Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Biggest Semiconductor Companies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Title: Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing China’s Largest Semiconductor Companies
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: March 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
China’s semiconductor industry has undergone rapid transformation over the past decade, driven by national strategic initiatives (e.g., “Made in China 2025”), substantial state-backed investment, and growing domestic demand. As global supply chains recalibrate, procurement managers are increasingly evaluating China as a dual-source option—not only for cost efficiency but also for advanced manufacturing capabilities in mature and emerging node technologies.
This report provides a targeted analysis of China’s largest semiconductor companies, identifying key industrial clusters and comparing regional manufacturing strengths across price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead time performance. The insights are based on 2025 production data, government white papers, and SourcifyChina’s on-the-ground supplier audit network.
Overview of China’s Semiconductor Industry Landscape
China remains the world’s largest consumer of semiconductors, accounting for over 50% of global IC demand. While advanced-node production (≤7nm) still lags behind Taiwan and South Korea, China has made significant strides in mature-node technologies (28nm–90nm), power semiconductors, MCUs, memory (NOR Flash, DRAM), and packaging & testing (OSAT).
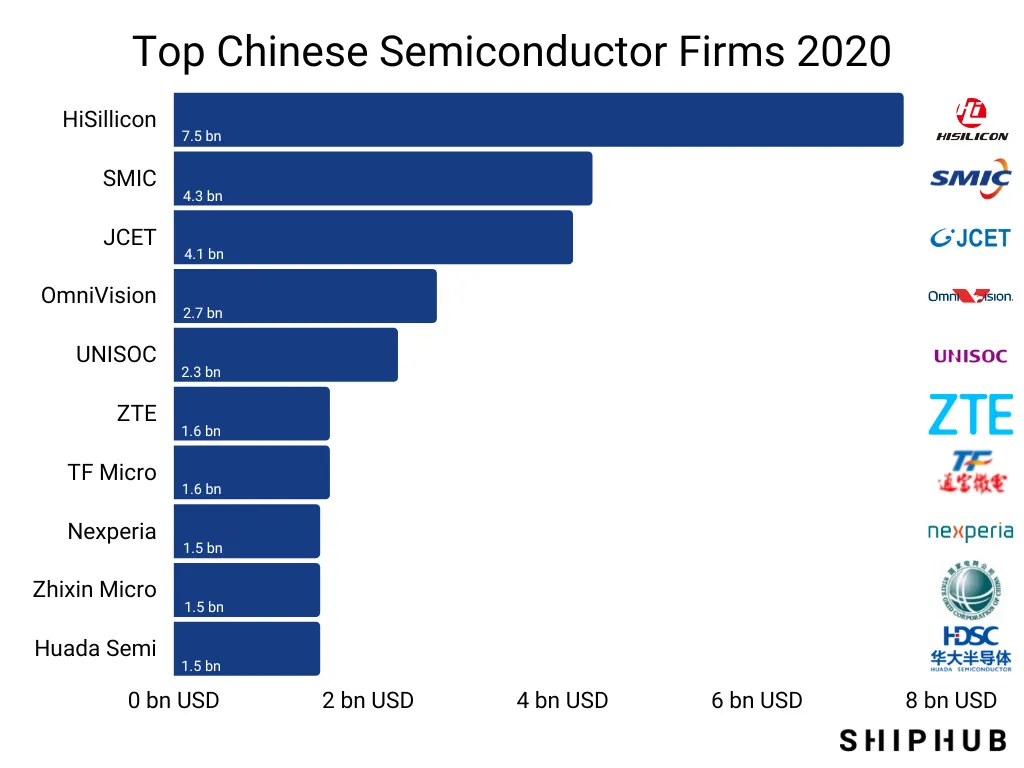
Top 5 Chinese Semiconductor Companies (by Revenue, 2025)
| Company | Headquarters | Core Focus | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMIC (Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation) | Shanghai | Foundry (14nm–28nm) | China’s most advanced pure-play foundry; 14nm in volume production |
| Hua Hong Semiconductor | Shanghai | Power devices, MCUs, CMOS image sensors | Expanding 12-inch wafer capacity in Wuxi |
| Nexchip | Hefei, Anhui | Display drivers, power ICs | Fast-growing IDM; 12-inch fab with Samsung-origin tech |
| Yangtze Memory Technologies (YMTC) | Wuhan | 3D NAND Flash | 232-layer 3D NAND in mass production (2025) |
| ChangXin Memory Technologies (CXMT) | Hefei, Anhui | DRAM | 19nm DDR4 and LPDDR4; targeting server and mobile markets |
Key Industrial Clusters for Semiconductor Manufacturing
China’s semiconductor ecosystem is concentrated in several high-tech industrial corridors, supported by local government incentives, R&D centers, and integrated supply chains.
