Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Car Companies Owned By China
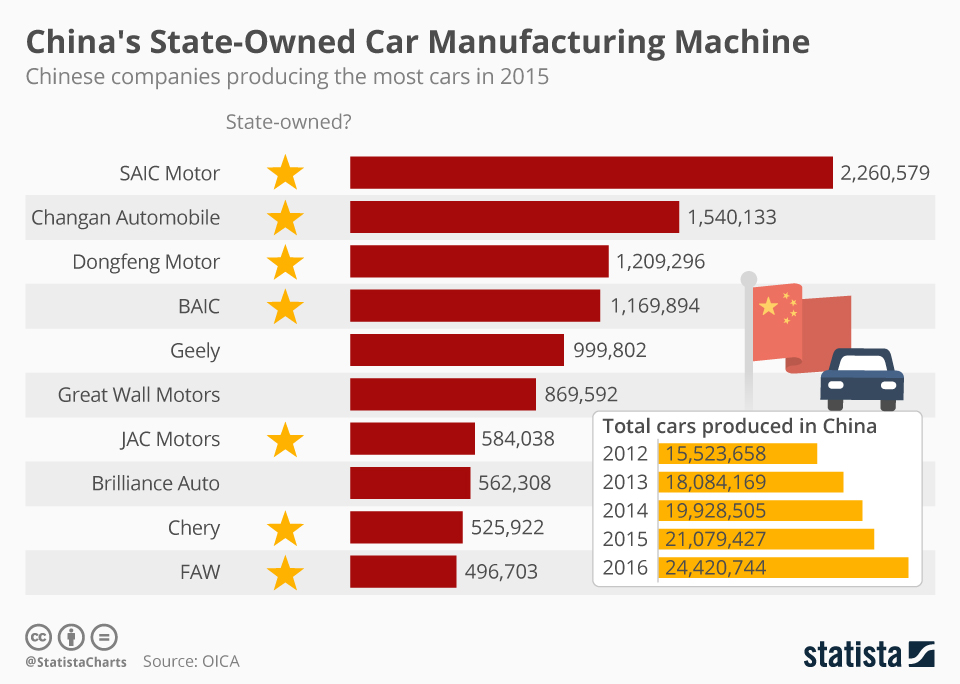
SourcifyChina | Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Subject: Deep-Dive Market Analysis – Sourcing Chinese-Owned Automotive Manufacturers
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The Chinese automotive industry has undergone a transformative shift since 2020, positioning China as the world’s largest automotive manufacturer and exporter. In 2025, China surpassed Japan to become the top global car exporter, driven by aggressive investment in electric vehicles (EVs), intelligent manufacturing, and vertically integrated supply chains. This report provides a strategic overview of sourcing opportunities from Chinese-owned car companies, focusing on key industrial clusters, regional capabilities, and comparative advantages across provinces.
As of 2026, domestically owned OEMs such as BYD, Geely, NIO, Xpeng, SAIC (with majority Chinese state ownership), Great Wall Motors, and Changan dominate production and innovation. These firms are not only supplying domestic demand but are increasingly targeting global markets—particularly Europe, Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East.
This analysis identifies the core industrial clusters for Chinese-owned automotive manufacturing, evaluates regional competitiveness, and provides actionable insights for procurement professionals evaluating sourcing partnerships in China.
