Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Breathable Leatherette
Procurement teams often face a simple problem with a complex trade-off: the leatherette looks great on a line card, yet fails in real conditions—too hot for end‑use, too stiff, or compliant only in one region. Breathability should not mean sacrificing durability or waterproofing; it must be engineered with proof and aligned to your specific region, category, and lifecycle cost.
This guide walks you from product selection to supplier governance across the USA and Europe. We decode performance claims, map EU/US compliance (EN 45545 for transport; CAL TB 117 and BIFMA for furniture; FR 701/ISO 3795 where applicable), and set practical procurement tests (MVTR, microperforation counts, hydrostatic head, Martindale, cold crack, and VOC limits). You’ll also learn how to qualify suppliers, structure pricing (per metre vs. roll), and de‑risk lead times and returns.
To illustrate the market reality, consider the signals from a current listing:
| Attribute | Signal |
| — | — |
| Width | 55″ / 140 cm (typical cut‑length widths) |
| Selling unit | Sold by the metre (cut‑to‑length) |
| Indicative price | ≈ USD $182 for ~14 m (~$13/m) |
| Region | CN/US fulfillment; US‑based return window |
| Vendor | Guo Yue Fei American Trading Co. (Amazon storefront) |
| Returns | Returnable until 31 Jan 2026 |
These metrics are not a recommendation; they’re a baseline for benchmarking. Next, we’ll translate them into decision rules you can apply in your RFQ and quality gate.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Breathable Leatherette Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for breathable leatherette
- Understanding breathable leatherette Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of breathable leatherette
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘breathable leatherette’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for breathable leatherette
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for breathable leatherette
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘breathable leatherette’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for breathable leatherette Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing breathable leatherette With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for breathable leatherette
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the breathable leatherette Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of breathable leatherette
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for breathable leatherette
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Breathable Leatherette Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. laif® technology | Breathable & air-permeable artificial leather – Skai
Domain: skai.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: The functional skai® VyP synthetic leathers shine in practical use with outstanding properties such as breathability, water and air permeability and soft, ……
2. Top 10 Synthetic Leather Suppliers in 2025 – BLUEC
Domain: bluectex.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Top 10 Synthetic Leather Suppliers in 2025 · 1. Shaoxing Bluec Industry and Trade Co., Ltd. (BLUEC) · 2. Nevotex · 3. Thomasnet · 4. Furnileather · 5. Weaver Leather ……
3. Synthetic, Imitation & Artificial Leather Manufacturers and Suppliers …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Sileather. Manufacturer of leather and silicone fabrics with features including extreme temperature, UV, and stain resistance. Suitable for marine, commercial ……
4. Alternative Leathers Co.: Plant-Based Leathers
Domain: alternativeleathers.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Alternative Leathers Co. is the world’s leading supplier of plant-based materials. We offer easy access to the most innovative and sustainable materials on ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Synthetic Leather Manufacturers and Suppliers – TradeWheel
Domain: tradewheel.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Find high-quality Synthetic Leather from global manufacturers, suppliers, and exporters at wholesale price on the world’s leading B2B industry portal ……
6. Garrett Leather Homepage
Domain: garrettleather.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: LeatherShield™ is a special classification designated to a select group of Garrett Leather products made to withstand the demands of high-traffic areas….
Understanding breathable leatherette Types and Variations
Understanding breathable leatherette: Types and Variations
Note: The provided source describes a 55″ (140 cm) wide upholstery material sold by the metre, offered in colour and size options, with “Waterproof” and “Fire Retardant” attributes. Breathability is not explicitly stated in the source; treat breathability and related performance (e.g., air permeability) as variable and supplier-specific unless explicitly documented in test reports.
Comparative overview
| Type | Key features (per source and common practice) | Typical applications (B2B) | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Leatherette | Standard PVC/PU upholstery fabric; typically not specified as waterproof or FR in the source | Furniture upholstery (seating, headboards); general contract furnishing | Cost-effective; wide colour range; easy to cut and sew | May lack waterproofing and FR; breathability/cleanability vary by composition |
| Waterproof Leatherette | Source explicitly marketed as “Waterproof”; often PVC/PU with sealed surface | Seating in high-traffic/hygiene-sensitive environments; hospitality; healthcare-adjacent seating | Surface liquid resistance; easy to wipe clean | Breathability/thermo comfort require testing; surface can feel warmer to touch depending on backing |
| Fire-Retardant (FR) Leatherette | Source explicitly marketed as “Fire Retardant”; FR chemistry incorporated | Contract/commercial upholstery; hospitality/public spaces requiring fire codes | Compliance-ready for specified FR standards; supports approvals for tender/specifications | FR performance varies by supplier and test method; maintenance specifics to confirm with supplier |
| Hybrid Waterproof + FR Leatherette | Source indicates combined “Waterproof” and “Fire Retardant” | High-spec projects needing both liquid resistance and FR compliance | Dual performance reduces need for separate fabrics; streamlines procurement | Higher cost than single-property grades; verify both properties and applicable standards (e.g., UFAC, CAL TB 117, CAL TB 133, EN standards) |
What matters when choosing a breathable leatherette
- Verify claimed properties with third-party reports: waterproofing (e.g., hydrostatic head or spray test) and FR certifications/standards (UFAC, CAL TB 117/133, EN standards as applicable).
- Confirm breathability and thermo comfort with air permeability or moisture vapor transmission data; do not assume from generic product titles.
- Check finish compatibility (e.g., antimicrobial, stain-resistant) and regulatory compliance for your target markets (US/EU).
- Validate backings (e.g., knit vs. woven), seam performance, and abrasion specs for durability.
Detailed type breakdown
1) Standard Leatherette
- Overview: Typical upholstery-grade faux leather/vinyl or PU. The source’s base offering is sold by the metre in multiple colours and sizes (e.g., 1.4x1m up to 1.4x10m), suitable for cut-and-sew workflows.
- Features: Supplier-provided colour and size options; surface resembling leather; unspecified waterproof/FR in this variant.
- Applications: Contract seating, headboards, wall panels, AV/pop-up furniture; suitable where moisture exposure is minimal and FR is not a tender requirement.
- Pros: Cost-efficient, easy fabrication, broad design palette.
- Cons: Without explicit waterproofing/FR, performance must be confirmed with lab reports; comfort and breathability require specification validation.
2) Waterproof Leatherette
- Overview: The source is explicitly described as “Waterproof,” indicating a liquid-resistant surface that can be wiped clean.
- Features: Sealed topcoat; designed for spill control in upholstery; colour/size options per the source listing.
- Applications: Hospitality seating, entryway lounges, waiting areas, dining chairs where routine cleaning is expected.
- Pros: Simplifies cleaning; limits liquid absorption; reduces stain risk.
- Cons: Comfort may be temperature-dependent; confirm breathability/air permeability and seam hydro-sealing if relevant.
3) Fire-Retardant (FR) Leatherette
- Overview: The source notes “Fire Retardant,” signalling the material meets specified FR criteria—confirm the exact standard and test method.
- Features: FR chemistry integrated into the formulation or finish; suitable for commercial projects with code requirements.
- Applications: Contract interiors, hospitality, transit lounges, event spaces where FR compliance is mandatory.
- Pros: Aligns with regulatory requirements; facilitates approvals and tender submissions.
- Cons: FR performance is formulation-specific; verify re-treatment implications and maintenance recommendations.
4) Hybrid Waterproof + FR Leatherette
- Overview: The source indicates the material can be both waterproof and fire retardant, providing dual functionality.
- Features: Liquid resistance plus FR compliance; sold by the metre in colour/size selections.
- Applications: High-traffic commercial settings needing both easy-clean surfaces and FR adherence (e.g., corporate lounges, hospitality venues).
- Pros: Consolidated performance; reduces need for multiple SKUs; simplifies specification.
- Cons: Typically higher cost; requires documentation for both properties and relevant certifications.
Key takeaway: Align selection with documented waterproof/FR claims and independent test data; specify breathability where climate or comfort is a concern, and validate colour/size logistics against project needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of breathable leatherette
Key Industrial Applications of breathable leatherette
| Industry / Application | Breathable Leatherette Features | Value / Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & Mobility | Micro-perforated surface for moisture management; waterproof; wipe-clean; abrasion-resistant; good seam strength | Improved seating comfort on long drives; reduced heat build‑up; lower maintenance; longer service life for seats, door panels, consoles; supports fleet downtime targets |
| Public Transport & Rail | Moisture control; easy-clean; wear-resistant; waterproof; often available with FR grades | Passenger comfort and hygiene; simplified cleaning protocols (e.g., end-of-shift); compliance-ready material selection for interior touchpoints; lifecycle cost control |
| Aviation & Marine | Breathable topcoats help manage condensation; waterproof; wipe-clean; abrasion-resistant | Enhanced seat comfort and durability in variable climates; quicker sanitation between voyages; resilient performance under frequent use |
| Office & Commercial Furniture | Breathable upholstery; wipe-clean; durable; cost-effective vs. full grain leather | Comfortable long-term seating; easy maintenance in high-traffic spaces; consistent look and feel across locations |
| Healthcare & Care Homes | Easy to disinfect; waterproof seams feasible; wipe-clean surfaces; often FR grades available | Infection-control friendly surfaces; reduced cleaning time and consumables; improved patient/staff comfort; faster room turnarounds |
| Hospitality (Hotels, Restaurants, Lounges) | Moisture management; stain-resistant finishes; wipe-clean; durable | Comfortable, low-maintenance guest seating; rapid spill cleanup; reduced replacement cycle costs; consistent brand appearance |
| Retail & Experiential Environments | Breathable, hard-wearing upholstery; easy refresh and reupholstery; wipe-clean | Strong visual impact with practicality; frequent cleaning without degradation; lower maintenance overhead for flagship stores |
| Education & Public Buildings | Comfort, hygiene, and abrasion resistance; low-maintenance; FR grades available | Reduced lifecycle costs; comfortable seating for extended use; compliance-ready interiors |
| Outdoor & Covered Seating | Breathable surface reduces stickiness; UV-stable options; waterproof; durable | Year-round comfort in covered patios; quick rain recovery; reduced fading and cracking; lower replacement frequency |
| Equipment Seats (Industrial, AG, Forklifts) | Breathable, supportive backrests; waterproof; abrasion-resistant; FR grades for machinery cabs | Operator comfort and productivity; protection against moisture and dust; simplified cleaning; extended seat life under industrial duty cycles |
| EV Battery Pack Wraps & Protective Covers | Non-porous waterproof barrier; flexible; tough; cleanable | Thermal and moisture protection for battery enclosures; quick cleaning after spills; efficient material handling in repair/servicing |
| Event & Rental Furniture | Consistent look; stain-resistant; easy wipe-down; durable; FR variants for venues | Rapid deployment and sanitation; uniform aesthetic across events; extended rental cycles; reduced damage and downtime |
Notes:
– Breathable leatherette typically denotes a micro-perforated or breathable topcoat structure that helps moisture vapor pass while retaining a non-porous barrier to liquids, enabling both comfort and easy cleaning.
