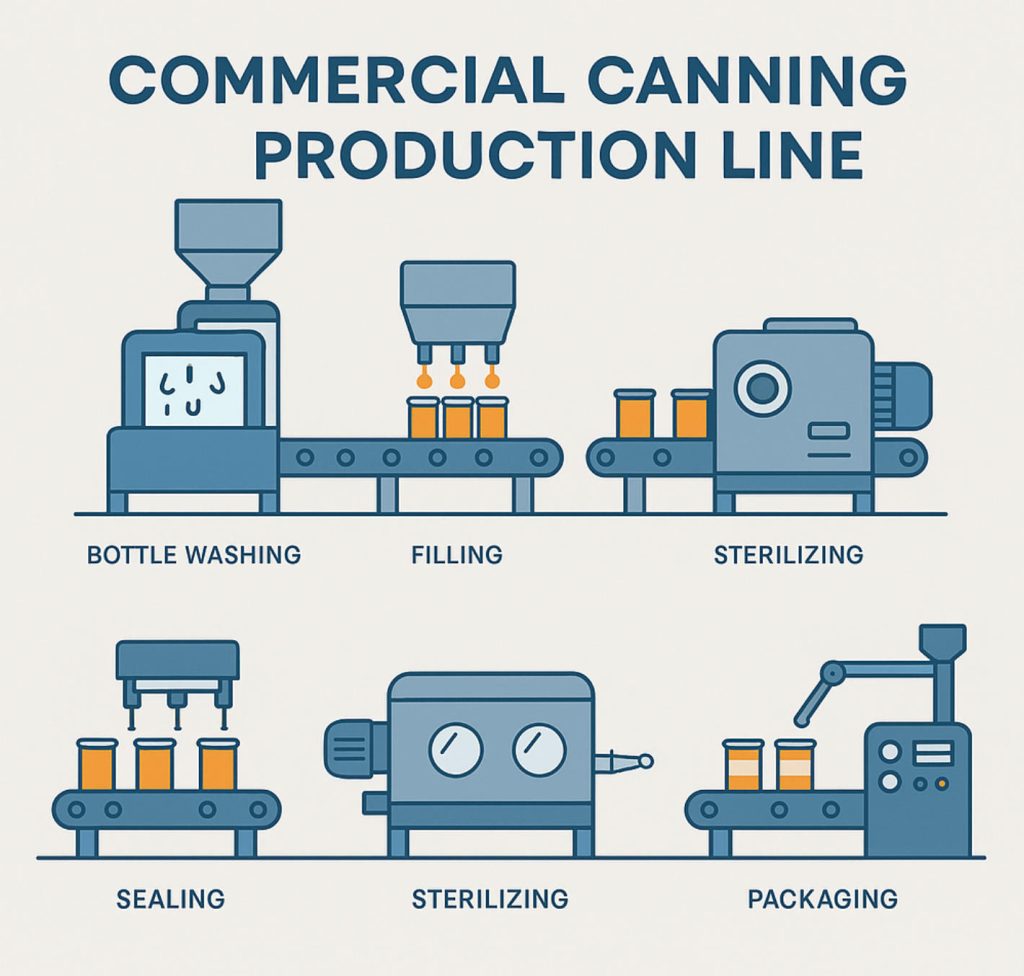
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Canning Machines
Demand for canned craft beverages is surging on both sides of the Atlantic—yet every week another brewery, cidery, or RTD start-up loses shelf space because the line they bought can’t hit the new SKU velocity, burns CO₂, or stalls on 330-ml slim cans. The gap between “entry-level” and “production-grade” has narrowed, but the spec sheets haven’t; one supplier’s 60 CPM is another’s 30 CPM with 2 % DO. Mis-read that line and you’re either over-paying for uptime you’ll never use—or under-automating and watching margin leak into overtime freight.
This guide cuts through the noise. Built for US and EU operations managers, it maps the 2024 vendor landscape—from American Canning’s AT-6 (65-inch footprint, dual-lane 30-60 CPM scalability) to GW Kent’s counter-pressure rigs engineered for oxygen-sensitive kombucha. You’ll get:
| Section | What You’ll Take Away |
|———|———————–|
| Capability Matrix | Match volume, can size range, and DO spec to 8 proven platforms |
| TCO Calculator | 5-year cost incl. air vs. CO₂ seaming, change-part kits, freight, CE/UL certification |
| Compliance Checklist | FDA, EG 1935/2004, and CBAM carbon tariff impacts on import ROI |
| Vendor Scorecard | Lead time, field-service hubs, and parts stocking in USD & EUR regions |
Bookmark the specs, plug in your forecast, and exit with a shortlist that scales from pilot batch to 100 000+ cases/year—without re-buying your seamer.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Canning Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for canning machines
- Understanding canning machines Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of canning machines
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘canning machines’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for canning machines
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for canning machines
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘canning machines’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for canning machines Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing canning machines With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for canning machines
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the canning machines Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of canning machines
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for canning machines
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Canning Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dixie Canner – Can Seamers, Retorts & Canning Equipment
Domain: dixiecanner.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Trusted since 1895, Dixie Canner manufactures can seamers, retorts, and canning systems for food, beverage, pharma and industrial applications across the ……
2. Canning Systems, Can Supply & Technical Service | Cask Global …
Domain: cask.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cask makes high quality beverage canning systems ranging from 10-100 cans per minute and supplies Aluminum cans and lids as a Distribution partner for Ball ……
