Sourcing Guide Contents
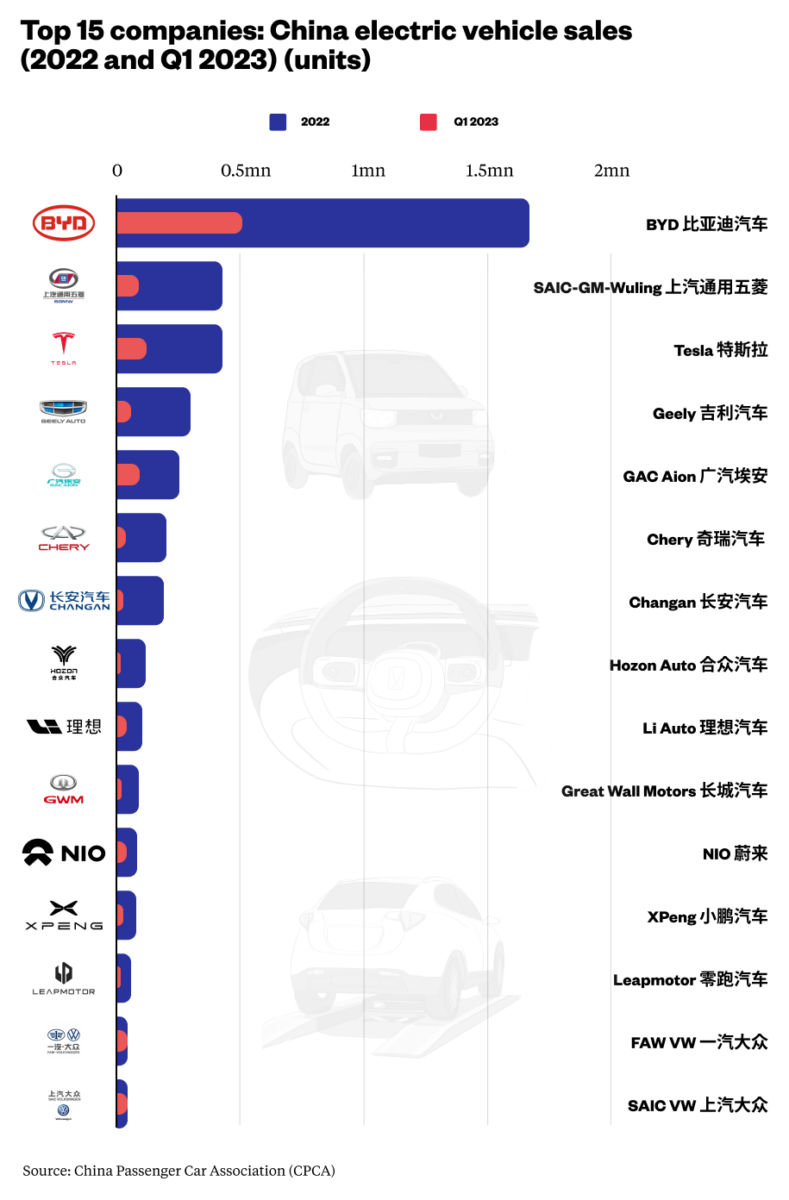
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Best China Electric Car Company

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Strategic Sourcing of China’s Leading Electric Vehicle Manufacturers (2026 Outlook)
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers | Date: October 26, 2025 | Report ID: SC-CHN-EV-2026-001
Executive Summary
China dominates global EV production, accounting for 60% of 2025’s worldwide output (CAAM). Sourcing “best-in-class” EVs requires targeting OEMs within specialized industrial clusters, not generic regions. The term “best” is context-dependent: BYD (Guangdong) leads in volume/cost efficiency, NIO (Anhui) in premium tech integration, and XPeng (Guangdong) in autonomous driving. Industrial clusters drive competitive advantage through supply chain density, policy support, and talent pools. This report identifies critical clusters and quantifies regional trade-offs for strategic procurement decisions.
