The global fastener market, driven by rising demand in automotive, construction, and industrial equipment sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. Within this expanding landscape, specialized components like M4 weldsprint barrel nuts—critical for secure, vibration-resistant joints in sheet metal applications—are seeing increased demand across manufacturing and automation industries. As production scales and precision engineering becomes paramount, sourcing high-quality barrel nut M4 weldspring components from reliable manufacturers is essential for maintaining assembly integrity and operational efficiency. Based on production capabilities, geographic reach, certifications, and customer reviews, the following four manufacturers have emerged as leaders in supplying high-performance M4 weldspring barrel nuts to global supply chains.
Top 4 Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
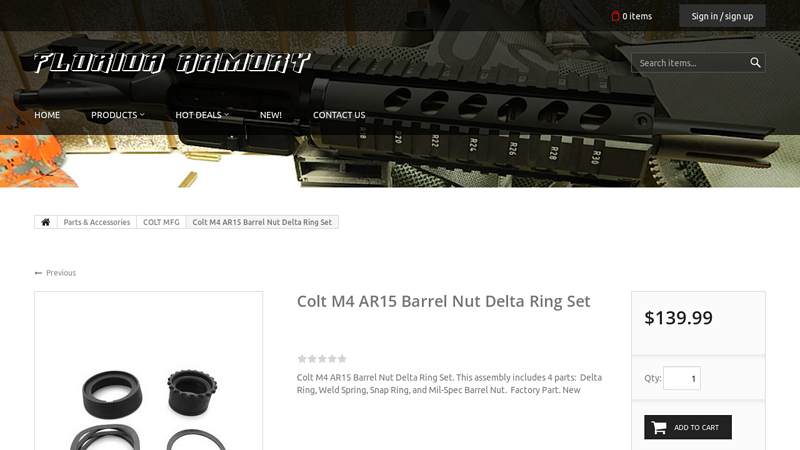
#1 Colt M4 AR15 Barrel Nut Delta Ring Set
Domain Est. 2003
Website: floridaarmory.com
Key Highlights: This assembly includes 4 parts: Delta Ring, Weld Spring, Snap Ring, and Mil-Spec Barrel Nut. Factory Part. New $139.99…
#2 The Official Retro Shorty Pic Thread (Page 1 of 18)
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ar15.com
Key Highlights: Post pics of your complete or work in progress retro “commando”! Barrel length can be anywhere from 10″ to 14.5″. 16″ clones are welcome too….
#3 Magpul MOE Drop
Domain Est. 2013
Website: at3tactical.com
Key Highlights: The Magpul M-LOK MOE Rifle-Length Handguard is a lightweight but durable replacement for standard AR15/M16 plastic handguards with rifle-length gas systems….
#4 Comprehensive Guide to Gun Schematics and Blueprints
Domain Est. 2007
Website: firearmsguide.com
Key Highlights: Gun blueprints are detailed technical drawings with original gun parts dimensions that provide an in-depth look at the design and construction ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring
The global market for specialized fastening components such as the Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring is expected to experience notable shifts by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising demand in automotive and industrial sectors, and increasing emphasis on lightweight and durable assembly solutions. Here’s an in-depth analysis of key trends shaping the Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring market in 2026:
-
Growing Demand in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive industry, particularly electric vehicle (EV) production, is a key growth driver. Barrel Nut M4 Weldsprings are increasingly used in chassis, battery enclosures, and motor assemblies due to their high tensile strength and weldability. As automakers streamline production and adopt modular platforms, the need for reliable, weld-integrated fasteners like the M4 Weldspring barrel nut is expected to rise significantly by 2026. -
Expansion in Industrial Automation and Robotics
Increasing deployment of automation in manufacturing processes requires robust and precision-engineered fasteners. The Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring offers secure thread retention in robotic arms, conveyor systems, and machine frames. With Industry 4.0 adoption accelerating globally, demand for such components is projected to grow steadily through 2026. -
Material and Coating Innovations
By 2026, manufacturers are expected to focus on enhanced corrosion resistance and thermal stability. Advanced coatings such as Geomet® or Dacromet® are likely to become standard for Barrel Nut M4 Weldsprings used in harsh environments, including outdoor infrastructure and marine applications. Additionally, the use of high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels will improve performance without increasing weight. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, is anticipated to dominate market growth due to expanding industrial and automotive production. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see steady demand driven by EV infrastructure development and aerospace applications, where reliability and precision are paramount. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience
Environmental regulations and supply chain transparency will influence sourcing and production practices. By 2026, manufacturers of Barrel Nut M4 Weldsprings are likely to adopt greener production methods, including energy-efficient welding and recyclable materials, to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards and comply with regulations like the EU Green Deal. -
Technological Integration in Quality Control
The integration of IoT and AI-driven quality assurance systems in fastener manufacturing will enhance consistency and traceability. Real-time monitoring of weld integrity and dimensional accuracy will become standard, ensuring higher reliability of Barrel Nut M4 Weldsprings in critical applications.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring will be shaped by technological advancement, sector-specific demand (especially in EVs and automation), and a stronger focus on sustainability and precision. Stakeholders who invest in innovation, regional diversification, and compliance will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring – Quality and IP Risks
