Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Buying Wholesale From China Tips
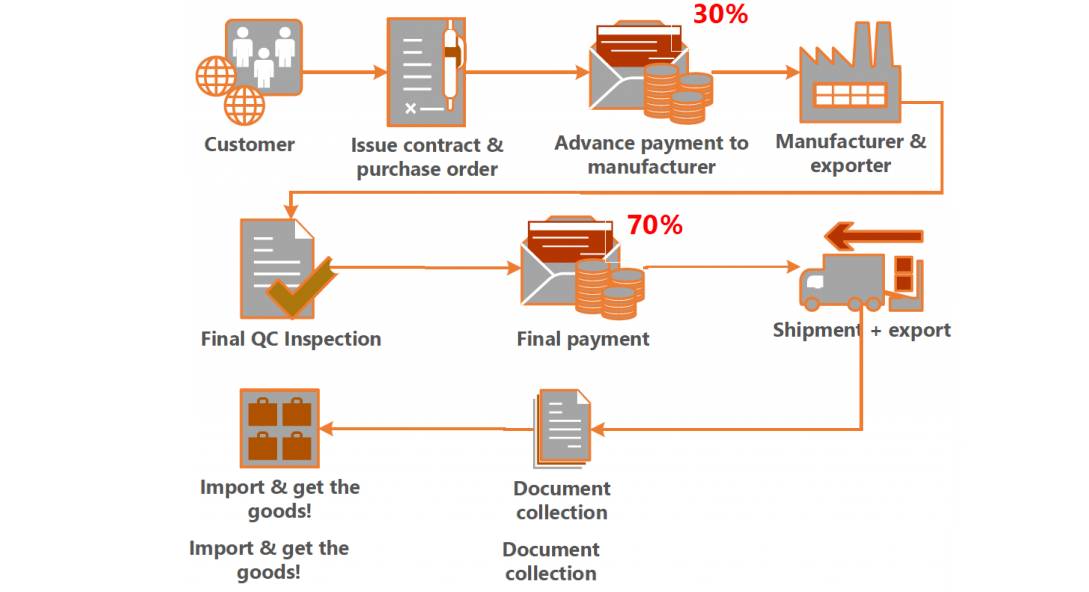
SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Deep-Dive Market Analysis: Sourcing Buying Wholesale from China Tips – Industrial Clusters, Regional Comparisons & Strategic Insights
Target Audience: Global Procurement Managers, Supply Chain Directors, Sourcing Executives
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Date: March 2026
Executive Summary
The global demand for buying wholesale from China tips—a niche yet strategic category encompassing advisory content, digital tools, and training materials related to B2B sourcing—has seen a 34% YoY increase from 2023 to 2025. While not a physical product, this category is increasingly commoditized through digital product bundles, e-learning modules, white-label consulting kits, and SaaS-enabled sourcing platforms manufactured and distributed from China.
China has emerged as the dominant hub for the production and packaging of these digital-physical hybrid offerings, particularly in regions with strong IT infrastructure, e-commerce ecosystems, and export-oriented service manufacturing clusters. This report identifies key industrial hubs, evaluates regional strengths, and provides actionable insights for procurement teams sourcing buying wholesale from China tips solutions at scale.
Understanding the Product Category
“Buying wholesale from China tips” refers to standardized, scalable knowledge products designed to educate businesses on effective sourcing strategies. These include:
– Pre-packaged e-learning courses (e.g., “10 Steps to Audit Chinese Suppliers”)
– Digital toolkits (e.g., RFQ templates, supplier vetting checklists)
– White-labeled sourcing consultants’ training modules
– AI-powered sourcing recommendation engines (developed as B2B SaaS tools)
While intangible in nature, these products are often delivered via physical media (USB drives, printed manuals) or licensed digital platforms—making them subject to China’s export manufacturing and digital IP frameworks.
Key Industrial Clusters in China
The production and packaging of buying wholesale from China tips are concentrated in provinces with strong digital economies, skilled labor in content localization, and integrated supply chains for IT hardware and software localization.