– Waterproof and fire-retardant properties are product-dependent; verify certifications (e.g., EN 1021, TB 117-2013, FMVSS 302) and performance ratings with your supplier.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘breathable leatherette’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘breathable leatherette’ & Their Solutions
Note: Breathability is commonly measured by Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) or Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR). Test and report results in g/m²/day at 38°C/90–95% RH, with method stated (e.g., ASTM E96, ISO 15496). The examples below reflect typical industry issues and solutions.
Pain Point 1: Breathability vs. Waterproofing Conflicting
| Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Product labeled “breathable leatherette” with waterproof vinyl face. | MVTR/WVTR of the film is near zero, so heat and moisture build up (stickiness, condensation, mildew risk). | – Request MVTR/WVTR measured at 38°C/90–95% RH (e.g., ASTM E96 Procedure B, ISO 15496). – Choose micro‑perforated or breathable‑membrane constructions. – Document finish type (PU/PA, DWR) and water column data (e.g., 1,500–5,000 mm). – Align target MVTR with end‑use (office: ~2,000–8,000; high‑heat: higher). – Verify that coatings don’t occlude pores and that seams maintain MVTR. |
Action checklist
– MVTR/WVTR test with method and conditions
– Water column test and seam testing
– Breathable construction detail (micro‑perforation/membrane)
– Finish data sheet confirming non‑blocking pores
Pain Point 2: FR Compliance vs. Comfort
| Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Furniture and contract interiors require FR performance (USA: California TB 117‑2013; Europe: EN 1021‑1/2; BS 5852; NF D 60‑013). | FR coatings/additives can stiffen resin, reduce porosity, and lower breathability. | – Choose FR resins that maintain elasticity and allow pore structure. – Request FR test results with MVTR/WVTR data pre‑ and post‑treatment. – Combine a breathable foam or open‑cell underlayer with breathable leatherette to improve comfort and manage moisture. – Validate end‑to‑end system (composite assembly) meets FR and comfort. |
Action checklist
– FR resin matrix and test reports (MVTR/WVTR pre/post)
– Foam or underlayer system that supports vapor flow
– Composite FR validation for target markets

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 3: Claims, Specs, and Data Integrity
| Scenario | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple vendors claim “breathable” but provide no comparable lab data; finish or backing blocks pores after lamination. | Hard to compare suppliers; performance may degrade after lamination or wear. | – Require ISO‑compliant certificates and third‑party test reports (e.g., TÜV, SGS). – Request MVTR/WVTR both for face and finished composite. – Verify backing/laminate method does not reduce breathability. – Set a minimum acceptable MVTR in purchase specs and require retesting per batch. – Review Amazon listings as marketing: verify technical details against test data (e.g., waterproof FR claims can exist alongside low breathability in vinyl constructions). |
Action checklist
– Third‑party MVTR/WVTR and FR certifications
– Composite‑level tests (laminate/backing impact)
– Batch‑to‑batch verification and traceability
– Purchase spec minimum MVTR and method
Standards commonly referenced
– FR and smoke: ASTM E662; NFPA 701; EN 1021‑1/2; BS 5852; NF D 60‑013
– Moisture: ASTM E96 (MVTR/WVTR); ISO 15496
– Water repellency: AATCC 22; ISO 4920
– Abrasion: Martindale/Taber results with finish intact
Strategic Material Selection Guide for breathable leatherette
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Breathable Leatherette
What “breathable” means for leatherette
In B2B upholstery, “breathable” means moisture vapor can pass through the material and out of the system. Practical measures include:
– Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) in g/m²/24h; breathable leatherette typically reaches 500–3,000 g/m²/24h.
– Air permeability (ISO 9237 / ASTM D737) at a specified pressure (e.g., 125 Pa) to confirm micro-perforation or open structures.
– Humidity buffering: the material reduces localized humidity spikes on user contact.
A material can be breathable without being waterproof. True waterproofing often requires continuous, sealed films/coatings that reduce or eliminate breathability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
How breathable leatherette is constructed
- Surface layer (topcoat): flexible PU or TPU films are most compatible with breathability. PVC films can be used but usually sacrifice vapor transmission unless specifically engineered with micro-perforations.
- Micro-perforation: a laser/needle-punched array of 30–120 µm holes providing vapor path while limiting liquid ingress.
- Backings: open knit polyester fabrics (interlock, warp knit) or low-density nonwovens; scrims improve dimensional stability without sealing the structure.
- Coatings: thin hydrophilic or porous coatings help vapor wicking while maintaining wear resistance.
- Finishes: abrasion/abrasive-resistant, anti-microbial, and hydro-oleophobic treatments can be added without blocking pores if applied in controlled thicknesses.
Waterproof vinyls typically use thick PVC topcoats and closed films; these block vapor and are not designed to breathe.
Analysis of common materials used
- PU/TPU films with micro-perforation: high breathability, good hand/softness, hydrolytic risk if humid/tropical; select hydrolysis-resistant grades and validate with ASTM D2247 or ASTM D2240-aged tests.
- PVC films: robust water barrier, cost-effective, easy to clean; poor breathability when sealed; can include flame retardants but moisture management is weak for seating comfort.
- Polyester knit backings: stable, breathable; support perforation integrity and improve seam strength.
- Aramid or glass scrim reinforcement: improves dimensional stability and flame performance but can reduce tactile feel; requires careful design to avoid wear points.
- Topical FR treatments: can affect breathability and migration; ensure compliance with REACH/SVHC and California Prop 65 where applicable.
Key performance claims to validate
- Breathability: ask for MVTR (ASTM E96 or ISO 15496) and air permeability (ISO 9237 / ASTM D737) at defined conditions.
- Liquid barrier: water repellency/column height (AATCC 22) or hydrostatic head (ISO 811) if required, while acknowledging most breathable solutions are water-resistant rather than fully waterproof.
- Flame behavior: NFPA 260 (USA), TB117-2013 or TB117-2020 (California), and EN 1021-1/-2 (EU); request test reports from accredited labs.
- Abrasion and tear: Martindale/Taber abrasion (ISO 12947/ISO 5470) and tear strength (ISO 4674 or ASTM D2261).
- Cold crack and UV: ASTM D2136 (cold crack) and ASTM G154 (UV aging); ensure formulation and stabilizers suit intended use.
- Cleanability: wipe, solvent, bleach tolerance and stain removal protocols; verify chemical compatibility.
- VOC/emissions: GREENGUARD/GREENGUARD Gold or French A+ for indoor emissions where relevant.
Selection criteria by application
- Seating: prioritize MVTR and air permeability; ensure hydrolysis-resistant PU/TPU and dimensional stability under humid conditions.
- Wall panels and partitions: weigh breathability against required fire performance and acoustic openness; consider perforated scrims.
- Transport (aviation/rail/automotive): combine EN/NFPA/NFPA requirements with abrasion and cold crack; verify flammability by component type.
- Medical and care environments: FR, wipeable surfaces, and emissions compliance (GREENGUARD/French A+); verify chemical lists and REACH declarations.
- Marine/outdoor undercover: prioritize hydrolysis resistance, UV stability, and salt spray resistance; breathable PU/TPU preferred over sealed PVC.
Sustainability and compliance
- Request REACH/SVHC statements and conflict minerals disclosure (US Dodd-Frank) if metallic finishes are present.
- Verify California Proposition 65 compliance and any local chemical restrictions.
- Confirm recycled content (e.g., post-consumer PET backings) and recyclability of the material assembly.
Supplier due diligence
- Ask for independent lab data: MVTR, air permeability, flammability, abrasion, tear, cold crack, UV, and VOC/emissions.
- Confirm batch-to-batch consistency and process control for perforation uniformity and coating thickness.
- Verify origin and traceability, and specify conditioning environments for all tests.
- For waterproof claims: treat as non-breathable unless proven otherwise with MVTR and air permeability data.
Reference case: “Waterproof Faux Leather Leatherette Vinyl Fabric Fire Retardant” (Amazon)
- Constructed for waterproof upholstery use, implying sealed PVC or closed-film PVC/vinyl structure.
- Fire retardant finish reported; flammability ratings should still be confirmed (NFPA 260, EN 1021, TB117).
- Price (sold by the metre) and width (55”) are typical for marine/contract upholstery vinyl.
- Breathability: likely low or nil due to waterproofing intent. Not recommended where moisture comfort, humidity control, or user well-being is essential.
Decision matrix
- Need moisture comfort, vapor transport, and user contact comfort: choose breathable PU/TPU leatherette with documented MVTR/air permeability and hydrolysis-resistant formulation.
- Need liquid barrier and low maintenance with limited user contact: sealed PVC/vinyl may suffice; accept trade-off in breathability.
- Need fire performance: validate EN 1021, NFPA 260, and TB117; select materials inherently or effectively treated for required level.
Comparison table: Waterproof vinyl vs breathable leatherette
| Attribute | Waterproof vinyl (non-breathable) | Breathable leatherette (PU/TPU with micro-perforation) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical use | Marine hulls, dashboard covers, protected surfaces, non-contact panels | Seating, headrests, wall panels, transport interiors |
| Breathability (MVTR) | Low/near zero due to sealed films | 500–3,000 g/m²/24h (product-specific; request MVTR and air permeability reports) |
| Liquid barrier | Strong water barrier | Water-resistant; hydrostatic head depends on design |
| Flammability | Often FR-treated; verify NFPA 260/EN 1021 | Often FR options available; verify NFPA 260/EN 1021 |
| Comfort | High heat/humidity buildup on contact | Reduced sweat/heat buildup; better humidity buffering |
| Cleanability | Excellent wipeability | Good wipeability; some perforation areas require careful cleaning |
| Durability | High abrasion; can crack if cold if not specified | High abrasion; select hydrolysis-resistant PU/TPU |
| Typical price band | Lower per metre; broad commercial options | Higher per metre; performance-focused SKUs |
| Sustainability/compliance | PVC-related questions; confirm REACH/VOC | Confirm REACH/VOC; breathable films may offer lower VOC emissions |
| Reference product example | “Waterproof Faux Leather Leatherette Vinyl Fabric Fire Retardant” (Amazon) | Breathable, micro-perforated PU/TPU leatherette from contract suppliers |
Recommendation
– Select breathable PU/TPU leatherette with verified MVTR/air permeability for seating and high-contact applications, especially in humid climates or where user comfort is a KPI.
