The global CNC machine market continues to expand at a robust pace, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the CNC machine market was valued at approximately USD 78.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing automation, advancements in Industry 4.0 technologies, and the integration of AI and IoT in machining processes. As demand intensifies, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, setting benchmarks in innovation, reliability, and global market share. Based on production volume, technological influence, and revenue, the following nine companies represent the largest CNC machine manufacturers shaping the future of smart manufacturing worldwide.
Top 9 Biggest Cnc Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Komo Machine Inc
Domain Est. 1995
Website: komo.com
Key Highlights: KOMO Machine, Inc. is the premier manufacturer of CNC routers for wood, plastics and metals. KOMO machines are made in the USA. Contact us today….
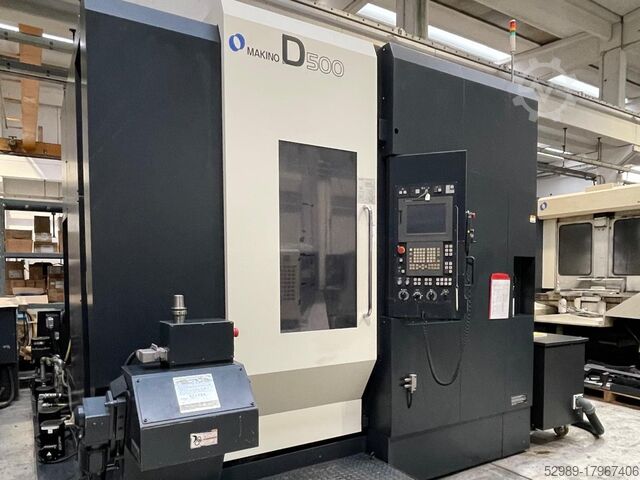
#2 Makino
Domain Est. 1996
Website: makino.com
Key Highlights: A Makino is more than a CNC machine. It’s relentless consistency, historic accuracy, industry leading expertise and game-changing digital technology….
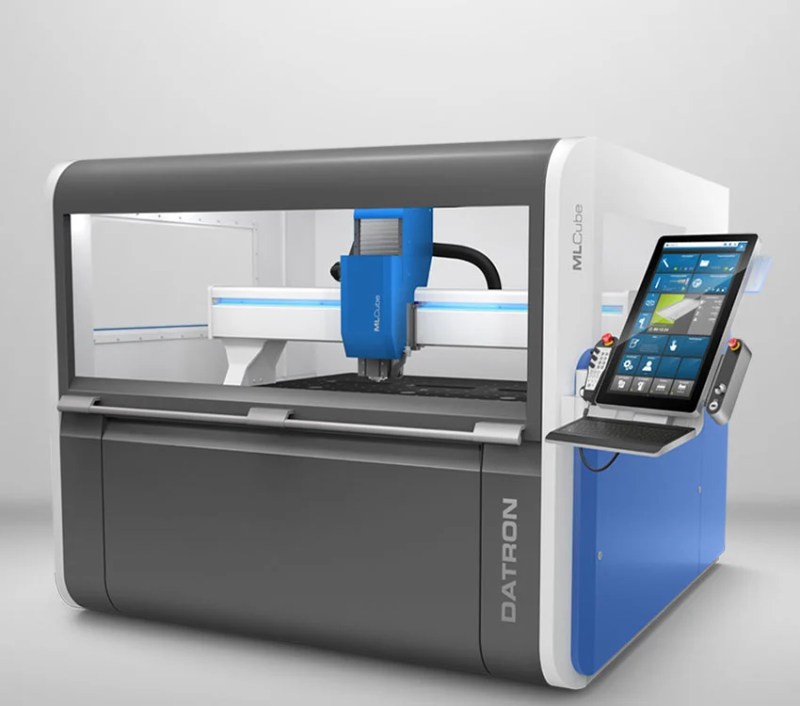
#3 DATRON High
Domain Est. 1995
Website: datron.com
