The global capacitive touch sensing market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by rising demand for intuitive user interfaces across consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 11.5 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 6.5% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research reports robust growth fueled by advancements in touchscreen technologies, increasing adoption of IoT-enabled devices, and the integration of touch sensors in next-generation automotive infotainment systems. With Asia Pacific leading in both production and consumption—attributed to strong electronics manufacturing in China, South Korea, and Japan—the competitive landscape is rapidly evolving. As innovation accelerates and demand for sleek, responsive interfaces grows, a select group of manufacturers are emerging as key players, shaping the future of human-machine interaction. Here are the top 10 capacitive touch sensing manufacturers leading this technological transformation.
Top 10 Capacitive Touch Sensing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PRODUCTS
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pixart.com
Key Highlights: Capacitive Touch · Integrated Chip Design Service · Customized ASICs Services … Proximity Alert & Ambient Light Sensing · Smart Input Technology. int(2) int ……
#2 Capacitive Touch Sensing Technology Overview
Domain Est. 1989
Website: synaptics.com
Key Highlights: Synaptics capacitive-touch sensing technology addresses both sides of that user-experience equation by enabling features such as vertical-dimension navigation….
#3 Capacitive Technology
Domain Est. 1995
Website: microtouch.com
Key Highlights: Projected capacitive touch technology has many benefits including multi-touch capability, extreme durability and superior optics….
#4 Capacitive Touch
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cirque.com
Key Highlights: The Technology of Touch Cirque solutions are all built upon the technology of capacitive touch sensing. By sensing the minute difference in electrical fields ……
#5 Capacitive Sensors
Domain Est. 1999
Website: kla.com
Key Highlights: Explore KLA’s OEM capacitive sensors — high‑performance, non‑contact measurement solutions for proximity, position, displacement, run‑out, autofocus and ……
#6 Touch the Future with Capacitive Sensing
Domain Est. 2015
Website: otto-controls.com
Key Highlights: Capacitive touch sensing is an evolving technology that is now found in next-generation grips and joysticks, providing operators with enhanced functionality….
#7 Capacitive Touch Panel & Overlay
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jae.com
Key Highlights: JAE’s automotive capacitive touch panels began mass production in 2012, which is earlier than other companies, and have more than seven years of results….
#8 Capacitive sensors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: balluff.com
Key Highlights: Capacitive sensors detect objects and the fill level of all non-conducting materials, liquids, pellets, and powders directly or through a container wall….
#9 Capacitive Touch HMIs
Domain Est. 2002
Website: renesas.com
Key Highlights: Explore Renesas’ advanced capacitive touch solutions for human-machine interfaces (HMIs), offering high sensitivity, noise tolerance, easy development tools ……
#10 Capacitive Sensors
Domain Est. 2019
Website: ams-osram.com
Key Highlights: ams OSRAM’s capacitive sensor provides flexible, reliable and long-lasting capacitive sensing for human interaction detection….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Capacitive Touch Sensing
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Capacitive Touch Sensing
The capacitive touch sensing market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding applications, and shifting consumer demands. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Proliferation in Automotive and Industrial HMI:
The automotive sector will be a major growth driver. Capacitive touch sensing will increasingly replace physical buttons in center consoles, climate controls, and lighting systems, enhancing aesthetics and enabling customizable user interfaces. Advanced features like in-display touch for infotainment, gesture recognition, and haptic feedback integration will become standard in mid-to-high-end vehicles. Similarly, industrial applications will leverage capacitive sensors for robust, sealed human-machine interfaces (HMIs) in harsh environments, improving reliability and design flexibility.
2. Rise of Advanced Sensing Technologies:
By 2026, there will be a notable shift toward more sophisticated capacitive solutions:
* Force Touch Integration: Combining capacitive touch with force-sensing capabilities will enable pressure-sensitive interactions, allowing for more intuitive control (e.g., zooming, menu navigation).
