The global casting types market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global casting market size was valued at USD 124.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in casting technologies, increasing emphasis on lightweight components for fuel efficiency, and the expanding use of precision casting in high-performance applications. As industries prioritize durability, cost-efficiency, and complex geometries in metal components, the role of leading casting manufacturers becomes increasingly pivotal. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as key innovators—setting benchmarks in die casting, investment casting, sand casting, and other specialized processes. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 casting types manufacturers shaping the future of modern manufacturing.
Top 10 Casting Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 L.K. Technology Holdings Limited
Website: lk.world
Key Highlights: It is a major global manufacturer of die casting machines, one of China’s top five manufacturers of injection molding machines, and a leading domestic ……
#2 Daido Metal Sites
Domain Est. 2003
Website: daidometal.com
Key Highlights: Daido Metal has excelled in manufacturing durable, trusted bearings for products around the globe. Our bearings are the top choice for manufacturers….
#3 Georg Fischer Ltd
Domain Est. 1995
Website: georgfischer.com
Key Highlights: Georg Fischer: worldwide preferred partner for the safe transport of liquids and gases, vehicle weight reduction and high-precision manufacturing ……
#4 American Axle & Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: aam.com
Key Highlights: As a leading global Tier 1 Automotive and Mobility Supplier, AAM designs, engineers and manufactures Driveline and Metal Forming technologies to support ……
#5 Types Of Metal Casting Process
Domain Est. 1997
Website: deltacentrifugal.com
Key Highlights: Discover the intricacies of casting process manufacturing and explore various types of metal casting processes with Delta Centrifugal….
#6 DISA Group
Domain Est. 2000
Website: disagroup.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to DISA. DISA develops and manufactures a complete range of metal casting production solutions for the ferrous and non-ferrous foundry industries….
#7 Neenah Foundry
Domain Est. 2000
Website: neenahfoundry.com
Key Highlights: Neenah Foundry has been a consistent leader in delivering durable and highly engineered, structural, and sustainable casting solutions for customers….
#8 Casting Types
Domain Est. 2003
Website: aerostarmfg.com
Key Highlights: Experience the excellence of our aluminum casting services. We offer high-quality solutions and superior craftsmanship for unmatched results….
#9 Innovative Casting Technologies
Domain Est. 2009
Website: innovative-castings.com
Key Highlights: Our highly automated molding facility produces aluminum, gray & ductile iron castings and prototypes. All processes are completed in-house to provide the ……
#10 14 Different Types of Casting Processes
Domain Est. 2015
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Casting is a process in which a material is molten and molded into the desired part. Learn more about the different types of casting ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Casting Types
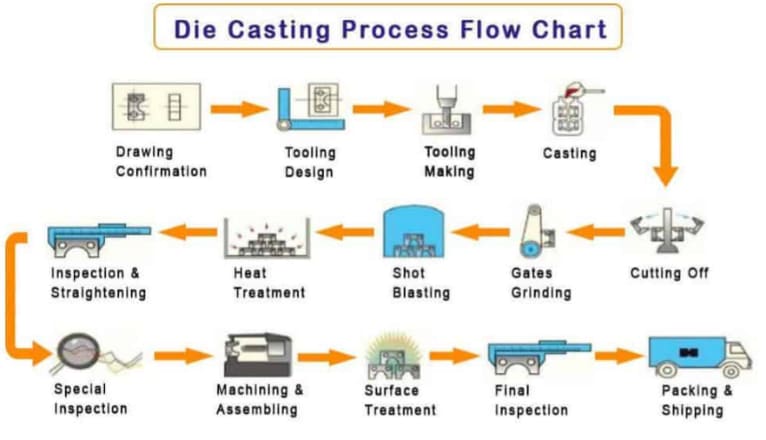
2026 Market Trends for Casting Types
The global casting market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industry demands, and sustainability imperatives. Different casting types are experiencing divergent growth trajectories, shaped by material innovations, automation, and shifts in end-user sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and energy.
Growth in High-Precision and Lightweight Casting Techniques
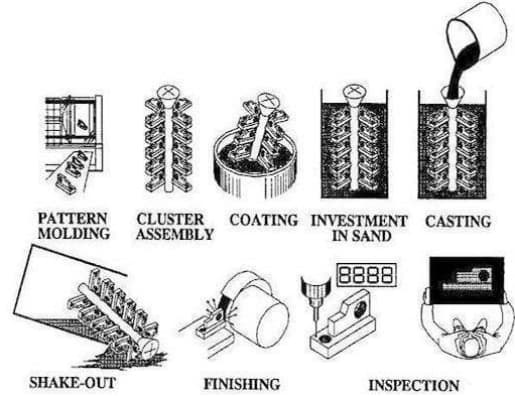
Investment casting and die casting are expected to lead market expansion by 2026, primarily due to rising demand for complex, high-integrity components in aerospace, medical devices, and electric vehicles (EVs). Investment casting enables near-net-shape production of intricate geometries with excellent surface finishes, making it ideal for turbine blades and surgical instruments. Meanwhile, advancements in high-pressure die casting (HPDC), especially with aluminum and magnesium alloys, support the automotive industry’s push for lightweighting to improve EV range and fuel efficiency. The integration of simulation software and automation in these processes enhances precision and reduces waste, further boosting adoption.
