The global capacitance battery market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy storage solutions in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and consumer electronics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global supercapacitor market—central to capacitance-based energy storage—was valued at USD 580.4 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1.26 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 13.7% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by advancements in materials science, increasing adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles, and supportive government policies promoting clean energy technologies. As industries prioritize high-efficiency, fast-charging, and long-cycle-life power solutions, capacitance battery manufacturers are at the forefront of innovation. The following list highlights the top nine companies leading this transformation through technological excellence, strategic partnerships, and substantial R&D investments.
Top 9 Capacitance Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Amperex Technology Limited
Domain Est. 2000
Website: atlbattery.com
Key Highlights: ATL is the world’s leading producer and innovator of lithium-ion batteries. We are known worldwide for our high-tech, high-volume prowess….
#2 Batteries
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata provides various kinds of battery systems and battery products such as storage battery systems, lithium-ion secondary batteries, micro fuel cells, ……
#3 High power energy storage solutions
Domain Est. 2009
Website: skeletontech.com
Key Highlights: Skeleton Technologies is the world’s leading manufacturer of graphene-based supercapacitors. Rebuilding industry for a net-zero future….
#4 NanoGraf Corporation
Domain Est. 2012
Website: nanograf.com
Key Highlights: NanoGraf leads in high-energy anode solutions for lithium-ion batteries, enhancing EV range, charging, and longevity. Discover our innovative technology ……
#5 LiCAP Technologies, Inc.
Domain Est. 2018
Website: licaptech.com
Key Highlights: The Activated Dry Electrode® process enables cost-effective and environmentally friendly manufacturing of batteries and capacitors with superior performance….
#6 American Battery Technology Company
Domain Est. 2020
Website: americanbatterytechnology.com
Key Highlights: ABTC is an advanced technology, first-mover lithium-ion battery recycling and primary battery metal extraction company that utilizes internally developed ……
#7 Group14
Website: group14.technology
Key Highlights: Group14’s newest silicon battery material factory, BAM-3, is delivering SCC55® to Asia’s battery industry and strengthening the global battery supply chain….
#8 Nichicon
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nichicon.com
Key Highlights: Nichicon is a global leader in advanced capacitor technologies. We offer a capacitor for every design need—from high temperature and high ripple current to ……
#9 Quality Deep Cycle Batteries
Domain Est. 1997
Website: usbattery.com
Key Highlights: Reliable, deep cycle batteries from U.S. Battery Mfg Co. High-quality 6V, 8V, 12V, 24V, and 48V batteries deliver power you can depend on!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Capacitance Battery

H2: Projected Market Trends for Capacitance Batteries in 2026
By 2026, the global capacitance battery market—particularly ultracapacitors and hybrid energy storage systems—is expected to experience significant growth driven by technological advancements, rising demand for energy efficiency, and increasing adoption in electric mobility and renewable energy integration. Below are key trends shaping the capacitance battery landscape:
-
Expansion in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Hybrid Transportation
Capacitance batteries are projected to play a critical role in regenerative braking systems and power-assist applications in EVs, buses, and rail systems. Their ability to charge and discharge rapidly makes them ideal for capturing energy during deceleration. Automakers are increasingly integrating hybrid systems that combine lithium-ion batteries with ultracapacitors to extend battery life and improve performance. -
Integration with Renewable Energy Storage
As renewable energy capacity grows, grid stability becomes a challenge due to intermittent generation. Capacitance batteries offer fast-response energy storage, helping to balance supply and demand fluctuations. By 2026, they are expected to be widely deployed in solar and wind farms for short-duration grid stabilization and frequency regulation. -
Advancements in Materials and Energy Density
Ongoing R&D in electrode materials—such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, and transition metal oxides—is expected to significantly improve the energy density of ultracapacitors. These innovations will narrow the performance gap with traditional batteries, making capacitance solutions more viable for longer-duration applications. -
Growth in Industrial and Consumer Electronics Applications
Capacitance batteries are finding new applications in industrial automation, backup power systems (UPS), and consumer electronics requiring burst power or rapid charging. Their long cycle life and reliability in extreme temperatures are driving adoption in harsh environments. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is expected to dominate the market due to strong government support for green technologies and a robust electronics manufacturing base. North America and Europe will see growth driven by clean energy policies and investments in smart grid infrastructure. -
Sustainability and Recycling Initiatives
With increasing focus on circular economy principles, manufacturers are developing more sustainable production methods and end-of-life recycling processes for capacitance batteries. This is expected to improve environmental credentials and reduce lifecycle costs. -
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Partnerships
Major players such as Maxwell Technologies (a Tesla subsidiary), Panasonic, Skeleton Technologies, and Ioxus are investing heavily in scaling production and forming strategic alliances with automotive and energy firms. Consolidation and joint ventures are expected to accelerate innovation and market penetration.