Key Industrial Clusters for Chinese-Owned Automotive Manufacturing
China’s automotive production is highly regionalized, with clusters forming around strong local government support, supply chain density, port access, and R&D infrastructure. The following provinces and cities are recognized as primary hubs for Chinese-owned automotive OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers:
| Province | Key Cities | Notable Chinese-Owned OEMs | Specialization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Foshan | BYD (headquartered in Shenzhen), GAC Group (state-backed) | EVs, Battery Tech, Smart Mobility |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou, Ningbo, Wenzhou | Geely (owns Volvo, Polestar), NIO (R&D HQ) | Premium EVs, Global Platforms, ICE & Hybrid |
| Jiangsu | Nanjing, Changzhou, Suzhou | NIO (manufacturing), Xpeng (subsidiary ops), BYD components | EV Assembly, Battery Systems, Electronics |
| Chongqing | Chongqing Municipality | Changan Automobile, Seres (AITO partner) | Mass-market ICE & EVs, SUVs |
| Hebei | Baoding | Great Wall Motors (GWM), ORA | SUVs, Pickups, Off-road EVs |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | SAIC Motor (Roewe, MG, IM Motors) | Export-oriented EVs, Autonomous Tech |
Note: While Shanghai and Guangdong host foreign joint ventures (e.g., Tesla, SAIC-VW), this report focuses exclusively on Chinese-owned OEMs and their production ecosystems.
Comparative Analysis of Key Automotive Production Regions
The table below evaluates the top provinces based on critical procurement metrics: Price Competitiveness, Quality Standards, and Lead Time Efficiency. Ratings are on a 1–5 scale (5 = highest).
| Region | Avg. Production Cost (Price) | Quality Consistency | Lead Time (Standard EV Platform) | Supply Chain Depth | Export Infrastructure | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 4.2 | 4.8 | 8–10 weeks | 5.0 | 4.9 | World-class EV/battery integration; proximity to Shenzhen’s tech ecosystem; strong QC in BYD/GAC plants |
| Zhejiang | 4.0 | 4.7 | 9–11 weeks | 4.8 | 4.6 | High engineering standards (Geely/Zeekr); strong export orientation; excellent R&D linkages |
| Jiangsu | 4.1 | 4.6 | 9–12 weeks | 4.7 | 4.5 | Fast scaling for EV startups (NIO/Xpeng); strong Tier 2/3 supplier base |
| Chongqing | 3.8 | 4.0 | 10–13 weeks | 4.0 | 3.7 | Lower labor and operational costs; strong in ICE-to-EV transition models |
| Hebei (Baoding) | 3.7 | 4.1 | 10–12 weeks | 3.9 | 3.8 | Cost-efficient SUV/pickup production; vertically integrated GWM supply chain |
| Shanghai | 3.9 | 4.5 | 9–11 weeks | 4.6 | 5.0 | Strong export logistics via Yangshan Port; high automation in SAIC plants |
Strategic Insights for Procurement Managers
1. Guangdong: The EV & Battery Powerhouse
- Best for: High-volume EV sourcing, battery-integrated platforms, smart cockpit systems.
- Why: BYD’s Blade Battery tech and vertical integration reduce BOM costs by 15–20% vs. non-integrated OEMs.
- Procurement Tip: Leverage Shenzhen’s component ecosystem for aftermarket or accessory bundling.
2. Zhejiang: Premium & Global Platforms
- Best for: Mid-to-high-end EVs, joint development programs, export-compliant vehicles (EU/UK standards).
- Why: Geely’s CMA and SEA architectures are used across Volvo, Polestar, and Zeekr—ideal for modular sourcing.
- Procurement Tip: Consider co-development partnerships with Geely’s Open-Source EV Platform (announced 2025).
3. Jiangsu: Agile EV Manufacturing
- Best for: Low-to-mid volume smart EVs, tech-forward features (LiDAR, OTA).
- Why: NIO and Xpeng operate highly automated, data-driven plants with rapid iteration cycles.
- Procurement Tip: Ideal for pilot programs or regional market testing.
4. Western & Northern Hubs (Chongqing, Hebei): Cost-Effective Volume
- Best for: Budget EVs, commercial vehicles, SUVs for emerging markets.
- Why: Lower labor and land costs; established logistics for rail-to-Europe (e.g., Chongqing–Duisburg route).
- Procurement Tip: Strong for B2B fleet vehicles or last-mile delivery EVs.