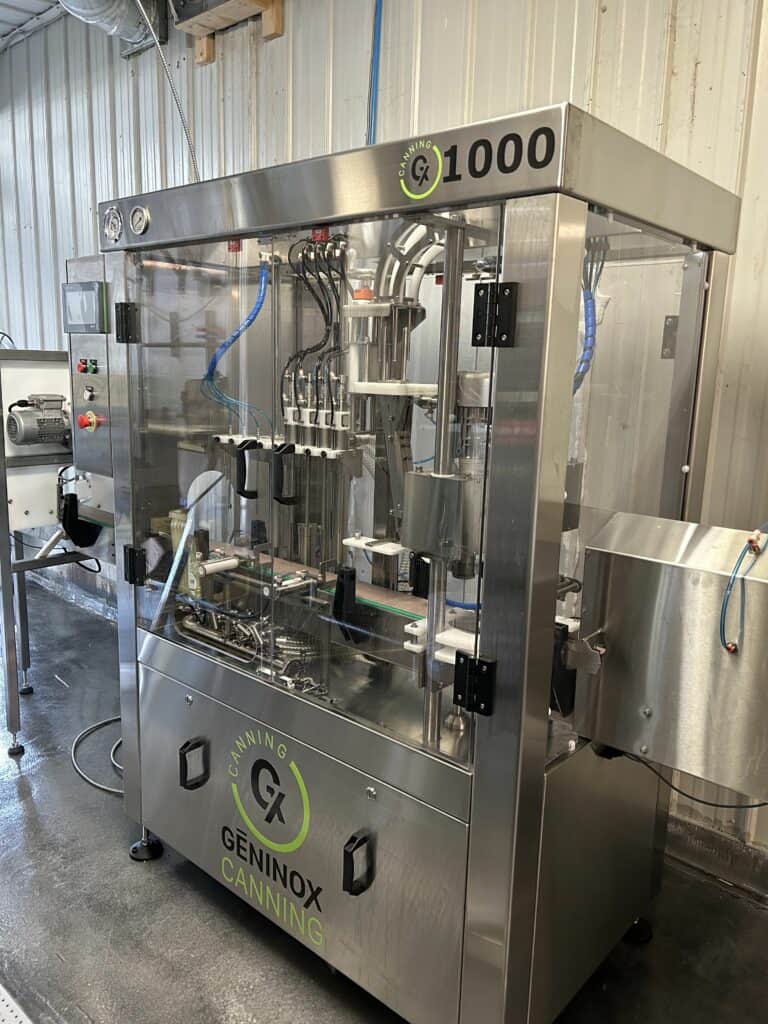
3. Crafting the most reliable bottling & canning equipments.
Domain: wildgoosefilling.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Wild Goose systems are known for their purpose-built capability, outstanding performance, and dependability….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Beverage Canning Machine – Canning Line – Rotary and In-Line
Domain: palmerbeverage.systems
Registered: N/A
Introduction: Palmer Beverage Systems provide complete solutions for beverage processing and packaging. With rotary and in-line fillers and seamers, range is 30-200 CPM….
5. Professional Canning Equipment | Counter Pressure Systems
Domain: gwkent.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: 4-day delivery 30-day returnsExplore GW Kent’s elite canning systems: The Mancos, Compass, Gunnison, and Cannon I & II. Elevate your output with top technology. Request a quote today!…
6. Iron Heart Mobile Canning | The Leader In Quality Canning
Domain: ironheartcanning.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Our full service mobile canning solution is second to none! Iron Heart is your economical, quality canning solution no matter what your size….
7. Top 20 Beer Canning Machine Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: finbolink.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Accutek Packaging Equipment is a leading innovator among beer canning machine manufacturers, specializing in fully automated canning systems. Their durable ……
8. Beer canning machine – Co.Mac. – Comac Group
Domain: comacgroup.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Co.Mac has been in the business of manufacturing beer canning machines for more than twenty years. The company has invested heavily on a talented workforce, ……
Understanding canning machines Types and Variations
Understanding Canning Machine Types and Variations
| Type | Key Features | Typical Applications | Pros / Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Counter-Pressure (Isobaric) Filler/Seamer | Pre-evacuation & CO₂ purge, multiple pressurisation cycles, closed filling valve, integrated seamer | Craft beer, cider, sparkling wine, RTD cocktails, any carbonated beverage | + Dissolved-O₂ ≤30 ppb, <0.05 CO₂ vol loss, shelf life 12 mo+ – Higher CAPEX, longer change-over, needs 3–3.5 bar CO₂ supply |
| Atmospheric Filler/Seamer | Open-fill under atmospheric pressure, short product path, gravity or light back-pressure, mechanical seamer | Still water, cold brew, juices, teas, wine, sauces, brine-based veg | + 30–50 % lower price, fast format swap, simple CIP – Not suitable for >2.5 vol CO₂, O₂ pickup 200–400 ppb, shorter shelf life |
| Rotary High-Speed Line | 24–180 valve turret, continuous motion, CIP/SIP loop, auto-lid magazine, 200–2 000 CPM | National beer brands, energy drinks, large co-packers | + Output >1 000 CPM, 1 % giveaway, Industry 4.0 data – €1–5 M investment, 4–6 mo lead time, 200 m² footprint |
| Semi-Auto (2–6 head) Bench/Linear | Manual load, pneumatic lift, single or dual lane, 10–60 CPM, 110 V / 230 V, <2 m² | Start-up breweries, mobile canners, pilot plants, R&D | + <$70 k, roll-on casters, 1 h install, 30 min change parts – Labour 1–2 FTE, 4–6 CPM per head, limited format range |
| Aseptic Canning System | H₂O₂ or PAA sterilisation, sterile filtration, positive-pressure enclosure, isolator seamer, log-5 bioburden reduction | Dairy-based coffee, kombucha, functional beverages, low-acid drinks | + 6–12 mo ambient shelf life, no preservatives, FDA/EFSA compliant – €300–800 k, validation 3–6 mo, needs sterile air & 0.2 µm filters |
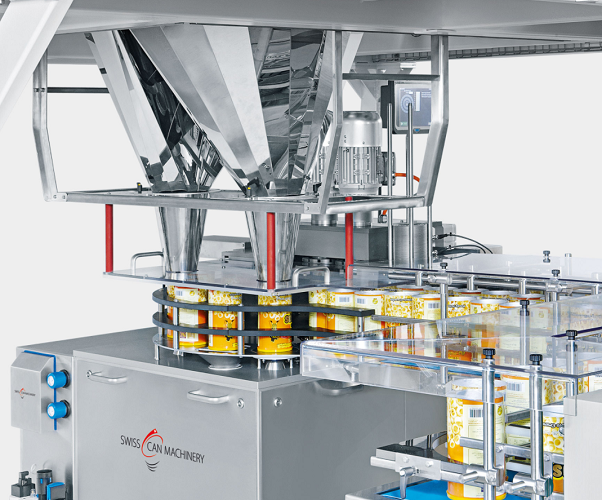
Counter-Pressure (Isobaric) Filler/Seamer
Designed for carbonated products, the machine purges the can with CO₂, pressurises to tank pressure, and fills under equal pressure to prevent foaming and CO₂ loss. Oxygen levels below 30 ppb are routine, giving craft brewers 12-month shelf life without pasteurisation. Common in 30–300 CPM mobile rigs and mid-scale rotary units.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Atmospheric Filler/Seamer
Best for still or lightly carbonated (<2.5 vol) liquids. Product flows by gravity or low back-pressure; seamer applies the lid immediately. Simpler valve architecture reduces CAPEX and change-over time, but oxygen pickup is higher; nitrogen dosing is often added to extend shelf life. Widely used by cold-brew coffee and ready-to-drink tea brands.
Rotary High-Speed Line
Turret-style systems merge filling and seaming in continuous motion. Electronic flow-meters or weight cells deliver ±1 g accuracy at 2 000 CPM. Integrated CIP/SIP, automatic non-destructive QC sampling, and OPC-UA data export support high-volume, low-giveaway operation. Justified at >20 million cans/year.
Semi-Auto Bench/Linear
Start-up workhorse: operator loads cans manually; pneumatic actuators lower the fill heads and seamer chuck. Models such as the AT-6 scale from 30 to 60 CPM via dual-lane toggle, fitting a 65″ × 23″ footprint. Ideal for tap-room canning or mobile services where capital must stay <€60 k and line relocations are frequent.