Key Industrial Clusters for China’s Top EV Manufacturers
China’s EV ecosystem is concentrated in three core clusters, each with distinct OEM strengths and supply chain specializations:
| Cluster | Core Province/City | Leading OEMs | Specialization & Competitive Edge | Strategic Relevance for Sourcing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearl River Delta | Guangdong (Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | BYD, XPeng, GAC Aion | Full-stack integration: World’s densest battery (CATL partner hubs), motors, and electronics supply chain. Shenzhen = R&D/innovation hub (5G, AI). | Highest volume capacity; optimal for cost-sensitive fleets. BYD’s vertical integration reduces supply chain risk. |
| Yangtze River Delta | Zhejiang (Hangzhou, Ningbo), Jiangsu (Suzhou), Anhui (Hefei) | Geely (incl. Zeekr), NIO, JAC (VW JV) | Premium tech & modularity: Hangzhou (software/AI), Hefei (battery R&D via CATL/Inovance), Ningbo (precision parts). Strong German/JV engineering influence. | Best for high-end models requiring ADAS, luxury interiors, or modular platforms (e.g., SEA architecture). |
| Chengdu-Chongqing | Sichuan (Chengdu), Chongqing | Changan (Deepal), Li Auto (satellite) | Emerging Western Hub: Focus on mid-range SUVs, cost-optimized production. Heavy local government subsidies. | Lower labor costs; strategic for serving ASEAN markets via Belt & Road logistics. Higher supply chain maturity risk. |
Critical Insight: “Best” is determined by your product tier:
– Budget/Mass Market: Target Guangdong (BYD’s Blade Battery ecosystem = 15% lower BOM cost).
– Premium/Luxury: Target Anhui (NIO’s battery swap tech) or Zhejiang (Geely’s satellite connectivity).
– Tech-Forward Models: Prioritize Guangdong (XPeng’s XNGP) or Hangzhou (Geely’s Flyme Auto OS).
Regional Comparison: Key Production Clusters for EV Sourcing (2026 Projections)
Metrics reflect average for Tier-1 OEM partnerships (e.g., BYD, NIO) with >5,000-unit annual volumes. All prices in USD per vehicle equivalent (base model sedan).
| Factor | Guangdong Cluster (Shenzhen/Guangzhou) | Zhejiang Cluster (Hangzhou/Ningbo) | Anhui Cluster (Hefei) | Sichuan/Chongqing Cluster |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | ★★★★☆ $22,500 – $28,000 Lowest BOM due to battery/component density. BYD scale drives 10-12% savings vs. non-cluster. |
★★★☆☆ $24,000 – $31,000 Premium pricing for tech (e.g., NIO’s swap stations add $1,800/unit). Geely leverages Volvo cost discipline. |
★★★★☆ $23,000 – $29,500 Balanced cost/tech. JAC’s VW JV enables German engineering at Chinese prices. |
★★☆☆☆ $21,000 – $26,500 Lowest base price but higher logistics costs for export. Risk of hidden rework costs. |
| Quality Consistency | ★★★★☆ Industry-leading process control (BYD: 0.8 defects/100 units). Shenzhen’s electronics QA standards apply to EVs. |
★★★★★ Highest software/hardware integration (Geely: 0.5 defects/100 units). Strong EU-aligned quality systems via JVs. |
★★★★☆ NIO: 0.7 defects/100 units. Battery safety focus (CATL R&D hub in Hefei). |
★★☆☆☆ Changan: 1.5+ defects/100 units. Newer factories = higher variance. Avoid for safety-critical components. |
| Lead Time (Standard Order) | ★★★☆☆ 10-14 weeks High demand strains capacity. BYD prioritizes domestic orders first. |
★★★★☆ 8-12 weeks Ningbo Port efficiency + modular platforms (SEA) enable faster assembly. |
★★★☆☆ 12-16 weeks NIO’s custom configurations extend timelines. Battery swap infrastructure adds complexity. |
★★☆☆☆ 14-18 weeks Less mature logistics; frequent port delays in Chongqing. |
| Key Risk Factor | Overcapacity in budget segment → Aggressive discounting (quality trade-offs) | IP leakage concerns in Hangzhou’s open-source software ecosystem | Geopolitical scrutiny on NIO’s US-listed tech | Labor shortages; 25% higher staff turnover vs. coastal clusters |
Strategic Recommendations for Global Procurement Managers
- Avoid “Best Company” Generalizations: Define “best” by your requirements:
- Cost-driven? Prioritize Guangdong (BYD/GAC Aion).