In summary, by 2026, capacitance batteries will be a cornerstone of next-generation energy storage solutions, complementing conventional batteries with superior power density, longevity, and efficiency. Their integration into diverse sectors underscores a transformative shift toward smarter, more resilient energy systems.
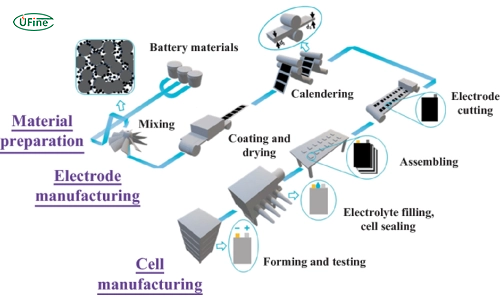
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Capacitance Batteries: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing capacitance batteries—often referring to supercapacitors or ultracapacitors—requires careful attention to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Inadequate due diligence can lead to performance failures, supply chain disruptions, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls in these two critical areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Insufficient Verification of Performance Specifications
Many suppliers, particularly in emerging markets, may exaggerate key performance metrics such as capacitance, energy density, cycle life, and temperature tolerance. Buyers often accept datasheets at face value without independent validation. This can result in batteries that degrade prematurely or fail under real-world conditions, leading to costly field failures.
2. Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Capacitance batteries are sensitive to variations in materials and production processes. Sourcing from manufacturers without certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of batch-to-batch inconsistencies. Poor electrode coating, electrolyte impurities, or sealing defects can significantly impact reliability and safety.
3. Lack of Long-Term Reliability Testing
Some suppliers provide only short-term test data, omitting accelerated life testing under stress conditions (e.g., high temperature, voltage ripple). Without access to robust aging data, buyers cannot accurately predict product lifespan, especially in demanding applications such as electric vehicles or renewable energy storage.
4. Use of Substandard or Counterfeit Components
Low-cost suppliers may use recycled or inferior-grade materials (e.g., contaminated activated carbon, low-purity electrolytes) to cut costs. These materials compromise efficiency, increase internal resistance, and pose safety risks such as swelling or thermal runaway.
5. Inadequate Environmental and Safety Certification
Capacitance batteries must meet safety standards such as UL, IEC, or UN38.3 for transportation. Sourcing without verified compliance increases the risk of regulatory rejection, shipment delays, or field incidents. Environmental certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH) are also often overlooked but essential for market access.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Technology
Some manufacturers may incorporate patented electrode designs, separator materials, or cell architectures without proper licensing. Buyers who source from these suppliers risk being drawn into infringement lawsuits, especially when integrating components into end-products sold in IP-sensitive markets like the U.S. or EU.
2. Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Contracts
Supply agreements often fail to clearly define IP ownership, particularly for custom-designed capacitors. This ambiguity can lead to disputes over who owns design improvements, tooling, or process innovations developed during production—potentially limiting future sourcing flexibility or product differentiation.
3. Reverse Engineering and Technology Leakage
Working with contract manufacturers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, increases the risk of design replication. Detailed technical drawings, material specifications, and test protocols shared during sourcing may be used to produce competing products without consent.
4. Inadequate Protection of Trade Secrets
Buyers may inadvertently disclose proprietary application requirements, integration methods, or performance targets without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or confidentiality clauses. This exposes sensitive R&D strategies to competitors through supplier networks.
5. Overlooking Freedom-to-Operate (FTO) Analysis
Before selecting a supplier or finalizing a design, companies should conduct FTO assessments to ensure the capacitance battery technology does not infringe existing patents. Skipping this step can result in costly redesigns, litigation, or blocked product launches.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Conduct independent lab testing of samples.
– Audit supplier facilities for quality certifications and manufacturing controls.
– Require full compliance documentation (e.g., test reports, safety certificates).
– Perform IP due diligence, including patent landscape reviews.
– Include robust IP clauses in contracts (ownership, confidentiality, indemnification).
– Use NDAs and limit technical disclosure to a need-to-know basis.
Proactive management of quality and IP risks ensures reliable performance, legal compliance, and long-term competitive advantage in capacitance battery sourcing.
