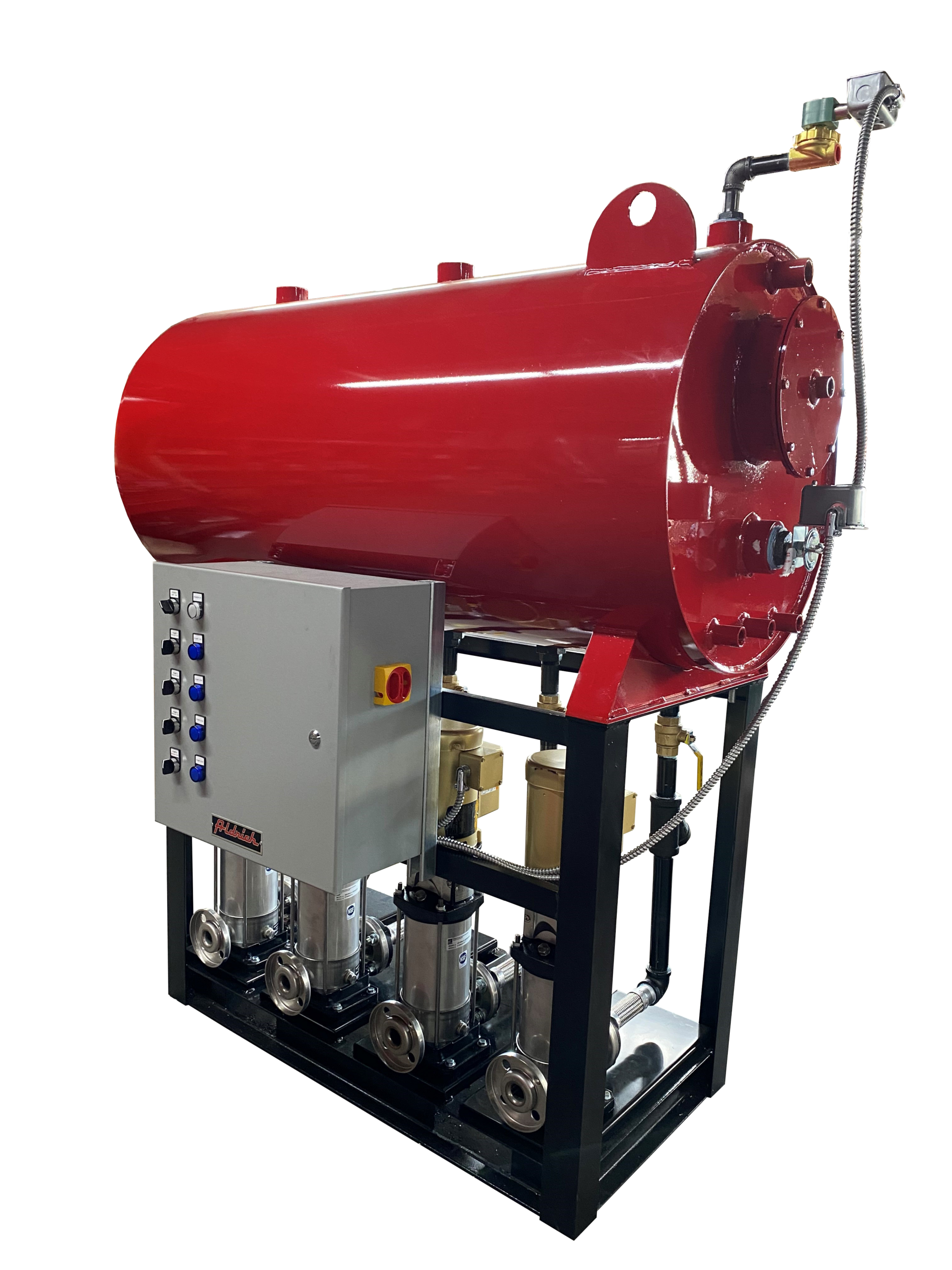
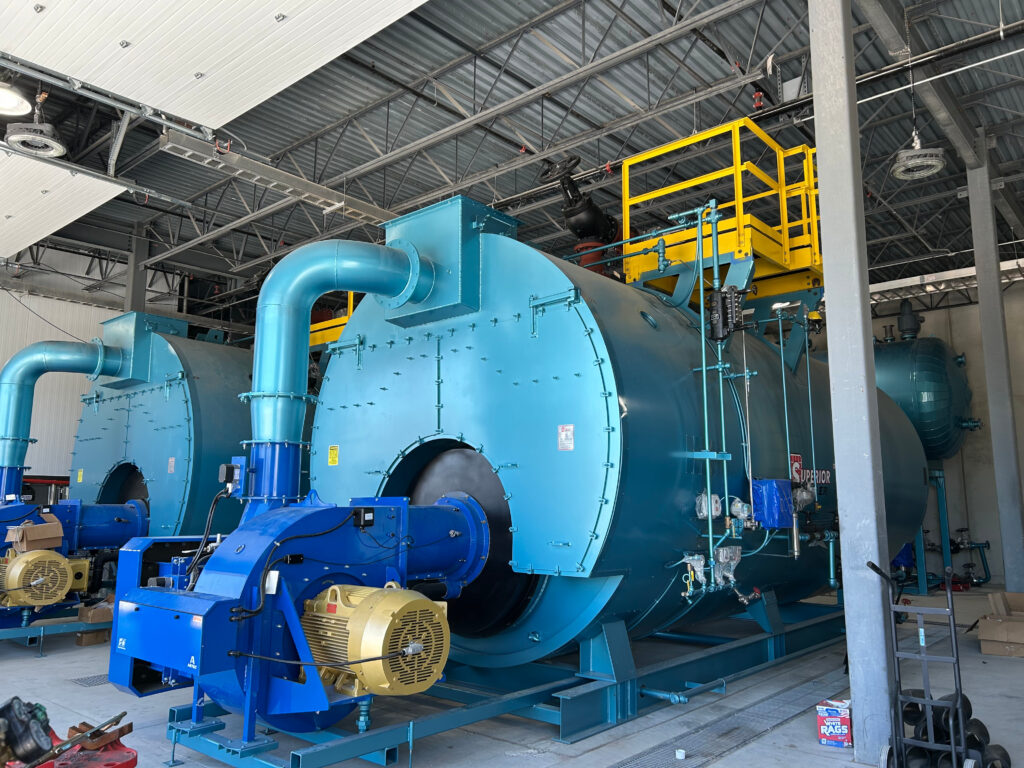
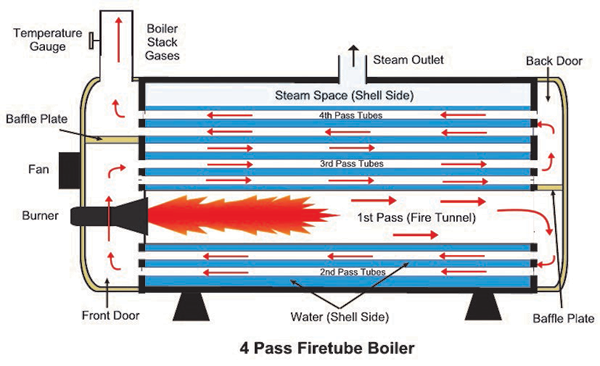
The global boiler tubes market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient power generation and industrial heating systems. According to Mordor Intelligence, the boiler tubes market was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by rising investments in thermal power plants, stringent environmental regulations promoting high-efficiency boilers, and growing industrialization across Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the growing adoption of supercritical and ultra-supercritical boiler technologies—requiring advanced alloy tubes—to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, further boosting market demand. As industries prioritize reliability and performance under extreme conditions, leading manufacturers are focusing on innovation in materials and production techniques. In this competitive landscape, the top 10 boiler tubes manufacturers are distinguished by their technological capabilities, global reach, and compliance with international quality standards.
Top 10 Boiler Tubes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Boiler Tubes
Domain Est. 2012
Website: industrialboilersamerica.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Boilers America is a trusted manufacturer of high-quality ASME-certified steel boiler tubes and pipes for industrial boiler systems worldwide….
#2 Boiler Tube Company of America|Pressure Parts & Services
Domain Est. 2002
Website: babcockpower.com
Key Highlights: Boiler Tube Company of America (BTA) manufactures replacement pressure boiler components and related auxiliary industrial boiler parts for all sizes and styles ……
#3 Boiler Tubes High Pressure High Temperature
Domain Est. 1995
Website: plymouth.com
Key Highlights: An experienced provider to the entire energy industry, Plymouth Tube Company is a reliable source for cold drawn and hot finished boiler tubing….
#4 Flexible Water Tube Boilers from Bryan Boilers High Efficiency …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bryanboilers.com
Key Highlights: Bryan Boilers from Bryan Steam include the latest flexible water tube boilers, high efficiency boilers and boiler accessory equipment….