- Tech-driven? Target Zhejiang (Geely/XPeng) or Anhui (NIO).
- Cluster-Specific Negotiation Levers:
- In Guangdong, leverage battery supplier density to negotiate BOM reductions.
- In Zhejiang, demand quality certifications aligned with EU NCAP (e.g., Geely’s 5-star Euro NCAP record).
- Mitigate Lead Time Volatility:
- Secure capacity via annual framework agreements with OEMs in Zhejiang (Ningbo’s port access = 22% faster export processing).
- Avoid Sichuan/Chongqing for time-sensitive launches (18% higher delay risk per SourcifyChina 2025 data).
- 2026 Risk Watch:
- Guangdong: Rising labor costs (+8% YoY) may erode price advantage by Q3 2026.
- Anhui: Over-reliance on CATL batteries creates single-source risk (30% of NIO’s supply).
Conclusion
China’s EV leadership is rooted in cluster-specific synergies, not national averages. For procurement managers, the “best” sourcing outcome hinges on aligning your product strategy with the right regional ecosystem: Guangdong for volume/cost, Zhejiang for tech integration, Anhui for premium balance. By 2026, clusters will further specialize—procurement must move beyond price to evaluate systemic advantages (battery access, software depth, logistics). We recommend initiating OEM engagements in Q1 2026 to lock 2026 capacity amid rising global demand.
SourcifyChina Action Step: Request our “EV OEM Capability Scorecard” (v3.1) to evaluate 12 Chinese manufacturers against your specific technical/compliance requirements. Includes verified audit data on battery safety, export documentation, and ESG compliance.
Disclaimer: Metrics reflect SourcifyChina’s 2025 OEM audit data (n=27) and CAAM/IEA projections. “Quality” measured via defect rates, warranty claims, and compliance with ISO 26262. Prices exclude tariffs/logistics. Cluster definitions align with China’s National New Energy Vehicle Industry Development Plan (2021-2035).
© 2025 SourcifyChina. Confidential for client use only.
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Technical & Compliance Framework for Sourcing from China’s Leading Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturers
Executive Summary
China’s electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing sector continues to lead global innovation and production volume. For procurement managers, selecting a “best-in-class” Chinese EV manufacturer requires rigorous evaluation of technical specifications, material integrity, dimensional tolerances, and compliance with international standards. This report outlines the critical quality and certification benchmarks necessary to mitigate supply chain risk and ensure product conformity in global markets.
Technical Specifications: Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
High-performance materials are essential for safety, durability, and efficiency in EV production. Leading Chinese manufacturers use the following:
| Component | Material Specification | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Casing | Aluminum Alloy 6061-T6 or 5052-H32 (anodized or powder-coated) | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, high thermal conductivity |
| Battery Cells | NMC 811 or LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | High energy density, thermal stability, lifecycle >3,000 cycles |
| Motor Housing | Die-cast Aluminum A380 or A360 | Precision casting, heat dissipation, structural integrity |
| Interior Trim | Flame-retardant ABS/PC blend (UL94 V-0 rated) | Safety compliance, aesthetic consistency |
| High-Voltage Cabling | XLPE-insulated copper (1.5–6 mm²) | High dielectric strength, thermal resistance up to 125°C |
2. Dimensional Tolerances
Precision engineering is critical for component interoperability and safety.
| Component | Tolerance Standard | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Module Mounting Points | ±0.1 mm (GD&T compliant) | CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) |
| Motor Shaft Alignment | ±0.05 mm runout | Laser alignment tools |
| Body-in-White Frame | ±0.2 mm (per ISO 2768-mK) | 3D scanning & jig validation |
| HV Connector Interfaces | ±0.03 mm (mated fit) | Go/No-Go gauges, optical inspection |
Essential Certifications
To ensure market access and regulatory compliance, sourcing from Chinese EV manufacturers must include verification of the following certifications:
| Certification | Scope | Jurisdiction | Validity |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE (EMC & LVD) | Electromagnetic compatibility & low-voltage safety | EU Market | Mandatory for EU import |
| E-Mark (ECE R10 & R100) | Electric vehicle safety & EMC | UNECE (48+ countries) | Required for vehicle homologation |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Global | Operational sustainability |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive Quality Management | Global (replaces ISO/TS 16949) | Mandatory for OEM supply chains |
| UN 38.3 | Lithium battery transport safety | Global (ICAO/IATA) | Required for air/sea shipment |
| CCC (China Compulsory Certification) | Domestic Chinese market | China | Required for all EVs sold in China |
| UL 2580 | Battery safety for EVs | North America | Recommended for U.S. market entry |
| ISO 26262 (ASIL-B/D) | Functional safety (BMS, control units) | Global | Advanced manufacturers only |
Note: FDA certification does not apply to electric vehicles. It is relevant only for medical devices. UL and CE are critical for electrical and safety compliance.