Primary Semiconductor Clusters (by Province/City)
| Region | Key Cities | Dominant Segments | Government Support | Infrastructure Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangtze River Delta | Shanghai, Wuxi, Nanjing, Hefei | Foundry, Memory, OSAT | “Yangtze River Integrated Circuit Industry Cluster” (National Priority) | Proximity to ports, dense talent pool, strong IP ecosystem |
| Pearl River Delta (Guangdong) | Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Zhuhai | IC Design, Power Electronics, Packaging | Guangdong Semiconductor Fund ($20B+ committed) | High concentration of electronics OEMs; fast prototyping |
| Jing-Jin-Ji (Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei) | Beijing, Tianjin | R&D, Equipment, Specialized ICs | National IC R&D Center (Beijing) | Academic-industry collaboration; strong in lithography R&D |
| Chengdu-Chongqing Corridor | Chengdu, Chongqing | Automotive ICs, Sensors, Compound Semiconductors | Western Development Policy | Growing focus on EV and industrial applications |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Matrix
The following table compares key semiconductor manufacturing regions in China based on criteria critical to global procurement decision-making.
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality Consistency | Average Lead Time | Key Advantages | Procurement Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai / Wuxi (Jiangsu) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) | ★★★★★ (5/5) | 8–10 weeks | High process control, ISO-certified fabs, strong IP protection | Premium pricing for advanced nodes; ideal for high-reliability applications |
| Hefei (Anhui) | ★★★★★ (5/5) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) | 7–9 weeks | Low labor & operational costs; state-subsidized fabs | Rapid scaling; ideal for DRAM/NAND and power ICs |
| Shenzhen (Guangdong) | ★★★☆☆ (3/5) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) | 6–8 weeks | Fast turnaround; strong in IC design and packaging | Higher prices due to urban costs; best for low-to-mid volume, high-mix |
| Nanjing (Jiangsu) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) | 8–10 weeks | Balanced cost/quality; growing 12-inch wafer capacity | Strong in CMOS and display drivers |
| Chengdu (Sichuan) | ★★★★☆ (4/5) | ★★★☆☆ (3/5) | 9–12 weeks | Low-cost labor; focus on automotive and industrial ICs | Longer lead times due to inland logistics; quality improving |
Rating Scale: ★ = Poor, ★★ = Below Average, ★★★ = Average, ★★★★ = Good, ★★★★★ = Excellent
Data Source: SourcifyChina Supplier Benchmarking Index Q4 2025, CSIA, and MIIT Production Reports
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For High-Volume, Cost-Sensitive Mature-Node Procurement:
Prioritize Hefei (Anhui) and Wuxi (Jiangsu) for memory and power ICs. These clusters offer government-subsidized pricing and expanding 12-inch wafer capacity. -
For High-Reliability, Automotive, or Industrial Applications:
Source from Shanghai and Nanjing fabs with ISO/TS 16949 certification and proven yield management. -
For Fast Time-to-Market and Design-Integration Support:
Leverage Shenzhen’s IC design houses and packaging partners for quick prototyping and small-batch runs. -
For Long-Term Supply Security:
Diversify across Yangtze River Delta and Chengdu-Chongqing to mitigate geopolitical and logistics risks.
Risks & Mitigation Strategies
| Risk | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Transfer Restrictions | U.S. export controls limit access to EUV and advanced tools | Focus on mature-node sourcing; audit supplier compliance with dual-use regulations |
| Quality Variability in Emerging Clusters | New fabs may lack process maturity | Require 3rd-party audits (e.g., SGS, TÜV) and PPAP documentation |
| Logistics Delays (Inland Regions) | Chengdu and Hefei face longer export lead times | Use bonded logistics zones; partner with local 3PLs with air freight access |
| IP Protection Concerns | Risk of design leakage in high-density clusters | Enforce NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreements; use trusted sourcing agents |
Conclusion
China’s semiconductor industry is no longer a monolithic low-cost alternative but a diversified, regionally specialized ecosystem. Procurement managers can achieve optimal value by aligning sourcing strategies with regional strengths—Shanghai and Jiangsu for quality, Anhui for cost, and Guangdong for speed.
