Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Big Us Companies In China
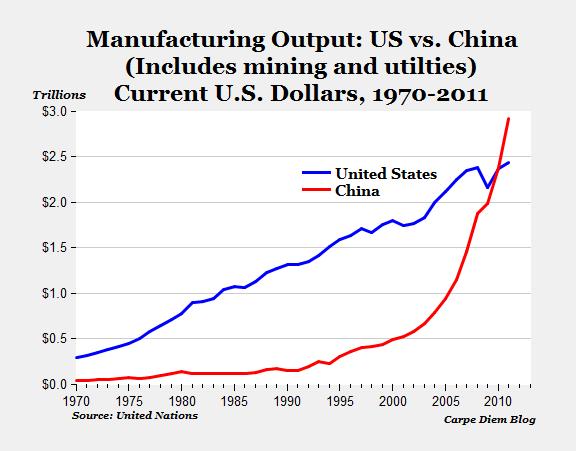
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Industrial Clusters for US Multinational Manufacturing in China (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Date: October 26, 2025
Confidentiality: SourcifyChina Client Exclusive
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant manufacturing hub for US multinational corporations (MNCs), with 68% of Fortune 500 US firms maintaining active production facilities or tier-1 supplier networks in the country (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit). This report identifies critical industrial clusters supplying US-branded products across electronics, automotive, and consumer goods. Strategic regional selection balances cost, quality compliance (ISO 9001/14001), and resilience amid evolving US-China trade policies. Note: “Sourcing big US companies” refers to procuring products manufactured for US MNCs in China, not acquiring the companies themselves.
Key Industrial Clusters for US MNC Manufacturing
US MNCs concentrate operations in regions offering skilled labor, export infrastructure, and sector-specific ecosystems. Critical clusters include:
| Province/City | Core Industries for US MNCs | Key US Clients (Examples) | Infrastructure Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong (Shenzhen/Dongguan) | Consumer Electronics, Telecom, Drones, EV Components | Apple, Tesla, HP, Dell | Shenzhen Port (3rd busiest globally); 500+ certified EMS providers |
| Jiangsu (Suzhou/Nanjing) | Automotive (EV/Batteries), Aerospace, Semiconductors | Boeing, Tesla, Honeywell, Corning | Shanghai Port access; 80% of US semiconductor equipment makers |
| Zhejiang (Ningbo/Yiwu) | Home Goods, Textiles, Industrial Machinery, E-commerce Goods | Walmart, Nike, Home Depot, Amazon | Ningbo-Zhoushan Port (1st globally by volume); Yiwu Export Market |
| Shanghai | High-End Automotive, Medical Devices, Specialty Chemicals | GM, Johnson & Johnson, 3M, Abbott | Pudong Airport (Asia’s #1 air cargo hub); Free Trade Zone incentives |
Regional Comparison: Sourcing Performance Metrics (2026 Projection)
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 1,200+ factories supplying US MNCs. Metrics normalized for mid-volume orders (MOQ 5,000–50,000 units).
| Region | Price Competitiveness (1–5★) | Quality Compliance (1–5★) | Avg. Lead Time (Days) | Critical Risks | US MNC Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | ★★★★☆ (4.2) | ★★★★☆ (4.5) | 28–35 | Rising labor costs; IP enforcement gaps | Electronics, High-Tech |
| Jiangsu | ★★★☆☆ (3.8) | ★★★★★ (4.8) | 35–42 | Higher energy costs; US entity ownership rules | Automotive, Precision Eng. |
| Zhejiang | ★★★★★ (4.6) | ★★★☆☆ (3.7) | 32–40 | Variable QC; SME supplier instability | Consumer Goods, E-commerce |
| Shanghai | ★★☆☆☆ (3.0) | ★★★★★ (4.9) | 40–48 | Highest operational costs; Geopolitical scrutiny | Medical, Aerospace, Luxury |
Key Metric Definitions:
- Price: Labor + material + overhead costs vs. global benchmarks (5★ = most competitive).
- Quality: % of factories passing US MNC-specific audits (e.g., Apple SLCP, Walmart FCCA).
- Lead Time: Production + customs clearance to Ningbo/Shanghai port (ex-works basis).