Key Highlights: For over 50 years, Germany-based DATRON AG has been designing and building high-speed CNC machines for some of the most advanced manufacturers in Europe. In ……
#4 Haas Automation Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: haascnc.com
Key Highlights: Haas Automation is the largest machine tool builder in the western world, manufacturing a complete line of CNC vertical machining centers, ……
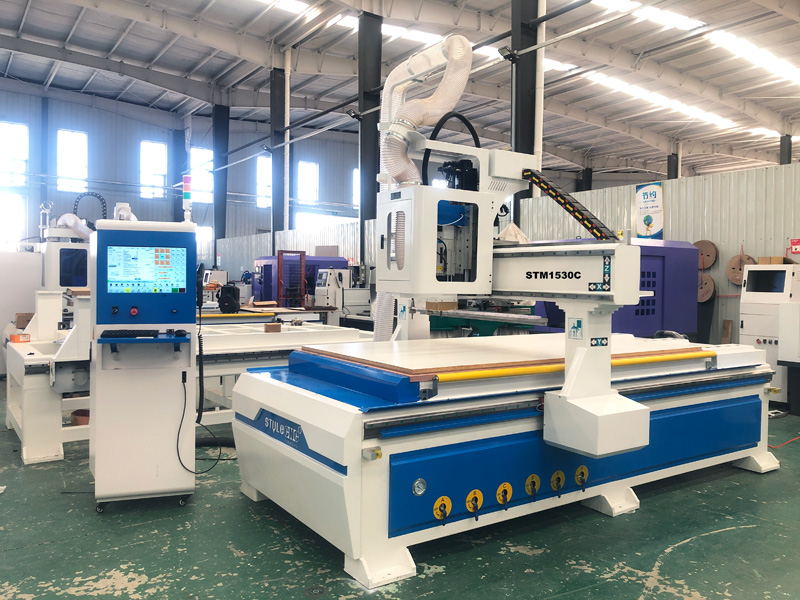
#5 STYLE CNC Machines
Domain Est. 2012
Website: stylecncmachines.com
Key Highlights: STYLE is the manufacturer of CNC milling machines specialised in single pieces and small series. Discover our CNC milling machines….
#6 OKUMA CORPORATION
Website: okuma.co.jp
Key Highlights: Okuma is a comprehensive machine tool manufacturer which produces not only lathes, machining centers, multitasking machines and grinders, but also control ……
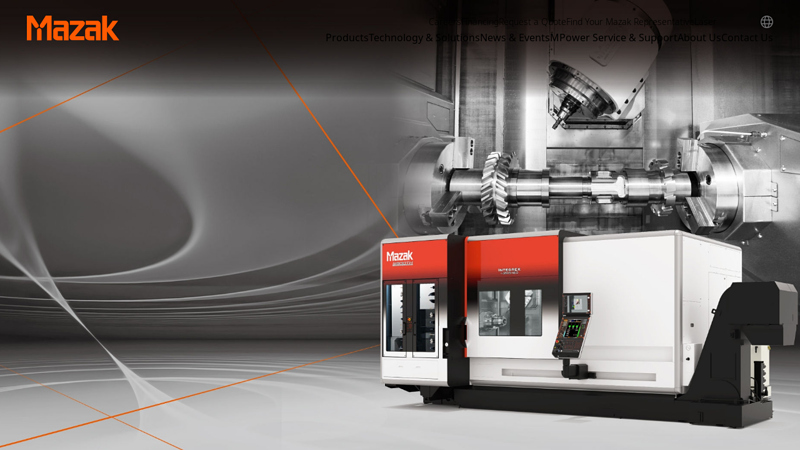
#7 to Mazak Corporation
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mazak.com
Key Highlights: Mazak provides products and solutions that can support a wide range of parts machining processes, such as high-speed and high-accuracy machines, various ……
#8 Jyoti CNC Automation Limited
Domain Est. 2005
Website: jyoti.co.in
Key Highlights: Jyoti CNC is the largest CNC machine tool manufacturing company of India and having a subsidiary “Huron” based at Strasbourg, France….