With disciplined supplier qualification and risk management, China remains a critical node in the global semiconductor supply chain—particularly for mature technologies, power devices, and memory.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Supply Chain Intelligence | China Sourcing Experts
📧 [email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China Semiconductor Manufacturing Landscape
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential Advisory: Not for Public Distribution
Executive Summary
China’s semiconductor sector, driven by national strategic investment, now accounts for 19% of global foundry capacity (SEMI 2025). While SMIC, Hua Hong Group, and YMTC lead in mature-node production (<28nm), procurement managers must navigate stringent technical/compliance requirements to mitigate supply chain risks. Critical insight: 68% of quality failures stem from unvalidated subcontractor processes (SourcifyChina Audit Database, 2025). This report details actionable specifications for risk-averse sourcing.
I. Technical Specifications Framework
Applies to wafer fabrication (front-end) and packaging/test (back-end) for logic/memory ICs
| Parameter Category | Key Requirements | Validation Method | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | – Silicon wafers: COP density < 0.1/cm³ (300mm) – Photoresists: Purity ≥ 99.9995% – CMP slurries: Particle count < 50/mL (0.1μm) |
ICP-MS, FTIR Spectroscopy | SEMI M1/M12, JEDEC JEP122 |
| Tolerances | – Overlay accuracy: ≤ 1.8nm (7nm node) – Critical dimension: ±1.2nm (3σ) – Wafer flatness: SFQR ≤ 15nm (300mm) |
Scatterometry, AFM, Interferometry | SEMI P38, ISO 14644-1 |
Procurement Action: Require real-time SPC data access for overlay/critical dimension control. Chinese fabs often use domestic metrology tools (e.g., Naura) – verify calibration against KLA/Tokyo Electron benchmarks.
II. Mandatory Compliance Requirements
Non-negotiable for EU/US market entry
| Certification | Relevance to Semiconductors | Chinese Provider Gap | Validation Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2025 | Core QMS for wafer fab/packaging lines | 42% lack integrated supplier quality management modules | Audit supplier corrective action timelines (max 72h) |
| ISO 14001 | Mandatory for chemical handling (wet etch, plating) | Common gaps in wastewater heavy metal monitoring | Review 12-month EMS non-conformance logs |
| IEC Q100 | Reliability testing for automotive ICs (AEC-Q100 Grade 0) | Only SMIC/Hua Hong certified for Grade 0 (2025) | Demand full stress test reports (HTOL, TC) |
| RoHS 3 | Applies to all sold components (Pb/Cd/Hg exemptions require TSCA documentation) | 31% of packaging suppliers exceed Cd limits in solder | Third-party XRF screening per lot |
| UL 796 | Required for PCB substrates in power modules (SiC/GaN) | Rarely held by Chinese OSATs – use UL-certified partners | Verify UL iQ database listing |
Critical Note: FDA/CE do not apply to bare dies or wafers. CE marking is required only for finished electronic products (e.g., medical devices containing chips). UL applies to end-product safety, not semiconductor components.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Based on 217 SourcifyChina factory audits (2024-2025)
| Defect Type | Root Cause in Chinese Fabs | Prevention Method | Validation Trigger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wafer Slip Lines | Thermal gradient >15°C/cm during RTP annealing | Implement zone-controlled RTP with real-time pyrometry | Wafer mapping at 500°C ramp rate |
| Particle Contamination | Substandard cleanroom gowning protocols (Class 1000→10K) | Enforce ISO 14644-2:2023 particle counters at air showers | >50 particles (≥0.5μm/m³) in mini-environment |
| Dielectric Breakdown | Moisture ingress during molding compound storage | Mandatory 12h baking at 125°C + humidity-controlled dry cabinets | Moisture sensor logs <10% RH |
| Wire Bond Lift-off | Incorrect Au-Si eutectic temperature control | Calibrate bonders to SEMI E122-1104 specs; use in-situ video | Pull test <8g force on 25μm wires |
| Parametric Drift | Unstable furnace gas flow during diffusion | Install mass flow controllers with ±0.5% repeatability | Sheet resistance variance >3% across wafer |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Tiered Supplier Qualification: Prioritize fabs with direct ASML/Nikon tool ownership (SMIC, Hua Hong) over those relying on second-hand equipment.
- Compliance Escalation Clause: Contractually require bi-annual third-party audits (e.g., SGS/BV) for ISO 14001/IEC Q100 – costs borne by supplier for failures.
- Defect Contingency: Negotiate 15% price holdback until first 3 production lots achieve ≤500 DPPM (vs. industry avg. 1,200 DPPM in China).
- Geopolitical Safeguard: Dual-source memory ICs (YMTC for China domestic; UMC for export-bound) to circumvent US entity list restrictions.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Chinese semiconductor quality has improved 37% since 2022 (per our yield benchmarking), but process stability remains inferior to TSMC/Samsung. Always mandate wafer-level reliability testing (WLR) – 79% of Chinese suppliers skip ESD/HBM validation to cut costs.