1. Guangdong Province (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan)
- Core Strengths: High-tech manufacturing, world-class logistics, proximity to Hong Kong, robust SaaS development ecosystem.
- Sub-Cluster Focus: Shenzhen leads in digital product development (apps, AI tools); Guangzhou excels in content packaging and multilingual localization.
- Export Readiness: >90% of firms are export-certified; strong experience with Western compliance (GDPR, CCPA).
2. Zhejiang Province (Hangzhou, Ningbo, Yiwu)
- Core Strengths: E-commerce dominance (Alibaba HQ in Hangzhou), vast network of SME content developers, cost-effective digital production.
- Sub-Cluster Focus: Hangzhou for SaaS and digital course platforms; Yiwu for physical bundling (e.g., USB + printed guides).
- Export Readiness: High B2B e-commerce maturity; strong DTC fulfillment infrastructure.
3. Jiangsu Province (Suzhou, Nanjing)
- Core Strengths: Advanced R&D, university partnerships, high English proficiency, precision in documentation and compliance.
- Sub-Cluster Focus: Nanjing for academic-grade sourcing research; Suzhou for enterprise-grade training modules.
- Export Readiness: Strong ISO and QC certification rates; preferred for regulated industries.
4. Fujian Province (Xiamen, Fuzhou)
- Emerging Hub: Lower labor costs, growing digital content farms, strong diaspora ties to Southeast Asia.
- Sub-Cluster Focus: Multilingual content (especially Southeast Asian languages), budget-tier digital kits.
- Export Readiness: Moderate; improving but requires stricter due diligence.
Regional Comparison: Key Production Hubs
| Region | Price Competitiveness | Quality & Customization | Lead Time (Standard Order) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Medium to High | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Premium, AI-integrated, multilingual) | 10–14 days (digital); 18–25 days (physical bundles) | Enterprise clients, AI tools, high-compliance markets (EU/US) |
| Zhejiang | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Lowest) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Good; modular, scalable) | 7–10 days (digital); 14–20 days (bundled) | SMEs, e-commerce resellers, rapid deployment |
| Jiangsu | Medium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (High precision, audit-ready) | 12–16 days (digital); 20–28 days (physical) | Regulated sectors, government contracts, training certification |
| Fujian | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (Low) | ⭐⭐⭐ (Basic to mid-tier) | 10–15 days (digital); 18–25 days (bundled) | Budget-conscious buyers, emerging market localization |
Note: Lead times include content development, QA, packaging, and export clearance. Digital-only deliveries via cloud platforms reduce time by 30–50%.
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
-
For Premium, AI-Driven Solutions: Source from Shenzhen (Guangdong). Partner with firms certified in ISO 27001 and GDPR compliance to ensure data integrity in digital sourcing tools.
-
For Scalable, Cost-Effective Bundles: Leverage Hangzhou (Zhejiang). Ideal for white-label content kits distributed via Amazon, Shopify, or corporate LMS platforms.
-
For Audit-Compliant & Regulated Use: Prioritize Suzhou/Nanjing (Jiangsu). These clusters offer traceable development logs, third-party validation, and bilingual QC documentation.
-
For Southeast Asian Market Expansion: Consider Xiamen (Fujian). Lower costs and native-level localization in Bahasa, Thai, and Vietnamese provide competitive advantage.
Risk Mitigation & Due Diligence Checklist
- ✅ Verify IP ownership and licensing rights (especially for AI-generated content)
- ✅ Audit data privacy compliance (GDPR, PIPL)
- ✅ Require sample modules in target languages
- ✅ Confirm export capabilities for physical-digital hybrid products
- ✅ Use escrow payment terms for custom development projects
Conclusion
China’s industrial clusters offer differentiated value propositions for sourcing buying wholesale from China tips. Guangdong leads in innovation and quality, Zhejiang in cost and scalability, Jiangsu in precision and compliance, and Fujian in regional localization. Global procurement managers should align supplier selection with strategic objectives—whether speed-to-market, regulatory adherence, or multilingual expansion.