Aseptic Canning System
Combines hydrogen-peroxide or peracetic-can sterilisation, sterile product filtration, and a positive-pressure seamer island to achieve commercial sterility. Enables ambient distribution of low-acid, preservative-free beverages. Validation protocols (FDA 21 CFR 113 / EU 2002/72) extend commissioning, but open retail channels for dairy-based coffees and probiotics.
Key Industrial Applications of canning machines
Key Industrial Applications of Canning Machines
| Industry / Application | Typical Throughput* | Core Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Craft Beer & Hard Seltzer | 30–90 CPM (AT-6, CP-4) | Counter-pressure filling locks in CO₂; oxygen pickup <30 ppb extends shelf life to 6–9 months; compact 5-ft footprint fits tap-room floors. |
| Wine & RTD Cocktails | 20–60 CPM | Inert-gas canopy prevents SO₂ loss; aluminium cans weigh 60 % less than glass, cutting freight cost by 30 % to EU & US distributors. |
| Cold-Brew Coffee & Nitro Infusions | 15–45 CPM | Nitrogen-dosing system creates stable micro-foam; hot-fill compatibility (185 °F) eliminates cold-chain for 120-day ambient distribution. |
| Functional Waters & Energy Drinks | 60–300 CPM (multi-lane) | Hygienic tri-clamp manifold allows 15-min CIP; servo-driven volumetric fill ±0.5 ml ensures label claim compliance on 250 ml slim cans. |
| Canned Wine Spritzers & Kombucha | 30–70 CPM | Magnetic flow meters handle 0–2 % pulp; quick-swap format tooling switches 200 ml to 500 ml in <30 min for seasonal SKUs. |
| Soups, Sauces & Ready Meals | 40–200 CPM | Retort-compatible double-seam (1.2 mm tightness) achieves F₀≥6 sterilization; BPA-free compound guarantees 24-month ambient shelf life. |
| Fruits, Vegetables & Pet Food | 60–400 CPM | Steam-flow closure removes 90 % headspace oxygen; water-bath retort cycle cuts energy 18 % vs glass jars. |
| Cannabis & CBD Beverages | 10–50 CPM | Light-proof aluminium blocks UV degradation; nitrogen headspace keeps cannabinoid loss <5 % over 12 months; child-resistant pull-tab options. |
| Dairy & Plant-Based Alternatives | 30–120 CPM | Aseptic magnetic flow meter keeps spoilage <0.01 %; ESL process delivers 90-day refrigerated life for oat lattes. |
| Industrial Chemicals & Aerosol Lubricants | 50–250 CPM | ATEX-rated seamer heads; chemical-resistant gaskets handle pH 1–14; UN-approved cans simplify haz-mat shipping. |
*CPM = cans per minute, based on GW Kent and American Canning model ranges.
Application-Specific Advantages
- Speed-to-market: 30-minute changeover times let craft producers launch seasonal SKUs without contract-pack minimums.
- Cost control: Switching from 12 oz glass to 12 oz can saves ~US $0.07 per unit in materials; payback on an AT-6 (<US $60k) occurs at 850k cans.
- Sustainability: Aluminium has a 70 % recycled content average in the EU & US, improving ESG scores versus multi-material cartons.
- Distribution reach: Slim-can format adds 18 % more units per pallet, cutting freight emissions 12 % on trans-Atlantic routes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘canning machines’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Canning Machines & Their Solutions
| # | Scenario / Problem | Root Cause | Business Impact | Solution & Proof-Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | “We can’t hit weekly order volumes because the line maxes out at 25 CPM.” Mid-size US craft-brewer adding 2–3 new tap accounts per month. |
Single-lane, entry-level filler/seamer purchased when volume was 2 000 cans/week; forecast now 7 000. | Overtime labor, missed distributor dock times, lost shelf space to faster competitors. | Upgrade to a dual-lane, 60 CPM compact unit (e.g. American Canning AT-6). Same 65″ × 23″ footprint doubles throughput without CAPEX for new floor space; ramp from 30→60 CPM as orders grow. Payback <9 months on labor savings alone. |
| 2 | “Dissolved-oxygen pickup is 60 ppb; shelf-life claims are failing in European retail audits.” Carbonated RTD brand shipping to EU supermarket chains. |
Atmospheric filler pulls CO₂ out of solution; no closed-loop purging; warm cans exacerbate O₂ ingress. | Product recalls, penalty clauses, forced discounting, brand damage. | Move to counter-pressure (isobaric) filling system with pre-evacuation & under-lid gassing. GW Kent’s CPS range hits ≤15 ppb TPO routinely; compliance with EUMO 1.4.1.11 for 12-month shelf life. ROI protected by eliminating 2% monthly spoilage write-offs. |
| 3 | “Changeover takes 90 min—kills our margin on short-run private-label SKUs.” Contract co-packer alternating 330 ml slim & 500 ml standard cans. |
Tooling bolts, manual height adjustment, unmarked settings, no recipe memory. | Line utilisation <55%, 3 shifts to hit 40 000-case month, quoting 6-week lead times. | Specify quick-change canning system: • Magnetic bell adapters (no tools) • Servo-driven lift & fill heads with pre-set recipes • Color-coded change parts cart. GW Kent & ACM both offer 15-min changeover kits; co-packer now quotes 48 h turnaround, adding €180k annual revenue from incremental campaigns. |
Use the checklist above as a shortlist when specifying your next canning line; matching throughput, filling technology, and changeover architecture to your growth model eliminates the three costliest pain points we see across US and EU plants.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for canning machines
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Canning Machines
The metallurgy and polymer choices built into a filler/seamer determine throughput consistency, chemical compatibility, regulatory acceptance, and lifetime operating cost. Below is a field-tested framework US and European plants use to match materials to product chemistry, line speed, and sanitation protocol.
1. Core Material Families & Key Properties
| Family | Typical Grades | Density (g/cm³) | Ra (µ-in) as-machined | 304/316 Passivation | FDA/EC 1935⁄2004 | Chloride Pitting Resistance* | Relative Cost Index** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 304L | 1.4307 | 7.9 | 16–20 | yes | yes | low (PREN 18) | 1.0 |
| AISI 316L | 1.4404 | 7.9 | 16–20 | yes | yes | good (PREN 26) | 1.3 |
| Duplex 2205 | 1.4462 | 7.8 | 20–25 | yes | yes | very good (PREN 34) | 1.8 |
| Hastelloy C-22 | 2.4602 | 8.7 | 16–20 | no (Ni-Cr-Mo) | yes | excellent | 7.5 |
| PTFE (virgin) | — | 2.2 | molded | n/a | yes | inert | 4.2 |
| PEEK (food grade) | — | 1.3 | 8–12 | n/a | yes | inert | 9.0 |
PREN = Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number.