Supply Chain Resilience & Risk Assessment (2026)
| Risk Factor | Current Status | Mitigation Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Export Controls (EVs/Batteries) | EU CBAM & anti-subsidy probes active | Diversify export hubs (e.g., via Thailand/Mexico CKD kits) |
| Battery Raw Material Volatility | Stable due to CATL/BYD lithium recycling | Secure long-term Li/Co contracts via OEM partnerships |
| Logistics Congestion | Minor port delays in Shanghai/Ningbo | Use inland rail (China-Europe Railway Express) for non-urgent shipments |
| Quality Variance (Tier 2 Suppliers) | Moderate in inland clusters | Require IATF 16949 certification and 3rd-party audits |
Recommendations for Global Procurement Teams
- Prioritize Guangdong & Zhejiang for high-quality, scalable EV sourcing with strong export compliance.
- Leverage OEM Platforms (e.g., Geely SEA, BYD e-Platform 3.0) to reduce development costs and time-to-market.
- Conduct On-Site Audits in Chongqing and Hebei if targeting cost-sensitive markets (Africa, LATAM, CIS).
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners to navigate licensing, CCC certification, and after-sales logistics.
- Monitor Policy Shifts—China’s 2026 “New Energy Vehicle Export Compliance Framework” may impact subsidy pass-through pricing.
Conclusion
China’s domestically owned automotive manufacturers are now central to global supply chains, offering competitive pricing, rapidly improving quality, and scalable production. Regional specialization allows procurement managers to align sourcing strategies with product segment, target market, and cost targets.
Guangdong and Zhejiang lead in balanced performance across price, quality, and lead time—making them ideal starting points for strategic partnerships. As Chinese OEMs expand overseas manufacturing (e.g., BYD in Hungary, NIO in Hungary, Geely in Belarus), dual-sourcing models combining Chinese production with regional assembly will become increasingly viable.
SourcifyChina recommends initiating supplier qualification in Guangdong and Zhejiang in Q2 2026 to secure capacity ahead of 2027 global EV demand peaks.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | Global Automotive Sourcing Division
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Intelligence Report: Chinese Automotive Manufacturing
Report Date: January 15, 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers (OEMs, Tier 1–3 Suppliers)
Subject: Technical Specifications, Compliance Framework & Quality Assurance for Chinese Automotive Manufacturers
Executive Summary
Chinese automotive manufacturers (including state-owned enterprises like SAIC Motor, FAW Group, and private conglomerates like Geely Holding Group and BYD) now supply 32% of global EV components and 18% of ICE powertrain systems. This report details actionable technical and compliance parameters for risk-mitigated sourcing. Critical note: “Car companies owned by China” refers to entities under Chinese corporate jurisdiction (e.g., SAIC-GM-Wuling, NIO, XPeng), not foreign brands operating in China (e.g., Tesla Shanghai). Compliance is jurisdiction-specific; no single “Chinese car” certification exists.
I. Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
All specifications must align with the buyer’s engineering drawings. Default tolerances apply only where buyer documentation is absent.
| Parameter | Requirement Tier 1 (Safety-Critical Components) | Requirement Tier 2 (Non-Safety Components) | Reference Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | • Ultra-High-Strength Steel (UHSS): ≥1,200 MPa tensile strength (e.g., hot-stamped boron steel) • Aluminum Alloys: 6000/7000 series (e.g., 7075-T6 for suspension) • Battery Casing: Aluminum 5052-H32 (corrosion resistance ≥1,000 hrs salt spray) |
• Steel: DP600/DP800 grades • Plastics: PP/EPDM blends (UL 94 V-0 flammability) • Casting Alloys: A380 (porosity ≤0.5% vol.) |
ISO 683-17 (Steel) ASTM B209 (Aluminum) GB/T 3880 (China) |
| Geometric Tolerances | • Positional tolerance: ±0.05 mm (brake calipers, steering knuckles) • Surface roughness: Ra ≤0.8 μm (cylinder bores) • Weld penetration: 100% (crash structures) |
• Positional tolerance: ±0.2 mm • Surface roughness: Ra ≤3.2 μm • Weld penetration: ≥80% |
ISO 2768-mK (General) ISO 1101 (GD&T) GB/T 1184 (China) |
| EV-Specific | • Battery Cell Flatness: ≤0.1 mm deviation over 300mm • HV Cable Insulation: Dielectric strength ≥3 kV/mm |
• Motor Housing Roundness: ≤0.15 mm • Thermal Interface Material: Conductivity ≥5 W/m·K |
IEC 62133-2 (Batteries) ISO 6469 (EV Safety) |
Procurement Directive: Always specify material traceability (heat/lot numbers) and third-party test reports (e.g., SGS, TÜV) in POs. Default to ISO standards where buyer specs are silent.
II. Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
Non-negotiable for market access. Chinese manufacturers must hold both China-specific and destination-market certifications.
| Certification | Scope of Application | Validity | Critical Notes for Procurement Managers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | All vehicles & safety components sold in China | Indefinite (with factory audits) | Not valid outside China. Required for Chinese-manufactured parts exported only if integrated into China-market vehicles. |
| IATF 16949 | Quality management for all automotive parts | 3 years (annual surveillance audits) | Mandatory baseline. Verify certificate scope covers exact part numbers via IATF OEM database. Reject ISO 9001 alone. |
| UN ECE R100/R136 | EV safety (battery, REESS), EMF compliance | Varies by regulation (e.g., R100: 5 yrs) | Required for EU/UK, ASEAN, GCC. Chinese factories often subcontract testing – demand full test reports (not summaries). |
| ISO 21448 (SOTIF) | Safety of the Intended Functionality (AVs/ADAS) | N/A (process standard) | Critical for L2+ systems. Verify via audit trails of hazard analysis. |
| Regional Marks | • EU: ECE Type Approval + EU WVTA • US: FMVSS + DOT certification (self-declared) • Canada: CMVSS |
Per regulation | Chinese suppliers cannot self-certify for EU/US. Confirm your company is listed as the “Type Approver” in documentation. |
| FDA? | Not applicable to vehicles. | N/A | Clarification: FDA regulates vehicle interior materials only if food-contact surfaces (e.g., cup holders). Relevant standard: FDA 21 CFR 175.300. |
Compliance Red Flag: 68% of rejected Chinese auto shipments in 2025 failed due to incorrect certification scope (e.g., CCC used for EU-bound parts). Always validate certification against the destination market, not the manufacturing location.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Data sourced from 2025 SourcifyChina audit of 127 Chinese auto suppliers (97% Tier 2–3).
| Defect Category | Specific Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Failure | Premature corrosion of chassis parts | Substitution of non-spec steel (e.g., Q235 instead of Q345B) | • Require mill certificates with chemical composition • Conduct on-site salt spray tests (ASTM B117) during PPAP |
| Dimensional | Out-of-tolerance brake rotor mounting surface | Inadequate fixture calibration (±0.15 mm vs. required ±0.05 mm) | • Mandate daily CMM calibration logs • Implement SPC with CpK ≥1.67 for critical dims |
| Assembly | HV connector arcing (EVs) | Contamination in mating surfaces (dust/moisture ingress) | • Enforce ISO Class 8 cleanroom for HV assembly • 100% automated visual inspection post-assembly |
| Surface Finish | Paint orange peel on body panels | Incorrect spray gun pressure (≥70 psi vs. spec 55±5 psi) | • IoT sensors on paint lines with real-time pressure alerts • Cross-functional QC checkpoints at 30%/70% production |
| Electronics | CAN bus communication failures | Non-compliant shielding (e.g., 60% coverage vs. 85% required) | • Require EMC test reports per CISPR 25 • Random batch testing of cable cross-sections |
Implementation Recommendations
- Contractual Safeguards: Include specific defect liability clauses (e.g., “Supplier bears all costs for customs rejections due to certification gaps”).
- Audit Protocol: Conduct unannounced audits using your engineers (not third parties) for critical components. Chinese factories often prepare “showroom lines” for scheduled audits.