– Use sealed waterproof vinyls for non-contact, water-barrier applications and accept the breathability trade-off.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for breathable leatherette
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Breathable Leatherette
Breathable leatherette is a composite textile typically comprising a knitted or woven backing, an inner breathable microporous coating or film (e.g., TPU/PU), and a topcoat with embossed grain and protective finishes. Breathability is enabled by a network of micron-scale pores that allow vapor transport while blocking liquid water and contaminants. For USA and Europe, process control and compliance to recognized standards ensure consistent performance across upholstery, contract interiors, and mobility markets.
Below is a practical manufacturing framework and QA plan aligned to ISO and EN/IEC standards commonly adopted by OEMs and Tier suppliers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Process Overview
| Step | Methods / Equipment | Key Controls / Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Prep | Greige inspection; desizing/scouring; tenter alignment | Defect mapping; dimensional stability; moisture control; ISO 3759, ISO 6348 |
| Reinforcing/Backing | Lamination of nonwoven/knit with flame-retardant (FR) adhesives or films | Adhesive grammage uniformity; FR compliance alignment; ISO 12947 abrasion |
| Breathable Core Layer | Microporous TPU/PU casting or blown film extrusion | Pore uniformity; MVTR target met; ISO 15496, ISO 15487 |
| Topcoat & Grain | Solvent-free PU topcoat; inline embossing | Coat weight control; tactile and visual grain consistency; ISO 7216 surface appearance |
| Finishing & Functionalization | DWR, anti-soiling, bactericidal finishes; calendaring | Hydrostatic head; surface tension control; anti-microbial protocols (ISO 20743 optional) |
| Assembly | Seam sealing; edge finishing; lamination to foam or substrates | Seam strength; hot-stamp or heat-seal integrity; ISO 4674 adhesive strength |
| Final QA & Packaging | Final inspection; meter-by-meter testing; roll wrapping | Traceability; dimensional checks; ISO 2419 sample prep consistency |
Notes:
– FR compliance varies by region; specify target class (e.g., EN 13501-1 B-s1,d0 for contract interiors; EN 45545-2 for transport). Validate FR resin/film selection and binder systems during prep.
– If film-based leatherette is supplied as 55″ (140 cm) width (as in the referenced product), verify seam allowances and lay-up methods to avoid edge distortions and grain mismatch.
– For mobility (automotive/marine), map materials and processes to FMVSS 302, ECE R118, and EN 45545-2.
In-Process QC Map
| Control Point | Metric / Test Method | Frequency | Acceptance (Typical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backing Dimensional Stability | ISO 3759 shrinkage | Per batch | ≤ ±2–3% (set target) |
| Abrasion Resistance | ISO 12947 (Martindale) | Per 5,000 m | ≥ 30,000–50,000 cycles (use-case dependent) |
| Breathability (MVTR) | ISO 15496 or ISO 15487 | Every 10,000 m | Within project-defined envelope (e.g., ≥ 2,000 g/m²/24h for breathable performance) |
| Hydrostatic Head | ISO 811 | Every 10,000 m | ≥ 3,000 mm (waterproof leatherette) |
| Surface Finish Integrity | ISO 7216 scratch; visual grain | Every roll | No cracking, acceptable gloss variation |
| Adhesive/Seam Strength | ISO 4674 peel; seam strength | Every seam lot | Meets specified peel/strength threshold |
| Color/Gloss | Spectro vs master; gloss meter | Every 100 m | ΔE tolerance per contract; gloss within band |
| VOC / SVOC | ISO 16000-6 or 11857 (foam lam.) | Per supplier batch | Meets project thresholds (OEM-specific) |
| FR Performance | FMVSS 302; EN 13501-1; EN 45545-2 | Per product family | Meets target class/pass |
Tip: Define project-specific acceptance bands and document them in a quality plan. This avoids ambiguity across USA and EU customers with differing test protocols.
Compliance Requirements (USA vs EU)
| Domain | USA | EU / Regional |
|---|---|---|
| Textile Performance | ISO tests widely accepted; OEM specs | EN tests prevalent; CE/UKCA alignment as required |
| Fire Performance | Contract interiors: local codes; FMVSS 302 for automotive | EN 13501-1 classification; EN 45545-2 for rail |
| Low VOC / Formaldehyde | OEM/contract requirements (e.g., CARB compliance for foams/laminates if applicable) | REACH restrictions; VOC labeling where required |
| Chemical Management | Zero-conflict policies; RoHS where applicable | REACH; POPs; RoHS cross-acknowledgement |
Note: The reference material is “waterproof faux leather leatherette vinyl fabric fire retardant,” indicating FR capability. Confirm FR class and supporting tests in the contract.
Supplier Snapshot and Audit Cues
- Lead time: Example listing shows December 18–January 5 delivery window to Jacksonville 32099; factor 3–4 weeks when planning pilot runs and inventory buffers.
- Returns: Returnable until Jan 31, 2026. For B2B, verify material lot traceability, QC certificates, and first-article inspections before scale-up.
- Technical notes from the reference listing:
- Width: 55″ (140 cm).
- Price point: Approx. $182.18 for 1.4 × 10 m roll.
- Free delivery for the example listing, but confirm Incoterms (EXW, FOB, DDP) for your region.
- FR status: indicated. Ask for test reports and certificate numbers.
Practical Implementation Checklist
- Define breathable performance envelope (MVTR, pore size, hydro head) and align with application.
- Lock FR system and adhesives early; map to USA/EU codes.
- Validate seam and edge performance in assembled parts, not just in raw rolls.
- Embed ISO 2419 sample prep across all labs to minimize variability.
- Maintain lot-level traceability and retain roll samples for dispute resolution.
- Use the 55″ width efficiently in nesting; verify side margin and edge quality before lamination.
This process and QA framework enables consistent production of breathable leatherette that meets USA and EU expectations for comfort, durability, and regulatory compliance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘breathable leatherette’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘Breathable Leatherette’
Audience: USA, Europe
Use this checklist to progress from requirement setting to order release with repeatable controls.
1) Pre-RFQ: Define Requirements Precisely
Clarify what “breathable” means in your application, using measurable metrics and test standards.
| Category | What to Decide | Examples/Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability metrics | Select method and minimums | MVTR (g/m²·24h) by ASTM E96 Procedure B or ISO 15496; Air permeability (L/min·cm² or CFM/ft²) by ASTM D737; Moisture management (wicking/absorption) if relevant |
| Water resistance (if needed) | Decide compatibility with breathability | Hydrostatic head (ISO 811 or AATCC 127); Water spray repellency (AATCC 22); If waterproofing is required, expect trade-offs with breathability |
| Durability | Specify end-use tests | Abrasion (ASTM D4157 Wyzenbeek or ASTM D4966 Martindale); Tear (ASTM D2261 or ISO 4674); Seam strength (ASTM D1683) |
| Flammability/smoke/toxicity | Required standards | USA: CA TB117-2013; CAL-117 (older models); NFPA 701 for curtains/drapery; NFPA 260 for furniture; Smoke density (ASTM E662); Toxicity (NES 713 or equivalent). Confirm whether end-use requires flame-retardant (FR) |
| Chemical/environmental | Compliance scope | Europe: REACH, POPs; USA: California Prop 65; VOC/emissions (e.g., BIFMA x7.1/ISO 16000 series) if for enclosed indoor furniture; RoHS if component-level exposure applies |
| Hand/softness/finish | Qualitative target | Surface feel, gloss level, grain, anti-stain/anti-microbial finish or topcoat |
| Color/lightfastness | Stability | Colorfastness to light (AATCC 16.3 or ISO 105-B02), rub fastness (AATCC 8 or ISO 105-X12) |
| Dimensions | Supplier tolerance | Width, thickness (± tolerance), roll length, roll weight |
| Labeling/safety | Regulatory marks | FR tags, care labels, compliance stamps |
| Application | Test alignment | Chair/sofa upholstery, automotive interiors, wall panels—tailor tests and thresholds accordingly |
| Documentation | Must-have | Technical data sheet (TDS), SDS, compliance statements, test reports, RoHS/POPs/REACH/Prop65 where applicable |
| QC plan | Incoming and periodic | AQL per ISO 2859-1, dimensional checks, visual defects, and any special tests |
Recommended “breathable” baselines (adjust for your end-use):
– MVTR: ≥ 500–1,000 g/m²·24h (ASTM E96 Procedure B)
– Air permeability: ≥ 10 L/min·cm² (ASTM D737)
If waterproofing is required, verify both properties simultaneously; the optimum set must be proven by test reports.