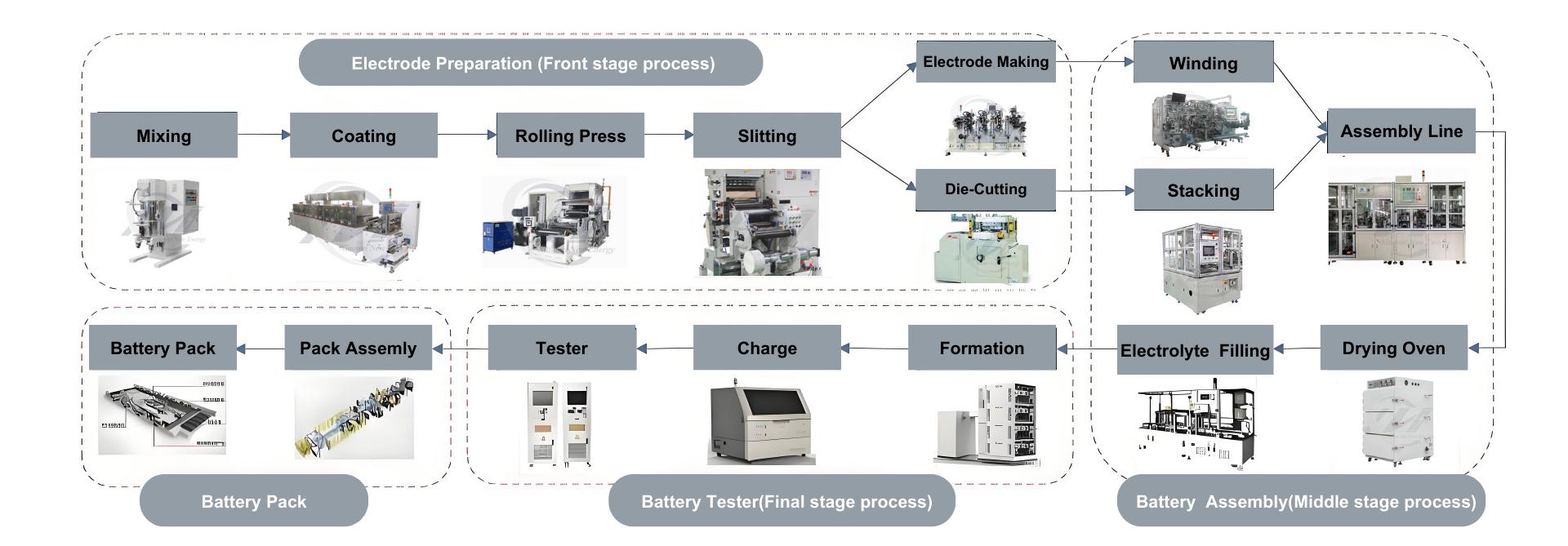
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Capacitance Battery
Overview
Capacitance batteries—commonly referred to as supercapacitors or ultracapacitors—are energy storage devices that store electrical energy through electrostatic charge separation rather than chemical reactions, as in traditional batteries. While they offer advantages such as rapid charging, long cycle life, and high power density, their logistics and compliance requirements differ from conventional batteries due to unique physical and electrical properties.
This guide outlines key logistics, transportation, safety, and regulatory compliance considerations for handling, storing, and shipping capacitance batteries globally, in accordance with international standards and regulatory frameworks.
Classification and Regulatory Framework
UN Number and Classification
Capacitance batteries are typically classified under the UN Model Regulations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods based on their design, energy content, and associated risks.
-
UN3499 – Batteries, electric storage, containing non-spillable electrolyte, not exceeding 12 V and 100 Wh
This classification often applies to supercapacitors with immobilized electrolyte and low voltage/energy thresholds, provided they meet vibration, pressure differential, and leakage tests. -
UN3171 – Batteries, wet, non-spillable, or containing sodium or other dangerous substances
May apply if the capacitance battery contains hazardous electrolyte materials or is considered a “wet” system.
⚠️ Note: Capacitance batteries are not classified as Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods (UN3536) unless they present a significant hazard (e.g., high energy density, reactive materials, or pressure build-up risk).
IATA, IMDG, and ADR Regulations
Capacitance batteries are subject to transport regulations depending on the mode:
- Air (IATA DGR):
- Must be shipped at ≤30% state of charge (SoC).
- Must pass vibration and altitude tests per Section 38.3 of the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria (if required).
- Packaging must prevent short circuits and physical damage.
-
Marked with “BATTERY, ELECTRIC STORAGE” and proper shipping name.
-
Sea (IMDG Code):
- Requires proper stowage and segregation.
- Must be secured to prevent movement.
-
Documentation must include UN number, proper shipping name, and hazard class.
-
Road (ADR – Europe):
- Applies to transport within Europe.
- Similar requirements to IMDG; exemption may apply for small quantities under Limited Quantity (LQ) rules.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packaging
- Use rigid, non-conductive outer packaging with internal separation to prevent terminal contact.
- Cushioning materials (e.g., foam inserts) must protect units from shock and vibration.