#9 DN Solutions
Domain Est. 2017
Website: dn-solutions.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to official website of DN Solutions! Here you can view our wide range of products from the very latest machines to our most popular models….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Biggest Cnc Machine
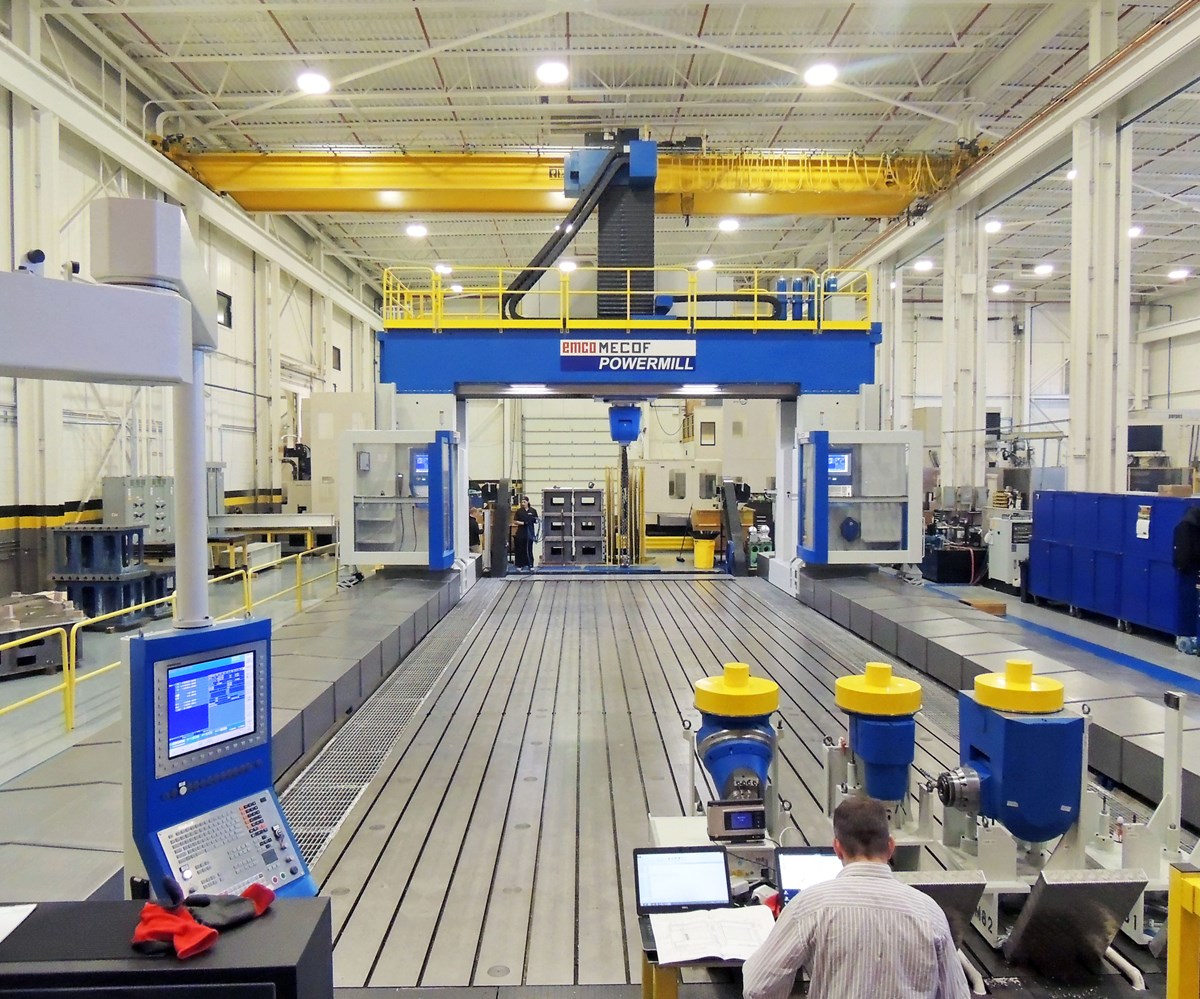

2026 Market Trends for the Biggest CNC Machines
As we approach 2026, the global market for the largest CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving industrial demands, and macroeconomic shifts. These massive machines—used primarily in aerospace, energy, heavy machinery, and defense sectors—are seeing renewed innovation and strategic investment. Below is an in-depth analysis of the key trends shaping the biggest CNC machine market in 2026.