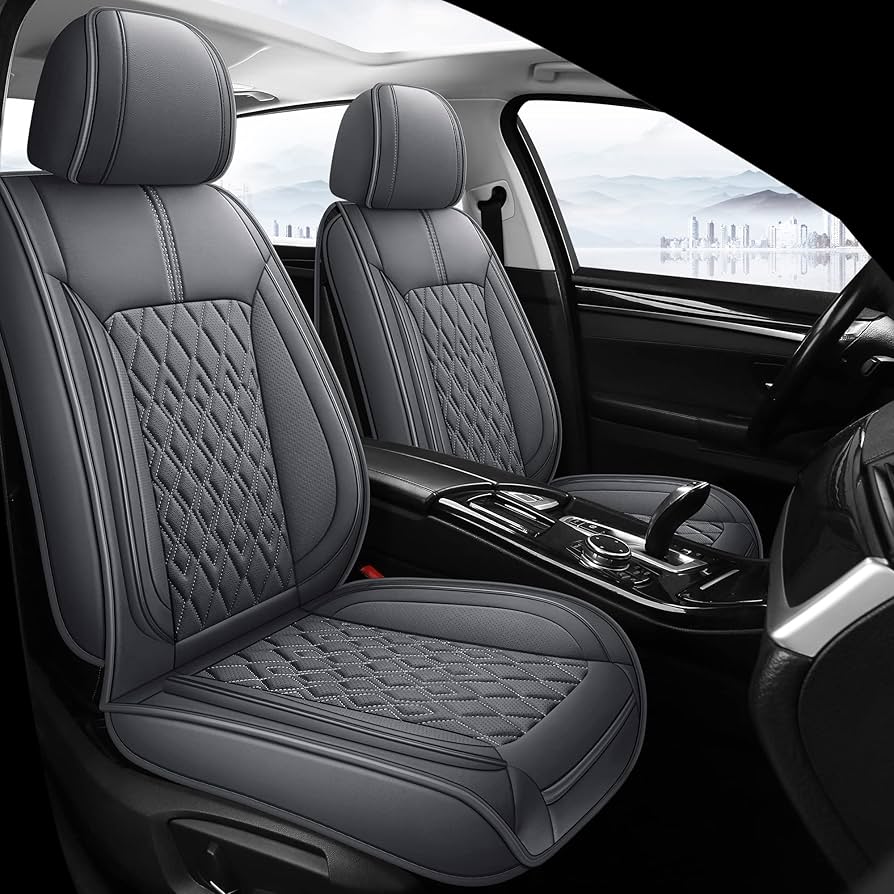

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2) Supplier Screening: Weed Out Non-Compliant or High-Risk Vendors
Use a short RFP with clear acceptance criteria; request declarations and test reports.
| Checkpoint | Evidence Required | Pass Criteria | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance declarations | REACH, Prop 65, RoHS, POPs; VOC/emissions if applicable | Statements + supporting SDS or test reports | Avoid “unknown/not applicable” responses |
| Flammability | Fire test reports aligned to your end-use | Meets or exceeds your requirements | Don’t assume “FR” from listing titles—validate with lab reports |
| Breathability proof | MVTR and/or air permeability test reports | Exceeds your baseline thresholds | Confirm method, conditions, and specimen prep |
| Manufacturing & QA | ISO 9001/14001 certificate; QC plan | Valid certificate and documented plan | Inspect reports for at least last 12 months |
| Sample policy | A/B samples for bench vs in-house testing | Delivered in agreed timeframe | Budget for independent lab testing |
| Traceability & labeling | Batch traceability, safety labels | Clear batches, labels match TDS | Ensures repro and recall control |
| Commercial terms | Payment terms, lead time, Incoterms | Terms acceptable to your finance/logistics | USA/EU buyers: use FOB, CIF, DAP; EU: consider EORI and duty handling |
| Sustainability | Recycled content, REACH, low-VOC options | Documentary proof | Useful for corporate ESG goals |
Red flags to watch for (drawn from the reference listing scenario):
– Fire-retardant, waterproof claims without test evidence or technical specs
– Very low price at large widths with minimal technical documentation
– Long/mixed delivery windows and unclear inventory buffers
– Seller/vendor ambiguity (e.g., unclear origin; shipping via trading companies)
3) Evaluate a Representative Sample
Request consistent sample sets, labeled with batch numbers.
| Test/Check | Standard | Acceptance Notes | Your Result (to fill) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breathability (MVTR) | ASTM E96 Proc B or ISO 15496 | ≥ target g/m²·24h | |
| Air permeability | ASTM D737 | ≥ target L/min·cm² | |
| Water resistance | ISO 811 or AATCC 127 | Meets hydrostatic head target | |
| Water repellency | AATCC 22 | ≥ score target (e.g., ≥90) | |
| Abrasion | ASTM D4157 or D4966 | ≥ cycles target | |
| Tear/seam | ASTM D2261/ISO 4674; ASTM D1683 | ≥ strength target | |
| Lightfastness | AATCC 16.3 or ISO 105-B02 | ≥ Grade X | |
| Flammability | Your end-use standard (e.g., CA TB117-2013, NFPA 701) | Pass | |
| VOC/emissions | BIFMA x7.1/ISO 16000 (if required) | Pass | |
| Visual/hand | – | No major defects; matches spec |
Run duplicate specimens or independent lab tests if breathability and waterproofing must coexist.
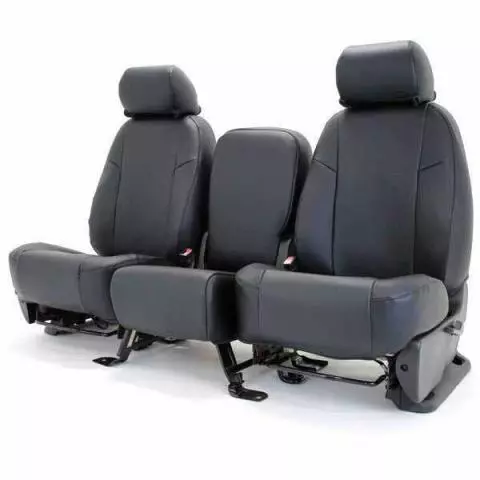

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4) Commercial and Risk Controls
| Control Area | What to Document | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| MOQs, lead times, price breaks | Agreed per width/color; time-to-ship | Align capacity with seasonality (USA/Europe) |
| Incoterms & logistics | DAP, FOB, CIF; consolidated shipping | Cost predictability; duty handling in EU |
| Order tolerances | Width, length, thickness, color delta | Avoid rework or claims |
| Rework/remedy process | How defects are handled (repair/replace/credit) | Service level clarity |
| Warranty & liability | Duration and scope | Risk transfer and stability |
| Change control | Substrate/topcoat/formulation changes require notice | Maintain performance consistency |
5) Purchase Order (PO) and Documentation
Ensure every PO references the same version of specifications, compliance reports, and test plans.
| Required Attachment | Included? | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Data Sheet (TDS) | ☐ | Version-controlled |
| Safety Data Sheet (SDS) | ☐ | Regional language if required |
| Compliance statements (REACH, Prop 65, RoHS, POPs, VOC/emissions) | ☐ | Dates aligned with batch |
| Test reports (breathability, waterproofing, flammability, durability) | ☐ | Last 12–24 months |
| QC plan and inspection procedures | ☐ | AQL levels agreed |
| Traceability and labeling requirements | ☐ | Batch IDs and FR labels |
| PO clauses on change notifications and approval | ☐ | Lock-in performance |
6) Incoming Inspection (When Goods Arrive)
Apply a pre-agreed AQL to keep quality predictable.
| Check | Standard | Min/Max | Sampling Plan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensional checks | – | ± tolerance as PO | ISO 2859-1 (e.g., Level II, AQL 1.5) |
| Visual defects | – | Zero critical defects | As above |
| Breathability spot-check | ASTM E96/ISO 15496 or D737 | Meets spec baseline | Reduced sample if lot is large |
| Colorfastness spot-check | AATCC 16.3/ISO 105-B02 | Meets target | |
| Flammability spot-check (if required) | Your standard | Pass | |
| Labeling verification | – | 100% | Match TDS and batch |
7) Escalation and Change Management
- Immediate hold if critical nonconformances appear (e.g., failing flammability or major dimensional defects).
- Suspend orders pending corrective action if suppliers cannot reproduce lab-tested performance.
- Require formal change notification for any substrate, coating, or chemical change; request updated test reports before first production lot.
This checklist creates a chain of evidence from requirement definition through production—making “breathable” measurable and auditable across USA and Europe.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for breathable leatherette Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Breathable Leatherette Sourcing
Cost drivers overview
- Materials: base fabric (e.g., warp knit, circular knit), TPU/PU topcoat, solvent/water-based foaming or microporous finishes, and micro-perforation or lamella ventilation.
- Labor: compounding, coating/foaming, embossing, slitting/rolling, QC, and packaging; labor share typically 8–18% ex-works, higher for small runs.
- Logistics: lane, mode (sea/air), duty/VAT, brokerage/terminals, and inland delivery; can add $0.20–$0.80/m² depending on lot size and shipping.
- Compliance/testing: REACH/SVHC, California Proposition 65, VOC/emissions, FR certifications (EN 1021-1/2, California TB 117-2013), and durability testing (Martindale 50k+ cycles).
- Commercial factors: lead time (18–28 days first order), payment terms, MOQ (often 500–2,000 m/col), and color count.
How market pricing translates to ex-works and delivered unit costs
To anchor discussion, a widely available “standard” faux leatherette on Amazon lists as $182.18 for a 1.4 m × 10 m roll. This implies:
– Implied unit price: ~$1.30/m².
– 1.4 m width is typical for upholstery.
– The price includes a premium for small-quantity e-commerce, rapid shipment, and retail-level packaging.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Breathable leatherette with foam/topcoat and micro-perforation typically prices higher:
– FOB China expected range: ~$5.50–$9.50/m² depending on construction (substrate, foam density, perforation density), FR level, and order quantity.
– Typical ex-works structure (illustrative range for foam-backed, micro-perforated, FR):
– Materials: $3.40–$5.80/m²
– Manufacturing/labor: $0.60–$1.20/m²
– Overhead/energy: $0.25–$0.50/m²
– Supplier margin: $0.50–$0.80/m²
– Ex-works total: $4.75–$8.30/m²
– With value-add (deeper emboss, lamella perforation, premium FR): +$0.75–$1.25/m²
Price ladder by trade term and mode
Values shown are added to ex-works FOB China per m². Duty and VAT apply at destination (see table below).
| Trade term | Description | Typical add-on per m² | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| FOB | Factory to vessel, China; buyer books freight | $0.00 | Buyer pays freight, insurance, duty, VAT |
| CFR | Cost + freight to destination port | $0.15–$0.40 | Freight included; duty/VAT not included |
| CIF | CFR + cargo insurance | $0.12–$0.25 | Add to CFR for ocean bill of lading, policy, fees |
| DDP (USA) | Delivered duty paid, all-in | $0.55–$0.80 | Includes freight, duty, VAT, customs clearance, last-mile |
For 100 m² orders, ocean LCL freight can be $120–$250 to USA/EU ports ($1.2–$2.5/m²); air can add $350–$550 ($3.5–$5.5/m²). The larger the order, the lower the per-m² freight.
Duty/VAT snapshot for USA and EU (HS 5903.20/5903.90)
- USA (HTS 5903.20): MFN duty 14.8% of CIF value; VAT is zero at import (use/sales tax applies later).