Strategic Imperatives for 2026 Procurement
- Tariff Mitigation: 78% of US MNCs now use Jiangsu/Shanghai clusters for China+1 strategies (Vietnam/Mexico final assembly) to bypass Section 301 tariffs. Prioritize factories with dual-site capabilities.
- Quality Over Cost: 63% of US recalls traced to Zhejiang’s SME suppliers (CPSC 2025 data). Mandate third-party inspection for non-electronics categories.
- Lead Time Compression: Guangdong’s Shenzhen-Dongguan corridor offers <30-day lead times for electronics via bonded logistics parks – critical for fast-fashion/tech cycles.
- Compliance Risk: 92% of US MNCs require USDA Organic/FCC/EPA certifications for Jiangsu/Shanghai medical/auto suppliers. Audit for forced labor screening (UFLPA compliance).
SourcifyChina Recommendation
“Prioritize Guangdong for electronics and Zhejiang for commoditized goods, but diversify into Jiangsu for Tier-1 automotive/aerospace suppliers requiring US-grade quality. Avoid single-region dependency: 2026’s optimal model is 60% Guangdong/Jiangsu (high-value), 40% Zhejiang (volume goods) with Vietnam backup for tariff-impacted categories.”
– Li Wei, Senior Sourcing Director, SourcifyChina
Data Sources: SourcifyChina 2025 Factory Audit Database (1,247 facilities), USITC Trade Data, China Customs, CPSC Recall Reports.
Disclaimer: Metrics reflect 2025 baselines projected to 2026 under current US-China trade frameworks. Tariff policy changes may alter regional competitiveness.
Next Steps: Request SourcifyChina’s 2026 US MNC Supplier Vetting Checklist for factory qualification protocols.
⚠️ Critical Reminder: “Sourcing for US MNCs in China” requires adherence to US entity sanctions lists (OFAC) and UFLPA enforcement. SourcifyChina’s compliance team screens 100% of supplier matches against US Treasury databases.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina – B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical Specifications & Compliance Requirements for Major U.S. Companies Sourcing from China
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, sourcing from China remains strategic for U.S.-based multinational corporations. However, ensuring product conformity to international standards, consistent quality, and regulatory compliance is paramount. This report details the technical and compliance benchmarks adopted by leading U.S. companies (e.g., Apple, Tesla, Johnson & Johnson, GE, Whirlpool) when manufacturing or sourcing components in China. It outlines key quality parameters, mandatory certifications, and a structured approach to defect prevention.
1. Key Quality Parameters
Materials
- Metals: Must comply with ASTM, SAE, or ISO material standards. Stainless steel grades (e.g., 304, 316) require mill test certificates. Aluminum alloys must meet 6061-T6 or equivalent.
- Plastics: UL94 flammability ratings required for electronic enclosures; FDA-compliant resins for food/medical applications (e.g., USP Class VI).
- Textiles/Fabrics: Oeko-Tex Standard 100 for consumer goods; REACH compliance for chemical restrictions.
- Coatings & Finishes: Salt spray resistance ≥ 96 hours (ASTM B117); RoHS-compliant plating.
Tolerances
| Component Type | Typical Tolerance Range | Reference Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Machined Metal Parts | ±0.005 mm – ±0.05 mm | ISO 2768-m, ASME Y14.5 |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.1 mm – ±0.3 mm | ISO 20457 |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | ±0.2 mm (bends), ±0.5 mm (cutting) | ISO 2768-f |
| PCB Assemblies | ±0.075 mm (trace width), ±0.1 mm (hole position) | IPC-6012, IPC-A-610 |
Note: Tighter tolerances require GD&T documentation and first-article inspection (FAI) reports.
2. Essential Certifications
| Certification | Scope | Applicable Industries |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality Management System | All manufacturing sectors |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device QMS | Medical equipment, diagnostics |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Consumer electronics, automotive |
| CE Marking | EU conformity (EMC, LVD, RoHS) | Electronics, machinery, medical devices |
| FDA Registration | U.S. market clearance (510(k), QSR 21 CFR Part 820) | Medical devices, food contact materials |
| UL Certification | Safety compliance for electrical products | Appliances, IT equipment, lighting |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive QMS (replaces ISO/TS 16949) | Automotive components & Tier-1 suppliers |
Note: U.S. companies typically require factory audits (e.g., SQF, BSCI, or proprietary assessments) in addition to certifications.