* 3D and Proximity Sensing: Enhanced multi-axis and proximity detection will support gesture-based controls and context-aware interfaces, particularly in consumer electronics and automotive applications.
* Transparent and Flexible Sensors: Growth in foldable devices, curved displays, and transparent electronics will fuel demand for flexible and transparent capacitive sensors using materials like silver nanowires and conductive polymers.
3. Demand for Enhanced User Experience (UX):
Consumers and OEMs will prioritize seamless, intuitive interactions. This will drive the integration of haptic feedback (tactile response) with capacitive touch, simulating physical button clicks and improving usability. Design trends will favor minimalism, pushing capacitive solutions to enable sleek, bezel-less, and button-free device designs.
4. Expansion into Wearables and Medical Devices:
Capacitive sensing will see increased adoption in wearables (smartwatches, AR/VR headsets) for gesture control and biometric integration. In healthcare, touch interfaces on medical equipment will benefit from capacitive technology’s durability, ease of cleaning, and ability to function through thin protective barriers.
5. Focus on Security and Reliability:
With broader deployment, ensuring touch reliability under challenging conditions (wet, gloved, or dirty environments) will be critical. Advancements in signal processing algorithms and sensor design will improve performance in these scenarios. Additionally, integration with authentication systems (e.g., touch-based biometrics) will grow, enhancing device security.
6. Sustainability and Material Innovation:
Environmental concerns will push manufacturers toward sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs. The development of eco-friendly conductive inks and substrates, along with low-power sensor architectures, will be key differentiators in the market.
In conclusion, by 2026, the capacitive touch sensing market will be characterized by smarter, more responsive, and versatile interfaces across diverse industries, underpinned by continuous innovation in materials, integration, and user-centric design.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Capacitive Touch Sensing Solutions (Quality and IP)
Sourcing capacitive touch sensing technology—whether as a component, module, or integrated solution—can introduce significant risks if not managed carefully. Two critical areas where companies often encounter problems are product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to delays, increased costs, legal disputes, and compromised product performance.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Sensor Performance Across Environments
A common quality issue arises when capacitive touch sensors perform well in controlled lab conditions but fail in real-world environments. Factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, electromagnetic interference (EMI), and proximity to conductive materials can drastically affect touch sensitivity and reliability. Sourcing from suppliers without rigorous environmental testing protocols can result in field failures and customer dissatisfaction.
Poor Manufacturing Consistency
Low-cost or inexperienced manufacturers may lack stringent quality control processes, leading to high variance in sensor performance across production batches. This inconsistency can manifest as differences in touch response, false triggers, or dead zones, undermining user experience and brand reputation.
Inadequate Durability and Longevity
Capacitive touch surfaces, especially those with printed or thin-film overlays, may degrade over time due to scratches, chemical exposure, or UV radiation. Sourcing without verifying material durability and lifecycle testing (e.g., millions of touch cycles) can lead to premature failure in end products.
Lack of Comprehensive Testing and Certification
Some suppliers may not provide full test reports or certifications (e.g., IEC 61000 for EMI, or IP ratings for dust/water resistance). Without these, it’s difficult to validate quality claims, increasing the risk of non-compliance and reliability issues.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unlicensed or Infringing Technology
A significant risk when sourcing from third-party vendors—especially in regions with weak IP enforcement—is the potential use of patented algorithms, firmware, or hardware designs without proper licensing. Integrating such technology can expose your company to infringement lawsuits, product recalls, or costly litigation.
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When working with suppliers on custom touch solutions, contracts may fail to explicitly state who owns the resulting IP. Suppliers might retain rights to design elements, firmware, or layout innovations, limiting your freedom to manufacture, modify, or sell the product without permission or royalties.