Expansion in Aerospace and Defense Sectors
One of the primary drivers of demand for large-scale CNC machines is the aerospace and defense industry. As global defense budgets rise—particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific—governments are investing heavily in next-generation aircraft, drones, and space vehicles. These applications require precision machining of large, complex components such as fuselage sections, turbine blades, and structural frames. By 2026, manufacturers are adopting oversized CNC gantry mills, five-axis machining centers, and hybrid additive-subtractive systems capable of handling workpieces over 30 meters in length. The integration of digital twins and AI-driven simulation tools is further enabling more efficient use of these machines.
Growth in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
The push toward clean energy is fueling demand for oversized CNC equipment. Wind turbine components—such as hubs, spindles, and gearbox casings—are growing in size to improve efficiency, especially in offshore installations. In 2026, manufacturers are investing in CNC machines with extended travel ranges and high torque to machine large-diameter components from advanced alloys and composites. Similarly, the nuclear and hydrogen energy sectors require precision-machined large-scale parts for reactors and storage systems, boosting demand for heavy-duty CNC lathes and boring mills.
Advancements in Automation and Smart Manufacturing
By 2026, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies into large CNC systems is accelerating. The biggest CNC machines are being equipped with IoT sensors, predictive maintenance algorithms, and real-time data analytics platforms. These smart capabilities allow for remote monitoring, reduced downtime, and optimized toolpath efficiency. Additionally, automated material handling systems—such as robotic loading/unloading and automated guided vehicles (AGVs)—are becoming standard, especially in high-volume production environments. This shift toward autonomous operation is improving throughput and reducing labor costs, making large CNC machines more viable for mid-sized manufacturers.
Regional Manufacturing Reshoring and Localization
Geopolitical instability and supply chain disruptions have prompted a trend toward reshoring and regionalization of manufacturing. In 2026, countries like the U.S., Germany, and Japan are investing in domestic production capabilities for critical components, including those requiring large CNC machining. This shift is increasing demand for locally manufactured CNC machines and encouraging regional OEMs to develop homegrown solutions. As a result, North America and Europe are expected to see a rise in high-value CNC installations, supported by government incentives and defense industrial policies.
Material Innovation and Multi-Tasking Machines
The adoption of advanced materials—such as titanium aluminides, high-strength composites, and metal matrix composites—is pushing the limits of traditional machining. In response, CNC machine builders are developing larger, more rigid platforms with enhanced thermal stability and vibration damping. Furthermore, multi-tasking CNC machines that combine milling, turning, and grinding in a single setup are gaining traction. These integrated systems reduce handling of large, delicate parts and improve accuracy, making them ideal for complex components in aerospace and energy applications.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing CNC machine design. By 2026, manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient spindle drives, regenerative braking systems, and recyclable coolant management in large CNC installations. Machine tools with lower carbon footprints and modular designs for easier repair and upgrade are becoming competitive advantages. Additionally, remanufactured and retrofitted large CNC machines are gaining market share, especially in emerging economies, as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to new builds.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for the biggest CNC machines is characterized by convergence between scale, intelligence, and sustainability. Driven by aerospace, defense, and renewable energy sectors, demand is shifting toward smarter, larger, and more adaptable systems. As automation, digitalization, and material science continue to evolve, the role of oversized CNC machines will expand beyond traditional manufacturing into next-generation industrial ecosystems. Companies that embrace these trends—through innovation, strategic partnerships, and sustainability—will lead the market in the coming years.