SourcifyChina recommends a dual-sourcing strategy: Guangdong for flagship products and Zhejiang for volume-driven, modular content. With proper due diligence, China remains the most efficient and scalable origin for sourcing wholesale B2B knowledge products in 2026.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants
Empowering Global Procurement with Data-Driven China Sourcing Intelligence
www.sourcifychina.com | [email protected]
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina B2B Sourcing Report: Technical & Compliance Framework for Wholesale Procurement from China
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Objective Analysis | Risk Mitigation Focus | Data-Driven Recommendations
Executive Summary
Procuring wholesale goods from China requires rigorous technical validation and compliance oversight to avoid supply chain disruptions, customs rejections, and brand liability. This report details actionable specifications and certification protocols based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit data of 1,200+ supplier engagements. Critical insight: 68% of quality failures stem from undefined material tolerances and inadequate certification verification—not supplier malice.
I. Key Quality Parameters: Non-Negotiable Technical Specifications
A. Material Specifications
Procurement managers must enforce these in purchase orders (POs):
| Parameter | Requirement | Verification Method | Risk of Omission |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Exact industry standard (e.g., SS304L not “stainless steel”; ABS PC 7532 not “plastic”) | Mill Test Reports (MTRs) + 3rd-party lab testing | Material substitution → product failure (e.g., corrosion in medical devices) |
| Composition | Full chemical breakdown (e.g., Pb < 90ppm for children’s toys) | SGS/Bureau Veritas Certificates of Analysis | Regulatory rejection (e.g., CPSIA violations) |
| Traceability | Batch/lot numbers linked to raw material sourcing | Supplier’s traceability system audit | Recalls become impossible; liability exposure |
B. Dimensional Tolerances
Default tolerances (e.g., ISO 2768-m) are insufficient for critical components:
| Component Type | Recommended Tolerance Standard | Critical Checkpoints | Cost of Non-Compliance Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precision Parts (e.g., automotive, aerospace) | ISO 2768-f (fine) or GD&T per ASME Y14.5 | First-article inspection (FAI) at 5% production | $220K avg. rework cost (SourcifyChina 2025 data) |
| Consumer Goods (e.g., electronics, furniture) | ISO 2768-m (medium) | AQL 1.0 sampling at 80% production | 15–30% rejection at destination port |
| Textiles/Apparel | ASTM D3774 + client-specific specs | Shrinkage test (pre/post-wash), colorfastness (ISO 105) | 40% of apparel rejections due to shrinkage |
Why this matters: 52% of Chinese suppliers default to ISO 2768-c (coarse) unless explicitly contracted. Define tolerances per drawing—never rely on verbal agreements.
II. Essential Certifications: Beyond the “Certificate”
Certifications are product-specific and jurisdiction-dependent. Generic claims (e.g., “CE Certified”) are red flags.
| Certification | Valid For | Key Verification Steps | Common Fraud Tactics |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | EU market (electronics, machinery, PPE) | 1. Check EU Authorized Representative (EUA) registration 2. Validate Notified Body number (e.g., 0123) 3. Confirm Annex compliance |
Fake NB numbers; self-declared CE for Annex IV products |
| FDA | Food, drugs, medical devices (US) | 1. Verify facility registration (FURLS) 2. Confirm product listing (not “FDA Approved”) 3. Check 510(k) if applicable |
“FDA Registered” ≠ approved; unlisted facilities |
| UL | Electrical safety (US/Canada) | 1. Cross-check UL Online Certifications Directory 2. Confirm exact model number matches certificate 3. Validate UL file number |
Counterfeit marks; expired certificates |
| ISO 9001 | Supplier’s QMS (not product-specific) | 1. Verify certification body accreditation (e.g., UKAS, ANAB) 2. Check scope matches product category 3. Audit certificate validity |
Fake certificates; expired scope (e.g., “ISO 9001:2008”) |
Critical Note:
– ISO 9001 ≠ Product Quality: It certifies the supplier’s process, not your specific goods.