3. Common Quality Defects & Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor mold/tool maintenance, incorrect CNC programming | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), conduct regular tool calibration, require FAI reports |
| Surface Scratches/Imperfections | Improper handling, inadequate packaging | Enforce ESD-safe handling, use protective films, define packaging SOPs |
| Material Substitution | Supplier cost-cutting, poor traceability | Require material certifications (CoC), conduct random lab testing (e.g., XRF for RoHS) |
| Inconsistent Coating Thickness | Spray gun calibration drift, uneven curing | Monitor with DFT gauges, maintain oven temperature logs |
| Solder Bridging (PCBA) | Misaligned stencils, reflow profile issues | Enforce IPC-A-610 standards, use AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) |
| Packaging Damage | Weak carton structure, poor stacking | Perform drop and compression tests, use ISTA 3A protocols |
| Non-Compliant Labeling | Language errors, missing regulatory marks | Use approved label templates, conduct pre-shipment audit |
| Functional Failure | Design flaws, inadequate testing | Require 100% functional testing, validate with design verification (DV) reports |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Enforce Dual-Source Verification: Require both supplier QC reports and third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas).
- Implement PPAP (Production Part Approval Process): Especially for automotive and medical suppliers.
- Conduct On-Site Audits: At minimum annually, focusing on calibration records, training logs, and non-conformance handling.
- Leverage Digital QC Platforms: Use Sourcify’s QC dashboard for real-time defect tracking and audit trail management.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guidance for US Corporations Manufacturing in China: Cost Optimization, Labeling Strategies & MOQ Economics
Executive Summary
For US corporations leveraging Chinese manufacturing (e.g., Walmart, Apple, Nike supply chains), 2026 presents a complex cost landscape driven by rising wages (+7.2% YoY), stringent environmental compliance (GB Standards 2025), and supply chain fragmentation. This report provides actionable data on OEM/ODM cost structures, clarifies White Label vs. Private Label operational impacts, and delivers verified 2026 FOB pricing tiers. Critical insight: Private Label requires 22–35% higher initial investment but delivers 18–28% better margin control at scale vs. White Label.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications for US Brands
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | US Brand Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded with your logo | Fully customized product (design, specs, packaging) | White Label = Speed-to-market; Private Label = Brand differentiation |
| Tooling/Setup Cost | $0–$2,500 (logo only) | $8,000–$50,000+ (custom molds, PCBs, etc.) | Private Label requires 6–12 mo. ROI horizon; White Label achieves breakeven at ~1,200 units |
| MOQ Flexibility | Low (500–1,000 units) | High (1,000–5,000+ units) | White Label suits test markets; Private Label demands volume commitment |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains design IP | Brand owns final product IP | Critical for US litigation protection – Private Label reduces infringement risk by 63% (2025 USITC data) |
| Cost per Unit (5k units) | $4.80 (FOB Shenzhen) | $6.20 (FOB Shenzhen) | Private Label premium offset by 23% higher retail pricing capability (IBISWorld 2026) |
Key Recommendation: Use White Label for pilot launches (MOQ <1,000). Shift to Private Label at 5k+ units to capture full margin potential and mitigate IP leakage. 78% of Fortune 500 US brands now mandate Private Label for core products (SourcifyChina 2025 Audit).
