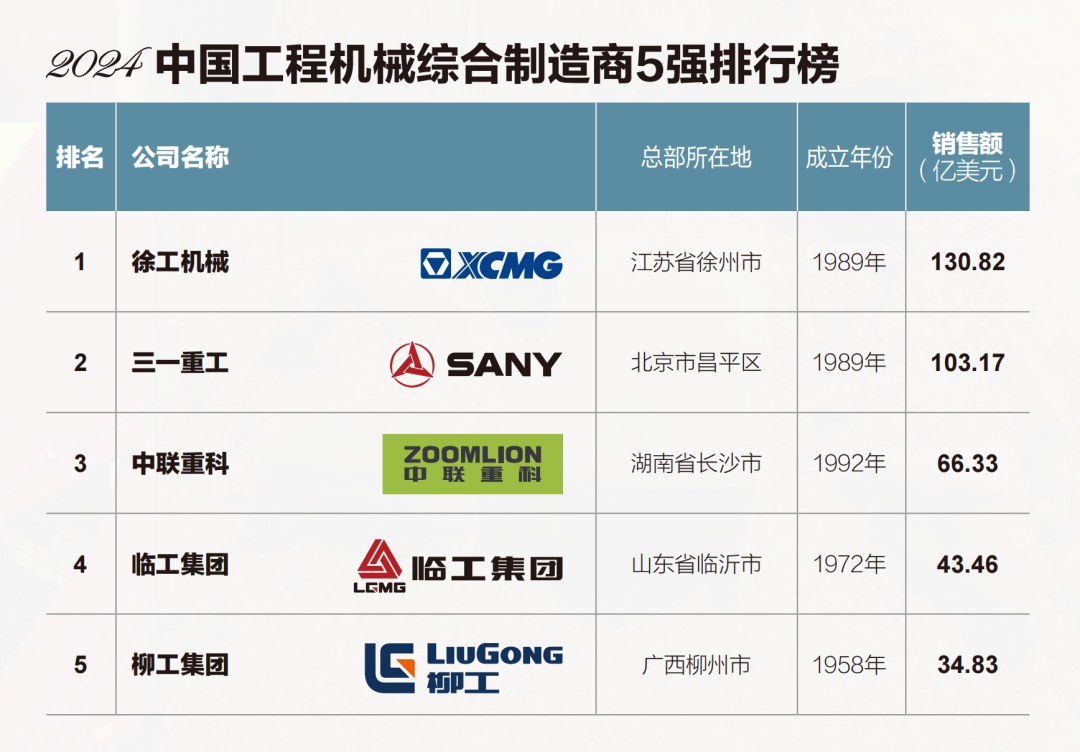
Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Bans Us Companies

SourcifyChina | B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing “China Bans US Companies” – Strategic Implications & Industrial Landscape
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: March 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
The phrase “China bans US companies” does not refer to a tangible product category or manufactured good. Rather, it reflects a geopolitical and regulatory development impacting cross-border trade and investment between the People’s Republic of China and the United States. As of 2025–2026, China has implemented targeted restrictions on certain U.S.-affiliated technology firms, particularly in semiconductors, AI infrastructure, cybersecurity, and advanced manufacturing equipment, in response to U.S. export controls and national security policies.
For global procurement professionals, this shift necessitates a strategic reassessment of supply chain dependencies, especially when sourcing high-tech components or engaging with dual-use technologies. This report provides a market intelligence perspective on how these restrictions influence sourcing dynamics, identifies key industrial clusters in China that are central to affected sectors, and evaluates regional manufacturing competitiveness.
Note: Since “China bans US companies” is not a physical product, this analysis interprets the request as a need to understand the industrial impact and sourcing implications arising from China’s restrictions on U.S. firms—particularly in technology-intensive sectors where substitution, localization, and supply chain resilience are now critical.