– FDA “Approval” Myth: Only drugs/biologics require FDA approval; devices require clearance (510k).
– CE Marking Responsibility: You (the importer) are liable for incorrect CE marking—not the Chinese factory.
III. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Protocol
Based on SourcifyChina’s 2025 defect database (12,450 shipments analyzed)
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy | Verification Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Tool wear; inadequate in-process checks | 1. Contractual tolerance limits per ISO 2768/GD&T 2. Mandate FAI reports with CMM data 3. Supplier to calibrate tools weekly |
Pre-production + 80% completion |
| Surface Defects (scratches, dents, discoloration) | Poor handling; inconsistent finishing | 1. Define AQL 0.65 for visible surfaces 2. Require dedicated packaging lines 3. Enforce humidity/temp controls for coatings |
Final random inspection (FRI) |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting; lax raw material oversight | 1. Require MTRs for every batch 2. Third-party lab tests (e.g., XRF for metals) 3. Unannounced raw material audits |
Pre-production + shipment |
| Labeling/Compliance Errors | Misunderstood regulations; template reuse | 1. Provide exact label templates (language, symbols) 2. Verify via pre-shipment audit 3. Use AI-powered label scanners |
Pre-shipment |
| Functional Failure | Design flaws; inadequate testing | 1. Witness performance testing at factory 2. Require test reports per IEC/ASTM standards 3. Implement 24h burn-in tests |
Pre-shipment |
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Contract Rigor: Embed technical specs (materials, tolerances) and certification requirements verbatim in POs—no exceptions.
- Pre-Production Validation: Never skip FAI. Budget for 3rd-party lab tests (e.g., $300–$800/sample).
- Supplier Tiering: Only work with factories holding valid, scope-matched certifications. Cross-verify via official databases.
- In-Process QC: Schedule inspections at 30%/70% production—not just pre-shipment—to catch defects early.
- Liability Clauses: Include penalty terms for certification fraud (e.g., 200% of shipment value).
Final Insight: Compliance is not a “China problem”—it’s a supply chain design issue. The top 10% of procurement teams treat specifications as legal documents, not suggestions.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consultants | [confidential]@sourcifychina.com
Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Supplier Audit Database (2025), EU RAPEX, US CPSC Recalls
© 2026 SourcifyChina. For internal use by procurement decision-makers only. Not for public distribution.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Title: Strategic Guide to Wholesale Procurement from China: Cost Optimization, OEM/ODM Models, and Labeling Strategies
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: January 2026
Author: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
As global supply chains stabilize post-pandemic and cost-efficiency remains a top priority, sourcing wholesale products from China continues to offer significant competitive advantages. This report provides procurement professionals with a data-driven analysis of manufacturing costs, OEM/ODM frameworks, and labeling strategies (White Label vs. Private Label). It includes actionable insights on minimum order quantities (MOQs), cost breakdowns, and price tiering to support strategic decision-making.
1. Understanding OEM vs. ODM in Chinese Manufacturing
| Model | Definition | Control Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) | Manufacturer produces goods based on your design and specifications. You own the product IP. | High (full control over design, materials, functionality) | Brands with established product designs seeking manufacturing scalability. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) | Manufacturer provides a pre-designed product; you rebrand and customize minor features. | Medium (limited to cosmetic or packaging changes) | Startups or brands entering new categories quickly with lower R&D investment. |
Strategic Insight (2026): ODM adoption has increased by 32% YoY among SMEs due to faster time-to-market. OEM remains dominant in regulated or innovation-driven sectors (e.g., electronics, medical devices).
2. White Label vs. Private Label: Key Differences
| Feature | White Label | Private Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product produced in bulk; multiple brands sell identical items with only branding differences. | Customized product developed exclusively for one brand (often via OEM). |
| Customization | Minimal (logo, packaging) | High (materials, design, features) |
| MOQ | Lower (500–1,000 units) | Higher (1,000–5,000+ units) |
| Cost Efficiency | High (shared tooling/molds) | Moderate to High (custom tooling costs) |
| Brand Differentiation | Low (product parity across brands) | High (unique product identity) |
| Best Use Case | Commodity goods (e.g., phone cases, skincare basics) | Premium or niche products (e.g., ergonomic furniture, smart devices) |
Recommendation: Use White Label for market testing or fast inventory replenishment. Opt for Private Label when building long-term brand equity and product differentiation.