#5 Aldrich Company
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1936
Website: aldrichco.com
Key Highlights: Aldrich Company has been designing, engineering and manufacturing boilers and water heaters since 1936. All of our boilers and water heaters are constructed, ……
#6 Superior Boiler
Domain Est. 1997
Website: superiorboiler.com
Key Highlights: Superior Boiler solves your most complex boiler challenges so you can get down to business – sterilizing essential hospital equipment, heating large facilities….
#7 Triangle Tube
Domain Est. 1997
Website: triangletube.com
Key Highlights: Triangle Tube, an innovator and industry leader in the manufacture and supply of quality stainless steel hot water heating equipment, has been keeping ……
#8 Firetube Boilers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cleaverbrooks.com
Key Highlights: 5-day delivery 30-day returnsCleaver-Brooks continues to manufacture the most reliable and efficient firetube boilers in a number of popular styles and sizes, including the CBEX, C…
#9 Metro Boiler Tube
Domain Est. 2002
Website: metroboilertube.com
Key Highlights: Metro Boiler Tube Co., Inc stocks over 500,000 feet of the most popular sizes and specifications of boiler tubing at our facilities making us a leading Boiler ……
#10 Boiler Tubes,Heat
Domain Est. 2019
Website: btboilertube.com
Key Highlights: Beite steel pipe (Boiler Tube Division) focuses on the production and sale of boiler pipes, pressure equipment pipes, heat exchanger pipes and related seamless ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Boiler Tubes

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Boiler Tubes
The global boiler tubes market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing energy demands, industrialization in emerging economies, and a renewed focus on energy efficiency and emissions reduction. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape over the coming years:
-
Rising Demand from Power Generation Sector
The power industry remains the largest consumer of boiler tubes, particularly in coal-fired, natural gas, and combined-cycle power plants. Despite the global shift toward renewable energy, fossil fuel-based power generation will continue to play a transitional role, especially in developing regions like Asia-Pacific and Africa. This sustained reliance on thermal power is expected to support demand for high-performance boiler tubes capable of withstanding high pressure and temperature. -
Growth in Industrial Boilers and Process Heating
Expanding industrial sectors—including petrochemicals, refining, food processing, and manufacturing—are investing in efficient steam generation systems. This is driving demand for industrial boiler tubes, especially in countries like India, China, and Indonesia, where industrial output is rising. Modernization of aging infrastructure is also contributing to replacement demand. -
Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
There is an increasing shift toward advanced materials such as high-temperature alloys (e.g., stainless steel, Inconel, and ferritic-martensitic steels) to improve thermal efficiency and durability. These materials are essential for next-generation ultra-supercritical (USC) and advanced ultra-supercritical (A-USC) boilers, which operate at higher efficiencies and lower emissions. Manufacturers are focusing on R&D to develop corrosion-resistant, creep-resistant tubes that extend operational life. -
Environmental Regulations and Emission Standards
Stricter environmental regulations are pushing utilities and industries to upgrade to cleaner and more efficient boiler systems. This includes retrofitting older plants with modern boiler tubes that support lower NOx and CO₂ emissions. Regulatory frameworks such as the EU’s Industrial Emissions Directive and China’s Ultra-Low Emission Standards are accelerating the adoption of high-efficiency boiler technologies. -
Asia-Pacific as the Dominant Market
The Asia-Pacific region is expected to maintain its leadership in the boiler tubes market by 2026, driven by rapid urbanization, energy infrastructure development, and government initiatives to improve power access. China and India are key growth engines, with significant investments in both conventional and supercritical power plants. -
Impact of Renewable Energy and Hydrogen-Ready Boilers
While renewable energy adoption may temper long-term demand for traditional boiler tubes, there is emerging interest in hybrid systems and hydrogen-compatible boiler technologies. Some manufacturers are developing boiler tubes suitable for hydrogen combustion, positioning the market for a potential shift toward low-carbon fuel sources. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Post-pandemic disruptions and geopolitical tensions have prompted a reevaluation of supply chains. There is a growing trend toward localizing boiler tube production to reduce dependency on imports, particularly in strategic sectors. Countries are incentivizing domestic manufacturing, which could reshape competitive dynamics in the market.
