The global battery holder market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global battery market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.8% from 2023 to 2028, with increasing adoption of lithium-based batteries and compact power solutions fueling demand for reliable battery holding components. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the broader battery enclosures and accessories market is expanding in tandem with advancements in consumer electronics and industrial applications, where secure, efficient, and scalable battery housing is critical. As product miniaturization and energy efficiency become central to design, manufacturers of battery holders are playing an increasingly vital role in ensuring performance, safety, and integration across industries. In this evolving landscape, identifying top-tier battery holder manufacturers with proven engineering capabilities, global supply chain reach, and compliance with international standards becomes essential for OEMs and innovators alike. Here are the top 10 battery holder manufacturers shaping the future of power management solutions.
Top 10 Battery Holder Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1
Domain Est. 1997
Website: batteryholders.com
Key Highlights: Memory Protection Devices, Inc. MPD is an ISO 9001 certified global manufacturer of battery holders, battery contacts, auto plugs, auto sockets, fuse holders ……
#2 Memory Protection Devices Corporate …
Domain Est. 2002
Website: memoryprotectiondevices.com
Key Highlights: MPD is a global manufacturer of battery holders, battery contacts, auto plugs, auto sockets, fuse holders, DC jacks, DC plugs, and other electronic ……
#3 Power-Sonic
Domain Est. 1995
Website: power-sonic.com
Key Highlights: Power-Sonic delivers innovative battery solutions with sealed lead acid and lithium batteries, energy storage systems, and EV chargers….
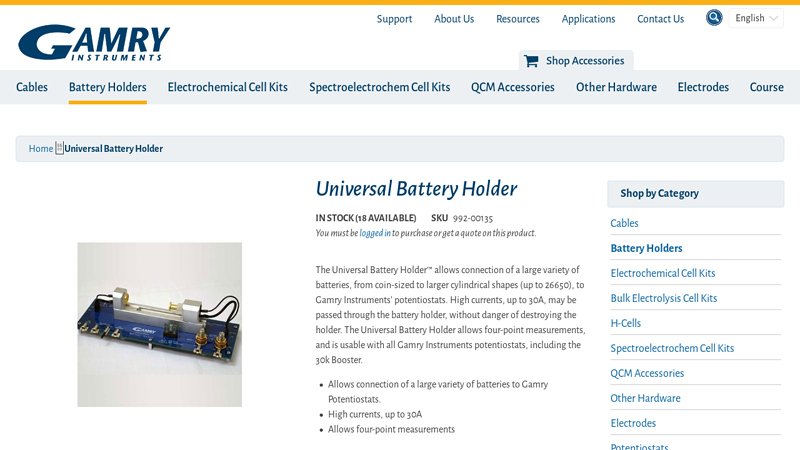
#4 Universal Battery Holder
Domain Est. 1996
Website: orders.gamry.com
Key Highlights: Universal Battery Holder · Allows connection of a large variety of batteries to Gamry Potentiostats. · High currents, up to 30A · Allows four-point measurements….
#5 Battery Holders
Domain Est. 1997
Website: renata.com
Key Highlights: Our battery holders are intended for a simple and fast change of the battery, with a secure hold and reliable connection of the coin cells….
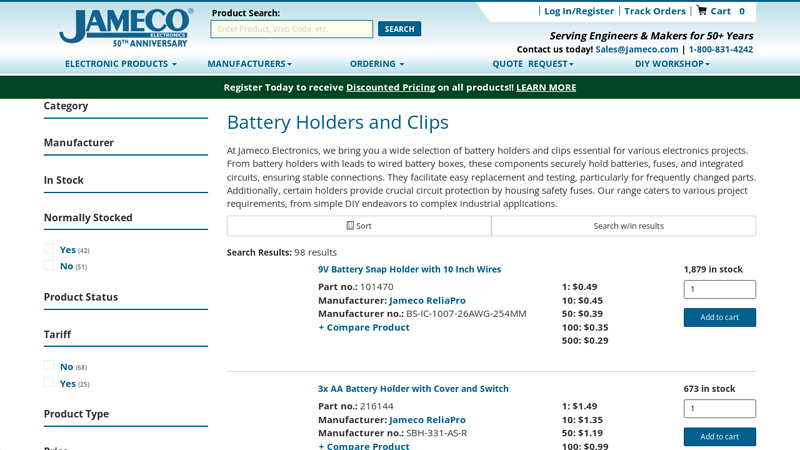
#6 Battery Holders and Clips
Domain Est. 1998
Website: jameco.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $50From battery holders with leads to wired battery boxes, these components securely hold batteries, fuses, and integrated circuits, ensuring stable connections….