Reverse-Engineered or Clone Components
Some vendors offer “compatible” or “cost-effective” capacitive controllers that are actually reverse-engineered versions of established brands. These clones may infringe on patents and often lack reliability, technical support, or long-term availability, posing both legal and operational risks.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
Poor documentation of design sources, component origins, and software licenses makes it difficult to perform IP audits or defend against infringement claims. This opacity can be especially problematic during mergers, acquisitions, or regulatory reviews.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, companies should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including on-site audits and reference checks.
– Require full test reports, environmental validation, and compliance certifications.
– Perform independent lab testing under real-world conditions.
– Engage legal counsel to review contracts for clear IP ownership and indemnification clauses.
– Verify component authenticity and ensure firmware/software licensing is legitimate.
– Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record and transparent development practices.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during the sourcing process, businesses can ensure reliable performance, protect their innovations, and reduce long-term liabilities.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Capacitive Touch Sensing
Capacitive touch sensing technology is widely used in consumer electronics, industrial controls, automotive interfaces, and medical devices. Ensuring proper logistics and compliance throughout the supply chain and product lifecycle is essential for reliability, safety, and market access. This guide outlines key considerations for managing the logistics and regulatory compliance of capacitive touch sensing components and systems.
Supply Chain & Inventory Management
Effective supply chain management ensures timely delivery, cost efficiency, and quality control of capacitive touch sensing components such as touch controllers, sensors, and overlay materials.
- Component Sourcing: Source capacitive touch ICs, conductive films (e.g., ITO), and glass or plastic overlays from reputable, certified suppliers. Prioritize partners with ISO 9001 certification.
- Lead Time Planning: Account for extended lead times for custom touch sensors or region-specific components. Maintain safety stock for critical items.
- Inventory Rotation: Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) practices to prevent aging of sensitive materials, especially conductive coatings prone to environmental degradation.
- Cold Chain & Environmental Controls: While capacitive sensors are generally not temperature-sensitive, store components in dry, climate-controlled environments to avoid moisture damage or delamination.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging and handling are crucial to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD), physical damage, and contamination.
- ESD Protection: Capacitive touch controllers and sensors are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Use static-shielding bags, conductive foam, and ESD-safe packaging materials.
- Mechanical Protection: Use rigid packaging with cushioning to protect fragile touch overlays and glass substrates during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “ESD Sensitive,” “Do Not Stack”) and include compliance markings such as RoHS or REACH.
- Clean Handling: Use lint-free gloves when handling touch surfaces to prevent oil contamination, which can affect sensor sensitivity and durability.
Regulatory Compliance
Capacitive touch devices must comply with regional and international regulations based on their application and market.
Electrical & Safety Standards
- IEC 62368-1 (Audio/Video, Information and Communication Technology Equipment): Required for consumer and commercial electronics incorporating capacitive touch interfaces.
- UL/CSA Certification: Mandatory in North America for end-use safety approval.
- Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU: Applies to devices operating within specified voltage ranges in the EU.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- FCC Part 15 (USA): Ensures devices do not emit harmful interference and are immune to common electromagnetic disturbances.
- CE-EMC Directive 2014/30/EU: Required for products sold in the European Union.
- Conducted and Radiated Emissions Testing: Capacitive touch systems must be tested to ensure they do not interfere with other electronics, especially in automotive and medical applications.
Environmental & Material Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): Prohibits the use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in electronic components (EU Directive 2011/65/EU).
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals): Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in materials used.
- Conflict Minerals Compliance (Dodd-Frank Act, Section 1502): Applies to companies supplying to the U.S. market; requires due diligence on sourcing of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold.
Industry-Specific Requirements
- Automotive: Compliance with AEC-Q100 for integrated circuits and ISO 16750 for environmental stress testing.
- Medical Devices: Must meet IEC 60601-1 for electrical safety and IEC 62304 for software lifecycle management if the touch interface includes embedded software.
- Industrial Equipment: May require IP (Ingress Protection) Rating for dust and water resistance, especially if used in harsh environments.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain comprehensive documentation to support compliance audits and ensure product traceability.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): Include full component traceability, including manufacturer part numbers, batch/lot numbers, and compliance status.