In conclusion, the boiler tubes market in 2026 will be shaped by a combination of technological innovation, regulatory pressures, and regional industrial growth. While challenges from the energy transition persist, the demand for high-efficiency, durable, and environmentally compliant boiler tubes is expected to sustain market expansion, particularly in developing economies and modernized industrial facilities.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Boiler Tubes: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing boiler tubes—a critical component in power generation, petrochemical, and industrial heating systems—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Failure to address these areas can lead to safety hazards, operational downtime, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
One of the most common issues is receiving tubes without proper material test reports (MTRs) or with falsified documentation. Boiler tubes must comply with strict standards (e.g., ASTM, ASME, EN), and lack of full traceability from the heat number to the final product can result in non-compliant materials entering service. This compromises safety and system integrity under high pressure and temperature.
2. Substandard Manufacturing Processes
Sourcing from suppliers that use outdated or inconsistent manufacturing methods—such as improper heat treatment, inadequate non-destructive testing (NDT), or poor welding techniques—can result in premature tube failure. Seamless vs. welded tube specifications are often misunderstood or misrepresented, affecting performance in high-stress environments.
3. Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish
Boiler tubes must meet tight tolerances for outer diameter, wall thickness, and straightness. Deviations can lead to improper fitting, reduced heat transfer efficiency, or flow restrictions. Surface defects like pitting, scale, or scratches may act as initiation points for corrosion or cracking.
4. Inconsistent Alloy Composition
Counterfeit or mislabeled tubes may contain incorrect alloying elements (e.g., insufficient chromium or nickel in stainless or high-temperature alloys), leading to reduced creep resistance, oxidation resistance, or corrosion resistance. Portable XRF analyzers can help verify composition, but reliance solely on supplier claims is risky.
5. Lack of Third-Party Inspection and Certification
Failing to engage independent inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, or authorized ASME inspectors) increases the risk of accepting subpar products. Mandatory certifications such as ASME “U” Stamp or PED compliance should be verified at the manufacturing stage.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Compliance Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Grades or Technologies
Some high-performance boiler tube alloys (e.g., T91, T92, Super 304H, or proprietary grades from companies like Sandvik or Vallourec) are protected by patents or technical know-how. Sourcing tubes labeled with these grades from unauthorized manufacturers may infringe IP rights and result in legal action or supply chain disruption.
2. Misrepresentation of Material Origin and Branding
Suppliers may falsely claim tubes are manufactured by well-known mills or use brand names without authorization. This not only breaches IP but also misleads buyers about quality and performance history. Always verify mill certifications and cross-check with original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
3. Use of Reverse-Engineered or “Equivalent” Materials
Some suppliers offer “equivalent” materials that mimic chemical composition but lack the proprietary processing (e.g., thermomechanical treatment) essential for performance. These tubes may not meet the mechanical or metallurgical specifications of the original IP-protected product, leading to in-service failures.
4. Non-Compliance with Licensing Agreements
For licensed technologies (e.g., certain high-efficiency alloys used in ultra-supercritical boilers), only authorized producers can legally manufacture and sell the tubes. Purchasing from unlicensed sources—even if the product appears identical—exposes the buyer to IP litigation and voids equipment warranties.
5. Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier Legitimacy
Failing to vet suppliers’ credentials, manufacturing licenses, and IP compliance history can result in procurement of counterfeit or infringing products. This is especially prevalent in global sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require full documentation: Demand certified MTRs, heat traceability, and third-party inspection reports.
- Verify supplier credentials: Confirm ASME, PED, or other relevant certifications and check for authorized licensing.
- Conduct pre-shipment inspections: Use independent inspectors to verify material, dimensions, and markings.
- Perform material testing: Conduct positive material identification (PMI), mechanical testing, and NDT where appropriate.
- Engage legal counsel: Review supply agreements for IP indemnification clauses and ensure compliance with international trade laws.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, organizations can ensure the reliability, safety, and legality of their boiler tube supply chain.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Boiler Tubes
Boiler tubes are critical components in power generation, industrial heating, and process systems. Their safe and efficient transportation, handling, and regulatory compliance are essential to ensure product integrity, operational safety, and adherence to international standards. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for boiler tubes.
Material Specifications and Standards Compliance
Boiler tubes must conform to rigorous material and manufacturing standards to ensure performance under high pressure and temperature. Key international standards include:
- ASME SA-213/ASTM A213: Standard specification for seamless ferritic and austenitic alloy-steel boiler, superheater, and heat-exchanger tubes.
- ASME SA-192/ASTM A192: Seamless carbon steel boiler tubes for high-pressure service.
- EN 10216-2: European standard for seamless steel tubes for pressure purposes.
- API 5CT: For casing and tubing used in certain high-temperature applications.
Compliance Actions:
– Verify mill test certificates (MTCs) or material test reports (MTRs) are provided with each shipment.
– Ensure tubes are marked with required identifiers: material grade, heat number, standard, manufacturer, and size.