- Terminals must be insulated (e.g., caps, tape, or recessed design) to prevent short circuits.
- Packaging must be sealed and strong enough to withstand stacking and handling.
Labeling
- Proper shipping name: “BATTERIES, ELECTRIC STORAGE”
- UN number: UN3499 (most common)
- Class label: Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods (if applicable)
- Handling labels: “Keep Dry,” “This Way Up,” “Fragile”
- If shipped under IATA, include Cargo Aircraft Only label if exceeding passenger aircraft limits.
State of Charge (SoC) and Safety Handling
- Transport at ≤30% SoC to minimize thermal and electrical risks.
- Fully charged units are more prone to thermal runaway or arcing during faults.
- Discharge units safely before packaging using controlled load methods.
- Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures (>60°C or <–20°C) during storage and transport.
Storage and Handling Guidelines
- Storage Environment:
- Dry, well-ventilated area with temperature between 15°C and 35°C.
- Away from flammable materials and direct sunlight.
-
Non-conductive flooring recommended to reduce static discharge risk.
-
Handling:
- Use insulated tools when handling bare units.
- Personnel should wear PPE (gloves, safety glasses).
- Avoid dropping or puncturing cells—mechanical damage can lead to internal short circuits.
Environmental and End-of-Life Compliance
-
Capacitance batteries are not typically classified as hazardous waste under RCRA (USA) or similar frameworks, unless they contain hazardous electrolytes (e.g., organic solvents like acetonitrile).
-
WEEE Directive (EU):
- Capacitance batteries fall under WEEE category 5 (monitoring and control instruments) or category 6 (electric tools), depending on application.
-
Producers must register and ensure recyclability.
-
RoHS Compliance:
- Must comply with RoHS 2 (2011/65/EU) for restriction of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, mercury).
-
Most supercapacitors are RoHS-compliant due to benign materials.
-
Recycling:
- Aluminum casings and carbon electrodes are recyclable.
- Electrolyte should be neutralized or reclaimed by authorized recyclers.
- Use certified e-waste handlers for disposal.
Documentation and Declarations
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Required under GHS (Globally Harmonized System). Must include:
- Composition and hazards
- First-aid and firefighting measures
-
Handling and storage instructions
-
Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods: Required for air/sea if classified as dangerous goods (e.g., UN3499).
- Commercial Invoice and Packing List: Include technical specifications (voltage, capacitance, chemistry).
Regional Compliance Summary
| Region | Key Regulations | Notes |
|——-|——————|——-|
| USA | DOT 49 CFR, EPA, OSHA | Non-spillable batteries may be exempt from full hazmat requirements if tested. |
| EU | ADR, IMDG, REACH, RoHS, WEEE | Full compliance with ADR for road; REACH applies if substances of very high concern (SVHC) are present. |
| China | GB Standards (e.g., GB 31241) | Requires CCC certification for certain electronic applications. |
| Japan | JIS C 8714, METI regulations | Follows IEC 62133 for safety; requires PSE mark for certain products. |
Emergency Response
- Fire: Use CO₂, dry chemical, or foam extinguishers. Do not use water if electrolyte is flammable.
- Leakage: Evacuate area, ventilate, and use PPE. Collect residue with non-sparking tools.
- Contact: Neutralize skin/eye exposure with water; seek medical attention if irritation persists.
Conclusion
Capacitance batteries offer efficient, durable energy storage but require careful logistics planning and compliance with international transport regulations. By following proper packaging, labeling, SoC management, and documentation procedures, shippers can ensure safe and compliant transportation across air, sea, and land.
Always consult the latest editions of IATA DGR, IMDG Code, and ADR, and verify classification with a certified dangerous goods safety advisor (DGSA) when in doubt.
Conclusion for Sourcing Capacitance Battery
In conclusion, sourcing capacitance-based energy storage solutions, such as supercapacitors or hybrid capacitive batteries, presents a promising alternative to traditional battery technologies in applications requiring rapid charge/discharge cycles, long cycle life, and high power density. While they may not yet match the energy density of lithium-ion batteries, their durability, efficiency, and performance in extreme temperatures make them ideal for specific use cases such as regenerative braking systems, backup power, and short-term energy storage.
When sourcing capacitance batteries, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on technical specifications, reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Prioritizing established manufacturers with certifications, quality control processes, and technical support ensures consistent performance and integration into existing systems. Additionally, considering environmental impact and end-of-life recycling options aligns with sustainability goals.
Moving forward, continued advancements in materials science and hybrid energy storage systems may further bridge the gap between capacitive and conventional batteries. Therefore, businesses should adopt a strategic sourcing approach that balances immediate technical needs with long-term innovation trends, ultimately enhancing system efficiency and resilience through capacitive energy solutions.