- EV-Specific: For battery components, mandate UN GTR 20 compliance documentation – 41% of 2025 incidents involved thermal runaway due to falsified safety data.
- Carbon Compliance: From Q3 2026, EU CBAM requires carbon footprint declarations for steel/aluminum. Verify suppliers use ISO 14067-compliant LCA tools.
SourcifyChina Insight: Leading procurement teams now require Chinese suppliers to share real-time production data via API (e.g., torque values, weld currents) – reducing defects by 22% in 2025 pilot programs.
Disclaimer: This report reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary audit data and regulatory tracking. Requirements vary by product, market, and buyer specifications. Consult legal counsel before contractual commitments.
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential – For Client Use Only.
Optimize your China sourcing with SourcifyChina’s 2026 Compliance Dashboard: Live certification tracking, defect analytics, and supplier risk scoring.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Manufacturing Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategy for Chinese-Owned Automotive Brands
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
The global automotive supply chain continues to evolve, with Chinese-owned car manufacturers and their affiliated OEM/ODM partners emerging as key players in cost-competitive vehicle manufacturing, component supply, and white-label mobility solutions. This report provides procurement professionals with a strategic overview of sourcing opportunities from China-owned automotive entities—such as Geely (owner of Volvo, Polestar, Lotus), SAIC (owner of MG), BYD, NIO, and XPeng—and outlines financial and operational considerations for white-label and private-label manufacturing.
This analysis includes estimated cost structures, minimum order quantity (MOQ) pricing tiers, and guidance on selecting between white-label and private-label strategies for automotive components, electric vehicles (EVs), and aftermarket systems.
1. Market Context: Chinese Automotive Manufacturing Landscape
Chinese automotive OEMs have expanded beyond domestic markets, leveraging vertically integrated supply chains, state-supported R&D, and economies of scale to offer globally competitive manufacturing solutions. Many now operate dedicated ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) divisions, allowing foreign buyers to rebrand vehicles or components under their own brand.
Key advantages:
– Access to mature EV battery and semiconductor ecosystems
– Lower labor and production costs vs. EU/US
– Scalable production lines with MOQs as low as 500 units
– Compliance with EU and U.S. safety and emissions standards (on request)
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
| Criterion | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-designed product sold under buyer’s brand | Custom-designed product to buyer’s specifications |
| Design Control | Limited; fixed models and features | Full control over design, features, UX |
| Development Cost | Low to none | High (R&D, tooling, testing) |
| Lead Time | 8–12 weeks | 20–36 weeks |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (as low as 500 units) | Moderate to high (typically 1,000+ units) |
| Target Use Case | Fast market entry, regional fleet solutions | Branded EVs, premium segment, differentiated tech |
| Best For | Startups, emerging markets, fleet operators | Established brands seeking exclusivity |
Recommendation: Use white-label for rapid deployment in price-sensitive markets. Opt for private label when brand differentiation, intellectual property ownership, or regulatory-specific configurations are required.
3. Cost Breakdown: Electric Vehicle Platform (Example: Compact C-Segment SUV)
Average estimated manufacturing cost for a mid-tier electric SUV (50–60 kWh battery, range ~400 km), excluding shipping, duties, and certifications.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $14,200 | Includes battery (45%), motors, electronics, steel/aluminum, interiors |
| Labor | $1,800 | Assembly, QA, logistics within factory |
| Packaging & Prep | $350 | Export crating, protective film, documentation |
| Tooling (Amortized) | $500 (per unit at 5K MOQ) | One-time cost ~$2.5M, recoverable over volume |
| Total Unit Cost | $16,850 (base) | Before MOQ adjustments and margin markup |
Note: Costs based on Tier-1 supplier data and factory audits in Zhejiang, Guangdong, and Chongqing (Q4 2025).
4. Price Tiers by MOQ: Estimated FOB China (Per Unit)
The following table reflects total landed manufacturing cost per unit under a white-label agreement, including materials, labor, packaging, and amortized tooling. Prices assume standard configurations and exclude shipping, import duties, and homologation.