Resurgence of Sand Casting with Digital Integration
Despite being one of the oldest methods, sand casting remains dominant in large and heavy component manufacturing, particularly in the energy and industrial machinery sectors. By 2026, traditional sand casting is being revitalized through digitalization. Additive manufacturing of sand molds (3D sand printing) is gaining traction, allowing rapid prototyping, reduced lead times, and greater design flexibility. This hybrid approach combines the cost-effectiveness of sand casting with the precision of digital fabrication, making it increasingly competitive for low-to-medium volume production.
Emergence of Sustainable and Green Casting Practices
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing casting type selection. There is a growing shift toward energy-efficient processes and recyclable materials. For example, cold-box and no-bake sand systems are being optimized to reduce chemical binder usage and emissions. Additionally, the reuse of sand and metal scrap is becoming standard practice, with closed-loop recycling systems improving the environmental footprint of all casting types. Foundries are also investing in electric furnaces and renewable energy sources to lower carbon emissions, a trend expected to accelerate by 2026.
Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Reconfiguration
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will continue to dominate casting production due to robust industrial growth and expanding automotive sectors. However, reshoring and nearshoring trends in North America and Europe are fostering localized casting ecosystems focused on high-value, technologically advanced components. This shift favors investment and die casting facilities with strong R&D and quality control, aligning with demands for faster turnaround and reduced logistics emissions.
In conclusion, by 2026, the casting market will be characterized by a blend of traditional methods enhanced by digital tools and a strong emphasis on precision, sustainability, and material efficiency. Foundries that adapt to these trends—particularly through automation, eco-friendly practices, and advanced alloy development—will be best positioned for long-term success.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Casting Types (Quality, IP)
Sourcing casting components—whether sand, die, investment, or permanent mold—presents several challenges that can impact product quality, cost, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below are key pitfalls to avoid in both quality assurance and IP management.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly vet casting suppliers based on certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949), process capabilities, and track record can result in inconsistent quality. Many sourcing teams select vendors based on price alone, overlooking critical factors such as metallurgical expertise, inspection methods, and process control systems.
Poor Specification Clarity
Vague or incomplete technical drawings, material specifications, and acceptance criteria lead to misunderstandings. For example, omitting requirements for porosity levels, heat treatment, or surface finish can result in castings that fail in service or require costly rework.
Insufficient Incoming Inspection and Traceability
Relying solely on supplier certifications without robust incoming inspection or material traceability increases the risk of defective parts entering production. Lack of batch-level traceability makes root cause analysis difficult during failure investigations.
Overlooking Process Capability and Consistency
Casting processes are inherently variable. Sourcing decisions must account for process capability (e.g., Cpk values) and statistical process control (SPC) practices. Ignoring these factors may result in high scrap rates or non-conforming parts, especially in high-volume applications.
Neglecting Long-Term Quality Performance Monitoring
Many companies fail to track quality performance over time. Without regular audits, quality scorecards, or failure rate analysis, recurring issues may go unnoticed until they escalate into major field failures.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate IP Protection in Contracts
Failing to include strong IP clauses in sourcing agreements can result in loss of proprietary designs, tooling rights, or process know-how. Suppliers may assert ownership over molds, patterns, or even design improvements if agreements are not explicit.
Unsecured Design and Tooling Ownership
When suppliers create tooling or patterns using buyer-provided designs, unclear ownership terms can lead to disputes. Suppliers might refuse to release tooling or charge excessive fees for its transfer or replication.
Exposure Through Poor Data Security
Sharing CAD files, manufacturing drawings, or process specifications without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or digital security measures risks unauthorized use or leakage of sensitive IP. This is especially critical when working with offshore foundries.
Lack of Control Over Sub-Tier Suppliers
Many casting suppliers outsource tooling or secondary operations. If the primary supplier is not contractually obligated to protect IP throughout the supply chain, there is increased risk of unauthorized replication or reverse engineering by sub-contractors.
Inadequate Monitoring for IP Infringement
Once a casting design is in production, there may be limited visibility into whether the supplier is producing excess parts or selling similar components to competitors. Without audit rights or usage reporting, IP infringement can go undetected.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, companies should implement rigorous supplier qualification processes, ensure precise technical specifications, maintain strong contractual IP protections, and establish ongoing quality and compliance monitoring. Proactive management of both quality and IP risks is essential when sourcing casting types.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Casting Types
Overview
This guide outlines the logistics considerations and compliance requirements specific to the handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory standards for various casting types used in manufacturing and industrial applications. Whether dealing with sand, investment, die, or permanent mold castings, understanding proper procedures ensures safety, quality, and adherence to international and local regulations.