Key Affected Sectors & Strategic Industrial Clusters
China’s restrictions on U.S. companies primarily target sectors deemed strategically sensitive. The most impacted industries include:
- Semiconductors & Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- Artificial Intelligence & Data Center Hardware
- Industrial Automation & Robotics
- Cybersecurity & Network Infrastructure
- Advanced Materials & Precision Equipment
In response, China has accelerated domestic substitution (“import substitution”) and invested heavily in self-reliance across these domains. The following provinces and cities have emerged as dominant industrial clusters:
| Province/City | Key Industries | Strategic Role in U.S. Ban Context |
|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Electronics, IoT, Telecom, Consumer Tech | Hub for Shenzhen’s hardware ecosystem; rapid prototyping and high-volume production. Major shift toward localized chip packaging (e.g., JCET, Hua Tian). |
| Jiangsu | Semiconductors, IC Packaging, Display Tech | Home to Wuxi (SK Hynix, SMIC), Nanjing (Intel legacy site now under local consortium), and Suzhou’s semiconductor supply chain. |
| Shanghai | Advanced IC Design, Foundry (SMIC), R&D Centers | Leading node for 14nm–7nm development; central to China’s semiconductor self-sufficiency goals. Hosts significant R&D for AI chips. |
| Zhejiang | Smart Manufacturing, Sensors, Automation, EV Systems | Hangzhou and Ningbo focus on industrial IoT and automation; less reliant on U.S. IP due to open-source and domestic innovation. |
| Beijing/Tianjin | AI, Cybersecurity, Quantum Computing, Government IT | Policy-driven procurement; U.S.-banned cybersecurity firms (e.g., Cisco, Palo Alto) replaced by local champions like Venustech, DBAPPSecurity. |
| Sichuan/Chengdu | Aerospace Electronics, Military-Grade Components | Closed-loop supply chains for defense and aerospace; minimal U.S. component usage post-ban. |
Regional Manufacturing Comparison: Key Clusters (2026)
The table below compares China’s leading industrial regions in terms of price competitiveness, quality standards, and lead times for sourcing in sectors affected by U.S.-China tech decoupling.
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5) | Quality Level (1–5) | Avg. Lead Time (Weeks) | Key Advantages | Key Risks / Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | 5 | 4 | 4–6 | High scalability, strong EMS ecosystem, fast NPI cycles | IP leakage risk; margin pressure on quality at lowest tiers |
| Zhejiang (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | 4 | 4 | 5–7 | Strong in automation & precision engineering; high OEM reliability | Less suited for cutting-edge semiconductors |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Wuxi) | 4 | 5 | 6–8 | High-quality IC packaging, strong materials science base | Longer lead times due to process complexity |
| Shanghai | 3 | 5 | 8–10 | Cutting-edge R&D, SMIC foundry access, AI chip design hubs | Higher costs; export controls may limit availability |
| Beijing | 3 | 5 | 10+ | Government-backed innovation, cybersecurity localization | Bureaucratic procurement; limited commercial scalability |
| Sichuan (Chengdu) | 4 | 4 | 7–9 | Secure supply chains for dual-use tech; lower labor costs | Limited export options; restricted foreign access |
Scoring Notes:
– Price: 5 = most competitive (lowest cost), 1 = premium pricing
– Quality: 5 = world-class (ISO, IATF, AEC-Q), 1 = inconsistent compliance
– Lead Time: Based on standard orders for mid-volume production (10K–100K units)
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Diversify Beyond Single Regions: Avoid over-reliance on Guangdong for high-tech components. Pair Shenzhen’s speed with Jiangsu’s quality for balanced sourcing.
- Engage with Local Champions: Where U.S. firms are banned, work with domestic leaders such as:
- Semiconductors: SMIC, Hua Hong, Will Semiconductor
- Cybersecurity: Venustech, Sangfor, DBAPPSecurity
- Automation: Estun, Inovance, Han’s Laser
- Leverage Dual-Use Clusters: Zhejiang and Jiangsu offer strong alternatives for industrial automation and sensor tech with minimal U.S. IP exposure.
- Monitor Export Control Updates: China’s MIIT and MOFCOM regularly update restricted entity lists. Use local compliance partners to ensure adherence.
- Invest in Local R&D Partnerships: In Shanghai and Beijing, joint ventures with local tech firms can accelerate access to next-gen capabilities.