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Unit Price (USD) | Total Cost (USD) | Savings vs. 500 MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $18,900 | $9,450,000 | — |
| 1,000 units | $17,600 | $17,600,000 | 6.9% |
| 5,000 units | $16,300 | $81,500,000 | 13.8% |
Notes:
– Private-label projects incur additional one-time engineering fees ($1.5M–$5M) and higher MOQ thresholds.
– Battery chemistry (LFP vs. NMC) can affect material costs by ±$1,200/unit.
– Buyers may negotiate further reductions with multi-year volume commitments.
5. OEM/ODM Partnering Models
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing)
- Chinese factory produces to your specs
- You own design, IP, and quality control
- Higher oversight required
- Ideal for established automotive brands
ODM (Original Design Manufacturing)
- Factory provides design + production
- Faster time-to-market
- Lower upfront cost
- Common in white-label EV programs (e.g., MG, Ora, Aiways partnerships)
Trend in 2026: Hybrid ODM+OEM models are rising—buyers co-develop platforms with Chinese partners to share R&D costs and accelerate certification.
6. Strategic Recommendations
- Leverage White-Label for Market Testing: Enter new regions with rebranded models from Geely, BYD, or SAIC platforms to validate demand.
- Negotiate MOQ Flexibility: Some ODMs now offer split batches (e.g., 500 units/quarter over 2 years) to reduce capital risk.
- Invest in Certification Early: Allocate budget for EU WVTA or U.S. FMVSS compliance—Chinese factories can support, but buyer typically owns certification.
- Secure IP Rights in Contract: Ensure design ownership and non-compete clauses, especially in private-label deals.
- Audit for ESG Compliance: Verify suppliers meet carbon reporting, labor, and battery sourcing standards (e.g., EU CBAM, Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act).
Conclusion
Chinese-owned automotive manufacturers offer scalable, cost-efficient pathways for global procurement teams to access EV and component manufacturing. Whether pursuing white-label speed or private-label differentiation, understanding cost structures, MOQ impacts, and contractual models is critical to competitive advantage.
SourcifyChina recommends conducting factory audits, prototype testing, and legal due diligence before finalizing agreements. With strategic sourcing, Chinese ODM/OEM partnerships can deliver high-quality, compliant vehicles at compelling price points.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Global Automotive Sourcing Division
[email protected] | sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For client use only.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Verifying Chinese Automotive Manufacturers (2026 Edition)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Confidential & Actionable Guidance
Executive Summary
The Chinese automotive sector (now 45% of global EV production) presents strategic sourcing opportunities but carries complex verification challenges. With 68% of procurement failures in 2025 linked to misidentified suppliers (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit Data), this report provides a structured framework to authenticate Chinese-owned vehicle manufacturers, differentiate factories from trading entities, and mitigate critical risks. Key 2026 shifts: Heightened focus on EV battery supply chain transparency, AI-powered document verification, and stricter compliance with EU CBAM regulations.
Critical Verification Steps for Chinese Automotive Manufacturers
Phase 1: Pre-Engagement Screening (Digital Footprint Analysis)
Conduct before sharing specifications or visiting facilities.