- EU (CN 5903.20): Typical MFN duty 8% of CIF; standard VAT varies by member state (e.g., 19–25%).
- Examples (CIF basis = ex-works + freight + insurance):
- Ex-works $7.00/m², freight + insurance $0.35/m² → CIF $7.35/m²
- USA: duty ≈ $7.35 × 14.8% ≈ $1.09/m²
- EU: duty ≈ $7.35 × 8% ≈ $0.59/m²; VAT applied to (CIF + duty + internal charges)
For goods not made entirely of leather, HS 5903.20 is typically the correct classification for PU-coated textile. Confirm fabric composition for a binding ruling if in doubt.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Landed cost model by order size (illustrative; foam-backed, FR, 1.4 m width)
Assumptions: ex-works $7.00/m²; freight to port as above; DDP includes duty and VAT estimates for USA (14.8%) and EU (8% + 21% VAT).
| Order size | Freight to port (ocean LCL) | USA duty + customs + last-mile | USA DDP | EU duty + VAT + customs + last-mile | EU DDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 m² | $0.60/m² | $1.45–$1.85/m² | $8.95–$9.35/m² | $2.00–$2.60/m² | $9.50–$10.10/m² |
| 800 m² | $0.30/m² | $1.35–$1.65/m² | $8.55–$8.85/m² | $1.90–$2.40/m² | $9.00–$9.50/m² |
| 1,500 m² | $0.20/m² | $1.30–$1.55/m² | $8.40–$8.65/m² | $1.80–$2.30/m² | $8.80–$9.30/m² |
| 1,500 m² (air) | $3.60/m² | $1.30–$1.55/m² | $12.40–$12.65/m² | $1.80–$2.30/m² | $12.80–$13.30/m² |
For comparison, the e-commerce baseline (implied $1.30/m²) is not breathable, nor does it carry FR/compliance certifications typical of contract interiors.
Manufacturing cost breakdown structure (illustrative per m²)
- Materials: $3.50–$5.80
- Base fabric: $0.70–$1.10
- Topcoat/TPU/PU and foam layers: $2.10–$3.80
- Micro-perforation/lamella: $0.35–$0.90
- Tinting/embossing: $0.25–$0.60
- Manufacturing/labor: $0.60–$1.20
- Overhead (energy, utilities, depreciation): $0.25–$0.50
- Quality/compliance (REACH, Prop 65, COAs): $0.08–$0.20
- Packaging and consolidation: $0.05–$0.12
- Supplier margin: $0.50–$0.90
- Ex-works total: $4.98–$8.72/m² (FR + perforation included)
- Value-add options:
- Additional FR certifications or FR topcoat upgrade: +$0.30–$0.70/m²
- Premium embossing or patterned lamination: +$0.25–$0.60/m²
- Anti-microbial, stain-resistant finish: +$0.15–$0.45/m²
Logistics levers and cost implications
- Mode:
- Ocean FCL (20′): $1.20–$2.00/m² typical for 5,000–10,000 m² shipments.
- Ocean LCL: optimal for 300–1,500 m²; $0.20–$0.60/m² depending on lane and seasonality.
- Air express (rolls): best for sub-300 m² or urgent samples; $3.00–$6.00/m².
- Packing density:
- Better cartonization and core consolidation can reduce CBM by 10–15%, cutting LCL freight.
- Consolidation:
- Multi-supplier aggregation into one LCL shipment reduces terminal/handling duplication.
- Compliance testing timeline:
- REACH full screening (SVHC): 3–6 weeks if pre-existing SDS absent; reuse supplier’s ECHA documents to save time and $200–$600/lot.
- Incoterm strategy:
- FOB/CFR for predictable freight; DDP when speed/complexity is prioritized and unit cost is acceptable.
Negotiation levers and cost optimization
- Roll width standardization: lock 1.37–1.40 m widths to match your cutting tables; misaligned widths drive waste and extra cost.
- Volume ladder with quarterly targets: target 1,000+ m²/color/shipment; price declines are typically 3–8% above 2,000–3,000 m²/season.
- Mix breathable SKUs on one roll via slitting: negotiate 5–10% savings by combining two standard colors on one master roll if permitted.
- Payment terms:
- 30–40 days vs. TT advances can carry 1.5–3.0% cost; offset via early payment discounts if you have short lead-time exposure.
- Duty recovery for exports:
- If you later export finished goods, capture 5903.20 duty drawbacks where applicable (document retention required).
- Vendor-managed inventory (VMI):
- Buffer stocking reduces airfreight and expedite fees; target 6–8 weeks’ cover instead of repeated small drops.
- FR strategy:
- Align with EN 1021-1/2 for EU furniture; confirm fire-blocking interliners are used where FR topcoats are not permitted by spec.
Risk and sensitivity
- Seasonality: ocean rates spike Q4; price increases 8–15% possible. Lock bookings early for holiday windows.
- Energy/chemical costs: PU/TPU market volatility can lift ex-works by $0.20–$0.60/m² in tight markets.
- MOQ penalties: color counts above agreed palette increase prices; standardize 3–4 core colors and use 1–2 seasonal variants to manage MOQ economics.
Action checklist
- Set spec: substrate weight, topcoat/foam type, perforation density, FR level, and colorfastness/durability minimums.
- Lock 1.37–1.40 m widths; define cutting yield targets; prohibit off-widths below 1.35 m without discount.
- Choose Incoterm: FOB for steady lanes; DDP for fast turnarounds; build an ocean vs. air contingency.
- Quote bands:
- 500 m²: $7.70–$9.20/m² FOB (breathable FR)
- 1,500 m²: $6.80–$8.40/m² FOB
- 5,000+ m²: $6.10–$7.80/m² FOB (plus potential tooling amortization if new embossing required)
- Request test data: Martindale 50k+, tear/tensile, VOC/emissions, REACH SVHC statements; reduce re-testing costs.
- Build a 90-day order plan to optimize freight consolidation and lower per-m² logistics add-ons.
Key takeaway: breathable leatherette typically lands at ~$8.5–$10/m² DDP USA and ~$9.0–$10.3/m² DDP EU for 800–1,500 m² batches with FR; savings come from spec clarity, consolidated shipments, standardized widths, and disciplined MOQ management.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing breathable leatherette With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Breathable Leatherette with Other Solutions
How to read this comparison
- Breathability refers to airflow/vapor permeability at the user interface (comfort), not surface water ingress.
- “FR” means flame retardancy. Availability depends on chemistry and treatment; confirm at roll level.
- Prices are indicative ranges. Expect significant variance by region, grade, and volume.
Comparison summary
| Attribute | Breathable Leatherette (micro-perforated PU with breathable backing) | Classic PU/PVC Vinyl Leatherette | Silicone Leather |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Micro-perforated PU (uniform perforation pattern) | Non-perforated PU or PVC (often with glossy or pebbled finish) | Micro-porous silicone sheet |
| Comfort | High (air + vapor permeability at contact) | Moderate (non-breathable; can feel warm) | High (inherently breathable/skin-friendly) |
| Vapor Permeability (ret, m²·Pa/W) | Low–moderate (typical breathable backs) | High (impermeable to vapor) | Low–moderate (varies by membrane/backing) |
| Hygienic Cleaning | Good; mild soap/water; disinfectants compatible; avoid harsh solvents | Good; disinfectants compatible; surface is non-porous | Excellent; alcohol/isopropyl OK; broad disinfectants supported |
| FR Options | Polyester back can be FR; FR availability depends on chemistry and treatment | Common FR grades: TB 117-2013, NFPA 701, EN 1021, IMO FTP; confirm grade per roll | Inherently good ignition resistance; FR depends on grade; consult brand-specific tests |
| Abrasion / Tear | Abrasion: good (e.g., ~50k–200k Martindale depending on grade) | Abrasion: strong (common grades ~50k–300k Martindale) | Abrasion: strong; often high flex fatigue resistance |
| UV/Light Fastness | 4–6 (PU surface + stabilizers) | 4–7 (PVC commonly higher UV stability; confirm grade) | 6–8 (excellent color retention) |
| Adhesive Compatibility | Good with PU/contact adhesives; needs breathable film if breathable backing used | Good with standard PU/contact/PSAs; non-breathable films common | Silicone adhesives required; compatibility can be costlier |
| Sustainability | Improved hygiene without solvents; recyclable films possible; bio-based/backings emerging | PVC may limit circularity; REACH-compliant formulations available | Platinum-cured options lower VOC; durability extends service life |
| Typical Use Cases | Hospitality seating, lounge areas, healthcare (dry environments), transit passenger seating where comfort and wipe-down are priorities | High-traffic hospitality, marine interiors, contract upholstery requiring strict FR and low maintenance | Marine, transit interiors, healthcare (frequent high-level disinfection), premium applications with sustainability focus |
| Indicative Price Range (USD/sq m) | ~20–40 (mid-range breathable grades; varies by backing, finishes, FR, region) | ~10–35 (standard PU/PVC; varies by durability, FR, finish) | ~30–65 (medical/marine and premium grades; varies by backing, certification, region) |
| Indicative Price Range (USD/sq ft) | ~1.9–3.7 | ~0.9–3.3 | ~2.8–6.0 |
Notes:
– Breathability and hydrostatic head are inversely related; micro-perforation improves comfort but sacrifices waterproofness at the seat surface. Where hygiene requires sealed surfaces, use breathable leatherette as accent/trim or specify waterproof breathable barriers beneath.
– Reference prices (listings and bulk) vary widely by volume, FR, thickness, backing type, and region; confirm current quotes from suppliers.
