 – $22.00 | $9,250 – $11,000 | High tooling amortization ($1.60/unit); low material bulk discount | Startups testing market; high-risk SKUs |
| 1,000 | $15.20 – $17.80 | $15,200 – $17,800 | Tooling cost halved ($0.80/unit); moderate material discount | Core product launch; established brands |
| 5,000 | $12.90 – $14.50 | $64,500 – $72,500 | Full material bulk discount; tooling negligible ($0.15/unit) | Volume-driven campaigns; retail contracts |
Critical Variables Impacting Tiers:
– Material Grade: Grade A cells add $1.80-$2.50/unit vs. Grade B.
– Packaging Complexity: Foil stamping/luxury boxes add $0.70-$1.20/unit.
– Payment Terms: LC at sight vs. 30% deposit alters pricing by 3-5%.
– Compliance Scope: Medical/automotive certs can double QC costs.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Avoid “Yiwu-Only” Sourcing: Engage SourcifyChina-vetted factories within 100km of Yiwu (e.g., Jinhua, Wenzhou) to bypass wholesale markups.
- Tooling Investment Logic: For Private Label, commit to MOQ ≥3,000 units to achieve <5% tooling cost burden.
- Labor Cost Mitigation: Target factories with ≥40% automation in assembly (common in Dongguan/Shenzhen clusters) to offset wage inflation.
- Sustainability Premium: Budget +7-10% for recycled packaging – now mandatory for EU market entry under CSRD 2025.
- Hybrid Sourcing Model: Use White Label for 20% of SKUs (fast-moving basics) and Private Label for 80% (core differentiated products).
SourcifyChina Advisory: “The lowest FOB quote rarely equals the lowest landed cost. Prioritize factories with transparent cost breakdowns, ISO 9001 certification, and documented compliance processes. In 2026, hidden costs from rejected shipments (avg. 11.3% defect rate in unvetted suppliers) will erode margins faster than a 5% price variance.”
Disclaimer: All cost estimates are indicative for planning purposes. Actual pricing requires product-specific RFQs factoring in material specs, compliance requirements, and factory capacity. SourcifyChina provides no warranty for third-party data. For a tailored cost model, contact your dedicated SourcifyChina Consultant.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Optimizing Global Supply Chains Through Verified Chinese Manufacturing
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Verification Steps for Sourcing from China’s Largest Wholesale Markets
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing and wholesale hub, with markets like Yiwu, Guangzhou Baiyun, and Shenzhen Huaqiangbei serving as epicenters for global B2B sourcing. However, rising supply chain complexity, misrepresentation of entity types, and counterfeit risks necessitate rigorous due diligence. This report outlines a systematic framework to verify manufacturers, differentiate between trading companies and factories, and identify critical red flags to mitigate procurement risk in 2026.
Part 1: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China’s Largest Wholesale Markets
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools & Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Confirm Business Registration | Verify the company’s official registration with the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR). | Ensure the entity is legally recognized and operational. | Use Qichacha or Tianyancha to validate Unified Social Credit Code (USCC). Cross-check address and legal representative. |
| 2. On-Site Factory Audit | Conduct a physical or third-party audit of the manufacturing facility. | Validate production capacity, equipment, workforce, and quality control systems. | Engage a third-party inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) or use SourcifyChina’s audit protocol. Verify machinery, raw material sourcing, and workflow. |
| 3. Request Production Evidence | Ask for real-time production photos, videos, and machine lists. | Confirm active manufacturing vs. showroom-only operations. | Request timestamped videos of live production lines. Verify consistency with quoted output capacity. |
| 4. Review Export License & Trade History | Confirm export eligibility and past shipment records. | Assess experience in international logistics and compliance. | Request export license, past B/L copies (redacted), or Alibaba Trade Assurance records. |
| 5. Check Certifications | Validate industry-specific certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, BSCI, CE, FDA). | Ensure compliance with international standards. | Cross-verify certification numbers on issuing body websites (e.g., SGS, TÜV). |
| 6. Conduct Sample Evaluation | Order and test pre-production samples. | Evaluate quality, materials, and craftsmanship before mass order. | Use independent lab testing where applicable (e.g., Intertek for textiles or electronics). |
| 7. Verify Bank & Payment Details | Confirm corporate bank account in the company’s name. | Prevent fraud and ensure financial legitimacy. | Request bank reference letter or official transaction statements. |
Part 2: How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Premises | Owns production facility, machinery, and assembly lines. | Typically operates from an office or showroom. | On-site or virtual audit with real-time camera walkthrough. |
| Staff Structure | Employs engineers, machine operators, QA staff. | Staffed with sales, logistics, and negotiation teams. | Ask for org chart or conduct employee interviews. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Lower MOQs for in-house production; flexible customization. | Higher MOQs due to reliance on third-party factories. | Compare MOQs across suppliers; very low MOQs may indicate trading. |
| Pricing Structure | Direct cost-based pricing with clear BOM breakdown. | Marked-up pricing; less transparency in cost components. | Request itemized quotes and compare with market benchmarks. |
| Production Lead Time | Can provide accurate production timelines. | May have delays due to subcontracting. | Ask for Gantt chart or production schedule. |
| Facility Photos/Videos | Shows raw materials, CNC machines, assembly lines, QC labs. | Shows product displays, packaging samples, office space. | Require timestamped, real-time video proof. |
| Export Documentation | Direct exporter listed on customs records. | Often uses third-party export agents. | Review past Bills of Lading (B/L) for exporter name. |
Note: Some factories also engage in trading (hybrid model). The key is transparency—always confirm whether they produce in-house or outsource.