#7 Ultralife Corporation
Domain Est. 2008
Website: ultralifecorporation.com
Key Highlights: We design complex battery and power systems for applications where safety, reliability, and performance are non-negotiable. Deep technical ……
#8 Storacell Battery Management Page
Domain Est. 2010
Website: storacell.net
Key Highlights: These are awesome! Good way to keep your batteries organized and from shorting out on metal things if you carry them in a bag….
#9 CellVault Battery Storage
Domain Est. 2013
Website: thyrm.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryThe CellVault Battery Storage (original size) offers waterproof and durable protection for AAA and CR123 batteries, keeping them organized and accessible….
#10 BSLBATT® Official
Domain Est. 2020 | Founded: 2012
Website: bslbatt.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 2012, BSLBATT is a lithium battery manufacturer offering smart, efficient, and certified Li-ion solutions for solar storage, forklifts, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Battery Holder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Battery Holders
As the global electronics and energy storage landscape evolves, the battery holder market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in battery technology, rising demand for portable and wearable electronics, and the expansion of IoT and smart devices, battery holders are becoming more specialized, compact, and integrated. Below are key H2-level trends expected to shape the battery holder market in 2026:
1. Miniaturization and Space Optimization
With consumer electronics trending toward smaller, lighter form factors—such as hearables, smartwatches, and medical wearables—battery holders must adapt to tighter spatial constraints. In 2026, manufacturers will increasingly focus on ultra-compact, high-density designs that support miniaturized batteries like coin cells and custom lithium-polymer packs. Surface-mount technology (SMT) battery holders are expected to dominate in high-volume automated assembly environments.
2. Integration with Smart and Rechargeable Systems
The shift toward rechargeable batteries—especially lithium-ion and solid-state—will drive demand for intelligent battery holders. By 2026, many battery holders will incorporate features like thermal protection, over-current safeguards, and communication interfaces (e.g., I2C or SMBus) to support battery management systems (BMS). This integration enhances safety and performance in applications ranging from drones to electric mobility devices.
3. Growth in Medical and Industrial IoT Applications
The healthcare sector’s reliance on portable, long-life devices—such as insulin pumps, hearing aids, and remote monitoring systems—will boost demand for reliable, sterilizable, and biocompatible battery holders. Similarly, industrial IoT sensors deployed in remote or harsh environments will require ruggedized holders with resistance to vibration, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
4. Sustainability and Design for Recyclability
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will influence material choices and end-of-life considerations. By 2026, battery holders made from recyclable plastics and metals, with modular designs that facilitate battery replacement and recycling, will gain market share. Designers will prioritize reducing electronic waste through longer product lifecycles and easier disassembly.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain dominant in manufacturing due to strong electronics supply chains. However, rising interest in supply chain resilience—especially in North America and Europe—may lead to localized production of critical components. U.S. and EU investments in domestic battery ecosystems could stimulate regional battery holder innovation and manufacturing.
6. Customization and Application-Specific Designs
Off-the-shelf battery holders will still serve general applications, but demand for application-specific solutions will grow. In 2026, OEMs will increasingly collaborate with component suppliers to co-develop holders tailored to unique mechanical, electrical, and environmental requirements—especially in automotive, aerospace, and defense sectors.
Conclusion
By 2026, the battery holder market will be characterized by innovation in form, function, and sustainability. As energy storage becomes more critical across industries, battery holders will transition from passive components to intelligent, integrated subsystems. Companies that invest in miniaturization, smart features, and sustainable design will be best positioned to capture value in this evolving landscape.