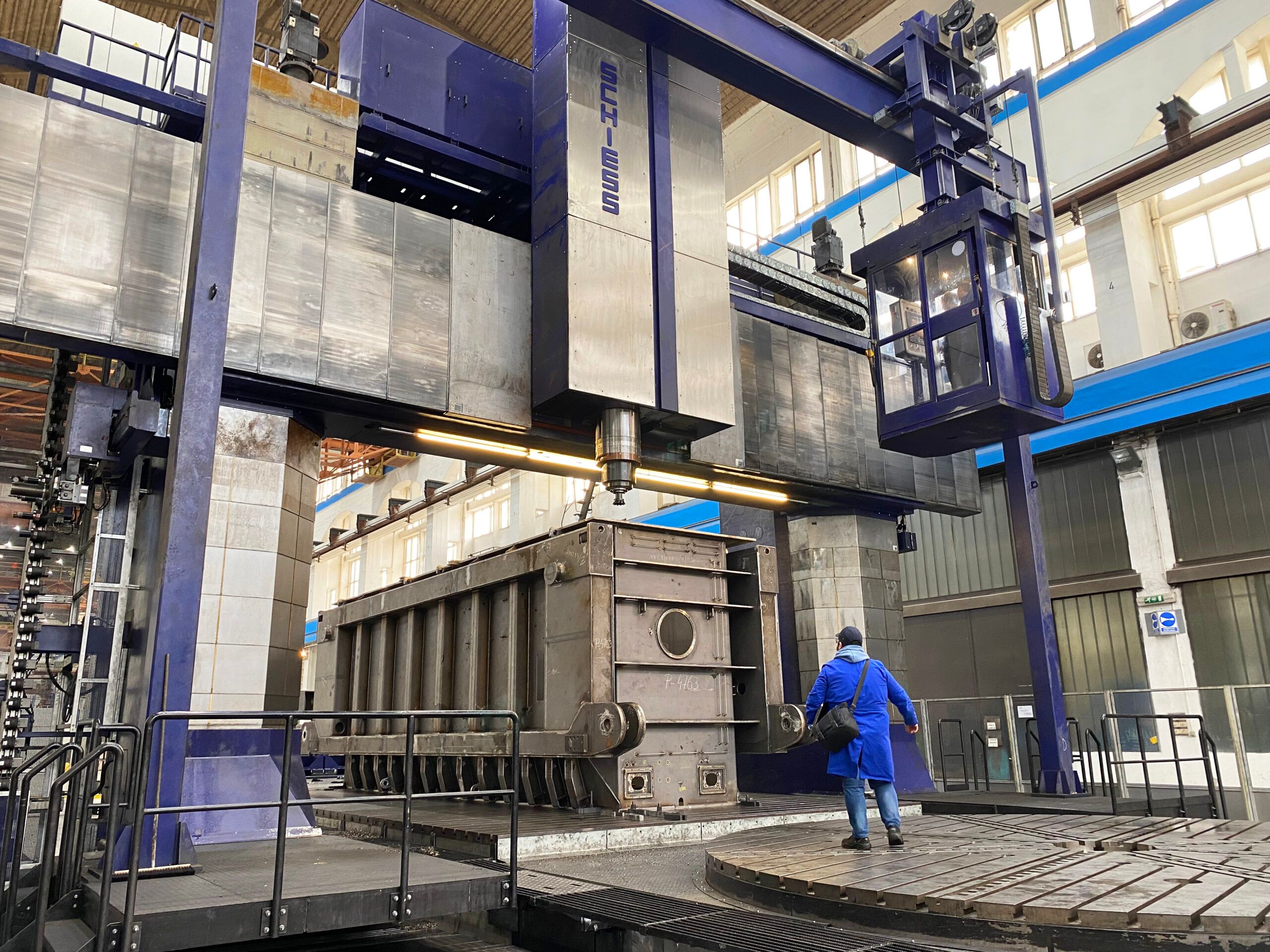

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing the Biggest CNC Machine (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the largest CNC machines—such as gantry mills, horizontal boring mills, or massive 5-axis machining centers—presents unique challenges that go beyond standard procurement. Among the most critical concerns are ensuring superior quality and protecting intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly delays, compromised production, and legal exposure.
Inadequate Quality Verification for Large-Scale Machines
One of the biggest risks in sourcing oversized CNC equipment is assuming specifications equate to real-world performance. Due to their size and complexity, these machines are more prone to structural deflection, thermal expansion, and alignment issues. Buyers often fall into the trap of accepting manufacturer claims without rigorous on-site validation.