- Certificates of Conformity (CoC): Obtain CoCs for critical components, especially touch controllers and sensors.
- Test Reports: Archive EMC, safety, and environmental test results from accredited labs.
- RoHS/REACH Declarations: Maintain supplier-provided compliance documentation for all materials.
End-of-Life & Recycling
Capacitive touch devices must be designed and managed with end-of-life considerations.
- WEEE Compliance (EU): Register products under the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive and provide take-back and recycling options.
- Design for Disassembly: Use modular designs to facilitate recycling of glass, plastics, and electronic components.
- Labeling: Include WEEE symbol and material identification codes on product packaging and devices.
Summary
Managing logistics and compliance for capacitive touch sensing systems requires careful coordination across sourcing, packaging, regulatory certification, and end-of-life planning. Adherence to international standards not only ensures market access but also enhances product reliability and user safety. By integrating compliance into every stage of the supply chain, manufacturers can reduce risk, avoid penalties, and support sustainable practices.
Conclusion for Sourcing Capacitive Touch Sensing
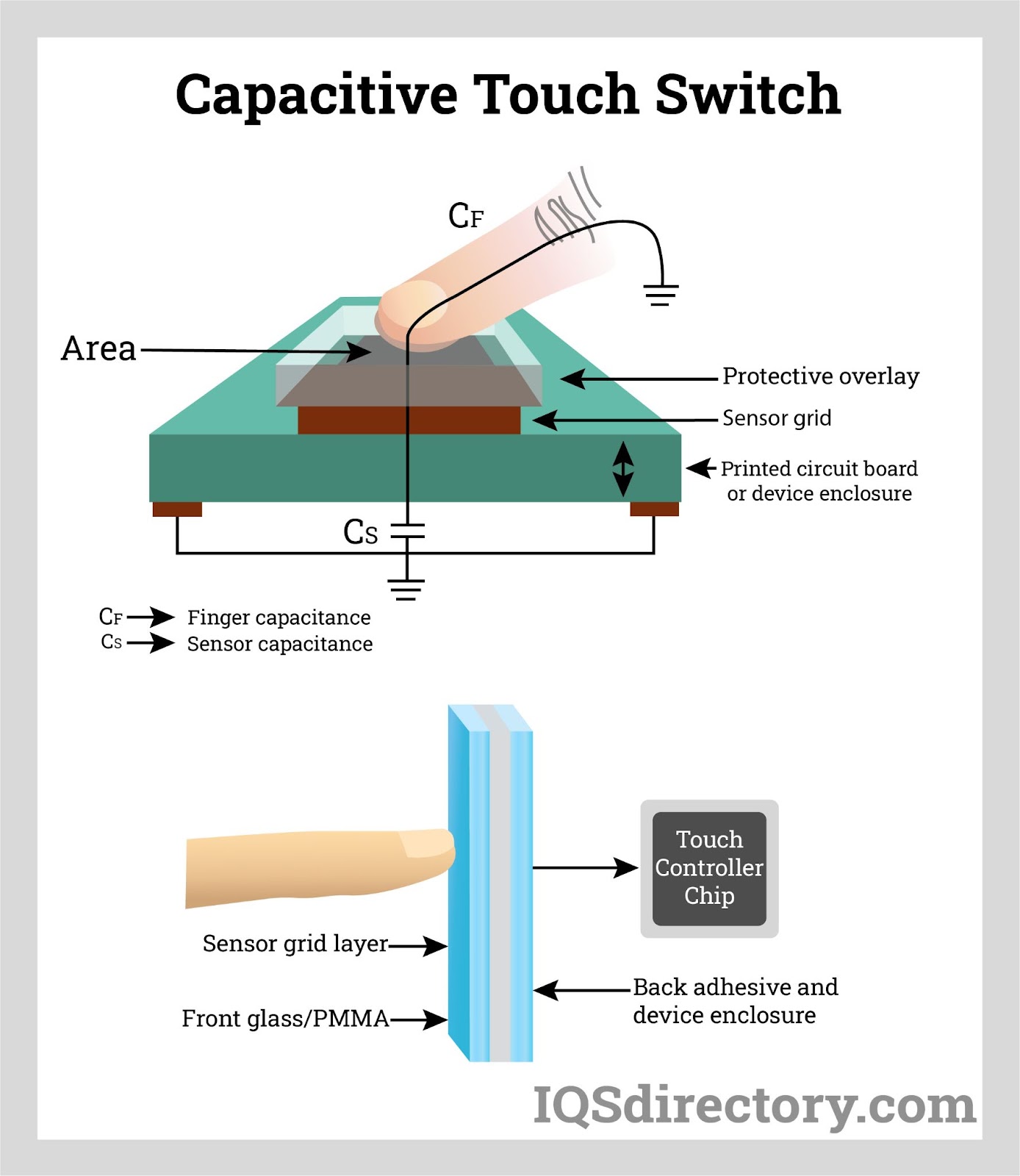
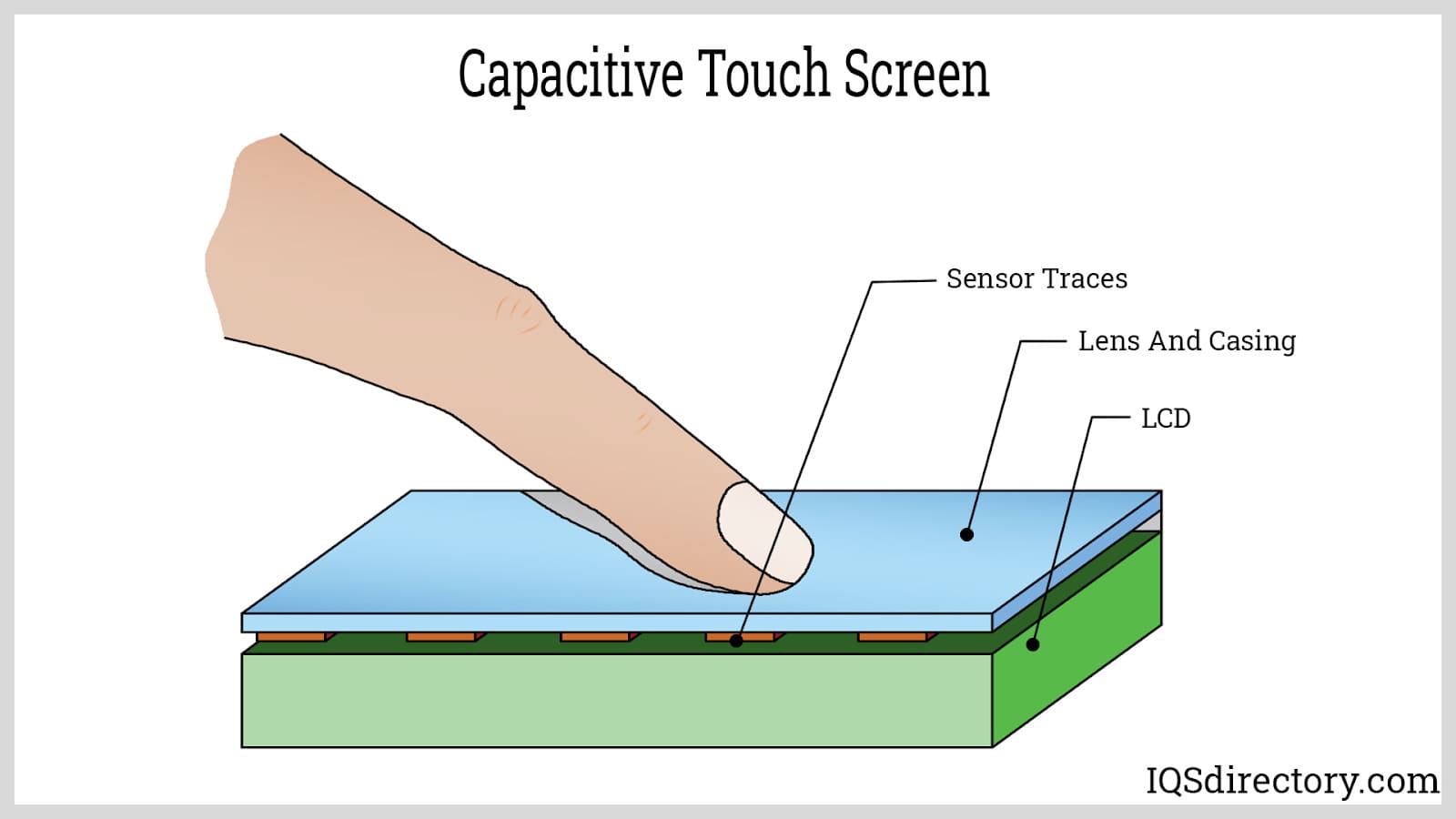