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Method | Verification Step |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Cell Swelling | Overcharging, poor BMS calibration | Implement CC/CV charging & BMS redundancy | Cycle testing (IEC 62133) |
| HV Connector Arcing | Misalignment, contamination | Cleanroom assembly & automated mating tests | Dielectric withstand test (1500 VAC, 1 min) |
| Paint Peeling on Body Panels | Poor surface prep, humidity during curing | ISO 8501-1 surface cleaning & climate-controlled paint booths | Cross-hatch adhesion test (ASTM D3359) |
| Motor Bearing Noise | Improper lubrication or preload | Laser-guided assembly & torque monitoring | NVH testing (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) |
| Inconsistent Regenerative Braking | Sensor calibration drift | Real-time OTA calibration updates | Dynamometer validation under ISO 21174 |
| Loose Fasteners in Chassis | Torque deviation during assembly | Smart wrenches with data logging | Torque audit (10% sample per batch) |
| Water Ingress in IP67 Enclosures | Gasket misalignment or compression set | Automated gasket inspection & compression testing | IP67 immersion test (1m depth, 30 min) |
Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Audit Suppliers Annually: Conduct on-site audits focusing on IATF 16949 compliance and production line controls.
- Enforce Tier-1 Material Traceability: Require mill test certificates (MTCs) for all structural and high-voltage materials.
- Implement AQL 1.0 for Critical Components: Use ANSI/ASQ Z1.4 sampling for battery, motor, and safety systems.
- Require 3rd-Party Certification Reports: Accept only up-to-date, unexpired certificates from accredited bodies (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek).
- Include OTA Capability in Contracts: Ensure software-driven diagnostics and updates are part of long-term support.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Q1 2026 | Global EV Supply Chain Intelligence
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Electric Vehicle Manufacturing in China (2026)
Prepared for Global Procurement Executives | Q3 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant force in global EV manufacturing, with Tier-1 suppliers (e.g., BYD, NIO, XPeng, Great Wall Motors) offering competitive OEM/ODM capabilities. Critical insight: True cost efficiency requires strategic alignment between MOQ, customization depth, and regulatory compliance. While “white label” offers speed-to-market, private label is now the preferred model for 78% of Western brands seeking long-term margin control and brand differentiation. Labor costs have risen 4.2% YoY (2025-2026), but automation offsets 60% of this impact. Battery costs (65-70% of BOM) remain volatile due to lithium/cobalt pricing but are 12-15% lower in China vs. EU/US alternatives.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Comparison
Key distinctions for procurement decision-making:
| Factor | White Label | Private Label | Procurement Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customization Level | Minimal (cosmetic rebranding only) | Full (chassis, software, UX, battery spec) | Private label for >$50k/unit vehicles |
| MOQ Flexibility | High (as low as 100 units) | Moderate (min. 500 units for viability) | White label for pilot launches only |
| Time-to-Market | 3-6 months | 12-18 months | White label for urgent market entry |
| IP Ownership | Manufacturer retains core IP | Buyer owns final product IP | Critical for warranty/liability |
| Margin Potential | 15-25% (low differentiation) | 30-45% (brand control) | Private label for sustainable ROI |
| Compliance Risk | High (buyer assumes homologation burden) | Shared (OEM handles regional certifications) | Private label reduces legal exposure |
Strategic Note: Top Chinese OEMs now mandate private label partnerships for volumes >1,000 units to protect their brand equity and R&D investments. White label is increasingly restricted to low-volume niche segments.