Sourcing Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring components involves several critical risks, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Key pitfalls include:
-
Inconsistent Material and Manufacturing Quality
Suppliers, especially those from low-cost regions, may use substandard materials or fail to adhere to specified tolerances and mechanical properties. This can compromise weld integrity and long-term performance. Lack of proper heat treatment or poor threading accuracy often results in field failures. -
Lack of Certification and Traceability
Many suppliers provide insufficient documentation (e.g., material test reports, ISO certifications), making it difficult to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., DIN, ISO, or automotive OEM specifications). This absence of traceability increases liability risks. -
Intellectual Property Infringement
Some manufacturers may produce reverse-engineered versions of patented or proprietary designs without authorization. Sourcing from such suppliers exposes buyers to legal risks, especially in regulated industries like automotive or defense. -
Counterfeit or Non-Compliant Products
Unverified suppliers may offer fake certifications or misrepresent compliance with standards. This is particularly problematic when components are used in safety-critical applications. -
Inadequate Welding Process Control
The “weldspring” feature requires precise manufacturing to ensure reliable spot or projection welding. Poorly controlled processes lead to weak welds or part deformation, affecting assembly line efficiency and product reliability. -
Limited Supplier Audits and Oversight
Without on-site audits or third-party inspections, it’s difficult to assess actual production conditions. Many suppliers outsource production, further diluting quality control and IP safeguards.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven quality management systems (e.g., IATF 16949), conduct regular audits, and ensure legal agreements include IP protection and liability clauses.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the Barrel Nut M4 Weldspring, ensuring safe, efficient handling, transportation, and adherence to relevant regulations throughout the supply chain.
H2: 1. Product Identification & Specifications
- Part Number: [Insert specific part number, e.g., BN-M4-WS-001]
- Description: Barrel Nut, M4 Thread Size, Weldspring Type (Press-fit, weldable flange).
- Material: Typically Steel (e.g., C15/C17, C45) or Stainless Steel (e.g., A2/AISI 304). Confirm exact grade per datasheet.
- Finish: Often Zinc Plated (e.g., ZnNi, Zn) or Passivated (Stainless). Confirm exact finish.
- Key Dimensions: M4 Internal Thread, Flange Diameter, Barrel Length, Press-fit Diameter. Refer to technical drawing.
- Function: Provides a permanent, weldable threaded insert for M4 fasteners into thin sheet metal or other base materials.
H2: 2. Packaging & Handling
- Standard Packaging:
- Inner Packaging: Polybags (e.g., PE bags) or cardboard boxes to prevent scratching and bulk handling. Quantity per bag/box must be consistent.
- Intermediate Packaging: Bundles of bags/boxes secured with strapping or placed in larger corrugated cardboard cartons.
- Outer Packaging: Robust, new corrugated cardboard shipping boxes. Size should minimize void space. Palletized shipments use standard EUR/ISO pallets (e.g., 1200x800mm, 1200x1000mm).
- Marking & Labeling:
- Inner/Intermediate: Part Number, Quantity, Lot/Batch Number, Date of Manufacture, Material/Finish Code (if applicable), “Fragile” (if sensitive to denting).
- Shipping Box/Pallet: Part Number, Full Description, Total Quantity, Gross/Net Weight, Dimensions (LxWxH), Pallet ID (if palletized), Handling Symbols (e.g., “This Way Up”, “Do Not Stack”, “Protect from Moisture”), Ship-To/Ship-From addresses, PO Number, Barcode/QR Code (essential for traceability).
- Handling Precautions:
- Use appropriate lifting equipment (forklifts, pallet jacks) for pallets. Manual lifting only for small cartons (observe weight limits).
- Avoid dropping or impacting packages to prevent deformation of the barrel nuts.
- Handle with clean, dry hands or gloves (especially for passivated/stainless parts to prevent fingerprint corrosion).
- Store and handle away from corrosive chemicals, excessive moisture, and direct sunlight.
H2: 3. Storage Conditions
- Environment: Dry, clean, well-ventilated indoor area. Controlled temperature (ideally 15°C – 25°C / 59°F – 77°F) and relative humidity (ideally < 60% RH).
- Shelving: Store packaged goods on pallets or racks off the floor (min. 15cm / 6in) to prevent moisture absorption and pest infestation.
- Stacking: Follow packaging strength limits. Do not exceed recommended stack height. Ensure stability.
- Segregation: Store away from incompatible materials (e.g., strong acids, alkalis, solvents, salt). Keep different finishes (e.g., zinc-plated vs. stainless) separate if required by customer specifications or to prevent galvanic corrosion in bulk.
- Shelf Life: Typically indefinite for properly stored steel parts. Verify with manufacturer if specific coating has limitations. Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory management.