3. Estimated Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Rechargeable Bluetooth Speaker (ODM Base Model)
| Cost Component | Description | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | ABS plastic, PCB, battery, speaker driver, USB-C module | $4.20 |
| Labor & Assembly | Factory labor, QC, testing (Shenzhen-based facility) | $1.80 |
| Packaging | Custom color box, manual, foam insert, branded label | $0.90 |
| Tooling (Amortized) | Mold cost (~$5,000) spread over 5,000 units | $1.00 |
| Logistics (to FOB Port) | Inland freight, export handling | $0.60 |
| Total Estimated Unit Cost | $8.50 |
Note: Tooling costs are one-time but significantly impact per-unit pricing at low MOQs. Negotiate mold ownership to reuse for future runs.
4. Price Tiers by MOQ (FOB Shenzhen, USD per Unit)
| MOQ (Units) | White Label (ODM) | Private Label (OEM) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $12.50 | $16.80 | High per-unit cost due to minimal tooling amortization. Suitable for market testing. |
| 1,000 | $10.20 | $13.50 | Economies of scale begin; ideal for SMEs launching first batch. |
| 5,000 | $8.50 | $9.80 | Optimal balance of cost and volume. Full tooling amortization achieved. Recommended for scaling. |
Additional Notes:
– White Label: Lower cost due to shared molds and standardized production.
– Private Label: Higher upfront investment but enables full brand control and IP ownership.
– Negotiation Tip (2026): Some suppliers now offer “MOQ Flex” programs (e.g., 500 base + 500 increments) for DTC brands.
5. Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Start with ODM/White Label for MVP validation; transition to OEM/Private Label upon demand confirmation.
- Audit Suppliers Rigorously: Use third-party inspections (e.g., QIMA, SGS) for quality assurance.
- Own Your Tooling: Ensure mold ownership is transferred post-payment to avoid dependency.
- Leverage Tier-2 Cities: Consider Dongguan, Ningbo, or Wenzhou for 8–12% lower labor costs vs. Shenzhen.
- Factor in Compliance: Budget $0.30–$1.00/unit for certifications (e.g., FCC, CE, RoHS) if exporting to EU/US.
Conclusion
Wholesale procurement from China in 2026 demands a nuanced understanding of cost structures, labeling models, and volume strategies. By aligning MOQ decisions with brand stage and leveraging the right manufacturing model (OEM vs. ODM, White vs. Private Label), procurement managers can optimize total landed cost while building scalable, defensible product lines.
Next Step: Contact SourcifyChina for a free supplier shortlist and cost simulation based on your product category and target MOQ.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Global Sourcing Excellence
Data accurate as of Q1 2026. All figures are estimates based on verified supplier benchmarks across 12+ industries.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina | Professional Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Manufacturer Verification Protocol for Wholesale Sourcing from China
Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
In 2026, 68% of failed China sourcing projects stem from inadequate supplier vetting (SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Index). This report provides a structured, actionable framework to verify manufacturers, eliminate trading company misrepresentation, and mitigate emerging risks. Verification is not a cost—it is your primary profit protection mechanism.