Sourcing capacitive touch sensing technology requires a strategic evaluation of technical requirements, application environment, cost constraints, and supplier capabilities. Capacitive touch sensing offers significant advantages over mechanical interfaces, including enhanced durability, improved aesthetics, and better user experience, making it ideal for applications in consumer electronics, industrial controls, automotive interfaces, and medical devices.
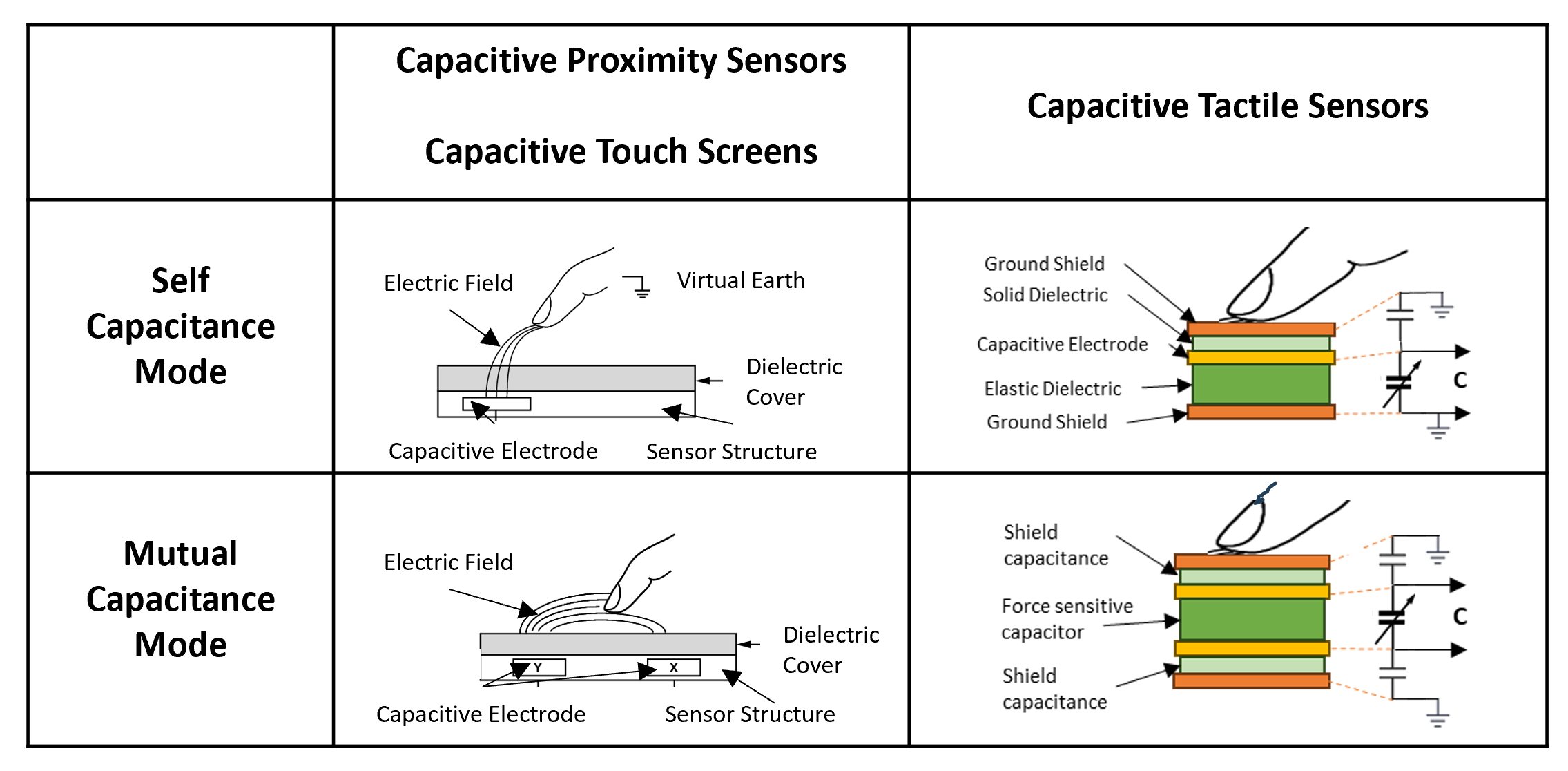
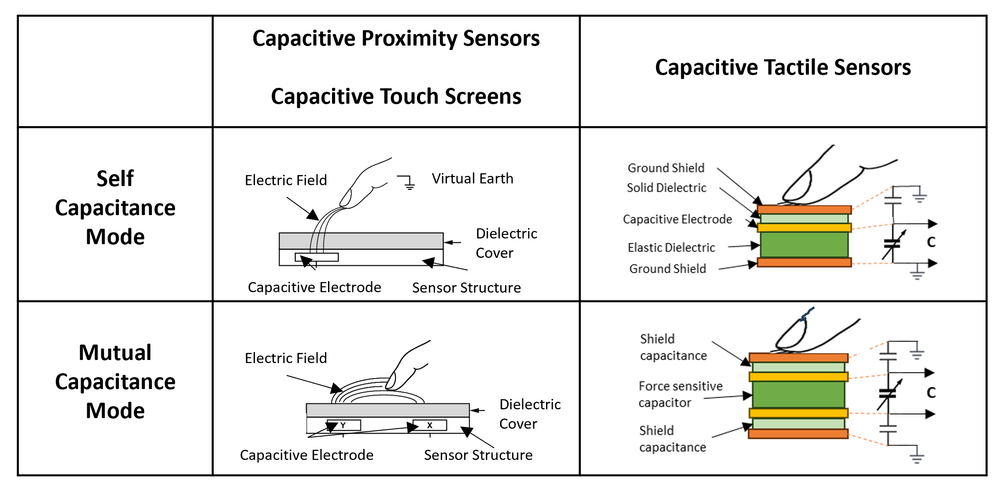
When sourcing, it is essential to consider factors such as sensor accuracy, responsiveness, environmental resilience (e.g., moisture, temperature, and glove touch support), and integration complexity. Choosing between self-capacitive and mutual-capacitive sensing depends on the desired functionality—such as single-touch vs. multi-touch support. Additionally, partnering with experienced suppliers or module manufacturers can accelerate development, reduce time-to-market, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
In summary, successful sourcing of capacitive touch sensing involves balancing performance needs with cost and supply chain reliability. By selecting the right technology, design approach, and supplier partners, companies can implement robust, responsive, and user-friendly interfaces that meet both current demands and future scalability.