H2: 4. Transportation
- Mode: Road (FCL/LCL), Air, Sea (Containerized). Choice depends on urgency, cost, and volume.
- Requirements:
- Protection: Pallets must be securely strapped/stretch-wrapped. Boxes must be robust to withstand stacking and handling.
- Documentation: Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Bill of Lading/Air Waybill, Certificate of Origin (if required), Safety Data Sheet (SDS – see Compliance).
- Labeling: Clear, durable labels on all transport units (boxes, pallets) with essential shipping info and handling marks.
- Cargo Securing: Pallets must be properly secured within trucks, containers, or aircraft holds using straps, dunnage, or load locks to prevent movement.
- Environmental Protection: Ensure cargo is protected from rain, snow, and excessive heat/cold during transit. Use weatherproof containers or tarps if necessary. Avoid condensation in sealed containers (consider desiccants for long sea voyages if humidity is a concern).
- Hazardous Goods Classification: NOT classified as hazardous for transport under ADR/RID (road/rail), IMDG (sea), or IATA (air) regulations. Standard industrial goods.
H2: 5. Regulatory Compliance & Documentation
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): A compliant SDS (GHS format) is mandatory for shipment, even though the part itself is non-hazardous. It covers potential hazards during manufacturing (e.g., metal dust, plating chemicals) and provides safe handling information. Ensure the latest version accompanies shipments if requested or required by jurisdiction/contract.
- REACH (EU): Confirm the product complies with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations. The manufacturer/supplier should provide a Declaration of Conformity (DoC) stating compliance, especially regarding Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC). The barrel nut itself is usually considered an article.
- RoHS (EU/Global): Confirm compliance with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (lead, cadmium, mercury, etc.). Most standard steel barrel nuts comply, but verify plating type (e.g., Zinc-Nickel plating is RoHS compliant). Obtain a RoHS DoC from the supplier.
- Conflict Minerals (US Dodd-Frank): If supplying to the US market, be prepared to provide information on the use of Tin, Tantalum, Tungsten, and Gold (3TG) in the supply chain, even if minimal (e.g., in plating baths). A CMRT (Conflict Minerals Reporting Template) may be required.
- Customs & Trade:
- HS Code: Determine the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for customs clearance (e.g., typically 7318.15.xx – Nuts, of iron or steel, threaded). Accuracy is crucial for duties and regulations.
- Export Controls: Verify if the product or its technology falls under any export control regimes (e.g., EAR – Export Administration Regulations). Standard barrel nuts are usually “EAR99” (low concern), but confirm.
- Certificate of Origin: May be required for preferential tariffs (e.g., under trade agreements) or import restrictions. Issue accurately (e.g., EUR.1 for EU, Form A for GSP).
- Traceability: Maintain records linking batches/lots of Barrel Nut M4 Weldsprings to raw material certs, production dates, inspection results, and shipping documents for at least [Specify Duration, e.g., 10 years] to support quality and compliance audits.
H2: 6. Quality & Inspection
- Incoming Inspection (Receiving): Verify quantity, packaging integrity, labeling accuracy (Part No, Lot), and obvious damage upon receipt. Perform dimensional checks and functional checks (e.g., thread fit, press-fit simulation) per agreed Quality Control Plan (QCP) or AQL sampling standard.
- In-Process/Outgoing Inspection: Supplier should perform inspections based on specifications (dimensions, thread, material, finish, weldability). Certificates of Conformity (CoC) or Inspection Reports should accompany shipments.
- Non-Conforming Material: Establish a clear process (e.g., Quarantine, RMA) for handling defective or non-compliant shipments.
H2: 7. Key Contacts & Responsibilities
- Logistics Provider: [Name, Contact Info]
- Supplier: [Name, Contact Info – for CoC, SDS, technical queries]
- Internal Logistics Coordinator: [Name, Contact Info]
- Quality Assurance: [Name, Contact Info]
- Compliance Officer: [Name, Contact Info – for REACH, RoHS, Export queries]
This guide provides a framework. Always consult the specific technical specifications, purchase agreements, and the latest regulations applicable to your location and supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Barrel Nut M4 Weld Spring:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, material specifications, manufacturing capabilities, and quality assurance processes, the sourcing of the M4 barrel nut weld spring can be successfully executed through a qualified supplier that meets military or industrial-grade standards (such as MIL-SPEC or ISO certifications). It is essential to prioritize suppliers with proven experience in precision fastener manufacturing, particularly in defense or firearms-related components, to ensure reliability, strength, and proper fit for M4 platforms.
Key considerations in the final decision include material composition (typically hardened steel with corrosion resistance), dimensional accuracy, weld compatibility, and consistent batch-to-batch quality. Additionally, establishing long-term supplier agreements with rigorous inspection protocols—such as lot sampling and metallurgical testing—will mitigate risks and ensure ongoing compliance with performance requirements.
In conclusion, by selecting a reputable supplier that adheres to stringent manufacturing and testing standards, the procurement of M4 barrel nut weld springs can support durable, high-performance firearm assembly with minimal risk of failure in critical applications.