*Index based on 304L plate, Q2-2024 US/EU mill pricing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. Selection Matrix by Product & Process
| Product Category | CO₂ content | pH | Pasteurised? | Chloride (ppm) | Recommended Wetted Alloy | Recommended Seals/Gaskets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Still cider, wine | <1 g/L | 3.2–3.8 | no | <40 | 304L | EPDM |
| Craft beer, seltzer | 2.5–5 g/L | 3.8–4.4 | tunnel/flash | <50 | 316L | PTFE-lined EPDM |
| Hard kombucha, NA beer | 0–2 g/L | 3.0–3.5 | hot-fill | 80–150 | Duplex 2205 | FKM |
| Ready-to-drink coffee | <1 g/L | 5.0–6.0 | retort | 60 | 316L | Silicone |
| High-nitro smoothie | 0 g/L | 3.8–4.2 | HPP | 120–200 | Hastelloy C-22 | PEEK |
3. Wear & Fatigue Considerations Above 60 CPM
High-speed rotary seamer spindles (≥60 cpm on the AT-6, CP-4, or GW Kent CP-6) generate 8–12 µm radial wear on 304L chuck threads within 3,000 h. Switching to hardened 17-4 PH (1.4548) or coating 316L with WC-Co HVOF extends MTBR to 9,500 h while maintaining food contact compliance.
4. Sanitation Chemistry Compatibility
- Chlorinated caustic (80 °C, 200 ppm NaOCl): 316L acceptable up to 100 ppm; Duplex above that.
- Peracetic acid (1 %, 40 °C): Hastelloy if pH <3 and chloride >150 ppm.
- Nitric acid passivation (20 %, 60 °C): 304L and 316L both pass, but free-machining grades (303) must be avoided—sulfide stringers create pitting sites.
5. Regulatory Snapshot
| Jurisdiction | Standard | Material Clause |
|---|---|---|
| USA | FDA 21 CFR § 177 & § 181 | Ni release <0.1 ppm; Cr(VI) ND |
| EU | EC 1935/2004 & EU 10/2011 | Specific migration of Cr ≤0.1 mg/kg |
| Germany | LFGB BfR XXXVI/1 | Co migration limit 0.02 mg/kg on coated steels |
6. Quick-Reference Comparison Table
| Attribute | 304L | 316L | Duplex 2205 | Hastelloy C-22 | PEEK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial price | $ | $$ | $$$ | $$$$$ | $$$$$ |
| Corrosion in 200 ppm Cl⁻ | poor | fair | good | excellent | inert |
| Weldability (autogenous) | excellent | excellent | good (low H₂) | poor | N/A |
| Machinability rating | 70 % | 55 % | 45 % | 30 % | 40 % |
| Availability (US/EU mills) | high | high | medium | low | specialty |
| Typical service life (h) at 60 cpm | 4,000 | 7,000 | 12,000 | 25,000 | 15,000 (seals) |
Selection Checklist (Plant Engineer)
- Map chloride, CO₂, SO₂, and titratable acidity—worst-case, not average.
- Define sanitation cycle: temperature, oxidiser, contact time.
- Specify target MTBR; multiply by hourly labour rate to justify alloy upgrade.
- Validate regulatory file: migration certificates for both alloy and any polymeric over-mould.
- Lock specification into PO; prohibit 303, 201, or non-stabilised replacements.
Use the matrix above to eliminate over-specification (and cost) while preventing unscheduled downtime caused by chloride-induced pitting or detergent stress-corrosion cracking.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for canning machines
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Canning Machines
| Step | Purpose | Key Controls | Typical Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Prep | Raw-material readiness & traceability | Mill certs, 3.1B EN 10204, incoming CMM scan | ±0.05 mm on critical weld edges |
| 2. Forming | Frame, bowls, seaming chucks to print | 5-axis laser cutting + robotic bend cell | ±0.1 mm flatness, ≤0.5° angular |
| 3. Assembly | Fit, form & function of sub-systems | Torque spec database, digital build book | 100 % leak-test at 6 bar, 30 s |
| 4. QC | Release to shipping | ISO 9001 stage-gate + FAT protocol | CpK ≥1.33 on fill volume & seaming |
1. Prep: Material & Documentation
- Stainless stock: 304L or 316L, 2B finish, Ra ≤0.4 µm on product-contact.
- Seals & gaskets: FDA 21 CFR §177, EU 10/2011 migration-certified.
- Traceability: Bar-coded heat/lot linked to MRP; retains 10 yr digital record.
2. Forming: Precision Machining & Welding
- Frame & seaming turret: 5-axis laser-cut, robot-welded, stress-relieved at 620 °C.
- Bowl surfaces: passivated 30 min, citric acid; ferrite level <0.5 % to prevent corrosion.
- Critical bores: finish-machined to H7 fit; roundness ≤8 µm for bearing life.
3. Assembly: Modular Build Strategy
| Sub-assembly | Key Process | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Filling valve block | 100 % pressure decay ≤0.2 bar/2 min | calibrated leak tester |
| Seaming head | 4-roller cam-profile grind | optical profiler Ra ≤0.2 µm |
| Drive pack | servo motor + gearbox backlash ≤3 arc-min | encoder closed-loop test |
| Controls cabinet | UL 508A build; 100 % point-to-point continuity | hipot 1 500 V, 1 mA |
- Software: version-locked firmware, CFR 21 Part 11 audit trail enabled.
- Clean-build protocol: ISO 8 enclosure; final IPA wipe, particle count ≤100 000 @0.5 µm.
4. Quality Standards & Certifications
- ISO 9001:2015 – corporate quality system.
- ISO 13849-1 – safety control reliability (PL “d” minimum).
- CE/UKCA – machinery directive 2006/42/EC, with full technical file.
- FDA registration for product-contact parts; material certificates provided with each machine.