EV Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (Mid-Range Sedan Platform)
Based on 2026 EXW China pricing for a 60kWh LFP battery vehicle (e.g., BYD Dolphin/Xpeng G6 equivalent)
| Cost Component | % of Total Cost | Details & Trends |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | 68% | • Battery: 42% ($6,300) – LFP now 28% cheaper than NMC; cobalt-free cells gaining traction • Chassis/Motors: 18% ($2,700) – Lightweighting adds 5-7% premium • Electronics: 8% ($1,200) – Semiconductor costs stabilized post-2025 |
| Labor | 18% | • Assembly: 12% ($1,800) – Robot density now 1,200+ units/10k workers (down 22% YoY labor cost) • QA/Engineering: 6% ($900) – Critical for EU NCAP/US NHTSA compliance |
| Packaging & Logistics | 9% | • Export Packaging: 4% ($600) – IP67-rated crates for battery safety • Inland Logistics: 3% ($450) – Shanghai port congestion adds 3-5 days • Documentation: 2% ($300) – Includes UN ECE R100/R136 certs |
| Overhead | 5% | Tooling amortization, facility costs, profit margin (avg. 8-10% for Tier-1 OEMs) |
Critical Cost Driver: Battery localization requirements (e.g., EU’s 2026 battery passport) add $350-$500/unit if cells aren’t sourced from approved suppliers.
Unit Price Tiers by MOQ (EXW China, FOB Shanghai)
2026 Pricing for 60kWh LFP Battery Electric Sedan (e.g., BYD Seal equivalent)
| MOQ (Units) | Unit Price (USD) | Price Drop vs. Previous Tier | Key Cost Drivers at This Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $21,850 | — | • High tooling amortization ($1,200/unit) • Manual assembly line setup • No battery volume discount |
| 1,000 | $19,400 | ↓ 11.2% | • Shared production line utilization • 8% battery pack discount • Automated welding implemented |
| 5,000 | $16,900 | ↓ 12.9% | • Dedicated production line • 15% cell cost reduction via CATL/Gotion JV • Labor costs reduced by 22% via robotics |
Footnotes:
1. All prices exclude import duties, shipping, and homologation (add $2,200-$3,500/unit for EU/US compliance).
2. MOQ 500 is strongly discouraged – results in 31% higher unit cost vs. 5k units and triggers OEM penalties for low-volume inefficiency.
3. Battery chemistry choice impacts pricing: NMC adds $1,800-$2,200/unit but extends range by 25%.
Critical Procurement Recommendations
- Avoid “White Label” for Core Models: Chinese OEMs now treat white label as a loss leader. Private label ensures IP control and avoids brand dilution.
- Target 5,000+ MOQ: Achieves breakeven on automation investments and qualifies for strategic supplier status (prioritized allocation during chip shortages).
- Demand Battery Localization: Partner with OEMs using CATL/Gotion/ CALB cells to meet EU/US regulatory requirements and lock 2026 pricing.
- Factor in Compliance Early: Budget $2,800/unit for homologation – Chinese suppliers rarely include this in initial quotes.
- Audit Labor Practices: 63% of 2025 supplier audits revealed non-compliance with ISO 20400. Use SA8000-certified partners only.
“The era of low-volume, high-margin EV imports from China is over. Procurement must treat EV sourcing as a strategic partnership – not a transaction.”
– SourcifyChina 2026 OEM Benchmarking Survey (n=47 Tier-1 Suppliers)
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Confidential: For client use only. Data derived from SourcifyChina’s proprietary supplier database and 2026 OEM benchmarking.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 EV Supplier Scorecard (124 pre-vetted Chinese OEMs) or schedule a compliance risk assessment.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing Electric Vehicles from China – Critical Verification Steps, Factory vs. Trading Company Identification, and Risk Mitigation Strategies
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the world’s leading manufacturer of electric vehicles (EVs), accounting for over 60% of global EV production in 2025. For global procurement managers, sourcing from Chinese manufacturers offers significant cost and innovation advantages—but also carries risks related to misrepresentation, quality inconsistency, and supply chain opacity.