– Confirm third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) when contractually required.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents mechanical damage, corrosion, and deformation during transit and storage.
Packaging Guidelines:
– Tubes are typically bundled (1–3 tons per bundle) with protective end caps to prevent damage to threads or bore.
– Use wooden or metal skids for secure stacking; avoid direct ground contact.
– Apply anti-rust oil or vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) for extended storage or maritime shipping.
– Seal bundles in waterproof plastic or use desiccants in enclosed containers to prevent moisture ingress.
Handling Best Practices:
– Use lifting straps or cradles—never chains or wire ropes that can gouge the tube surface.
– Avoid dragging or dropping bundles.
– Store tubes horizontally on level, dry ground; elevate off soil with skids.
Transportation Logistics
Boiler tubes are often long, heavy, and susceptible to bending, requiring specialized logistics planning.
Transportation Modes:
– Maritime: Most common for international shipments. Use flat-rack or open-top containers for oversized tubes (>12m). Waterproof tarpaulins or enclosed containers are preferred.
– Rail: Suitable for long-haul domestic transport; requires secure bracing.
– Road: Use extendable flatbed trailers with support cradles. Confirm local regulations on load length and weight limits.
Loading & Securing:
– Distribute load evenly to prevent sagging.
– Secure bundles with steel straps or chains at multiple points.
– Use dunnage to prevent crushing and allow ventilation.
– Protect tube ends with wooden or plastic caps during transit.
Import/Export Regulations and Documentation
Cross-border shipments require strict adherence to trade and safety regulations.
Key Documentation:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List (detailing bundle count, dimensions, weights)
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Material Test Reports (MTRs)
– Phytosanitary Certificate (if wooden skids are used – ISPM 15 compliant)
Regulatory Compliance:
– Comply with customs requirements in destination country (e.g., FDA, CE marking, GOST, BIS).
– Adhere to REACH (EU), TSCA (USA), and other chemical substance regulations for coatings or inhibitors.
– Ensure compliance with anti-dumping or safeguard measures if applicable (e.g., steel-related tariffs).
Storage and Inventory Management
Improper storage can lead to corrosion, deformation, or mix-ups.
Storage Best Practices:
– Store indoors if possible; otherwise, use elevated, covered areas with good drainage.
– Cover bundles with weather-resistant tarps while allowing airflow.
– Separate grades and sizes to avoid cross-contamination.
– Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory rotation.
Quality and Inspection Protocols
Pre-shipment and post-delivery inspections help ensure compliance and integrity.
Inspection Points:
– Dimensional checks (OD, wall thickness, length)
– Visual inspection for dents, corrosion, or surface defects
– Non-destructive testing (NDT) records (e.g., hydrostatic, eddy current, ultrasonic)
– Verification of markings and documentation match
Third-Party Involvement:
– Engage independent inspectors (e.g., API 510/570 certified) for high-value or safety-critical shipments.
– Conduct pre-shipment inspections at manufacturer facilities when possible.
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Considerations
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) during handling: gloves, hard hats, steel-toe boots.
- Ensure proper ventilation when applying or removing protective coatings.
- Dispose of used oils, packaging, and inhibitors according to local environmental regulations.
- Train staff on safe lifting techniques and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for boiler tubes ensures product reliability, regulatory adherence, and operational safety. By following standardized packaging, transport, documentation, and inspection practices, stakeholders can mitigate risks and ensure seamless delivery of high-integrity components.
Conclusion for Sourcing Boiler Tubes
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of boiler tubes requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Boiler tubes are critical components in power generation, industrial, and heating systems, where performance under high pressure and temperature demands materials of the highest integrity. Therefore, selecting suppliers with proven expertise, stringent quality control processes, and certifications such as ASME, ASTM, or ISO is essential.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include material specifications (such as carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel), dimensional accuracy, thermal efficiency, corrosion resistance, and delivery timelines. Engaging with reliable manufacturers or authorized distributors, conducting thorough supplier evaluations, and performing material testing (e.g., NDT, chemical analysis) help mitigate risks associated with premature failure or downtime.
Additionally, building long-term partnerships promotes supply chain stability and facilitates technical support and traceability. With growing emphasis on efficiency and sustainability, sourcing decisions should also consider the environmental impact and lifecycle performance of boiler tubes.
Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy ensures operational reliability, enhances boiler efficiency, and contributes to the overall safety and longevity of thermal systems. Regular market assessment and staying informed about technological advancements will further support optimal procurement outcomes in the future.