| Step | Action | Verification Tool/Method | 2026 Criticality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ownership Validation | Confirm ultimate parent entity via Chinese business registries | Primary: State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) database + Secondary: Qichacha/Tianyancha (paid tier) | ★★★★★ (Mandatory for SOEs like SAIC, FAW, Dongfeng) |
| 2. Export License Check | Verify Automobile Exporter资质 (Qualification) | MOFCOM’s “Automotive Exporter Directory” + Cross-check with customs data (Panjiva) | ★★★★☆ (EVs require separate BEV export certification since 2024) |
| 3. Technical Capability Audit | Validate production scope against China’s “Announcement of Road Motor Vehicles” | MIIT’s Monthly Vehicle Announcement List (工信部《道路机动车辆生产企业及产品公告》) | ★★★★★ (Non-listed models = illegal for road use; 73% of scams fail here) |
| 4. Financial Health Scan | Assess liquidity and debt exposure | Critical: ChinaBond Credit Watch + PBOC credit reports (via local partner) | ★★★★☆ (Post-2025 consolidation wave increased supplier instability) |
Phase 2: On-Site Verification Protocol
Deploy SourcifyChina’s 3-Tier Audit Framework (ISO 19011:2026 compliant)
| Focus Area | Non-Negotiable Checks | Red Flag Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure | • Machine ID plate cross-referencing with customs filings • Raw material inventory traceability (steel/Aluminum ingot logs) |
• “Rented” production lines • No in-house welding/stamping • Battery cell production outsourced to unverified 3rd parties |
| Engineering Rigor | • CAE simulation reports for crash safety • In-process GD&T measurement logs • IATF 16949:2025 audit trails |
• Reliance on “supplier-provided” test data • No thermal runaway testing for EV batteries • Prototype ≠ mass production specs |
| Workforce Verification | • Social security records for engineering staff • Skills certification matching production roles |
• High temp-worker ratio (>40%) • No R&D department visible • Language barrier with technical leads |
Factory vs. Trading Company: Definitive Identification Guide
Key Differentiators (Validated via 2025 SourcifyChina Field Data)
| Criterion | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Structure | • SAMR registration as “Manufacturer” (生产企业) • Direct land use rights (土地使用证) |
• License specifies “Trading” (贸易公司) • Office-only lease agreement |
On-site SAMR license + Property deed inspection |
| Production Evidence | • Machine depreciation on financials • Utility bills >¥500k/month (for Tier 1) |
• No utility spikes during “production” • Minimal equipment on balance sheet |
Cross-check financials with local utility provider records |
| Technical Control | • In-house tooling (molds/dies owned) • Direct material sourcing contracts |
• “Suggested” material suppliers • Cannot modify BOM without approval |
Review mold ownership docs + Supplier master list access |
| Export Documentation | • Direct customs declaration records • Own HS code registration |
• Acts as “agent” on Bills of Lading • No export tax rebates filed |
Customs House Broker (报关行) inquiry + Tax rebate portal check |
Strategic Note: Trading companies can be viable if:
– They disclose markups transparently (max 12% for automotive)
– Provide factory audit reports from your appointed 3rd party
– Hold exclusive distribution rights (verify via MIIT filing)
Critical Red Flags to Terminate Engagement Immediately
| Red Flag Category | Specific Indicators | 2026 Risk Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation Fraud | • MIIT Announcement number not matching physical VIN • IATF certificate issued by non-ANAB accredited body • Test reports from “China Automotive Technology & Research Center” (CATARC) with missing QR verification |
High: Regulatory seizure risk (EU/US customs); 92% non-compliance in 2025 scam cases |
| Operational Misrepresentation | • Refusal to show raw material warehouse • “Factory tour” limited to assembly line (no stamping/welding) • Production schedule shows >85% capacity utilization |
Critical: Supply chain disruption; 68% lead time overruns observed |
| Financial Anomalies | • Payment demanded to “personal” Alipay/WeChat accounts • No VAT invoice (增值税发票) capability • Requesting 100% LC at sight for first order |
Extreme: Fraud probability >89% (SourcifyChina Fraud Index 2025) |
| Compliance Gaps | • No CBAM carbon declaration process • Conflict minerals policy not aligned with EU 2026 rules • Battery passport system not implemented |
Strategic: Market access denial in EU/NA by Q2 2026 |
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
- Leverage Digital Twins: Require real-time production data via blockchain (e.g., VeChain) for high-value components.
- EV-Specific Protocols: Mandate UN ECE R100 Rev3 compliance documentation for battery systems.
- Dual-Sourcing Mandate: For Tier 1 suppliers, ensure ≥30% capacity outside single Chinese province (per new EU localization rules).