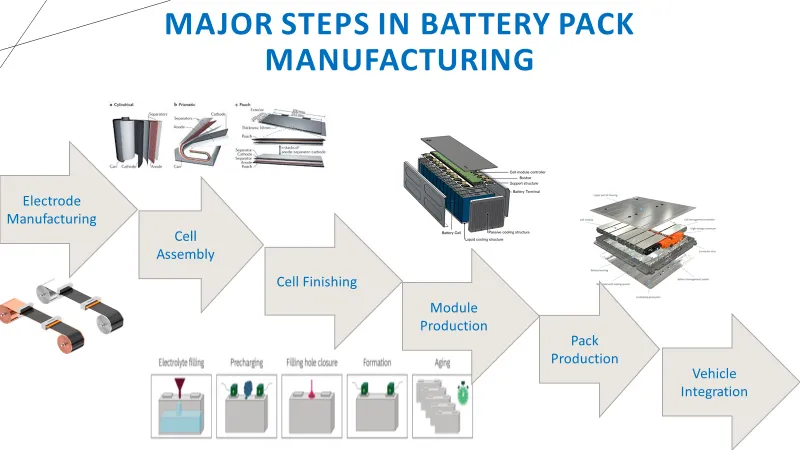
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Battery Holders (Quality and IP)
Sourcing battery holders may seem straightforward, but overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to product failures, safety hazards, and legal risks. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Material and Construction Quality
Using substandard materials or poor manufacturing practices is a primary quality concern. Low-cost battery holders may use brittle plastics prone to cracking, or contacts made from inferior metals that corrode or lose spring tension. This can result in intermittent connections, increased resistance, overheating, and premature failure—especially under vibration or thermal cycling. Always verify material specifications (e.g., UL94 flammability ratings, contact plating thickness) and conduct rigorous environmental and durability testing.
Poor Contact Design and Retention
Battery holders with weak or poorly designed spring contacts fail to maintain reliable electrical connection. This is especially problematic in applications subject to movement or shock. Inadequate retention can also allow batteries to dislodge, causing power loss or short circuits. Ensure contacts are made from appropriate spring alloys (e.g., phosphor bronze, beryllium copper) with sufficient force and wear resistance, and validate performance under expected mechanical stress.
Lack of Environmental Protection (IP Rating Mismatch)
Many battery holders are marketed with an IP (Ingress Protection) rating, but the actual performance often fails to match specifications. A common pitfall is assuming the holder alone provides full environmental protection. In reality, the entire enclosure, including battery compartment seals and cover integration, determines the effective IP rating. Sourcing a holder rated IP67 without ensuring proper mating surfaces and sealing methods leads to moisture and dust ingress. Always test the complete assembly under real-world conditions.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
Battery holders must comply with relevant safety standards such as UL, IEC, or RoHS. Using non-certified components can delay product certification, trigger recalls, or pose fire and electrical hazards. Verify that the supplier provides valid certifications and that the holder meets requirements for creepage, clearance, and flammability based on the application’s voltage and environment.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement
Copying or reverse-engineering patented battery holder designs—especially from major manufacturers like Keystone, Molex, or Panasonic—exposes your company to infringement claims. Many holders feature proprietary contact geometries, locking mechanisms, or mounting systems protected by patents. Sourcing generic versions from suppliers without proper IP clearance is a high-risk practice. Always conduct IP due diligence and source from reputable suppliers who guarantee freedom to operate.
Inconsistent Quality from Low-Cost Suppliers
While cost is a major driver, especially with Asian suppliers, inconsistent quality control is a frequent issue. Batch-to-batch variations in dimensions, plating, or mechanical performance can disrupt assembly lines and compromise reliability. Implement supplier audits, require first-article inspections, and establish clear quality agreements to mitigate this risk.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, clear technical specifications, and strong supplier relationships. Prioritizing quality and IP integrity from the outset protects your product’s performance, safety, and marketability.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Battery Holders
Overview and Importance
Battery holders are essential components in electronic devices, securing batteries and enabling electrical connectivity. While seemingly simple, their logistics and compliance requirements are critical due to the hazardous nature of the batteries they contain or are designed for. Ensuring proper handling, transportation, labeling, and regulatory adherence reduces risks of fire, environmental damage, and legal penalties.