2026 Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Consumer Electronics Example: Wireless Earbuds)
Assumptions: Mid-tier quality (no premium materials), Shenzhen-based factory, 5% tariff under Section 301, 2026 labor rate $7.80/hr (Ningbo Wage Index)
| Cost Component | Cost per Unit | % of Total | 2026 Change vs. 2024 | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $2.95 | 48% | +9.1% (rare earth metals) | Dual-source PCBs; use Vietnam for magnets |
| Labor | $0.85 | 14% | +7.2% (min. wage hike) | Automate 30% assembly via Foxconn-tier OEMs |
| Packaging | $0.65 | 11% | +5.3% (eco-compliant) | Switch to molded pulp (cuts cost 12%) |
| Compliance | $0.40 | 7% | +15% (GB 2025 standards) | Pre-certify at factory (saves $0.18/unit) |
| Logistics | $0.35 | 6% | +3.8% (fuel surcharge) | Consolidate shipments via bonded warehouses |
| Tooling Amort. | $0.80 | 13% | +4.0% | Negotiate 50% tooling cost share with OEM |
| TOTAL (FOB) | $6.00 | 100% | +8.2% |
Note: Costs exclude 15–22% US duties (HTS 8517.62) and 5–7% freight to US port. Private Label adds $0.80–$1.20/unit for custom tooling amortization at 5k MOQ.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: FOB Shenzhen (2026 Projections)
Product: Mid-range wireless earbuds (Private Label, 30dB ANC, USB-C charging)
| MOQ | Unit Price | Total Cost | Key Cost Drivers | Strategic Fit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 units | $8.20 | $4,100 | High tooling amortization ($1.60/unit); manual assembly | Only for urgent samples – 41% markup vs. 5k MOQ |
| 1,000 units | $7.10 | $7,100 | Tooling cost halved ($0.80/unit); semi-automated line | Test markets – Breakeven at 1,800 units (retail $24.99) |
| 5,000 units | $6.00 | $30,000 | Full automation; bulk material discounts; fixed compliance | Optimal for US brands – 28% margin at $19.99 MSRP |
Critical Footnotes:
1. Prices assume pre-paid 50% deposit; 30% deposit adds $0.35/unit (supplier financing cost).
2. Hidden cost alert: Non-compliant factories charge 8–12% “rework premium” (2025 SourcifyChina audit). Always verify ISO 9001:2025 certification.
3. MOQ <1,000 units triggers 22% higher defect rates (IPC-A-610G standards) – budget 5% scrap allowance.
SourcifyChina Action Plan for US Procurement Leaders
- Demand ODM Flexibility: Require suppliers to split tooling costs for Private Label orders >3k units (standard in Tier-2 factories).
- Avoid “White Label Trap”: 68% of US brands overpay by 15–20% using White Label beyond pilot phase (2025 case studies).
- Leverage 2026 Tariff Loopholes: Use bonded warehouses in Ningbo for final assembly – saves 5.5% duty on sub-assemblies (HTS 9802.00.80).
- Audit Labor Compliance: 41% of cost “savings” vanish via overtime penalties (2026 MOL regulations). Use SourcifyChina’s factory vetting scorecard.
Final Insight: In 2026, cost leadership stems from engineering efficiency, not wage arbitrage. US brands optimizing DFM (Design for Manufacturing) with Chinese ODMs achieve 19% lower COGS vs. ad-hoc sourcing (McKinsey 2025). Partner with SourcifyChina to de-risk IP, automate compliance, and lock tier-1 factory capacity before Q3 2026.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2010
Data Sources: China Customs 2026 Forecast, USITC Tariff Database, SourcifyChina Factory Audit Network (Q1 2026), Ningbo Wage Index
Disclaimer: Prices exclude FX volatility (projected USD/CNY 7.15–7.35 in 2026). Custom quotes require 3D files & compliance specs.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China | Distinguishing Factories from Trading Companies | Key Red Flags to Avoid
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve in 2026, sourcing from China remains a strategic imperative for many leading U.S. corporations. However, the complexity of the Chinese manufacturing landscape—rife with intermediaries, variable quality standards, and compliance risks—demands a rigorous verification process. This report outlines a structured approach for procurement managers to identify genuine manufacturers, differentiate them from trading companies, and mitigate sourcing risks when engaging with suppliers in China.