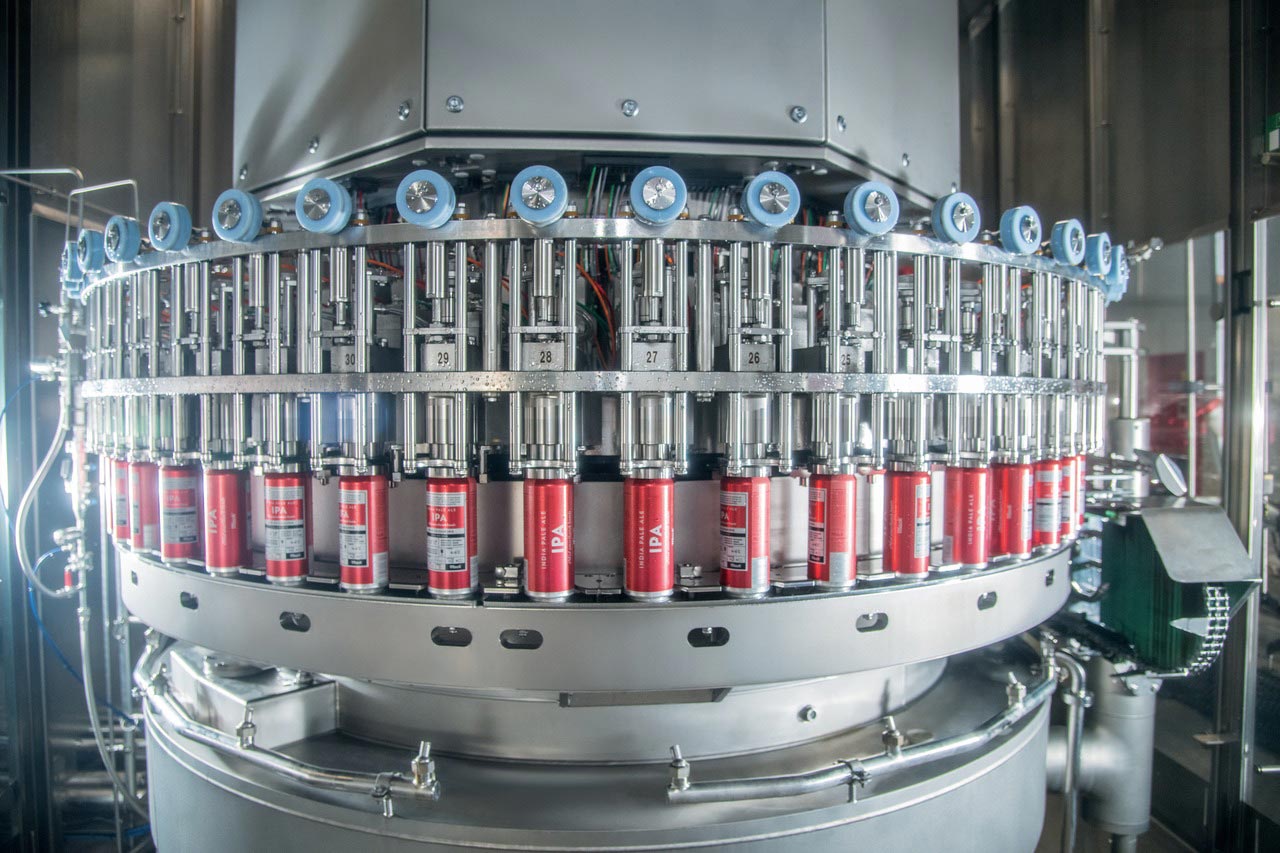
Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) – Standard Scope
- 2-hour dry cycle @100 % set speed (e.g., 60 CPM for AT-6).
- Product run: 500-can batch, target ±1 g fill deviation, <1 % DO pickup.
- Seaming: 1st/3rd/5th can pull-tests—cover-hook ≥1.95 mm, body-hook ≥1.85 mm, tightness ≥70 %.
- Documentation: dimensional report, torque log, electrical drawings, spares list, multilingual O&M manual.
Site Acceptance Test (SAT) mirrors FAT on customer floor; CpK study run over 3 shifts to confirm process stability before hand-off.
Outcome: Machines leave the plant ready for craft-beverage or food production, repeatable within ±1 % fill weight and ≤0.1 % leaker rate at rated speed.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘canning machines’
Practical Sourcing Guide: Step-by-Step Checklist for Canning Machines
Use the table below as a one-page, print-ready checklist. Tick every box before you sign a PO; 90 % of post-installation surprises are eliminated when this list is complete.
| Step | Checkpoint | Verified (√) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Output Targets | Daily / weekly can volume now and +24 mo. | |
| Peak-season surge factor (%) | ||
| Target CPM (cans/min) – e.g., 30, 60, 120 | ||
| 2. Map Product Specs | Liquid type: still, carbonated, hot-fill, viscous | |
| CO₂ volume (for counter-pressure requirement) | ||
| Can size range (202, 204, 206, 209, 211 ⌀, sleek, standard) | ||
| End type (B64, CDL, Super-End) | ||
| 3. Plant Constraints | Available line length (ft / m) | |
| Ceiling height (in / cm) | ||
| Power: V, Ph, Hz, Amps (USA vs. EU) | ||
| Compressed-air scfm @ psi / bar | ||
| Floor load limit (kg / m²) | ||
| Door width for skid entry | ||
| 4. Regulatory & Safety | UL / CSA (USA) or CE (Europe) on entire system | |
| FDA / EC 1935/2004 product-contact materials | ||
| EHEDG / 3-A sanitary design if dairy or juice | ||
| OSHA / EU guarding category 3 PL “d” minimum | ||
| 5. Technology Choice | Atmospheric filler acceptable? (still products only) | |
| Counter-pressure needed? (CO₂ ≥ 2.5 vol or TPO < 50 ppb target) | ||
| In-line vs. rotary; mono-block vs. split filler-seamer | ||
| 6. Supplier Short-List | ≥ 3 OEMs with ≥ 5 yr track record in beverage canning | |
| Reference sites visited or video-called | ||
| Spares held in USA & EU (48 h delivery guarantee) | ||
| 7. Life-Cycle Costing | Price FOB + freight + duties | |
| Installation & commissioning days | ||
| Training hours included (maintenance + operators) | ||
| Annual OEM service contract | ||
| Typical wear-part cost per 1 000 cans | ||
| Power & air consumption per 1 000 cans | ||
| 8. QA / QC Integration | Inline check-weigher interface yes / no | |
| X-ray or vision system ready | ||
| Automated reject gate | ||
| Data export format (OPC-UA, Ethernet/IP, CSV) | ||
| 9. Uptime & Changeover | Tool-less changeover time (min) | |
| Mean time between failure (MTBF) hrs (OEM spec) | ||
| Mean time to repair (MTTR) min | ||
| Remote diagnostics capability | ||
| 10. Commercial Terms | Incoterms (FCA, CPT, DAP) | |
| Warranty months (parts & labor) | ||
| Performance guarantee (% of rated speed for 72 h) | ||
| Liquidated damages for late delivery | ||
| Payment schedule (max 30 % after FAT) | ||
| 11. FAT & SAT Protocol | Factory acceptance test agenda signed | |
| Site acceptance test criteria (OEE ≥ 85 %) | ||
| 12. Documentation Package | 3-A / CE dossier, wiring diagrams, PLC backup | |
| Spare-parts list with part numbers & prices | ||
| SOPs in US-English + local EU language |
Quick-Reference Benchmarks
- Entry semi-auto: 8–15 CPM, <$90 k
- Mid-tier in-line (e.g., AT-6): 30–60 CPM, $120–180 k
- High-speed rotary: 150–300 CPM, $350 k–$1 M
Complete every row, file the signed checklist with procurement, and schedule the FAT date before releasing the down-payment.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for canning machines Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost & Pricing Analysis for Canning Machines Sourcing (USA & Europe)
| Cost Component | Typical % of Total CAPEX | 2024 USA Benchmark | 2024 EU Benchmark | Hidden / Volatile Items |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment EXW | 65 – 75 % | AT-6 60 CPM: US $89 k | Same unit: €95 k | Firmware updates, spare-kit bundling |
| Shipping & Import | 4 – 8 % | US $3.8 k (Austin→Denver) | €2.2 k (Rotterdam→Milan) | ISPM-15 crates, post-Brexit EU→UK |
| Installation & IQ/OQ | 5 – 9 % | US $6 k (1 day) | €7.5 k (CE mark docs) | Travel days, compressed-air loop |
| Starter Spares | 3 – 5 % | US $4 k seals & belts | €4.3 k | Exchange-rate hedging |
| Training & Start-up Beer | 1 – 2 % | US $1.5 k | €1.8 k | CO₂, product loss on 2 h ramp-up |