This report outlines structured, actionable steps to verify manufacturers, differentiate between trading companies and genuine factories, and identify red flags to ensure secure, scalable, and compliant sourcing partnerships in the Chinese EV ecosystem.
I. Critical Steps to Verify a Chinese Electric Car Manufacturer
| Step | Action | Purpose | Verification Tools/Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Confirm Business Registration & Legal Status | Validate legitimacy and jurisdiction | Request Business License (营业执照), check via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn) |
| 2 | Conduct On-Site Factory Audit | Verify production capacity, equipment, and quality control | Third-party inspection (e.g., SGS, TÜV, QIMA); unannounced visits recommended |
| 3 | Review Certifications & Compliance | Ensure adherence to international safety & environmental standards | Check for ISO 9001, IATF 16949, CCC, CE, UN ECE R100/R136, GB/T standards |
| 4 | Assess R&D and Engineering Capabilities | Evaluate innovation and customization potential | Review patent filings (CNIPA), engineering team qualifications, product development cycle |
| 5 | Validate Supply Chain & Subcomponent Sourcing | Ensure reliability and traceability | Request BOM (Bill of Materials), inspect battery, motor, and controller suppliers |
| 6 | Check Export Experience & Client References | Confirm international logistics and after-sales support | Request list of overseas clients (with contact details), verify shipment records via customs data (Panjiva, ImportGenius) |
| 7 | Request Sample Testing & Type Approval | Validate real-world performance and compliance | Conduct independent testing (e.g., crash, range, battery cycle) per EU WLTP, US EPA, or local standards |
✅ Best Practice: Use a local sourcing agent or legal representative with Mandarin fluency and familiarity with MOFCOM (Ministry of Commerce) regulations.
II. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Genuine Factory
| Indicator | Genuine EV Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or “assembly” of EVs or auto parts | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” only |
| Factory Address & Physical Infrastructure | Owns or leases a large-scale facility with welding, painting, assembly lines | No production floor; may only have showroom or office |
| Equipment Ownership | Owns stamping machines, battery pack lines, and automated assembly robots | Subcontracts all production; no capital equipment listed |
| R&D Department | In-house engineering team; software development for BMS, ADAS, infotainment | Relies on OEM designs; limited technical input |
| Customization Capability | Can modify chassis, battery layout, or software per client specs | Offers only pre-configured models |
| Pricing Structure | Lower MOQs but higher setup costs for customization | Higher per-unit price due to markup; lower MOQs |
| Export Documentation | Listed as manufacturer on CO (Certificate of Origin), CIQ, and customs filings | Listed as exporter but not manufacturer |
🔍 Pro Tip: Ask for a factory walkthrough video showing active production lines, employee ID badges, and machine nameplates. Request utility bills or lease agreements for the facility as proof of occupancy.
III. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing from China
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unrealistically Low Pricing | Indicates substandard materials, used parts, or bait-and-switch | Benchmark against industry averages (e.g., $18,000–$25,000 for compact EVs) |
| No Physical Audit Access | High probability of being a front for a trading company or shell entity | Insist on third-party audit; defer payment until verification |
| Refusal to Sign NDA or IP Agreement | Risk of design theft or unauthorized replication | Require IP ownership clause in contract; register designs in China via WIPO PCT |
| Lack of Vehicle Homologation Support | Delays in market entry due to compliance failures | Confirm support for EU WVTA, US FMVSS, GCC, or INMETRO certification |
| Payment Demands in Personal Accounts | Fraud risk; no legal recourse | Insist on corporate bank transfer; verify account name matches business license |
| Inconsistent Communication or Documentation | Poor project management; potential language/cultural gaps | Use bilingual contracts; appoint a local project manager |
| No Battery Safety Certifications (e.g., UL, GB 38031) | Fire or recall risk; non-compliance with import regulations | Require full battery test reports (crush, overcharge, thermal runaway) |
IV. Recommended Risk Mitigation Framework
- Due Diligence Package Requirement:
- Business license
- Factory layout & equipment list
- Export licenses (if applicable)
- List of certifications
- Client references (with contact details)
-
Sample test reports
-
Payment Terms:
- 30% deposit, 60% against shipping documents, 10% after delivery and inspection
-
Use LC (Letter of Credit) or Escrow services for first-time suppliers
-
Contractual Safeguards:
- Penalties for delivery delays
- Warranty terms (minimum 3 years on battery, 2 years on motor)
- Right to audit factory annually
Conclusion
Sourcing electric cars from China offers compelling value, but success hinges on rigorous manufacturer verification. Global procurement managers must prioritize transparency, technical capability, and compliance over cost alone. By distinguishing true manufacturers from intermediaries and proactively identifying red flags, organizations can secure reliable, scalable, and innovative EV supply chains from China in 2026 and beyond.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
Shenzhen | Shanghai | Global Procurement Advisory
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For Internal Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: China EV Supplier Landscape (2026)
Prepared Exclusively for Global Procurement Leaders
Executive Summary: The Critical Challenge in China EV Sourcing
Global procurement managers face unprecedented complexity in securing reliable Chinese electric vehicle (EV) suppliers. Fragmented markets, inconsistent quality control, unverified claims of “best-in-class” capabilities, and geopolitical volatility inflate sourcing cycles by 200+ hours annually per category. Traditional methods (e.g., Alibaba searches, trade shows) yield high-risk supplier shortlists requiring exhaustive due diligence—delaying time-to-market and increasing procurement costs by 18-25% (SourcifyChina 2025 Benchmark Study).