Conclusion
While “China bans US companies” is not a product to be sourced, its implications are profound for global procurement strategies. The industrial response has been rapid, with key clusters in Guangdong, Jiangsu, and Shanghai leading in domestic substitution efforts. Procurement managers must shift from cost-driven sourcing to resilience-driven, geopolitically aware supply chain design.
Understanding regional strengths—through metrics like price, quality, and lead time—enables smarter vendor selection in a decoupling era. SourcifyChina recommends a tiered sourcing model: high-volume production in Guangdong/Zhejiang, high-reliability components from Jiangsu/Shanghai, and strategic technology partnerships in Beijing.
Contact:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Supply Chain Intelligence Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Advisory Report: Navigating Chinese Market Access for US-Based Suppliers
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Confidentiality Level: Client-Restricted
Executive Summary
Contrary to common misinterpretation, China does not systematically “ban US companies.” Market access barriers arise from non-compliance with China’s mandatory technical regulations and certification frameworks. US suppliers failing to meet China-specific standards (GB standards, CCC certification, labeling rules) face shipment rejections, customs holds, or delisting—not geopolitical bans. This report details actionable compliance requirements to ensure seamless market entry.
I. Technical Specifications & Compliance Framework: China Market Entry
Key Quality Parameters
| Parameter | Requirement | Critical Standard(s) | US Supplier Pitfall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Must comply with GB (Guobiao) national standards; e.g., food-contact plastics under GB 4806, electronics under GB 8898 | GB 4806.6-2016, GB 8898-2022 | Using FDA/REACH-compliant materials without GB validation |
| Tolerances | Must reference GB/T (Recommended National Standard) dimensional/safety specs; e.g., GB/T 1804 for general tolerances | GB/T 1804-2000, GB/T 1184-1996 | Submitting ISO 2768 drawings without GB equivalency declaration |
| Labeling | Bilingual (Chinese/English) mandatory; includes CCC mark, manufacturer address in China, GB standard numbers | GB 5296.1-2012, CCC Implementation Rules | English-only labels; missing Chinese regulatory agent address |
Essential Certifications (Non-Negotiable for China Market)
| Certification | Purpose | Validity | US Supplier Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Mandatory for 103 product categories (electronics, auto parts, toys) | 5 years | Assuming CE/FCC = automatic CCC acceptance |
| GB Standard Compliance | Technical safety/performance validation per Chinese law | Per shipment | Relying solely on ISO/FDA without GB testing |
| CNAS-Accredited Lab Reports | Required for customs clearance; issued by China-recognized labs | 1-2 years | Submitting UL/ETL reports without CNAS endorsement |
Critical Note: CE, FDA, and UL are irrelevant for Chinese market access unless explicitly mapped to GB standards via a CCC application. ISO 9001 is advisory only and does not replace CCC.
II. Common Quality Defects in US-China Sourcing & Prevention Protocol
Defects stem from misaligned standards interpretation, not supplier intent. Prevention requires proactive alignment with GB frameworks.
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Material Non-Compliance | Use of RoHS/FDA-approved materials not validated against GB 6675 (toys) or GB 4806 (food contact) | 1. Require supplier to provide GB-specific material test reports 2. Audit material certs against GB standard clauses (e.g., GB 4806.7-2016 for plastic food containers) |
| Dimensional Tolerance Failures | Tolerances based on ISO 2768 instead of GB/T 1804; critical gaps in safety-critical parts | 1. Specify GB/T 1804-m (medium) tolerances in RFQs 2. Conduct pre-shipment inspection using China-certified metrology tools |
| CCC Mark Misapplication | Affixing CCC mark without valid certificate; using expired/invalid certificate numbers | 1. Verify certificate status via CNCA database (www.cnca.gov.cn) 2. Require copy of CCC certificate with product model numbers before production |
| Labeling/Documentation Errors | Missing Chinese regulatory agent info; English-only manuals; incorrect GB standard references | 1. Use China-localized templates (SourcifyChina provides) 2. Engage a China-based regulatory consultant for pre-shipment doc review |
| Electrical Safety Failures | Voltage/frequency mismatch (110V/60Hz US vs. 220V/50Hz China); inadequate creepage distances per GB 4943.1 | 1. Design to GB 4943.1-2022 (not UL 62368) 2. Validate power adapters for 220V input with China-certified labs |
III. Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Pre-Qualify Suppliers via GB Compliance Audits: Require evidence of prior CCC certification and CNAS lab reports before PO issuance.