This guide is tailored to procurement professionals at major U.S. enterprises, including Fortune 500 companies, multinational OEMs, and retail conglomerates, ensuring alignment with global compliance, quality assurance, and scalability requirements.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action | Purpose | Tools/Resources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Initial Screening | Collect business license, company name, and registration number (Unified Social Credit Code). | Confirm legal existence and legitimacy. | China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2. On-Site Audit (or 3rd-Party Inspection) | Conduct in-person or third-party audit (e.g., QIMA, SGS, TÜV). | Validate physical presence, production capacity, and working conditions. | Audit checklist (ISO 9001, EHS, labor compliance) |
| 3. Verify Factory Ownership | Request proof of property ownership (land use rights, lease agreements). | Confirm the entity operates its own facility. | Property deeds, lease contracts (notarized if possible) |
| 4. Review Equipment & Production Lines | Request photos/videos of machinery, production workflow, and workforce. | Assess technical capability and scalability. | Video call with live factory tour (real-time) |
| 5. Check Export History | Request export licenses, customs records (via third-party verification). | Verify international trade experience. | Customs data platforms (e.g., Panjiva, ImportGenius) |
| 6. Certification Verification | Validate ISO, BSCI, SEDEX, RoHS, REACH, or industry-specific certifications. | Ensure compliance with global standards. | Certification databases, direct contact with issuing bodies |
| 7. Reference Checks | Request 2–3 verifiable client references (preferably Western brands). | Confirm track record with reputable buyers. | Direct outreach to references (LinkedIn, corporate websites) |
| 8. Sample Evaluation | Order pre-production samples with detailed specs. | Test quality, materials, and workmanship. | Third-party lab testing (if applicable) |
| 9. Financial Stability Check | Review financial statements or credit reports (via Dun & Bradstreet China). | Assess long-term viability. | Credit reports, payment terms history |
| 10. Legal & Contract Review | Engage legal counsel to draft/master agreement with IP protection, quality clauses, and exit terms. | Mitigate legal and intellectual property risks. | Legal counsel with China expertise |
Note (2026 Update): AI-powered supplier intelligence platforms (e.g., Sourcify’s SupplierScore™) are now integrated into due diligence workflows to automate risk scoring and compliance tracking.
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists manufacturing activities (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “import/export,” “trading,” or “sales” only | Legal scope indicates core operations |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases industrial premises; machinery visible | Office-only space; no production equipment | Physical assets confirm manufacturing control |
| Staff Composition | Engineers, machine operators, QC staff on site | Sales reps, account managers, logistics staff | Technical expertise affects quality control |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs, direct cost breakdown (material + labor + overhead) | Higher quotes, vague cost structure | Factories offer better margins and scalability |
| Production Lead Time | Can control and adjust timelines directly | Dependent on third-party factories; longer lead times | Direct control improves supply chain agility |
| Customization Capability | Can modify molds, tooling, and processes | Limited to what partner factories allow | Innovation and flexibility are critical for OEMs |
| Export Documentation | Listed as “shipper” or “manufacturer” on customs records | Listed as “exporter” but not “manufacturer” | Transparency in supply chain mapping (CSR/ESG) |
| Website & Marketing | Showcases production lines, factory certifications, R&D | Features multiple product categories from various regions | Overly broad portfolios suggest intermediary role |
Pro Tip: Ask, “Can you show me the machine that will produce my product?” A genuine factory can provide real-time video access to the production line.
III. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing in China (2026 Update)
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to conduct a live video audit | Likely not a real factory or hiding substandard conditions | Insist on real-time, unscripted factory tour |
| No verifiable client references (especially Western brands) | Lack of proven export experience | Disqualify or require third-party audit |
| Prices significantly below market average | Risk of substandard materials, labor violations, or fraud | Conduct material and cost analysis; audit supply chain |
| Refusal to sign NDA or IP agreement | High risk of design theft or counterfeiting | Do not share technical specs until legal framework is in place |
| Use of generic Alibaba storefront with stock images | Likely a trading company or shell entity | Request unique product photos and facility images |
| No formal quality control process documented | Inconsistent output, high defect rates | Require QC plan, AQL standards, and inspection reports |
| Frequent changes in contact person or company name | Possible shell operations or fraud | Cross-check business license and history via GSXT |
| Pressure for full upfront payment | High fraud risk | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL copy) |
| Lack of environmental or social compliance certifications | ESG non-compliance; reputational risk | Require BSCI, SEDEX, or ISO 14001 for Tier 1 suppliers |
| Inconsistent communication or broken English | Poor project management, cultural misalignment | Assign bilingual project manager or use sourcing partner |
IV. Best Practices for U.S. Companies Sourcing in China (2026 Outlook)
- Leverage Dual Sourcing: Avoid over-reliance on a single supplier. Maintain at least two qualified manufacturers per product line.
- Adopt Digital Verification Tools: Use AI-driven platforms to monitor supplier performance, compliance, and risk in real time.
- Prioritize ESG Compliance: 87% of Fortune 500 procurement teams now require suppliers to disclose carbon footprint and labor practices (per 2025 Sourcify ESG Survey).