Pitfall: Skipping comprehensive factory acceptance testing (FAT) or third-party inspection. Without witnessing the machine perform precision cuts under load, it’s difficult to assess true accuracy, repeatability, and long-term stability. Poor-quality castings, substandard linear guides, or underpowered spindles may not surface until after installation—leading to rework, downtime, and lost revenue.
Lack of Robust Intellectual Property Safeguards
Large CNC machines are often used to manufacture high-value, proprietary components—such as aerospace parts, medical devices, or defense systems. When sourcing from overseas suppliers or third-party integrators, the risk of IP exposure increases significantly.
Pitfall: Failing to enforce strong contractual IP clauses and data security measures. Without clear agreements on data ownership, software encryption, access controls, and non-disclosure, sensitive CAD models, toolpaths, and production data could be copied, reverse-engineered, or shared. Some suppliers may retain unauthorized backups or use customer designs for demonstration purposes.
Insufficient Due Diligence on Supplier Reliability
The biggest CNC machines require long lead times and significant capital investment. Choosing a vendor based solely on price or size capability—without vetting their track record, service support, and financial health—can lead to project failure.
Pitfall: Partnering with suppliers lacking post-installation support or proven experience with ultra-large machines. If the vendor cannot provide timely technician support, spare parts, or calibration services, machine uptime suffers. Additionally, weak suppliers may lack the infrastructure to handle logistics, foundation requirements, or integration with existing systems.
Overlooking Integration and Future-Proofing Needs
Procuring the largest CNC machine isn’t just about fit and function today—it must align with future production demands and digital workflows.
Pitfall: Ignoring compatibility with existing CAM software, Industry 4.0 systems, or automation lines. Machines without open communication protocols (e.g., MTConnect) or secure remote monitoring capabilities can become isolated assets. Without planning for upgrades or retrofitting, the machine may become obsolete or a bottleneck.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers must prioritize hands-on quality validation, enforce strict IP protections, conduct thorough supplier audits, and ensure seamless integration. Investing time upfront in due diligence and contractual safeguards will protect both the integrity of the machine and the confidentiality of critical manufacturing data.
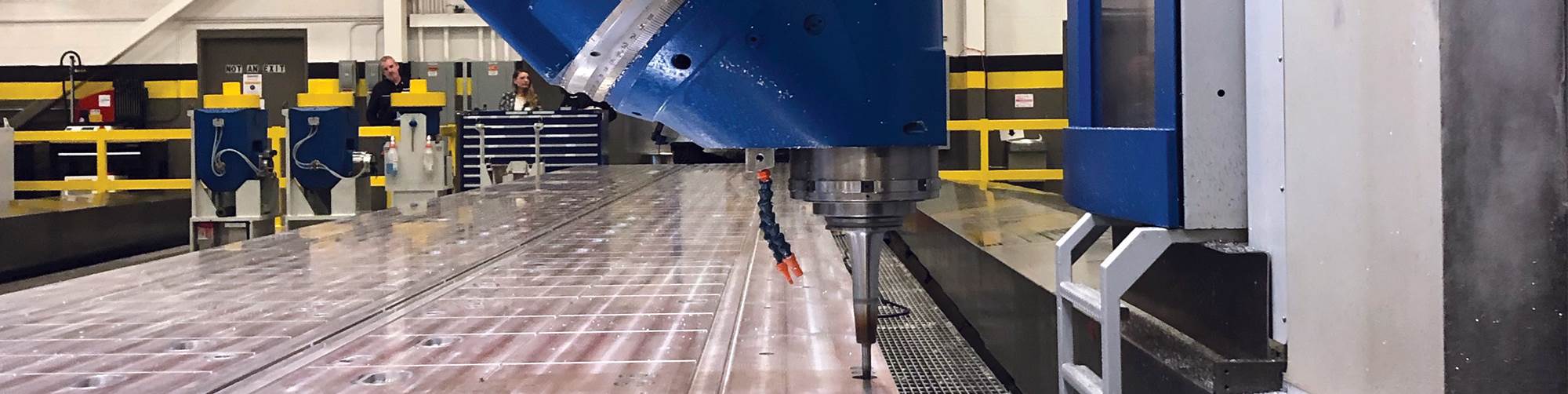

Logistics & Compliance Guide for the Biggest CNC Machine
Transporting and installing the world’s largest CNC machine presents unique logistical challenges and compliance requirements. This guide outlines critical considerations to ensure a successful and compliant operation.