Classification and Regulatory Frameworks
Battery holders themselves are typically classified as electronic components. However, they fall under regulatory scrutiny when associated with batteries, especially lithium-based types. Key frameworks include:
– UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods (UN Model Regulations)
– International Air Transport Association (IATA) Dangerous Goods Regulations
– International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code
– European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR)
– U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) Hazardous Materials Regulations (49 CFR)
Even if the holder is shipped empty, compliance depends on its intended use with regulated batteries.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging ensures safety during transit and compliance with international standards:
– Use robust, non-conductive packaging to prevent short circuits.
– Individually insulate battery terminals if batteries are installed.
– Clearly label packages with:
– Proper shipping name (e.g., “Batteries, wet, non-spillable”)
– UN number (e.g., UN2800 for certain battery-powered equipment)
– Class 9 Miscellaneous Hazard label if applicable
– Include orientation arrows if required
– Mark packages as “Fragile” and “This Way Up” as needed
Note: If battery holders are shipped without batteries, they may not require hazardous labeling, but documentation should clarify contents.
Documentation and Declarations
Accurate documentation is mandatory:
– Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods – Required when shipping with regulated batteries.
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – Recommended even for non-hazardous components to clarify material content and handling.
– Commercial Invoice and Packing List – Must clearly describe goods (e.g., “Plastic Battery Holder for AA Cells – No Battery Included”).
Misdeclaration can lead to shipment rejection, fines, or safety incidents.
Storage and Handling Precautions
During warehousing and handling:
– Store away from flammable materials and sources of heat.
– Prevent physical damage that could compromise integrity when used with batteries.
– Implement electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection if handling sensitive electronic inventory.
– Segregate battery holders pre-assembled with batteries according to local hazardous materials storage codes.
Environmental and RoHS Compliance
Battery holders must comply with environmental directives, particularly if sold in the EU or other regulated markets:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – Prohibits use of lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in electrical equipment.
– REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) – Requires disclosure of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
– WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) – Mandates proper end-of-life recycling; battery holders should be designed for disassembly.
Ensure suppliers provide compliance certificates and material declarations.
Import/Export Considerations
Cross-border shipments require attention to:
– Harmonized System (HS) Codes – Typically classified under 8537.10 (parts of electrical apparatus) or 8507.90 (parts of batteries), depending on configuration.
– Country-Specific Regulations – Some nations impose additional restrictions on battery-related components.
– Customs Clearance – Accurate product descriptions and compliance documentation expedite processing.
Consult with customs brokers to verify requirements for target markets.
Best Practices for Logistics Management
To ensure smooth and compliant operations:
– Conduct regular audits of packaging and labeling procedures.
– Train staff on hazardous materials handling, even for components.
– Maintain a compliance file with up-to-date SDS, test reports, and certifications.
– Partner with certified logistics providers experienced in battery-related shipments.
– Monitor changes in global regulations (e.g., IATA annual updates).
Conclusion
While battery holders are passive components, their association with batteries necessitates strict attention to logistics and compliance. Adhering to international standards, maintaining accurate documentation, and ensuring proper handling protect supply chain integrity, ensure safety, and support market access. Proactive compliance is not just regulatory—it’s a strategic advantage.
Conclusion for Sourcing Battery Holders
In conclusion, sourcing battery holders requires a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors, including compatibility with battery type and size, material quality, mounting options, environmental resistance, and compliance with industry standards. Both cost-efficiency and reliability must be balanced to ensure long-term performance and safety in the intended application. Whether sourcing locally or internationally, establishing relationships with reputable suppliers, reviewing certifications, and conducting sample testing can significantly reduce risks related to quality and supply chain disruptions. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach that considers technical specifications, volume requirements, lead times, and total cost of ownership will enable the selection of optimal battery holders that support product functionality, durability, and scalability.