| Financing & FX | 2 – 4 % | 8 % APR CTL | 5 % EUR Libor | 90-day USD exposure |
| TOTAL LANDED COST | 100 % | ≈ US $105 k | ≈ €111 k | +/- 7 % on currency swing |
1. Materials & Build-Spec Cost Drivers
| Sub-Assembly | Stainless Grade | % of Unit Cost | USA Sourcing Tip | EU Sourcing Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filling tank & valves | 316L | 18 % | Order during Q4 Ni-price low | Negotiate “duty-drawback” if re-export |
| Seaming chuck & rolls | 440C hardened | 7 % | Buy spare set with machine to avoid MOQ | Request EU-reg food-contact declaration up-front |
| Frame & guarding | 304L | 5 % | Choose modular frame → cheaper LTL freight | Prefab TIG-welded frame saves 2 site-days |
| PLC + HMI | Allen-Bradley / Siemens | 4 % | 3-year service pack locks price | EU: insist on CE & UKCA in same firmware load |
2. Labor & Service Pricing
| Activity | USA Typical | EU Typical | Cost-Control Tactic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Factory acceptance (FAT) | 1 tech × 2 days = US $1.6 k | 1 tech × 2 days = €1.8 k | Swap FAT for live-stream & signed video protocol – save 40 % |
| Site commissioning | US $125 /hr after 8 h | €135 /hr after 8 h | Pre-install utilities; 80 % of over-time is chasing air leaks |
| Operator training | Included 8 h | Included 8 h | Record Zoom session; reduces repeat on-site visits |
3. Logistics & Tariff Matrix
| Trade Lane | Incoterm | 2024 Duty | 2024 Freight (40” HQ) | Lead-Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China → USA | FOB Shenzhen | 0 % (HS 8422.30) | US $4 200 W.Coast | 18-22 days |
| China → EU | FOB Shenzhen | 1.7 % | €3 100 Rotterdam | 24-28 days |
| USA → EU | FCA Austin | 3.2 % | €2 400 | 14 days |
| EU → USA | FCA Netherlands | 0 % (quota) | US $2 800 | 12 days |
Note: Section 301 tariffs apply to Chinese-origin PLCs; specify “USA/EU origin controller” to avoid 25 % surcharge.
4. Five Levers to Cut 8-12 % off Landed Cost
-
Bundle Spares at PO Stage
Negotiate 10 % discount when spares are added to the machine PO; ordering later triggers separate freight + 15 % margin.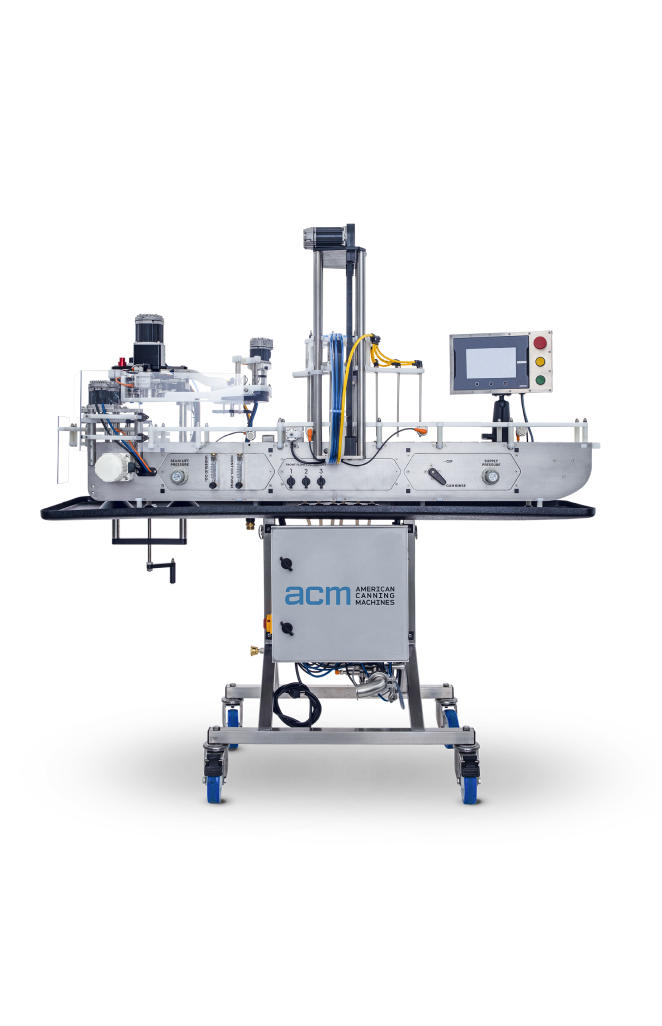
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Ship “Knock-Down” Frame
American Canning AT-6 fits 65” × 23” skid; request removal of infeed table → reclassify as “machinery parts” and cut freight by 18 %. -
Use Q1 FX Forward
EUR/USD volatility ±6 % last 24 mo; lock 50 % of exposure 90 days out to protect budget. -
Self-Perform IQ/OQ with Remote Support
Vendors provide template docs; remote sign-off saves 2 onsite days ≈ US $2 k. -
Consolidate with Peer Breweries
Two-machine shared container EU → USA drops per-unit freight from US $4.2 k to US $2.6 k.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. OpEx Items to Forecast (3-Year)
| Item | Annual USA | Annual EU | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sealing compound rolls | US $2 400 | €2 600 | Buy 2-year volume, vacuum-packed |
| CO₂ for counter-pressure | US $0.08 /can | €0.09 /can | Re-capture system pays back <14 mo |
| Power (3-phase 15 kW) | US $6 500 (@$0.10/kWh) | €9 100 (@€0.18/kWh) | Run high-fill campaigns off-peak; VFD saves 12 % |
| Water & effluent | US $1 200 | €2 000 | Closed-loop rinser option ROI 20 mo |
Key Takeaway
A 60 CPM mid-range canning line lands at roughly US $105 k USA / €111 k EU; currency, tariff classification and freight modality swing the needle ±7 %. Locking spares, shipping knock-down and remote commissioning are the fastest, lowest-risk tactics to drive the figure below the six-digit mark without compromising warranty or throughput.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing canning machines With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Canning Machines With Other Solutions
| Evaluation Criteria | Rotary Canning Line (e.g., AT-6) | Counter-Pressure Bottle Filler | Mobile Canning Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typical Speed | 60 cans/min (3,600/hr) – dual-lane scalable from 30 | 12–20 bottles/min (720–1,200/hr) | 0 (outsourced); 1-day slot ≈ 6–10k cans |
| Package Format | 202/204/206 dia. aluminum cans; optional ends | 12 oz – 750 ml glass; crown or swing-top | Supplier’s can inventory (often 202 LOE) |
| Dissolved-O2 Pick-up | <30 ppb with under-lid gassing | 50–120 ppb (head-space dependent) | Unknown; varies by contractor |
| Floor Space | 65″ × 23″ (1.65 m × 0.6 m) | 8–12 m² incl. rinser & capper | 0 (no equipment) |
| Capex (USA/EU) | $55–75k (AT-6 class) | $40–60k (4-head counter-pressure) | $0 |
| Cost per 1,000 units | $0.08–0.12 (can + end) | $0.28–0.35 (glass + closure) | $1.40–1.90 (all-in mobile fee) |
| Change-over Time | 10–15 min (tool-less) | 20–30 min (bottle height + diameter) | N/A |