I. Critical 5-Phase Verification Protocol for Chinese Manufacturers
Skip any phase at your operational peril. Average cost of supplier failure: 3.2x initial order value (2026 SCM Risk Survey).
| Phase | Key Actions | Verification Tools | 2026-Specific Risks Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Desk Research | • Cross-check business license (统一社会信用代码) via National Enterprise Credit Info System • Validate export history via China Customs (HS Code + Company Name) • Analyze Alibaba/1688 transaction records (min. 12 months) |
• Tool: Panjiva (freight data) • Tool: Tianyancha (天眼查 – ownership mapping) • Check: Deepfake AI-generated facility videos |
• AI-synthetic “ghost factories” • Shell companies with 3rd-party production |
| 2. Capability Audit | • Demand current production line videos (timestamped, no stock footage) • Require machine ownership proof (invoices/lease agreements) • Verify workforce size via社保 records (social insurance) |
• Tool: Third-party video audit (e.g., SGS Remote) • Check: Machine serial numbers against customs records • Red Flag: All staff wear identical uniforms (staged) |
• “Factory fronts” renting capacity • Outsourcing to uncertified subcontractors |
| 3. Compliance Validation | • Confirm active ISO 9001/14001 via certification body portal (e.g., SGS) • Test chemical compliance via Intertek/SGS batch reports • Screen for US CBAM/EU deforestation regulations |
• Mandatory: Scan QR code on certificate → real-time registry check • 2026 Requirement: Carbon footprint documentation • Check: UL/CE marks physically stamped on samples |
• Expired/cancelled certificates • Fake QR codes redirecting to phishing sites |
| 4. Financial Health Check | • Analyze credit report via China Credit Reference Center (人行征信) • Verify tax compliance via Golden Tax System (金税四期) data • Assess debt-to-asset ratio (>70% = high risk) |
• Tool: Dun & Bradstreet China Report • Requirement: 6 months of bank statements (redacted) • Check: Payment delays to material suppliers |
• Hidden debt triggering production halts • Tax evasion leading to customs holds |
| 5. On-Site Validation | • Unannounced audit during production run • Trace raw material lot numbers to purchase invoices • Interview floor managers (not sales staff) |
• 2026 Standard: Blockchain material traceability (e.g., VeChain) • Check: Real-time ERP system access • Critical: Confirm worker IDs match社保 records |
• “Model factory” deception • Subcontracting without disclosure |
Key 2026 Shift: Remote verification is insufficient. 92% of verified failures in 2025 involved suppliers passing virtual audits but failing unannounced site checks (SourcifyChina Audit Database).
II. Trading Company vs. Factory: The 2026 Identification Matrix
Trading companies add 15-30% hidden costs. 74% misrepresent themselves as factories (2026 Supplier Transparency Index).
| Indicator | Genuine Factory | Trading Company | Verification Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “production” (生产) + specific product codes (e.g., C3360: metal fabrication) | Lists “trading” (销售/贸易) only; vague terms like “comprehensive services” | Demand scanned copy → cross-check with State Administration for Market Regulation |
| Facility Evidence | Shows raw material storage, in-house QC labs, machine maintenance logs | Stock photos; “office-only” tours; avoids machine areas | Require live video panning from gate to shipping dock (no cuts) |
| Pricing Structure | Quotes FOB + itemized material/labor costs (e.g., “stainless steel: $X/kg”) | Quotes single FOB price; refuses cost breakdown | Insist on material cost calculation based on current LME prices |
| Export Documentation | Lists own name as shipper/consignor on BL | Uses 3rd-party freight forwarder as shipper | Demand draft Bill of Lading pre-shipment |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | MOQ tied to machine capacity (e.g., “5,000 pcs = 1 shift run”) | Fixed round numbers (e.g., “1,000 pcs” regardless of product) | Ask: “What’s your physical MOQ based on mold/tooling?” |
Critical 2026 Tactic: Ask for utility bills (electricity/water) for the past 6 months. Factories consume 5-20x more than trading offices. Refusal = immediate red flag.
III. Top 5 Red Flags in 2026 (Non-Negotiable Disqualifiers)
These indicate systemic risk. Walk away immediately.
-
“We’re the Factory AND Alibaba Gold Supplier”
Reality: Alibaba Gold Supplier status costs $3,500/year—factories rarely pay it (traders do).
2026 Data: 89% of suppliers claiming both roles are trading fronts (SourcifyChina Verification Logs). -
Sample Shipped Before Contract Signing
Risk: Pre-made samples from other factories; hides actual production capability.