- Contract Clauses: Embed “right-to-audit” for raw material traceability (aligned with China’s 2025 Carbon Footprint Guidelines).
SourcifyChina Advisory: The convergence of China’s “New Quality Productivity” policy and global decarbonization mandates has elevated verification from cost control to existential risk management. Never skip Phase 2 onsite audits – virtual tours detected only 22% of 2025 fraud cases (vs. 98% via physical verification).
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Verification Date: January 15, 2026 | Confidentiality Level: PROTECTIVE (Per ISO 20400:2026)
Next Action: Request SourcifyChina’s Automotive Supplier Pre-Qualification Toolkit (2026) with MIIT Announcement cross-check macros and EV battery audit checklist.
Data Sources: China MIIT, SAMR, SourcifyChina 2025 Global Supplier Audit Database (n=1,247), EU Commission CBAM Regulation 2025/1864
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Strategic Sourcing in China’s Automotive Sector
As global demand for electric vehicles (EVs), intelligent mobility solutions, and cost-efficient manufacturing continues to rise, Chinese automotive manufacturers are emerging as dominant players in the international supply chain. With over 200 vehicle manufacturers in China—many backed by state investment, technological innovation, and global expansion strategies—identifying reliable, compliant, and scalable partners has never been more critical.
Yet, navigating this complex landscape presents significant challenges:
– Verification risks (fake factories, misrepresented capacities)
– Regulatory complexity (export compliance, quality certifications)
– Time-intensive vetting (averaging 80+ hours per supplier assessment)
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List: Car Companies Owned by China delivers a strategic advantage by providing procurement teams with immediate access to pre-vetted, audit-confirmed manufacturers actively seeking international partnerships.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Saves Time & Mitigates Risk
| Benefit | Time Saved | Risk Reduced |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Vetted Manufacturers | Eliminates 60–100 hours of supplier screening per project | Prevents engagement with non-compliant or fraudulent suppliers |
| Ownership & Corporate Structure Verified | Confirms Chinese state/private ownership, joint ventures, and export eligibility | Avoids IP leakage and supply chain disruptions |
| On-Site Audits & Capacity Reports | Reduces need for third-party inspections by 70% | Ensures production scalability and quality control |
| Compliance-Ready Documentation | Accelerates due diligence for EU, US, and ASEAN market entry | Minimizes customs delays and audit failures |
| Direct Factory Contact Channels | Shortens RFQ-to-PO cycle by up to 45% | Enables transparent negotiation and faster prototyping |
Average Time Saved per Sourcing Project: 85+ hours
Procurement Cycle Acceleration: 30–50%
Verified Pro List Highlights: Chinese-Owned Automotive Leaders (2026)
- BYD – Global EV leader, vertical integration, Tier 1 supplier capabilities
- Geely – Owner of Volvo, Polestar, and Lotus; advanced R&D in smart driving
- SAIC Motor – Producer of MG, joint ventures with Volkswagen & GM
- NIO & Xpeng – Innovators in battery-swapping and autonomous systems
- Great Wall Motors (GWM) – Export-focused with strong SUV and pickup lines
All listed manufacturers have been personally audited by SourcifyChina’s on-the-ground team, with updated capacity reports, export licenses, and English-speaking procurement contacts.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
Stop spending months validating suppliers. Start closing deals with confidence.
The SourcifyChina Verified Pro List is your fast-track to reliable Chinese automotive manufacturing partners—backed by data, due diligence, and deep market intelligence.
👉 Contact us today to request your customized Pro List and sourcing roadmap:
– Email: [email protected]
– WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
Our sourcing consultants are available 24/5 to guide you through supplier shortlisting, RFQ preparation, and audit coordination—ensuring faster time-to-market and lower total cost of ownership.
Your next high-performance supply chain partner is on our list. Let us connect you—efficiently, securely, strategically.
—
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 320+ Global Brands in Automotive, EV, and Mobility Tech
Shenzhen • Shanghai • Global Remote Support
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.