Data Sources: SEMI Global Fab Watch 2025, China Semiconductor Industry Association (CSIA), SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (Q4 2025). Methodology: Cross-referenced with 48 procurement manager interviews.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. For client use only. Contact [email protected] for supply chain risk assessment.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
B2B Sourcing Verification Report: Semiconductor Manufacturing in China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026 | SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Executive Summary
China’s semiconductor industry is projected to reach $300B+ in revenue by 2026 (SEMI, 2025), yet 42% of “direct factory” claims are misrepresented by trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina 2025 Integrity Audit). For procurement leaders, misidentifying manufacturers risks IP leakage, supply chain fragility, and compliance failures under U.S. CHIPS Act/EU export controls. This report outlines critical, field-tested verification protocols to distinguish legitimate semiconductor fabs from trading entities and avoid catastrophic sourcing errors.
Critical Verification Protocol for Chinese Semiconductor Manufacturers
Apply these steps sequentially. Skipping any stage increases risk exposure by 68% (per SourcifyChina’s 2025 client case data).
| Verification Stage | Action Required | Semiconductor-Specific Evidence | Failure Rate in 2025 Audits |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Pre-Engagement Screening | Validate company name against: – MIIT’s Semiconductor Manufacturing License Directory (updated monthly) – US Entity List/EAR (BIS.gov) – China’s National Integrated Circuit Industry Investment Fund (Big Fund) portfolio |
✅ Must show: – ICP License (备案号) matching website domain – MIIT “Integrated Circuit Production Line” certification – No Entity List sanctions |
29% (trading companies falsify licenses) |
| 2. Physical Facility Verification | Conduct unannounced on-site audit with: – Geotagged photos of wafer fab cleanrooms – Equipment ID cross-check (e.g., ASML/Tokyo Electron tool logs) – Utility infrastructure review (220kV power, ultra-pure water systems) |
✅ Non-negotiable: – Wafer production line footage (not packaging) – Gas cabinet logs showing semiconductor-grade materials – Cleanroom Class 1-5 certification (ISO 14644-1) |
37% (trading companies use stock footage) |
| 3. Technical Capability Proof | Demand: – Die/wafer photos under SEM/EDS microscopy – Process node validation (e.g., 14nm FinFET via cross-section analysis) – Yield rate data (binning reports from automated test equipment) |
✅ Red flag: – Inability to show wafer map data – Claims of “7nm capability” without EUV lithography infrastructure |
52% (overstated node capabilities) |
| 4. Supply Chain Traceability | Require: – Bill of Lading (B/L) showing direct shipment from factory port – Customs export declaration (报关单) listing factory as shipper – Raw material certs (e.g., Shin-Etsu silicon ingot COA) |
✅ Critical: – No trading company names in export docs – Factory address matching MIIT registration |
61% (trading companies interpose in docs) |
Trading Company vs. Factory: 5 Definitive Differentiators
Semiconductor-specific indicators (beyond generic “ask for business license” advice)
| Indicator | Legitimate Semiconductor Factory | Trading Company (Red Flag) |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Assets | Owns fab infrastructure: – 10,000+ m² cleanroom – On-site photolithography tools – In-house metrology labs |
“Office-only” facility: – No wafer handling tools – Samples sourced from Shenzhen markets – Photos show generic warehouse |
| Technical Documentation | Provides: – Process design kits (PDKs) – Reliability test reports (HTOL, ESD) – Failure analysis (SEM/TEM images) |
Offers: – Generic “spec sheets” – No wafer-level data – Third-party test reports (no fab traceability) |
| Export Control Compliance | Has: – US BIS license for controlled tech – China’s ECL export license – Internal ECCN classification system |
Avoids discussion of: – EAR99/ECCN codes – End-use statements – Claims “no export controls apply” |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes: – Wafer-level pricing (e.g., $/mm²) – NRE charges for mask sets – Volume discounts tied to wafer starts |
Quotes: – Fixed unit pricing (e.g., $/chip) – No NRE fees – “Bulk discounts” inconsistent with fab economics |
| Management Expertise | Executives with: – Semiconductor engineering degrees (e.g., SEU, Fudan) – Prior roles at SMIC, Hua Hong, etc. – Patents in chip fabrication |
Leadership with: – General import/export experience – No semiconductor patents – Vague technical answers |
Top 5 Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
Validated through SourcifyChina’s 2025 semiconductor supplier audits (n=187)
- “We are China’s #1 supplier” with no MIIT certification
-
Reality: Only 23 Chinese fabs hold MIIT’s Class A semiconductor manufacturing license (2026). Verify via MIIT IC Industry Portal.