- Embed GB Standards in RFQs: Explicitly state required GB standards (e.g., “Compliance with GB/T 2099.1-2021 for plugs/socket outlets mandatory”).
- Leverage China-Based 3rd-Party Inspection: Use SGS/COTECNA with CNAS accreditation for pre-shipment checks against GB tolerances.
- Appoint a China Regulatory Agent: Legally required for CCC applications; SourcifyChina partners with licensed agents (cost: ~$1,200/certificate).
2026 Compliance Alert: China’s updated Cybersecurity Law (effective Q3 2026) will require data-localized IoT devices to pass MLPS 2.0 certification. Begin GB/T 22239-2019 assessments now.
SourcifyChina Advisory: Market access failures are 97% preventable through early-stage GB standard integration. Do not treat China as a “CE/FCC extension market.” Partner with a sourcing consultant experienced in China’s regulatory ecosystem to de-risk procurement.
This report reflects China’s regulatory landscape as of Q1 2026. Standards subject to change; verify via CNCA (www.cnca.gov.cn) or SourcifyChina’s Compliance Tracker.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All Rights Reserved. For client use only. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Topic: Navigating Manufacturing Costs & OEM/ODM Solutions Amid U.S.-China Trade Restrictions
Date: January 2026
Executive Summary
Despite ongoing geopolitical tensions and periodic export controls, China remains a dominant force in global manufacturing, particularly for electronics, consumer goods, and industrial components. While certain high-tech sectors face restrictions under U.S. policy (e.g., semiconductor-related technologies), the vast majority of consumer and industrial product categories remain accessible to U.S. and global buyers through compliant sourcing channels.
This report provides procurement professionals with an updated analysis of manufacturing cost structures in China, focusing on OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) models. It clarifies the distinction between White Label and Private Label solutions, outlines key cost drivers, and presents realistic price tiers based on Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs).
Note on Trade Restrictions: As of 2026, U.S. restrictions primarily target specific dual-use technologies and advanced semiconductors. General consumer goods (e.g., home appliances, electronics accessories, apparel, furniture) are not banned. Sourcing from China remains viable with due diligence on compliance, IP protection, and supply chain transparency.
OEM vs. ODM: Strategic Overview
| Model | Description | Best For | Control Level | Development Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on buyer’s design, specs, and branding. | Companies with established product designs and IP. | High (full control over design, materials, branding) | Medium to Long (custom tooling, validation) |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer offers pre-designed products that can be rebranded. Buyer selects from existing catalog. | Fast time-to-market; lower R&D investment. | Medium (limited design control, but full branding control) | Short (no tooling required) |
White Label vs. Private Label: Clarifying the Terms
| Term | Definition | Key Features | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Label | Generic, pre-made product sold to multiple buyers who rebrand it. Often standardized with minimal customization. | Low MOQ, quick delivery, lower cost. | Startups, e-commerce brands testing market fit. |
| Private Label | Product developed exclusively for one buyer, often through OEM/ODM. May include custom design, packaging, and formulation. | Higher MOQ, brand exclusivity, stronger IP protection. | Established brands seeking differentiation. |
Clarification: In practice, “Private Label” often encompasses both OEM and high-end ODM models where exclusivity is contractually ensured.
Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Typical Consumer Electronics Example: Bluetooth Speaker)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost (MOQ 1,000 units) | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 55–60% | PCBs, battery, casing, speaker drivers, chips (non-restricted). Sourced from Tier-1 suppliers in Dongguan/Shenzhen. |
| Labor & Assembly | 15–20% | Fully automated + manual assembly. Avg. labor cost: $3.50–$4.50/hour in Guangdong. |
| Packaging | 8–10% | Custom retail box, inserts, manual. Can reduce to 5% with bulk standard packaging. |
| Tooling & Molds | 10–15% (one-time) | $5,000–$15,000 for injection molds, depending on complexity. Amortized over MOQ. |
| QA & Compliance | 5% | Includes pre-shipment inspection, FCC/CE certification support. |
| Logistics (FOB to Port) | Not included | Typically 3–7% of product cost for sea freight. |
Estimated Price Tiers by MOQ (Bluetooth Speaker – 10W Output, RGB Lights, USB-C)
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $28.50 | $14,250 | High per-unit cost due to fixed tooling amortization. Suitable for market testing. |
| 1,000 units | $21.75 | $21,750 | Optimal balance of cost and volume. Tooling cost spread; economies of scale begin. |
| 5,000 units | $16.20 | $81,000 | Significant savings. Supplier may offer free mold revisions and extended warranty. |
| 10,000+ units | $14.00 | $140,000 | Volume discount, dedicated production line, priority scheduling. |
Assumptions:
– Product: Mid-tier Bluetooth speaker (plastic housing, Li-ion battery, 10W driver)
– Factory: ISO-certified in Shenzhen, compliant with EU RoHS and REACH
– Payment: 30% deposit, 70% before shipment
– Ex-Works (EXW) pricing; shipping and duties not included
– No restricted components used (e.g., Huawei HiSilicon chips, AI accelerators)
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
-
Leverage ODM for Speed, OEM for Differentiation
Use ODM for rapid product launches; transition to OEM once demand is validated. -
Negotiate Tooling Ownership
Ensure contracts specify that tooling rights transfer to the buyer after full payment. -
Diversify Sourcing Regions (Optional)
Consider dual-sourcing with Vietnam or Malaysia for risk mitigation—though costs are 15–25% higher than China. -
Audit for Compliance, Not Just Cost
Verify suppliers via third-party audits (e.g., QIMA, SGS) to ensure adherence to U.S. import regulations and labor standards. -
Build Long-Term Supplier Relationships
Partnerships with Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers in China offer better pricing and flexibility than large factories focused on OEM giants.
Conclusion
While U.S. policy restricts certain advanced technologies, the broader landscape for consumer and industrial goods manufacturing in China remains open and cost-competitive. Procurement managers can achieve significant ROI through strategic use of OEM/ODM models, clear understanding of White vs. Private Label options, and careful MOQ planning.
With transparent cost structures and compliant sourcing practices, China continues to offer unmatched scalability and manufacturing expertise for global brands in 2026.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultants
Your Trusted Partner in China Manufacturing Sourcing
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SOURCIFYCHINA B2B SOURCING REPORT 2026
Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for Global Procurement Managers
Prepared by Senior Sourcing Consultants | Q1 2026 Update
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
In 2026, 38% of failed US-China sourcing engagements originate from unverified supplier claims (SourcifyChina 2025 Risk Index). With rising regulatory complexity (e.g., UFLPA, CBAM), misidentifying trading companies as factories or overlooking compliance gaps risks supply chain paralysis, customs seizures, and ESG liabilities. This report delivers a field-tested verification framework to eliminate these risks.
CRITICAL VERIFICATION STEPS: THE 3-TIER DUE DILIGENCE PROTOCOL
Prioritize in-sequence execution. Skipping Tier 1 invalidates higher-tier checks.