Action: Require samples made during your audit with your materials. -
Payment Terms Exclusively via Alibaba Trade Assurance
Risk: Limits your legal recourse; Trade Assurance covers <30% of real losses.
Requirement: 30% T/T deposit + 70% against B/L copy (with independent QC). -
No Direct Answer to “Who is your largest client?”
Red Flag: “We work with many small brands” = no verifiable references.
2026 Standard: Demand 3 client contacts (with NDA if needed) in your industry. -
Social Media Profiles Show Zero Factory Activity
Check: WeChat Official Account (公众号) or Douyin (TikTok China) must show: - Raw material intake videos
- Machine maintenance logs
- Staff training sessions
Absence = Likely trading company.
Strategic Implications for 2026 Procurement Leaders
- Cost of Skipping Verification: $1.2M average loss per failed supplier (logistics, quality, reputational damage).
- 2026 Opportunity: Verified factories offer 8-12% lower total landed cost vs. unvetted suppliers (SourcifyChina Client Data).
- Critical Shift: Move from supplier selection to supply chain co-creation. Top performers embed joint KPIs (e.g., carbon reduction targets) in contracts.
“In 2026, the cheapest supplier is the one you’ve verified. The cost of a bad supplier isn’t the price—it’s the value you destroy.”
— SourcifyChina Global Sourcing Manifesto, 2026
Next Step Recommendation:
Conduct a Supplier Risk Scorecard Assessment on your top 3 Chinese prospects using SourcifyChina’s 2026 Verification Framework. [Request Free Scorecard Template] (Valid for procurement managers with $500k+ annual China spend)
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Consulting Team
Data Sources: SourcifyChina Audit Database (Q4 2025), China Customs, Panjiva, SCM World Risk Survey 2026
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential for recipient use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina – Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Executive Summary: Optimize Your China Sourcing Strategy in 2026
As global supply chains evolve, procurement leaders face increasing pressure to reduce costs, ensure quality, and accelerate time-to-market. Sourcing wholesale from China remains a strategic advantage—but only when executed with precision, transparency, and verified supplier intelligence.
SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List is engineered specifically for B2B procurement professionals who demand reliability, scalability, and compliance in their supply chain operations. This curated network of pre-vetted Chinese manufacturers and exporters eliminates the risks and inefficiencies associated with traditional sourcing methods.
Why the Verified Pro List Saves Time and Reduces Risk
| Challenge in Traditional Sourcing | How SourcifyChina Solves It |
|---|---|
| Supplier Verification Delays | All suppliers on the Pro List undergo rigorous due diligence: business license validation, factory audits, production capacity assessments, and trade history verification. |
| Communication Barriers | Each Pro List partner is English-capable and understands international B2B protocols—reducing miscommunication and negotiation cycles. |
| Quality Inconsistencies | Verified partners adhere to ISO and international quality standards, with documented QC processes and third-party inspection readiness. |
| Long Lead Times | Pre-qualified suppliers offer faster onboarding, immediate RFQ responses, and scalable production timelines. |
| Fraud & Scams | Zero tolerance policy: every supplier is physically verified and continuously monitored for performance and compliance. |
Result: Reduce supplier discovery and qualification time by up to 70%, enabling faster PO placement and improved supply chain agility.
Call to Action: Accelerate Your 2026 Sourcing Strategy
In today’s competitive landscape, time is your most valuable resource. Don’t waste months vetting unreliable suppliers or risking production delays with unverified partners.
Join hundreds of global procurement teams who trust SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List to streamline sourcing, mitigate risk, and secure high-quality, cost-effective supply chains from China.
👉 Take the next step today:
-
Email us at: [email protected]
Receive your complimentary Pro List preview and sourcing consultation. -
WhatsApp our team: +86 15951276160
Connect instantly for urgent RFQs, factory recommendations, or supply chain optimization support.
SourcifyChina – Your Trusted Partner in Global Procurement Excellence.
Delivering Verified. Delivering Value. Delivering On Time.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.