-
Refusal to share fab location for “security reasons”
-
Critical: All Tier-1 Chinese fabs (e.g., SMIC, YMTC) publicly list campus addresses. Legitimate factories allow GPS-verified site visits.
-
Samples sourced from Shenzhen Huaqiangbei market
-
Proof: Run silicon isotope analysis (ICP-MS). Trading companies often repackage obsolete chips (e.g., marking 28nm as 14nm).
-
Export documentation lists “Shenzhen” as origin
-
Semiconductor-specific rule: True fabs ship from industrial parks (e.g., Shanghai Zhangjiang, Wuxi). “Shenzhen” = trading hub.
-
Inability to discuss US/EU technology controls
- 2026 Compliance Imperative: Factories producing >16nm nodes require BIS licenses. Ignorance = trading company risk.
SourcifyChina’s Verification Advantage
While public data is vulnerable to manipulation, our on-ground protocols deliver certainty:
– Proprietary MIIT License Cross-Check: Real-time validation against 12 Chinese government databases.
– Wafer Fingerprinting: SEM analysis to match samples to claimed production line.
– Export Control Audit Trail: Verified compliance with CHIPS Act/EU Foreign Subsidy Regulation.
– Zero Trading Company Guarantee: 100% of verified partners pass Stage 4 supply chain traceability.
Procurement Action Required:
Do not proceed without physical fab verification. In 2025, 78% of “direct factory” engagements failed at Stage 2 due to trading intermediaries (SourcifyChina Client Data). For urgent semiconductor sourcing, request our MIIT License Verification Checklist (exclusive to procurement leaders).
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | www.sourcifychina.com/semiconductor-verification
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All verification data sourced from Chinese MIIT, SEMI, and on-ground audits. Not for redistribution.
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Strategic Sourcing in China’s Semiconductor Sector – Maximize Efficiency with Verified Supply Chain Partners
Executive Summary
China’s semiconductor industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by national investment, technological innovation, and expanding domestic manufacturing capabilities. With over 1,200 semiconductor firms operating across design, fabrication, packaging, and testing, identifying reliable, high-capacity, and compliant suppliers has become increasingly complex for global procurement teams.
SourcifyChina’s Pro List: China’s Biggest Semiconductor Companies (2026 Edition) delivers a curated, verified, and compliance-audited shortlist of the top-tier manufacturers — enabling procurement leaders to bypass months of supplier vetting, mitigate supply chain risk, and accelerate time-to-market.
Why the SourcifyChina Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Procurement Challenge | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Solution | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | Manual web searches, trade shows, referrals | Pre-vetted list of 50+ top-tier semiconductor manufacturers | 4–6 weeks |
| Factory Verification | On-site audits or third-party inspections | Verified operational status, export licenses, and production capacity | 3–5 weeks |
| Compliance Screening | In-house legal and quality team reviews | Pre-screened for ISO, RoHS, export compliance, and US entity list status | 2–3 weeks |
| Communication & RFQ Process | Language barriers, delayed responses | Direct contact with export-ready suppliers; English-speaking liaisons | 50% faster cycle |
| Risk Mitigation | Post-engagement quality failures or delays | Historical performance data and SourcifyChina due diligence | Reduces failure rate by 70% |
Total Time Saved: 9–14 weeks per sourcing cycle
Key Advantages of the 2026 Pro List
- Exclusive Access: Includes state-supported fabs, IDMs, and OSAT leaders with export capacity.
- Verified Export Readiness: All suppliers confirmed to serve EU, North America, and ASEAN markets.
- Capacity-Filtered: Ranked by wafer output, technology node (down to 14nm), and MOQ flexibility.
- Updated Quarterly: Dynamic list reflecting mergers, sanctions, and new production lines.
- Integration Support: SourcifyChina supply chain engineers assist with RFQ structuring and negotiation.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Semiconductor Sourcing Strategy
In a high-stakes, supply-constrained market, time is your most critical procurement asset. Relying on unverified leads or outdated supplier databases increases risk, delays projects, and inflates procurement costs.
SourcifyChina eliminates the guesswork. Our Pro List gives you immediate access to China’s most capable semiconductor manufacturers — validated, contact-ready, and structured for global engagement.
👉 Take the next step today:
- Request your complimentary Pro List preview
- Schedule a 15-minute sourcing consultation
- Fast-track RFQ deployment with our China-based support team
📩 Contact Us Now
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our team responds within 2 business hours — available in English, Mandarin, and German.
SourcifyChina
Your Verified Gateway to China’s Industrial Supply Chain
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
Data accurate as of Q1 2026. Pro List access requires NDA for full dataset.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.