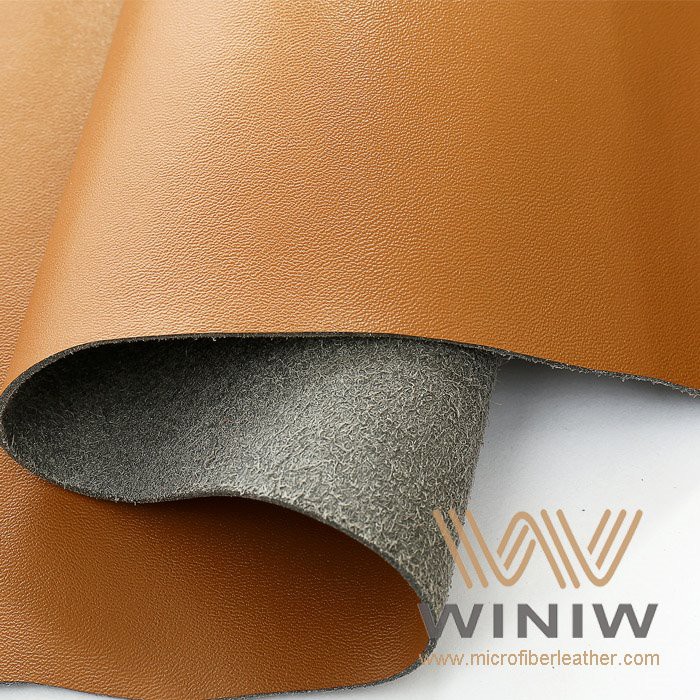

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
When breathable leatherette is the better fit
- Comfort-sensitive environments: hotel lobbies, lounges, and long-haul passenger seating where airflow at touch points matters.
- Hygiene-first cleaning: daily cleaning with soap/water and moderate disinfectants, without using abrasive or solvent-heavy cleaners.
- Balanced durability and easy fabrication: good abrasion performance with adhesive compatibility similar to PU leatherette; simpler than silicone adhesives.
When classic PU/PVC vinyl is the better fit
- Sealed surfaces and frequent wet cleaning: non-porous films are preferred for spill-proof surfaces.
- Strict FR and certifications required: broad FR options are available (TB 117-2013, NFPA 701, EN 1021, IMO FTP) with supplier declarations; verify grade.
- Cost optimization: typically lower or mid-low unit cost for high-abrasion grades.
When silicone leather is the better fit
- Intense cleaning regimes: alcohol/isopropyl and aggressive disinfectants tolerated; low VOC and odor.
- Marine and transit interiors: excellent UV stability, flex fatigue, and color fastness.
- Sustainability orientation: platinum-cured silicone chemistry; long service life can reduce lifecycle impacts.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for breathable leatherette
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Breathable Leatherette
Breathability, waterproofing, and fire performance are often positioned together, but material structure dictates whether a product is truly breathable, effectively waterproof, and compliant. Buyers should clarify the technical basis of each claim and align specifications with application-specific standards and test methods.
Breathability
- Defined as water vapor transport through the composite (coating + backing). Often measured by ASTM E96 (Proc B/WVTR), ASTM F1249 (MOCON), or ISO 15496. Typical values are expressed as g/m²/day or perm.
- Micro-perforation/“breathable” finishes increase vapor permeability but reduce hydrostatic head. Porous structures can allow wind penetration; test at relevant wind conditions if critical for outdoor or automotive use.
- Always request WVTR at specified temperature and RH (e.g., 38°C, 90% RH).
- Typical acceptance criteria:
- Automotive seating: WVTR ≥ 500–800 g/m²/day (varies by OEM).
- Furniture upholstery: WVTR ≥ 200–400 g/m²/day, with a backer that supports vapor transport without compromising hydrostatic head.
- Lightweight “leatherette” for garments/accessories: WVTR ≥ 300–600 g/m²/day.
Water Resistance and Waterproofing
- Hydrostatic head (ISO 811; ASTM D751) is the pressure water can exert before penetration. “Waterproof” vs “water-repellent” depends on the coating and seams.
- Seam sealing is essential for waterproof claims; specify tape type and seam weld integrity (ASTM D751 Seam Strength).
- Breathability and waterproofing trade off. Seek the highest hydrostatic head that still meets WVTR for the intended use:
- Typical targets:
- Upholstery: ≥ 1,500 mm (breathable).
- Outdoor/medical: ≥ 3,000–10,000 mm with breathable membranes.
- Repellency tests (AATCC 22 spray rating) should be ≥ 90/100; waterproof laminates target ≥ 100.
Abrasion Resistance and Durability
- Martindale (ASTM D4966; ISO 12947) is the standard for seating. Request end-weight result and weight change per ASTM D3514.
- Residential furniture: ≥ 25,000 cycles (min).
- Contract/commercial: ≥ 50,000 cycles (min); high-duty ≥ 100,000.
- Wyzenbeek (ASTM D4157) for North American seating: ≥ 30,000 (double rubs; min).
- Adhesion (ASTM D751; ISO 2411): ≥ 2.0 N/mm for upholstery; ≥ 3.0 N/mm for contract/marine.
Tear and Tensile Strength
- Tear strength (ASTM D1424 or ISO 13937) should be ≥ 20–25 N in warp and ≥ 25–35 N in weft.
- Tensile strength (ASTM D5034) should be ≥ 200–350 N/50 mm in both directions.
- Seam slippage and strength (ASTM D1683; ISO 13936): slippage ≤ 6 mm at specified load; seam strength ≥ 100–150 N/2 cm.
Low-Temperature Flexibility and Cold Crack
- Cold crack (ISO 4676; ASTM D2136) must be stated. Typical performance:
- Upholstery-grade: −15 to −20°C.
- Contract/marine/outdoor: −25 to −40°C.
- Specify whether values are measured on face, backer, or composite; adhesives and backing films shift performance.
UV Aging and Weatherability
- UV/weathering: ASTM G154 (UVA-340/UVB-313) and ASTM D573 (heat aging). Report color change (ΔE) and tensile retention after cycle exposure.
- Typical targets:
- ΔE ≤ 3–5 after 200–400 hours UVA/UVB.
- Tensile retention ≥ 80% post-aging.
- For outdoor use, request accelerated weathering with appropriate salt spray/mold/fungal resistance.
Flammability and Fire Ratings
- Verify “fire retardant” claims with test methods and certifications (report numbers, lab, date).
- USA: California TB 117-2013 (UFAC-labeled; open flame and smoldering).
- Contract seating (USA/Europe): TB 133 (high-risk environments) and EN 1021-1/-2 (cigarette and match).
- Europe: EN 13501-1 surface spread and EN 1021 series for upholstery. BS 5852:1990 Crib 5/7 often specified for contract furniture.
- Automotive: FMVSS 302; EU 118 (formerly ECE R118 for external fuel and burn-through).
- Breathability via microholes may reduce hydrostatic head and change flame spread. Request hydrostatic head and flammability on the same lot.
Dimensional Stability and Cold-Creep
- Cold-creep (ISO 18999): specify strain under load at low temperatures; request if used for cold climates or high tension applications.
- Shrinkage (ISO 5077) and thermal cycling (ASTM D1203) help predict fit and seam integrity over time.
Colorfastness and Cleaning
- Crocking (ASTM D3511; ISO 105-X12): dry ≥ 4; wet ≥ 3–4.
- Xenon light (ISO 105-B02): ≥ 4–5 for furniture; ≥ 5 for automotive/contract.
- Stain/soil resistance reports (ASTM D1308) demonstrate cleanability without surface damage.
Acoustic and Hand/Palm Impression
- Sound absorption (ISO 354) varies by backing and microstructure; specify if acoustic performance is required (e.g., vehicles, contract seating).
- Palm impression/hand softness tests (ASTM D2247) help compare feel; not critical for specification, useful for acceptance criteria.
VOC Emissions and Odor
- Request emissions testing (e.g., ISO 16000 series) and odor panels (VDA 270 for automotive) if indoor air quality or odor is a concern.
Composition and Backing
- Typical structure: 2-way stretch knit (often nylon/polyester) or woven polyester/cotton/polyester, with polyurethane (PU) or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) coatings. Waterproof products often use PU/TPU films or microporous coatings. Surface finishes may include PFAS-free DWR or topical anti-microbial coatings.
- Clarify whether backing is laminated (film vs nonwoven knit) and whether adhesives may impact breathability or waterproofing.
Typical Spec Ranges (For Buyer Reference)
- WVTR (ASTM F1249/E96 Proc B): 200–800 g/m²/day depending on use.
- Hydrostatic head (ISO 811): 1,500–10,000+ mm; ≥ 3,000 mm for marine/outdoor.
- Abrasion (Martindale): 25,000–100,000+ cycles (residential → contract/high-duty).
- Wyzenbeek (D4157): ≥ 30,000 double rubs.
- Cold crack (ISO 4676): −15°C to −40°C.
- UV aging (G154; 200–400 hrs): ΔE ≤ 3–5; tensile retention ≥ 80%.
- Crocking (ISO 105-X12): dry ≥ 4; wet ≥ 3–4.
- Xenon light (ISO 105-B02): ≥ 4–5.
Trade Terminology Buyers Should Confirm
Use these terms in RFQs and POs to align expectations across USA and Europe.
Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
- MOQ is often set by the smallest roll length and dye lot. Specify acceptable roll variation (e.g., ±10% total). For custom finishes or films, MOQs are usually higher due to setup and coating runs.
Lead Time
- Stock: typically 3–7 days (USA/EU distribution).
- Standard widths/colors: 3–6 weeks.
- Custom colors and finishes: 6–8 weeks (up to 10–12 weeks during peak).
Widths and Roll Length
- Common widths: 54″–58″ (137–147 cm).
- Roll length: typically 30–40 meters. Specify:
- Maximum roll length tolerance (±10–15%).
- Acceptable cut length tolerance (±5%).
Tolerances
- Specify thickness and weight tolerances per roll/lot. Common practice:
- Thickness ±10%.
- Weight ±7–10%.
- WVTR and hydrostatic head tolerances: ±10–15% from target.
Cut Lengths and Packaging
- Acceptable cut length increments: 1 meter minimum; 0.5 meter increments for premium grades.
- Packaging: wound facedown or face-in; specify core type (cardboard/plastic), labeling (lot/width), and protective wrapping.
Shipping Terms
- Prefer EXW or FOB in USA/EU. State maximum roll diameter (e.g., ≤ 75–80 cm) and freight consolidations. Ensure Incoterms clarity across multi-country shipments.
Invoices and Labeling
- Declare composition (e.g., “PU-coated polyester knit”) and country of origin per region. Provide MSDS for chemical handling.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Lot Control
- Specify 2–4 rolls per lot for sampling (WVTR, hydrostatic head, abrasion, cold crack, light, crocking).
- Define acceptance bands for breathability/waterproofing vs test method and condition.
Compliance and Certifications
- Request proof of:
- Flammability: TB 117-2013 and/or EN 1021; TB 133 for high-risk contracts; FMVSS 302 for automotive (USA), EU 118 for EU vehicles.
