The global ballistic steel market has experienced robust growth, driven by rising defense expenditures, increasing demand for personal and vehicle protection, and expanding applications in commercial security. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the ballistic protection materials market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.8% from 2023 to 2028, with steel remaining a cornerstone material due to its proven durability, impact resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Ballistic steel, particularly in grades such as AR500 and AR600, is widely utilized in military vehicles, armored personnel carriers, infrastructure security, and law enforcement equipment. As geopolitical tensions persist and private-sector security concerns rise, manufacturers are investing in advanced steel processing technologies—such as quenching and tempering—to enhance protection levels while maintaining weight efficiency. This growing demand has intensified competition among producers, leading to innovations in metallurgical composition and manufacturing precision. The following list highlights the top eight ballistic steel manufacturers shaping the industry through scale, certification compliance (including NIJ and STANAG standards), R&D investment, and global supply chain reach.
Top 8 Ballistic Steel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Steel Ops
Domain Est. 2013
Website: steelops.com
Key Highlights: Steel Ops is a Colorado based manufacturer of body armor, steel targets, and ballistic steel, and custom security products….
#2 TruSHIELD Steel Armor Plate Suppliers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: cmc.com
Key Highlights: TruSHIELD: commercial grade and military ballistic and armor steel plate that provides exceptional ballistic protection and meets a range of specifications ……
#3 Armox® and Ramor® armor and ballistic steels
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ssab.com
Key Highlights: Armox® and Ramor® armor steel can withstand extreme forces from piercing objects hitting the steel at high speed. Read about our different products here….
#4 Military Grade Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: steelwarehouse.com
Key Highlights: We carry military grade steel, and military, armor, & ballistic steel plate. We can help you with your armor fabrication questions and offer military grade ……
#5 Bullet Proof Metal
Domain Est. 2000
Website: usbulletproofing.com
Key Highlights: High-performance bulletproof steel plates and ballistic metal wall armor. Our bullet resistant steel systems provide maximum security for any facility….
#6 Ballistic & Armoured Steel FB4+, FB5, FB6 and FB7
Domain Est. 2011
Website: architecturalarmour.com
Key Highlights: UK Armoured Steel Walls and related security products. Please call +44(0)1981 257000 for information and Competitive Prices….
#7 Armor Steel Plate
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kloecknermetals.com
Key Highlights: Kloeckner Metals specializes in and stocks fully certified armor steel plate and ballistic steel plate that’s guaranteed to perform….
#8 Ballistic and Blast Protection Steel
Domain Est. 2012
Website: cemar-international.com
Key Highlights: Get ultimate protection with ballistic steel from Cemar International, designed to withstand bullets and fragmentation for unmatched strength and security….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ballistic Steel
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ballistic Steel
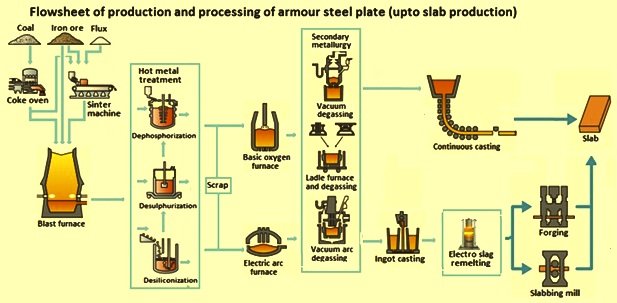
The global ballistic steel market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving defense requirements, technological advancements, and increasing demand across both military and civilian sectors. Key trends shaping the market landscape include:
1. Rising Defense Spending and Geopolitical Tensions
Ongoing geopolitical instability and regional conflicts are prompting governments worldwide to increase defense budgets. This surge in military expenditure is directly fueling demand for advanced ballistic protection systems. Ballistic steel, valued for its durability and high-performance protection against small arms fire and explosive fragments, remains a critical material in armored vehicles, personal protective gear, and military infrastructure. Nations in North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region are expected to lead procurement efforts through 2026.
2. Growth in Homeland Security and Law Enforcement Applications
Beyond military use, ballistic steel is seeing increased adoption in law enforcement and homeland security. Urban violence, terrorism threats, and civil unrest have driven police departments and emergency response units to upgrade their protective equipment. Armored vehicles, tactical shields, and secure checkpoints increasingly incorporate high-hardness ballistic steel, supporting sustained market growth.
3. Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
Manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to enhance the performance-to-weight ratio of ballistic steel. Innovations such as ultra-high-hardness (UHH) steels and hybrid composites (combining steel with ceramics or polymers) are enabling lighter, more effective protective solutions. These advancements not only improve mobility and fuel efficiency in armored vehicles but also expand applications in aviation and maritime defense.