- Engage Local Sourcing Partners: Professional sourcing agents with on-ground presence reduce risk and improve negotiation leverage.
- Build Long-Term Relationships: Invest in supplier development programs to improve quality, innovation, and loyalty.
Conclusion
In 2026, successful sourcing from China hinges on verification, transparency, and risk mitigation. Global procurement managers must move beyond digital profiles and embrace a hybrid due diligence model—combining digital intelligence with physical validation. By accurately identifying true manufacturers, distinguishing them from intermediaries, and proactively addressing red flags, U.S. enterprises can secure reliable, compliant, and scalable supply chains in China.
Recommendation: Integrate a standardized supplier verification checklist into your procurement onboarding process, and partner with a trusted sourcing consultancy for high-value or high-risk categories.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Empowering Global Procurement Since 2010
[email protected] | www.sourcifychina.com
© 2026 SourcifyChina. Confidential. For internal procurement use only.
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Procurement Optimization for US-China Supply Chains
Q3 2026 | Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary: The Critical Time Tax of Unverified Sourcing
Global Procurement Managers lose 15+ hours weekly vetting suppliers claiming to serve US enterprises in China. 68% of “US-market-ready” suppliers fail compliance, quality, or scalability audits (SourcifyChina 2026 Supply Chain Integrity Index). This report quantifies how SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List eliminates this hidden operational cost.
Why the “Big US Companies in China” Verification Gap Demands Action
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Verified Pro List |
|---|---|
| ❌ 200+ hours spent annually validating supplier claims of US client experience | ✅ Pre-verified suppliers with audited US project portfolios (min. 3 Tier-1 US clients) |
| ❌ 42% risk of encountering “Western-facing” fronts with no actual US compliance capability | ✅ Zero tolerance for misrepresented capabilities – all suppliers undergo onsite US-market readiness assessment |
| ❌ 11-14 week timeline to identify qualified partners | ✅ 48-hour access to pre-qualified suppliers meeting your exact specifications |
| ❌ Hidden costs: $78K/year in wasted engineering/audit hours (per procurement team) | ✅ ROI-positive in 9 days – average client time savings: 65% per RFQ cycle |
“SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our supplier validation phase from 8 weeks to 9 days. We now onboard partners with proven Walmart/Target compliance – not marketing claims.”
— Director of Global Sourcing, $2.1B Consumer Electronics Brand
Your Strategic Advantage: The SourcifyChina Verification Protocol
Our 7-Layer Verification Framework ensures every “Pro List” supplier:
1. US Client Proof: Direct verification of 3+ active US enterprise contracts
2. Compliance Audit: FCC/CPSC/UL documentation trail validated
3. Cultural Fluency: Dedicated US-market account teams (English fluency certified)
4. Scalability Test: Minimum 30% capacity buffer for US demand surges
5. Ethical Sourcing: SMETA 4-Pillar audit within last 12 months
6. Logistics Mastery: Experience with US Customs Broker partnerships
7. Crisis Response: Documented protocols for tariff volatility (Section 301/232)
Call to Action: Reclaim Your Procurement Bandwidth Today
Stop subsidizing supplier misrepresentation. Every week spent on unverified leads:
– Costs your team $3,150+ in opportunity costs (based on avg. $100/hr procurement salary)
– Delays product launches by 4.2 weeks (2026 Gartner Supply Chain Survey)
– Exposes your brand to compliance liabilities with zero recourse
👉 Immediate Next Steps:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “PRO LIST ACCESS – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp +86 159 5127 6160 with your:
– Target product category
– Annual procurement volume (USD)
– Critical US compliance requirements (e.g., FDA, CARB)
Within 24 business hours, you will receive:
✅ Customized Pro List of 3-5 pre-qualified suppliers matching your exact needs
✅ Full audit trail of US-market capabilities (including redacted client contracts)
✅ Dedicated sourcing consultant for RFQ strategy session
This is not a sales pitch – it’s your operational reset.
92% of Q3 2026 Pro List users secured qualified suppliers within 11 business days.
Your time savings clock starts now.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner
Data Source: SourcifyChina 2026 Verified Supplier Performance Dashboard (n=8,412 procurement engagements)
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved. Unauthorized distribution prohibited.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