- REACH (EU); California Proposition 65 (USA) compliance and declarations.
- VOC/emissions testing (automotive or indoor environments as applicable).
Testing and Reporting
- Require test reports with lab name, date, method, and lot identification. Report values at stated conditions (temperature, RH, wind). Request copies of original lab certificates.
After-Sales and Service
- State shelf life and warranty terms (e.g., “warranty excludes UV exposure beyond stated G154 cycles”). Define technical support for field issues (adhesion, seam sealing, dye lot checks).
Key Takeaways for Buyers
- Separate breathability, waterproofing, and flammability into distinct claims with test methods and conditions.
- Verify whether backing and adhesives impact the stated performance; many composites trade waterproofing for breathability.
- Align minimum performance with use:
- Residential: breathable, abrasion ≥ 25,000 Martindale, standard flammability.
- Contract/commercial: ≥ 50,000 Martindale, cold crack ≤ −25°C, full fire compliance.
- Marine/outdoor: ≥ 3,000–10,000 mm hydrostatic head, UV aging and ΔE controls, fungal resistance if relevant.
- Automotive: FMVSS 302; EU 118; WVTR and odor/VOC as per OEM specifications.
- Normalize tolerances and include QA sampling to ensure batch consistency.
Suggested Specification Matrix (Fill and Use as Appendix)
| Property | Test Method | Standard Target | Result (per lot) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breathability (WVTR) | ASTM E96/B or ASTM F1249 | 200–800 g/m²/day (by use) | |
| Hydrostatic Head | ISO 811 (or ASTM D751) | ≥ 1,500–10,000 mm | |
| Abrasion | ASTM D4966 (Martindale) | ≥ 25,000–100,000 cycles | |
| Crocking | ISO 105-X12 / ASTM D3511 | Dry ≥ 4; Wet ≥ 3–4 | |
| Lightfastness | ISO 105-B02 | ≥ 4–5 | |
| Cold Crack | ISO 4676 (ASTM D2136) | −15°C to −40°C | |
| UV Aging | ASTM G154; D573 | ΔE ≤ 3–5; ≥ 80% tensile | |
| Flammability | TB 117-2013; EN 1021; FMVSS 302; EU 118 | As per application | |
| Seam Slippage | ASTM D1683 / ISO 13936 | ≤ 6 mm at specified load | |
| Adhesion | ASTM D751 / ISO 2411 | ≥ 2.0 N/mm (upholstery); ≥ 3.0 N/mm (contract) |
Note: “Fire retardant” must be substantiated with an official certificate referencing a recognized test method (e.g., Cal TB 117-2013, EN 1021, FMVSS 302).
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the breathable leatherette Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Breathable Leatherette Sector
1. Market Overview
Breathable leatherette (often a PU‑coated or laminated faux leather with micro‑perforations) is gaining share in furniture, automotive interiors, apparel, and protective equipment.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Segment | Primary Drivers | Typical MOQ (sq m) |
|---|---|---|
| Furniture (contract & residential) | Aesthetic flexibility, fire‑retardancy, cost vs. genuine leather | 500 – 1 500 |
| Automotive (seats, dashboards) | Durability, low VOC, regulatory compliance | 1 000 – 3 000 |
| Sportswear & Outerwear | Breathability, moisture‑wicking, vegan branding | 500 – 2 000 |
| Medical & Protective Gear | Bacterial resistance, easy clean, flame‑retardant | 300 – 1 000 |
2. Historical Context
| Year | Milestone | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Early PU‑coated fabrics appear in low‑cost upholstery | Seed market for faux leather |
| 2005–2010 | Introduction of micro‑perforation technology | Enabled moisture‑vapor transmission (MVTR) |
| 2015–2020 | Rising vegan/sustainability demand | Accelerated R&D, price compression |
| 2022‑present | Mandatory fire‑retardancy in US/EU for certain applications | Drives need for certified breathable leatherette |
3. Regulatory Landscape (US & EU)
| Region | Key Standard | Relevance to Breathable Leatherette |
|---|---|---|
| US – California | TB 117‑2013 (furniture) | Requires low‑flame spread; fire‑retardant finishes |
| US – Federal | ASTM D642‑19 (flame spread) | Test method for interior finishes |
| EU | EN 1021‑1/‑2 (furniture) | Ignition resistance for upholstery |
| EU – REACH | Substances restriction | Limits on plasticizers, VOC emissions |
| Global | OEKO‑TEX Standard 100 | Confirms low‑level harmful substances |
Compliance tip: Request REACH‑SVHC reports and a California TB 117‑2013 compliance letter from the supplier before purchase.
4. Sourcing Landscape
| Region | Typical Supplier Types | Lead Time (weeks) | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| China (mainland) | OEM factories, trading companies | 3‑6 | Cost‑effective, wide range of finishes, fire‑retardant options |
| Taiwan / South Korea | Specialty PU producers | 4‑7 | High‑quality coatings, tighter tolerance on MVTR |
| EU (Italy, Spain) | Local converters | 5‑8 | Proximity to EU market, easier REACH compliance |
| USA (custom manufacturers) | Domestic fabricators | 2‑5 | Fastest fulfillment, reduced import duties |
Trend: A growing number of US/EU buyers are dual‑sourcing—one high‑volume Asian supplier for price and a European partner for compliance‑critical batches.
5. Supplier Example – Amazon Listing
| Attribute | Value (as of 2025) |
|---|---|
| Brand / Seller | KHPGQIAS – Guo Yue Fei American Trading Co. |
| Product | Waterproof faux leather leatherette, fire‑retardant, 55 in (1.4 m) wide |
| Price (1.4 × 10 m) | US $182.18 ≈ US $13 / m² |
| Shipping | US $4.99, delivery Dec 18 – Jan 5 |
| Returns | 30 days (up to Jan 31 2026) |
| Compliance notes | Fire‑retardant claim; waterproof claim (breathability not specified) |
| Typical use case | Furniture upholstery, DIY upholstery projects |
Interpretation: The price point sits in the mid‑range for fire‑retardant PU leatherette. Buyers must verify MVTR and breathability if these are required for the final product.
6. Cost & Pricing Trends
| Cost Component | Typical Range (US $/m²) |
|---|---|
| Base PU‑coated fabric (non‑fire‑retardant) | 9‑12 |
| Fire‑retardant finish (add‑on) | +1‑2 |
| Waterproof coating (hydro‑philic) | +0.5‑1 |
| High‑MVTR perforation (micro‑perforation) | +1‑1.5 |
| Finished goods (cut‑to‑size) | +2‑3 (labour) |
Observed trend: 2023‑2025 price compression of ~8 % due to scale manufacturing and competition among Asian OEMs. However, logistics volatility ( freight rates up 12 % YoY) can offset savings.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7. Sustainability & Circularity
| Sustainability Criterion | Common Approach | Market Expectation |
|---|---|---|
| VOC emissions | Water‑based PU, low‑VOC additives | < 30 g L⁻¹ (EU limit) |
| Recyclability | Polyester backing + PU top‑coat | > 50 % recyclable at end‑of‑life |
| Renewable content | Bio‑based PU (e.g., soybean oil) | Growing request for ≥ 30 % bio‑content |
| Circularity | Take‑back schemes, post‑consumer reprocessing | Pilot programs in EU |
| Certifications | OEKO‑TEX 100, GREENGUARD, GRS | Mandatory for many contract buyers |
8. Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Qualification audit – Verify fire‑retardant certifications and MVTR data (e.g., ASTM E96‑95).
- Sample testing – Conduct a lab test for breathability and durability (Martindale abrasion ≥ 30 000 cycles).
- Supply diversification – Keep at least two qualified suppliers per region.
- Contractual clauses – Include price‑lock for 12 months and minimum‑order guarantees to protect margins.
- Logistics buffer – Build a 4‑week inventory safety stock to absorb shipping delays.
9. Actionable Recommendations
- Prioritize suppliers with REACH & TB 117‑2013 certificates; request the full test reports.
- Request a “breathability” spec sheet (MVTR ≥ 5 000 g m⁻² 24 h) before production to avoid post‑purchase failures.
- Negotiate volume pricing (≥ 5 000 m²) to unlock a 5‑7 % discount; align orders with Asian factory’s bulk production windows (Q2/Q3).
- Implement a two‑tier QA plan: inline inspection for fire‑retardant coating density and final testing for MVTR.
- Plan for sustainability reporting (carbon footprint, recycled content) as many OEMs now demand ESG data in RFPs.
By integrating compliance, sustainability, and cost discipline, procurement teams in the US and Europe can confidently source breathable leatherette that meets performance, regulatory, and market expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of breathable leatherette
FAQs: Breathable Leatherette for B2B Buyers (US & EU)
1) What is breathable leatherette and how does it differ from standard faux leather/vinyl?
Breathable leatherette is a synthetic upholstery leather alternative engineered to allow moisture vapor transmission. Compared to fully sealed vinyl or standard faux leather, it balances hand, durability, and vapor permeability, improving comfort in seated contact surfaces.
Key differences:
– Moisture management: higher MVTR compared to conventional PU/PVC; reduced heat buildup and stickiness.
– Surface finish: micro-perforated or “breathing” grain with controlled pore structures.
– Use cases: commercial contract furniture, hospitality seating, healthcare chairs; environments where prolonged sitting and hygiene are priorities.
2) What are typical performance metrics for breathable leatherette?
The table below summarizes common specifications. Exact figures vary by construction and supplier—verify with your vendor’s technical data sheet.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Metric | Typical range/behavior | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Vapor Transmission Rate (MVTR) | Mid- to high-permeability; relative breathing when compared to non-breathable vinyl | Test per ASTM E96 (Proc B, 22°C, 50–55% RH) or ISO 15496; report g/m²/day |
| Water Resistance (hydrostatic head) | Low to medium (splashes/rinse tolerant) | Not equivalent to fully waterproof; avoid prolonged saturation |
| Abrasion (Martindale) | 25k–100k+ cycles depending on construction | Higher cycles suit high-traffic hospitality/healthcare |
| Tear strength | Specified per ASTM D751 or ISO 4674 (values vary by weight) | Seam slippage more critical than tear for furniture |
| Pilling (Martindale) | Pass (no significant pilling) | Verify per ISO 12945-2 |
| Seam slippage | Report for 80–120 N (typical) | Critical for upholstery reliability |
| Colorfastness to rubbing | ≥ 4 dry; ≥ 3–4 wet (ISO 105-X12) | Consider dry-clean solvencys when relevant |
| Flammability | Fire-retardant formulations available; specify region | See FAQ 4 for details |
| Cleanability | Spot-clean; dilute surfactants; no harsh solvents | Follow supplier guidance; test disinfectants for compatibility |
3) Can breathable leatherette meet fire safety and regulatory requirements?