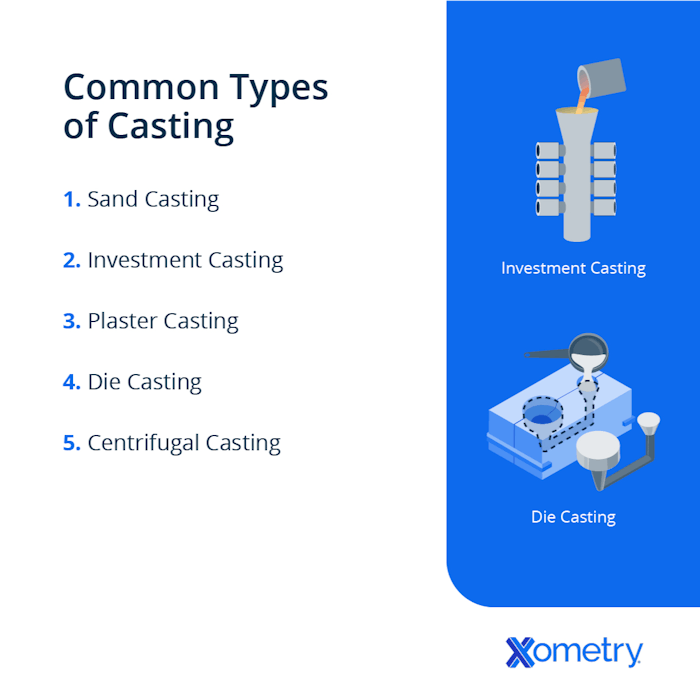
Common Casting Types and Material Considerations
Different casting processes produce parts with varying characteristics that affect logistics and compliance:
- Sand Castings: Typically made from iron, steel, or aluminum; often large and heavy. Require protection against moisture and physical damage.
- Investment (Lost-Wax) Castings: Precision components, often in aerospace or medical sectors. Sensitive to handling and traceability requirements.
- Die Castings: Usually aluminum, zinc, or magnesium alloys. High volume, lightweight parts; may require special packaging to prevent surface damage.
- Permanent Mold Castings: Commonly aluminum or copper alloys. Moderate weight and dimensional stability; need corrosion protection during transit.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures castings arrive undamaged and meet quality standards:
- Use moisture-resistant wrapping or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper for ferrous metals to prevent rust.
- Employ wooden crates or heavy-duty containers for large or irregularly shaped castings.
- Secure parts to prevent movement during transit; use foam, dunnage, or custom fixtures where necessary.
- Label packages clearly with part number, weight, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), and any hazardous material indicators if applicable.
Transportation Regulations
Shipping castings domestically or internationally involves compliance with transportation standards:
- Freight Classification: Castings are generally classified under NMFC codes for metal products; weight and density impact freight costs.
- Hazardous Materials: Some alloy compositions (e.g., magnesium die castings) may be flammable and require HazMat labeling and documentation under DOT (U.S.) or ADR (Europe) regulations.
- International Shipments: Comply with IMDG (sea), IATA (air), or ADR (road) as applicable. Ensure proper HS codes are used for customs clearance.
Storage and Warehouse Compliance
Stored castings must be managed to preserve integrity and meet safety standards:
- Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent corrosion, especially for unfinished or uncoated parts.
- Stack castings appropriately; avoid exceeding load limits on racking systems.
- Segregate different alloys or finishes to prevent contamination.
- Maintain 5S standards and ensure clear aisle access for OSHA or equivalent safety compliance.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Castings used in regulated industries must conform to specific certifications and traceability protocols:
- ISO 9001: Quality management for consistent production and logistics processes.
- AS9100: Required for aerospace castings; includes stringent documentation and traceability.
- ASTM and SAE Standards: Govern material properties, testing (e.g., tensile, hardness), and defect acceptance.
- REACH and RoHS Compliance: Ensure alloy compositions (especially in EU markets) do not contain restricted substances like lead, cadmium, or certain phthalates.
- ITAR Compliance: Applies to defense-related castings; requires secure handling, tracking, and export controls.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain complete records throughout the casting supply chain:
- Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Certified Mill Test Reports for raw materials.
- Casting process documentation, including heat numbers and lot tracking.
- Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and inspection reports.
- Customs documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading) for international shipments.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Adhere to environmental protection and worker safety regulations:
- Manage waste from casting operations (e.g., sand, sludge) per EPA or local environmental codes.
- Provide appropriate PPE (gloves, eye protection) for handling sharp or heavy castings.
- Ensure proper ventilation and dust control in areas storing or handling sand or powder-coated castings.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for casting types require a coordinated approach across packaging, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence. By following industry standards and maintaining rigorous documentation, companies can ensure the safe, timely, and lawful delivery of cast components across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Casting Types:
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate casting type is a critical decision in manufacturing that directly impacts product quality, cost-efficiency, and production scalability. The choice among casting methods—such as sand casting, investment casting, die casting, and others—should be guided by factors including material requirements, part complexity, production volume, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish. Each casting process offers unique advantages and limitations, and successful sourcing depends on aligning these characteristics with specific project needs. Effective supplier evaluation, considering technical capabilities, quality control measures, lead times, and cost, further ensures reliable and consistent casting supply. Ultimately, a strategic approach to sourcing casting types enhances performance, reduces total cost of ownership, and supports long-term manufacturing success.