| Shelf Life (pasteurized) | 12–18 months | 9–12 months | 12 months (if contractor pasteurizes) |
| Regulatory Risk | CE & UL listed; in-house QA | CE & UL listed; in-house QA | Shared liability; audit trail required |
| Scalability | Add second AT-6 or integrate depal/labeler | Limited by glass supply & labour | Bottlenecked by contractor calendar |
| Sustainability | 70% recycled Al; 55% lighter freight vs. glass | Glass 100% recyclable; 3× weight → higher CO₂e | Transport footprint per batch |
Analysis
- Rotary Canning Line
- Best for: Mid-scale craft breweries, kombucha, cold-coffee & wine spritz brands that need weekly volumes of 25–150k cans.
- Key advantage: Lowest package cost, smallest oxygen pickup, and compact footprint allow producers to hit retail price-points while preserving flavour stability.
-
Trade-off: Requires skilled operator and preventive-maintenance budget (~$4k/year).
-
Counter-Pressure Bottle Filler
- Best for: Premium Belgian styles, barrel-aged releases, or wineries targeting on-premise glass markets.
- Key advantage: Perceived luxury image and established glass recycling streams in EU markets.
-
Trade-off: 2–3× packaging material cost and higher freight weight erode margin on export or e-commerce sales; head-space O₂ pickup shortens hoppy beer shelf-life by ~3 months versus cans.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Mobile Canning Service
- Best for: Start-ups (<3k bbl/yr) testing demand or seasonal brands with cash-flow constraints.
- Key advantage: Zero capital deployment; supplier brings seam QA and can inventory.
- Trade-off: Unit economics become prohibitive above 40k cans/month; scheduling risk during peak season can stall production; limited control over dissolved oxygen and seam specs—may trigger retailer charge-backs.
Bottom line: If annual packaged volume exceeds 500k cans or margin per case is mission-critical, investing in an in-house rotary system (AT-6 tier) delivers the lowest total cost of ownership and highest quality control. Bottle fillers remain niche for image-driven SKUs, while mobile services are a tactical bridge—not a strategic replacement—for owned canning capacity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for canning machines
Essential Technical Properties & Trade Terminology for Canning Machines
| Property | Industry Range | What to Specify in RFQ / PO |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | 10 – 600 cans/min (CPM) | Target CPM @ 12-oz format; single- or dual-lane capability |
| Fill Accuracy | ±0.5 % – 2 % by volume | Tolerance at 2 σ, product temp & CO₂ spec |
| Counter-Pressure (Isobaric) Rating | 2 – 4.5 bar | Required for CO₂ ≥ 2.6 vol; specify max working pressure |
| D.O. Pick-Up | ≤ 30 ppb (brewery spec) | Measured inline; affects shelf-life |
| Seam Integrity | 0.80 – 1.25 mm body-hook overlap | 1st-operation & 2nd-operation roll profile must match can maker spec |
| Change-Over Time | 5 – 30 min | Tool-less preferred; list can heights/diameters |
| Footprint (L×W) | 28″×20″ (table-top) – 144″×48″ (monoblock) | Verify plant ceiling & door clearance |
| Power | 208–480 V, 3-ph, 50/60 Hz | Specify plug type & local electrical code |
| Air Consumption | 1.5 – 6 CFM @ 6 bar | Include dryer & filter requirement |
| CIP/SIP Compatibility | 85 °C, 2 % caustic, 5 min cycle | Confirm seal materials (EPDM, PTFE) |
| Automation Level | Manual – Full servo | Ask for PLC brand, remote-access licence, OPC-UA availability |
| Safety Rating | UL 508A, CE (MD 2006/42/EC), ISO 13849-1 PL “d” | Needed for USA & EU compliance |
Trade Terms Used in Canning-Machine Quotations
| Term | Definition | Typical B2B Context |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | 1 machine for semi-auto; 3–5 units for OEM private-label volume discount |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | Vendor will badge machine with buyer’s brand & HMI skin |
| FOB | Free On Board | FOB Kent, OH or FOB Rotterdam; buyer pays freight & insurance after named port |
| EXW | Ex-Works | Title & risk transfer at factory loading dock; buyer arranges export haulage |
| LT | Lead-Time | 8–14 weeks standard; 4 weeks expedite fee ≈ 10 % |
| HS Code | Harmonized System Code | 8422.30.91 (beverage-can seaming/filling machinery) for EU & US import docs |
| Incoterms® 2020 | — | Specify in quote: CPT, CIP, DAP, or DDP for turnkey install |
| SKU | Stock-Keeping Unit | Each can diameter/height combo = unique change-part SKU |
Quick Checklist for RFQ
- State target CPM and current can specs (202/211×413, 200×204, etc.).
- Attach product data sheet: viscosity, pulp, CO₂ vol, filling temp.
- Declare local utilities: voltage, compressed-air class, floor load limit.
- Ask for list of wear parts & annual consumption cost.