Yes. Provide target environment:
– Contract furniture: typical compliance includes CA TB 117-2013 (with NFPA 260/UFAC for cigarette ignition if required); TB 133 for some transport/seating in the US. For bedding, CA TB 129.
– Contract textiles: NFPA 701 (vertical flame) common for drapes/panels; furniture-specific standards may apply by market.
– Marine/offshore: IMO FTP Code Parts 2/3 (MED certification) for bulkhead insulation and panels—verify textile-specific scope with supplier.
– EU: EN 1021 Parts 1/2 for ignitability; EN 13773 for flammability class; EN ISO 11925-2, EN ISO 9239-1 for wall coverings as required.
– RoHS/REACH: Request compliance declarations and material disclosure for PVC/PU/PES systems.
Fire-retardant variants are often supplied by default in contract-grade lines. Order to spec and require test certificates.
4) What customization options are available?
Breathable leatherette can be tailored to your application:
| Option | Typical availability | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Widths | 54–60 in (137–152 cm) | Width varies by line; confirm roll lengths |
| Colors | 10–30+ per line | Pantone or RAL matching may be available |
| Surface textures | Breathable grain, pebbled, smooth | Micro-perforations can be added |
| Backing | Polyester knit/foam | Foam backing reduces breathability |
| Fire-retardant treatments | FR versions available | Maintain FR labels across dye lots |
| Perforation | Micro-perforated topcoats | Confirm pore density vs MVTR |
| Special finishes | Easy-clean topcoats, anti-microbial, abrasion-boosters | Confirm durability and regulatory scope |
MOQs vary by finish; coordinate sampling and lead times early.
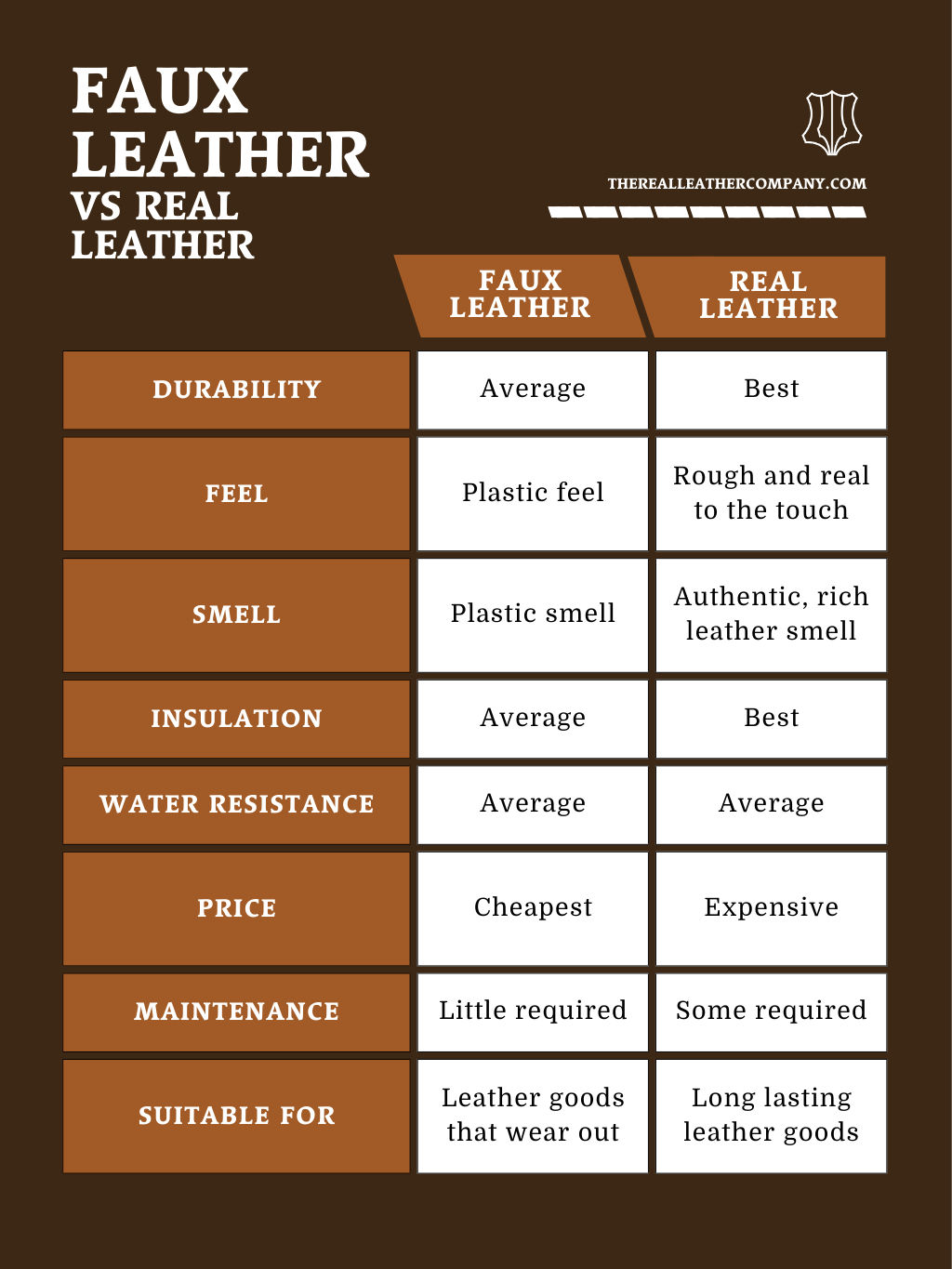
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5) How do I specify breathable leatherette for a project?
Use a performance-led specification that covers both breathing and upholstery performance.
Example:
– Material: breathable leatherette upholstery fabric, 55–60 in width
– Surface: micro-perforated PU or hybrid PU/PVC; breathable grain
– Performance: MVTR ≥ [X] g/m²/day at 22°C/50–55% RH; hydrostatic head [Y]; abrasion ≥ [Z] cycles; seam slippage ≥ [A] N; pilling Grade [B]; colorfastness dry ≥ 4, wet ≥ 3–4
– Flammability: Contract—CA TB 117-2013; TB 133 where applicable; Marine—IMO FTP (if required)
– Chemical: RoHS/REACH declarations; SVHC screening below thresholds
– Maintenance: clean per supplier method; disinfectant compatibility statement
– Continuity: colorway and finish availability for reorders
6) Breathability vs waterproofing: how do I balance requirements?
Breathability and waterproofing are a trade-off. Sealed topcoats raise water resistance but lower MVTR.
| Attribute | Non-breathable vinyl/PU | Breathable leatherette | Fully waterproof textile |
|---|---|---|---|
| MVTR | Low | Mid–high (relative) | Low–mid (surface sealed) |
| Spill resistance | High | Medium | Very high |
| Contact comfort | Lower (heat buildup) | Higher (reduced stickiness) | Variable |
| Seam sealing | Recommended | Recommended | Often required |
| Use case | Medical/sterile environments; splash zones | Office/hospitality seating; long sitting sessions | Rain gear; protected interiors with high wet exposure |
For seating, choose breathable leatherette and add water-resistant backs or barrier layers if needed. For wet areas, confirm seam sealing and drainage design.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7) How do I care for and disinfect breathable leatherette?
Recommended practice:
– Routine cleaning: wipe with mild soap solution; avoid ammonia-based or harsh organic solvents; rinse with clean water and air-dry.
– Disinfection: use EPA/EU-compliant disinfectants with <30–60 seconds dwell time; rinse if residue remains; verify compatibility with color and topcoat.
– Stain management: blot—not rub—spills; for persistent stains, consult supplier for approved agents.
– Drying: avoid high heat; let air-dry; do not iron.
– Maintenance: inspect seams and high-wear zones every 6–12 months; tighten/adjust covers as needed.
8) Pricing, MOQs, and logistics
Indicative sample for a fire-retardant, waterproof breathable vinyl leatherette:
| Item | Example detail |
|---|---|
| SKU | FR breathable vinyl leatherette, 55 in width |
| Typical price | ~$15–$20 per linear yard (tiered) |
| MOQ | 100–500 yd per color (varies by line) |
| Lead time | 4–6 weeks for stocked colors; 8–12 weeks for custom |
| Packaging | Roll-wrapped; protective film; tube core |
| Returns | B2B returns vary by policy; verify restocking fees |
| Region | US/EU distribution; confirm compliance and lead times |
Prices vary by width, performance package (FR, easy-clean finish), and volume. Request FOB quotes and confirm total landed costs including freight, duties, and inspection.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for breathable leatherette
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for breathable leatherette
Breathable leatherette advances comfort and durability without sacrificing compliance, provided sourcing is anchored in verifiable performance and material transparency. Accessible options like “Waterproof Faux Leather Vinyl Fabric” (e.g., approx. $182 for a 1.4 m × 10 m roll) indicate a robust base of FR-compliant, wipe-clean, waterproof SKUs suitable for high-use interiors.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Short-term outlook: Supply of general-purpose FR-grade leatherette remains stable. Advanced micro-perforated or membrane-based formulations with certified breathability and lower VOC profiles may carry longer lead times and tighter MOQs.
- Must-have criteria
- Verified breathability (MVTR or test method per end-use)
- FR alignment (e.g., NFPA 260, CAL TB 117-2013, EN 1021-1/2)
- Mechanical robustness (Martindale, seam/bond strength, tear)
- Hydrolysis resistance and colorfastness; easy-clean, waterproof finishes
-
Full material disclosure (backs, layers, PFAS-free where required)
-
Procurement checklist
- Request third-party lab reports and QC documents
- Confirm consistent dye lots and color metamerism targets
- Pilot with swatches, seam bonding, and cleaning trials
- Negotiate lead times, safety stock, and transparency clauses
The bottom line: Breathable leatherette delivers comfort, compliance, and lifecycle value—if sourced with test-backed performance and clear BOMs. Prioritize certified materials, validate lab data, and lock long-term agreements to stabilize quality, cost, and delivery across USA and Europe.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.