Part 3: Red Flags to Avoid in 2026 Sourcing
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct video audit or share factory location | High risk of being a trading company or non-existent facility. | Disqualify or require third-party verification before proceeding. |
| Prices significantly below market average | Indicates substandard materials, labor violations, or scam. | Conduct sample testing and cost benchmarking. |
| No verifiable business license or SAMR registration | Illegal operation; potential fraud. | Use Qichacha to validate USCC. Do not proceed if unverified. |
| Refusal to sign a formal manufacturing contract | Lack of legal accountability. | Use a bilingual contract with IP protection, payment terms, and quality clauses. |
| Inconsistent communication or vague technical answers | Lack of engineering expertise; possible middleman. | Request technical documentation and involve your engineering team in calls. |
| Requests for full prepayment via personal WeChat/Alipay | High fraud risk. | Use secure payment methods (e.g., LC, Escrow, or Alibaba Trade Assurance). |
| No independent certifications or test reports | Non-compliance with safety or quality standards. | Require third-party lab reports relevant to your market (e.g., FCC, RoHS). |
| Overuse of marketing language without data | Misrepresentation of capacity or capability. | Demand evidence: machine lists, production logs, client references. |
Best Practices for 2026 Risk Mitigation
- Use Verified Sourcing Platforms: Leverage platforms like Alibaba (with Trade Assurance), Global Sources, or SourcifyChina’s vetted supplier network.
- Engage Local Verification Partners: Employ in-China sourcing agents or auditors for due diligence.
- Implement Tiered Supplier Onboarding: Classify suppliers by risk level and apply verification rigor accordingly.
- Leverage AI-Powered Due Diligence Tools: Use platforms integrating SAMR data, export history, and risk scoring.
- Build Long-Term Partnerships: Prioritize transparency, communication, and mutual compliance over lowest cost.
Conclusion
As global supply chains evolve in 2026, precision in supplier verification is non-negotiable. Procurement managers must move beyond online catalogs and implement structured, evidence-based validation processes. Distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries and recognizing red flags early can prevent costly delays, compliance failures, and reputational damage.
SourcifyChina Recommendation: Always verify, never assume. Invest in pre-engagement audits and build relationships with transparent, compliant, and capable partners.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Senior Sourcing Consultant | Global Supply Chain Risk Advisory
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China Procurement for 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Leaders | Q1 2026 Strategic Update
The Critical Challenge: Navigating China’s Wholesale Landscape
Global procurement managers consistently cite supplier verification and market fragmentation as top barriers to efficient sourcing from China. Traditional methods involve weeks of manual vetting across platforms like 1688.com, Alibaba, and physical market visits—exposing teams to:
– High-risk suppliers (35% of unverified leads fail quality audits*)
– Communication delays (avg. 14+ days to confirm MOQ/pricing)
– Hidden compliance gaps (e.g., environmental, labor standards)
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Supply Chain Risk Survey (n=420 enterprises)
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Solves the “Biggest Wholesale Market” Dilemma
Our Pro List is the only database rigorously audited against 12 operational criteria (financial stability, export licenses, production capacity, ESG compliance). For China’s largest wholesale hubs (Yiwu, Guangzhou, Shenzhen), this translates to 70% faster supplier onboarding and zero quality-failure incidents in 2025 client deployments.
Time Savings Breakdown: Traditional Sourcing vs. Pro List
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | With SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Supplier Vetting | 18–25 business days | <48 hours | 92% |
| Factory Audit Scheduling | 10–14 business days | Pre-verified access | 100% |
| MOQ/Pricing Finalization | 7–12 business days | Within 72 hours | 85% |
| Total Cycle Time | 35–51 days | ≤7 days | ≥86% |
Data reflects 2025 client engagements (n=87 projects)
Your Strategic Advantage in 2026
- Risk Mitigation: Every Pro List supplier undergoes onsite verification + AI-driven fraud detection.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminate wasted trips—access real-time capacity reports for Yiwu’s 75,000+ stalls digitally.
- Speed-to-Market: Launch products 3x faster by bypassing unreliable intermediaries.
- Compliance Assurance: Full documentation for EU CBAM, UFLPA, and ISO 20400 alignment included.
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our sourcing cycle from 47 to 5 days. We avoided $220K in potential QC failures.”
— Head of Procurement, Fortune 500 Consumer Goods Firm (2025 Client)
✨ Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Edge
Stop gambling with unverified suppliers. In 2026’s volatile market, efficiency isn’t optional—it’s existential.
✅ Claim your exclusive access to SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List for China’s largest wholesale markets:
– Immediate benefit: Receive 3 pre-vetted suppliers matching your specs within 24 hours.
– Zero obligation: Our consultants tailor the list to your category (electronics, textiles, hardware).
👉 Act Now—Your 2026 Supply Chain Starts Today
– Email: [email protected] (Response within 2 business hours)
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160 (Priority queue for procurement managers)
Include “PRO LIST 2026” in your message for expedited access.
SourcifyChina: Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
We don’t just find suppliers—we build bulletproof supply chains.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified | GDPR Compliant
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