- Require 2-year spare-parts price lock and remote-support package SLA.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the canning machines Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Canning Machines Sector
| Driver | 2023–2025 Outlook | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Craft-to-Craft-Plus migration | 60 CPM “micro-line” demand >25 % CAGR (USA) | Spec dual-lane fillers (ex. AT-6) that start at 30 CPM and retrofit to 60 CPM without new footprint |
| EU Green Deal / PPWR* | 50 % rPET in beverage cans by 2030 | Require counter-pressure systems rated for 25 % thinner-wall aluminum and lightweight ends; verify seamer chuck compatibility now |
| Energy inflation (EU +35 % YoY) | TCO audits > CapEx price | Demand VFD-controlled seamer motors & regenerative brakes; lock energy-use clauses in SLAs |
| Reshoring of beverage production | US can plants +18 % announced capacity 2024 | Shorten delivery windows; pre-book slots for Q1 installs to avoid 14-week lead times |
| Right-to-Repair laws (EU 2025) | OEMs must supply spare parts 7–10 years | Insert parts-availability clause; source from suppliers with EU parts hubs (GW Kent, ACM) |
*Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation
1. Sustainability: From “Nice-to-Have” to Tender Gatekeeper
- Lightweighting: Wall thickness moving from 0.203 mm → 0.180 mm saves 4 % aluminum/unit but requires seamer recalibration; confirm chuck profile and 1st-operation roll spec in PO.
- Water-use KPIs: Best-in-class lines now <0.4 L water/1,000 cans (rinse + filler). Ask for NEP or EPD documentation; embed in RFP scoring.
- rPET ends & pull-tabs: PTA applicators must handle 15 % softer tabs; run qualification batches before SOP.
2. Technology Shifts Affecting Sourcing Windows
| Tech | Maturity | Adoption Trigger | Sourcing Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric-to-counter-pressure retrofit kits | Early commercial | Hazy/juicy IPAs need <30 ppb DO | Add retrofit optionality in MSA; negotiate tech-upgrade clause priced at 2024 dollars |
| IoT-enabled seam monitors | Mainstream | Retailers demand full traceability | Specify OPC-UA data export; require open API, not locked SaaS |
| Mobile “canning-as-a-service” | Growth | CAPEX avoidance by nano-brewers | If 3rd-party canning expected, buy only seamer module (no filler) to cut cost 28 % |
3. Historical Context: From 1900 RPM to 60 CPM Craft Lines
- 1890s–1950s: Triple-seam technology standardized; lines ran 2,000 cans/min for national beer brands.
- 1980s: Aluminum supplants tinplate; seamer chucks re-engineered for softer metal.
- 2010: US craft brewers <5 % share; canning lines >300 CPM unaffordable.
- 2015: Entry-level 10 CPM manual seamers launch; price drops 70 %.
- 2023: 60 CPM “right-sized” systems (AT-6, CP-4) dominate mid-scale; ROI <12 months at 5,000 BBL/year.
4. Checklist: Qualify a Canning Machine Supplier in 2024
- Energy-use guarantee at 80 % throughput (kWh/1,000 cans).
- Spare-parts price freeze for 36 months; 48 h delivery to USA & EU.
- Upgrade path: single-lane to dual-lane within same frame.
- Seam data export to SQL for 10 years (compliance with EU digital product passport).
- Local field-service techs within 500 km for both markets.
Use this framework to de-risk CapEx while aligning with tightening sustainability mandates and volatile demand cycles.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of canning machines
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Canning Machines
| # | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What throughput range should I plan for? | Entry-level inline systems start at 8–12 cans per minute (CPM) for pilot batches; mid-scale dual-lane rotary fillers such as the AT-6 deliver 30–60 CPM; high-speed European monoblock lines reach 150–600 CPM. Match name-plate speed to 1.5× your peak daily forecast to avoid overtime shifts. |
| 2 | Counter-pressure vs. atmospheric filler—which is mandatory for my product? | Counter-pressure (isobaric) is required for carbonated beverages >2.5 vol CO₂ to prevent foaming loss and dissolved-oxygen pickup. Atmospheric gravity fillers are acceptable for still wine, kombucha, sauces, and water. Confirm DO specs <30 ppb for shelf-stable craft beer. |
| 3 | How fast can I change can height or diameter on the same line? | Tool-less changeover is now standard on US and EU machines. Expect 10–20 min to switch 202➜206 ends and 15–30 min for 211➜300 body heights if quick-release spindles and change parts are pre-staged. Budget for an extra set of change parts (~8–12 % of machine cost) to avoid line idle time. |
| 4 | What floor-space and utilities must I reserve? | Allow 2× the machine footprint for safe access. A 60 CPM dual-lane filler/seamer needs 2.0 m × 1.0 m; add 1 m infeed and 1 m discharge conveyor. Utilities: 6-bar oil-free air, 20 A 3-phase 400 V (EU) or 480 V (US), 8 L/min chilled water at 2 °C for CO₂ pre-cooler. |
| 5 | Is nitrogen dosing necessary for still products? | Yes, if hot-fill >80 °C is not possible. A 0.5–1.0 g liquid N₂ drop before seaming rigidizes the can, allowing 4-high pallet stacking without paneling. ROI is <9 months versus corrugated shippers. |
| 6 | How do I validate seam integrity without a full QC lab? | Specify a semi-automatic seam projector (×50 magnification) and digital micrometer; 5-can check every 30 min meets FDA & EU 2024/0021 guidelines. Modern machines store seam data in CSV for audit trails. |
| 7 | What’s the realistic CAPEX vs. OPEX split? | Rule of thumb: 70 % CAPEX (machine, change parts, depalletizer); 30 % first-year OPEX (CO₂, ends, labor, spare septums). A 60 CPM line typically pays back in 14–18 months when utilized >65 % of 2-shift capacity. |
| 8 | Can I integrate OEM data into my MES/ERP? | Most 2024-spec machines offer EtherNet/IP or OPC-UA ports; insist on a documented protocol stack during FAT. GW Kent and American Canning supply ready-made APIs for SAP, Microsoft Dynamics, and BrewMan. |
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for canning machines
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook
| Decision Lens | 2024 Action | 2025-26 Watchlist |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput ROI | AT-6 (60 CPM) delivers payback in <9 mo at 3 shift/day vs. 40 CPM legacy rigs | Electric servo seaming—30 % energy cut, EU carbon credit eligible |
| Floor Space | 23 ft² footprint now houses full dual-lane filler-seamer | Micro-canning pods (<15 ft²) for tap-room add-ons |
| Compliance | NSF/UL certified US builds; CE mark & IIoT data logging for EU traceability | Draft EU packaging regulation—recycled-content cans, RFID on every lid |
| Supply Chain | GW Kent 3-week US/EU stock; spare-part kits under 2-day ship | Stainless lead times stabilizing; hedge 12 mo of change-parts |
Key takeaway: Spec speed-per-dollar first, then lock in regional service density. Machines like the AT-6 prove 60 CPM is the new 40 CPM—without extra square meters. Prioritize suppliers that bundle OEE software and can upgrade seaming modules to electric drives; carbon tariffs will reward early adopters.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.