Planning and Route Survey
Before initiating transport, conduct a comprehensive route survey to identify potential obstacles such as low bridges, narrow roads, tight turns, and weight-restricted infrastructure. Engage local authorities and engineering consultants to assess road conditions, overhead clearances, and bridge load capacities. Develop a detailed transport plan that includes alternative routes and contingency measures.
Transportation Regulations and Permits
Secure all necessary permits from state, provincial, and federal transportation authorities. Oversized and overweight load permits are typically required, and regulations vary by jurisdiction. These permits may mandate special routing, escort vehicles (pilot cars), restricted travel hours (e.g., nighttime or weekends), and advance notifications to law enforcement and utility companies.
Equipment and Handling Requirements
Use specialized heavy-lift transport equipment such as modular self-propelled trailers (SPMTs) capable of carrying hundreds of tons. Ensure the CNC machine is properly secured using cradles, bracing, and tie-downs designed to withstand vibrations and dynamic forces during transit. Coordinate with rigging experts and crane operators experienced in handling ultra-heavy industrial machinery.
Site Preparation and Installation
Prepare the installation site in advance to accommodate the machine’s dimensions and weight. This includes reinforced flooring, proper foundation construction, and clear access pathways. Verify ceiling height, door dimensions, and turning radii at the facility. Work with structural engineers to confirm the building can support the machine’s static and dynamic loads.
Safety and Risk Management
Develop a comprehensive safety plan covering transport, offloading, and installation phases. Conduct risk assessments for lifting operations, confined space work, and electrical connections. Provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and ensure all personnel are trained in heavy machinery handling protocols. Implement traffic control and exclusion zones during movement and setup.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
Comply with environmental regulations during transport and installation, particularly regarding hazardous materials (e.g., coolants, lubricants). Obtain necessary environmental permits if fluid handling or waste disposal is involved. Adhere to OSHA (or equivalent) safety standards, machine guarding requirements, and electrical codes (e.g., NEC, IEC) for installation.
Documentation and Certification
Maintain detailed records of permits, inspections, engineering certifications, and compliance documentation. Ensure the CNC machine meets international standards such as CE (Europe), UL (North America), or other regional certifications. Provide operators with manuals, safety data sheets (SDS), and training materials as required by law.
Coordination with Stakeholders
Collaborate closely with manufacturers, freight forwarders, local authorities, utility providers, and facility managers throughout the process. Establish clear communication channels and designate a project lead to oversee logistics and compliance. Schedule regular progress reviews to address issues promptly.
Post-Installation Verification
After installation, conduct alignment checks, calibration, and operational testing per manufacturer guidelines. Verify compliance with noise, emissions, and energy consumption standards. Document final inspections and obtain sign-off from regulatory or safety officers where applicable.
Following this guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient deployment of the biggest CNC machines, minimizing risks and avoiding costly delays.
Conclusion: Sourcing the Largest CNC Machine
Sourcing the largest CNC machine requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, facility requirements, production needs, supplier reliability, and long-term operational costs. After thorough research and analysis, it is clear that selecting the right machine is not solely about size, but about aligning the machine’s capabilities—such as bed dimensions, axis travel, power, precision, and control system—with the organization’s manufacturing goals.
Key considerations include ensuring the facility can accommodate the machine physically and electrically, providing adequate foundation and environmental controls. Additionally, partnering with a reputable manufacturer that offers robust technical support, training, and service is critical to maximizing uptime and performance.
Investing in the largest CNC machine represents a significant capital commitment, but when chosen strategically, it can enhance production capacity, improve machining accuracy for large-scale components, and provide a competitive edge in industries such as aerospace, energy, and heavy manufacturing.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by a balance of current needs and future scalability. With proper planning, integration, and maintenance, sourcing the largest CNC machine can deliver substantial long-term value and operational efficiency.