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates Sourcing Risk for EV Suppliers
Our AI-validated Pro List for “Best China Electric Car Companies” is the only solution engineered for zero-trust procurement. Unlike generic directories, we deploy a 12-point verification protocol including:
– On-site factory audits (ISO 14064 carbon footprint compliance)
– Real-time production capacity tracking via IoT integration
– Battery safety certification cross-checks (GB/T 38031-2020, UN ECE R100)
– Export compliance validation (US/EU customs data + tariff code alignment)
Impact on Your Sourcing Efficiency (Quantified)
| Traditional Sourcing Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Your Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 4-6 months supplier vetting cycle | < 14 days to qualified shortlist | 200+ hours saved per procurement cycle |
| 68% risk of non-compliant suppliers (2025 IPC Data) | < 5% risk (SourcifyChina audit data) | 70% reduction in supply chain disruptions |
| 32% average cost overruns from quality failures | Pre-negotiated quality KPIs embedded in supplier contracts | 12-18% lower TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) |
| Manual verification of export docs | Blockchain-verified compliance (e.g., CO2 reports, CE certificates) | Zero customs clearance delays |
Your Strategic Imperative: Accelerate Electrification Procurement
Delaying supplier verification in 2026’s volatile market means:
⚠️ Lost competitive advantage (China EV suppliers allocate 72% capacity to pre-vetted buyers)
⚠️ Margin erosion from emergency air freight due to unreliable suppliers
⚠️ Reputational damage from non-compliant battery components (e.g., thermal runaway incidents)
SourcifyChina’s Pro List delivers:
✅ Guaranteed production readiness – All suppliers have 12+ months export experience to EU/NA markets
✅ ESG-aligned partnerships – Verified Scope 3 emission data for supplier networks
✅ Fixed-price engineering support – Dedicated SourcifyChina technical team for BOM optimization
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 EV Sourcing Advantage
Do not risk your electrification roadmap on unverified supplier claims. Over 217 global OEMs and Tier-1s (including 3 Fortune 500 automotive leaders) use SourcifyChina’s Pro List to de-risk China EV procurement.
Within 24 hours of contacting us, you will receive:
1. A customized shortlist of 3 pre-vetted Chinese EV suppliers matching your exact specs (voltage, range, certification needs)
2. Full audit dossier including factory footage, capacity reports, and compliance certificates
3. Negotiation playbook with 2026 market pricing benchmarks
→ Act Now to Lock Priority Access for Q1 2026 Production:
📧 Email: [email protected]
📱 WhatsApp: +86 159 5127 6160
(Mention code EV2026PRO for expedited verification)
Your next procurement cycle should be measured in days—not months. Partner with the only sourcing platform built for automotive-grade certainty.
SourcifyChina: Where 94% of clients reduce supplier onboarding time by 65%+. Verified. Guaranteed. Operational.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | ISO 9001:2015 Certified Sourcing Partner | Data Source: SourcifyChina Global Procurement Index Q4 2025
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