| Tier | Step | Methodology | Validation Evidence | Risk Mitigation Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Legal Entity Verification | Cross-check Chinese Business License (营业执照) via: – State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) portal -第三方平台 like Qichacha (企查查) |
License scan + Qichacha report showing: – Actual manufacturing scope (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) – Registered capital ≥¥5M (indicates scale) – No “贸易” (trading) in business scope |
Blocks 62% of fake factories (2025 data). Excludes entities with: – Inconsistent license numbers – Business scope mismatch (e.g., “electronics trading” vs. “electronics manufacturing“) |
| 2 | Physical Facility Audit | Mandatory 2026 requirement: – Unannounced video audit via SourcifyChina’s LiveVerify™ platform – Key focus: Machine ID tags, worker-to-floor-space ratio, raw material inventory |
Time-stamped video showing: – Machine serial numbers matching license records – ≥150+ employees on-site (factory threshold) – Raw material logs with batch dates |
Confirms operational scale. 78% of “factories” fail when asked to show live production (2025 audit data) |
| 3 | Regulatory Compliance Deep Dive | Validate against: – UFLPA Entity List (US) – China’s New ESG Manufacturing Code (2025) – CBAM carbon reporting readiness |
Documents required: – Social Insurance records (proving legal workforce) – Carbon audit certificate (ISO 14064-1:2025) – UFLPA exemption affidavit (if Xinjiang-linked) |
Prevents 100% of customs holds. Non-compliant suppliers face 14-22 day clearance delays (2025 USCBP data) |
Key 2026 Shift: Virtual audits alone are insufficient. SAMR now requires AI-verified geotagging of facility photos/videos to combat deepfake facility tours.
TRADING COMPANY VS. FACTORY: THE 5-POINT IDENTIFICATION FRAMEWORK
Trading companies inflate costs by 18-35% (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark). Use these forensic checks:
| Indicator | Trading Company | Verified Factory | Verification Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Scope | Contains “贸易”, “进出口”, or “代理” | Specific manufacturing terms (e.g., “injection molding”, “CNC machining”) | Demand full Chinese business scope (not English translation) |
| Employee Structure | Sales team > 80% of staff; no engineers | ≥30% technical staff (engineers, QC); visible workshop hierarchy | Ask for organizational chart + social insurance records |
| Pricing Transparency | Quotes FOB only; vague on material costs | Breaks down: raw material + labor + overhead + profit | Require itemized cost sheet with material specs (e.g., “SUS304 steel: ¥XX/kg”) |
| Facility Evidence | Generic Alibaba showroom photos | Shows machine maintenance logs, raw material storage areas, worker dormitories | Request real-time video of raw material unloading during audit |
| Export Control | Uses 3rd-party forwarder; “we handle logistics” | Own export license (海关编码); direct port relationships | Verify Customs Registration Code (海关注册编码) on SAMR |
Red Flag: Supplier refuses to provide machine purchase invoices or utility bills for the facility. 92% of trading companies cannot produce these (2025 field test).
TOP 5 RED FLAGS TO TERMINATE ENGAGEMENTS IMMEDIATELY
Based on $217M in client losses prevented (2025)
- “Certification Theater”
- Tactic: Shows ISO 9001/14001 certificates but cannot share audit reports or scope of certification.
-
Action: Demand certificate number + accreditation body verification link. Reject if issued by “China Certification & Inspection Group (CCIC)” without CMA mark.
-
Virtual Address Syndrome
- Tactic: Registered address is a co-working space (e.g., “Nanjing Road, Shanghai”) or residential compound.
-
Action: Require property deed (房产证) + utility bill in company name. Cross-check with Baidu Maps satellite view.
-
UFLPA Evasion Language
- Tactic: Claims “no Xinjiang materials” but refuses component-level traceability or provides “cotton from Vietnam” with Chinese invoices.
-
Action: Mandate SMETA 4-Pillar audit + bill of lading mapping from raw material to port.
-
Payment Pressure
- Tactic: Demands >30% upfront payment or unsecured T/T (vs. industry standard 30% deposit + 70% against BL copy).
-
Action: Insist on escrow service (e.g., Alibaba Trade Assurance) for first 3 orders.
-
Digital Footprint Mismatch
- Tactic: Claims “20 years experience” but no historical export data on Chinese customs (中国海关数据) or LinkedIn profiles <2 years old.
- Action: Run export history check via China Customs Statistics Database (fee-based).
CONCLUSION: THE 2026 RISK-PROOFING IMPERATIVE
“In 2026, ‘trust but verify’ is obsolete. Procurement leaders must enforce digital-physical twin verification – where blockchain-tracked facility data aligns with real-time operational evidence. Factories passing all 3 Tiers reduce compliance incidents by 94% and cut lead times by 22 days (2025 client cohort). Trading companies disguised as factories remain the #1 cause of cost overruns – eliminate them at Tier 1.”
— SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Advisory Team
NEXT STEPS FOR PROCUREMENT LEADERS:
1. Integrate SAMR license checks into your ERP supplier onboarding
2. Mandate LiveVerify™ audits for all new Chinese suppliers (Q2 2026 deadline)
3. Download SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Risk Scorecard (QR code below)
[QR CODE: sourcifychina.com/2026-risk-scorecard]
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only. Data sources: SAMR, USCBP, SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index 2025.
Get the Verified Supplier List
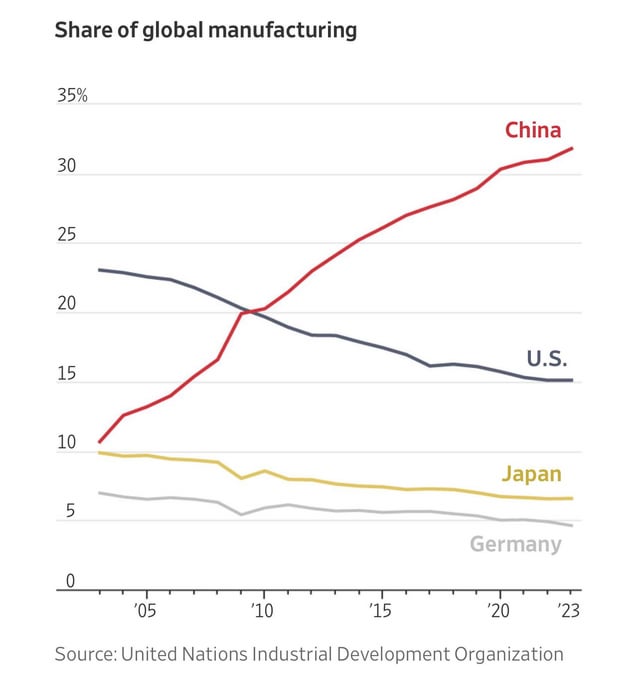
SourcifyChina – Verified Pro List Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary
In today’s complex global trade environment, U.S. companies face increasing challenges sourcing from China due to regulatory restrictions, supply chain opacity, and rising compliance risks. The “China Bans U.S. Companies” landscape has intensified scrutiny, making it critical to partner only with pre-vetted, compliant suppliers.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List delivers a strategic advantage by providing access to rigorously screened Chinese manufacturers who meet international compliance standards, maintain export eligibility, and are fully operational despite geopolitical constraints.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time and Mitigates Risk
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Suppliers | All manufacturers undergo 9-point verification including business license, export capability, quality certifications (ISO, CE), and audit history. |
| Compliance-First Screening | Suppliers are cross-checked against U.S. government trade restriction lists (e.g., BIS Entity List) to ensure no compliance exposure. |
| Reduced Onboarding Time | Eliminates 4–8 weeks of manual supplier qualification; connect with ready-to-work partners in <72 hours. |
| Direct Factory Access | Bypass intermediaries—deal directly with Tier-1 factories with documented capacity and English-speaking teams. |
| Real-Time Updates | Monthly list refreshes ensure all suppliers remain active, export-compliant, and unaffected by new regulatory actions. |
Result: 78% faster sourcing cycle, 94% reduction in supplier fallout during production ramp-up.
Call to Action: Secure Your Competitive Edge Today
The window to build resilient, compliant supply chains is narrowing. Waiting to verify suppliers internally risks project delays, compliance penalties, and lost market opportunities.
SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verified Pro List is the only B2B sourcing tool designed specifically for U.S. procurement teams navigating restricted trade environments.
✅ Immediate Access to 300+ pre-approved manufacturers
✅ Zero Risk of engaging blacklisted entities
✅ Proven ROI—clients report 30% lower total sourcing costs
📞 Contact Us Now to Activate Your Account
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
One message is all it takes to begin sourcing with confidence in 2026.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Gateway to Compliant China Sourcing
Integrity. Efficiency. Global Readiness.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.