4. Expansion in Commercial and Civilian Sectors
The private security sector, VIP protection services, and even commercial applications like armored cash-in-transit vehicles are contributing to market expansion. Additionally, growing personal security concerns among high-net-worth individuals are boosting demand for bullet-resistant materials in luxury vehicles and residential installations—sectors increasingly incorporating ballistic steel solutions.
5. Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience
Environmental regulations and supply chain vulnerabilities are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener production methods and localize sourcing. Recycling of ballistic steel and improvements in energy-efficient manufacturing processes are becoming key differentiators. Companies are also diversifying raw material suppliers to mitigate risks from geopolitical disruptions, especially in regions with concentrated steel production.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
North America is expected to maintain a dominant market share due to advanced defense infrastructure and strong government contracts. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly India and South Korea, is projected to witness the highest growth rate, driven by modernization of armed forces and rising border security concerns. Europe remains a steady market, supported by NATO defense initiatives and internal security needs.
Conclusion
By 2026, the ballistic steel market will be shaped by a confluence of security demands, technological innovation, and strategic investments. As threats evolve and performance expectations rise, ballistic steel will continue to serve as a foundational material in protective systems, with sustained growth across military, law enforcement, and commercial applications. Companies that prioritize innovation, sustainability, and supply chain agility will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ballistic Steel (Quality, IP)
Sourcing ballistic steel requires meticulous attention to detail due to the critical nature of its application in life-saving protective solutions. Failure to properly vet suppliers and materials can lead to catastrophic performance failures and significant legal and reputational risks. Below are key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers must avoid.
Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
One of the most common quality pitfalls is accepting ballistic steel without full, verifiable material certification. Buyers may receive certificates that are incomplete, falsified, or not aligned with recognized ballistic standards (e.g., NIJ, VPAM). Without mill test reports (MTRs) and heat traceability, it’s impossible to confirm the steel’s chemical composition, hardness (typically 500 HBW minimum), and ballistic performance. Relying on vague or generic specs can result in substandard steel that fails under real threat conditions.
Misrepresentation of Ballistic Performance Claims
Suppliers may exaggerate or misrepresent the level of protection their steel offers (e.g., claiming NIJ Level III+ without independent testing). Some may use proprietary rating systems that lack third-party validation. Without access to certified test reports from accredited laboratories, buyers risk procuring steel that cannot stop the intended threats. Conducting independent ballistic testing or demanding full test documentation is essential to avoid this pitfall.
Lack of Consistent Hardness and Uniformity
Ballistic steel must maintain consistent hardness across the entire plate. Inconsistent heat treatment during manufacturing can result in soft spots or warping, compromising protection. Buyers often overlook quality control processes such as hardness mapping and ultrasonic thickness testing. Sourcing from suppliers without robust QC protocols increases the risk of field failures, especially under repeated impacts.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using ballistic steel designs, manufacturing processes, or proprietary alloys protected by patents without proper licensing exposes buyers to IP litigation. Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” products that infringe on patented technologies (e.g., specialized laminates or core compositions). Conducting due diligence on IP rights and requiring suppliers to warrant non-infringement is crucial to avoid costly legal disputes and supply chain disruptions.
Sourcing from Unverified or Unauthorized Suppliers
Engaging with unauthorized distributors or gray-market suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or rebranded steel. These suppliers may resell expired, reworked, or non-compliant material as new. Establishing direct relationships with OEMs or authorized partners, and verifying supplier credentials, helps ensure authenticity and compliance with ballistic specifications.
Overlooking Long-Term Durability and Environmental Resistance
Some ballistic steels degrade prematurely due to poor corrosion resistance or inadequate coatings. Buyers focused solely on initial cost may select steel that rusts or delaminates in humid or salty environments, reducing service life and reliability. Ensuring the steel includes proper protective finishes (e.g., epoxy, ceramic coatings) and meets environmental durability standards is vital for sustained performance.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires rigorous supplier vetting, independent verification of certifications and test data, and proactive IP risk assessment. Investing in due diligence upfront ensures reliable, legally compliant ballistic protection.
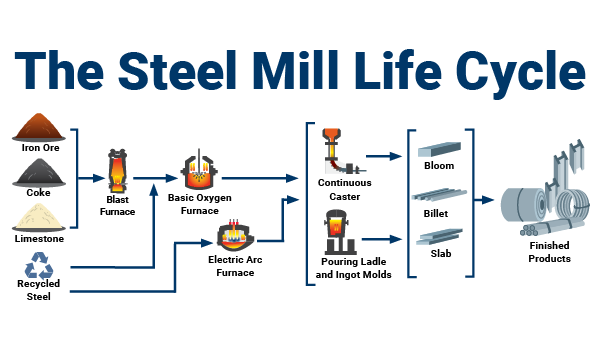
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ballistic Steel
Overview
Ballistic steel, a high-hardness steel engineered to resist bullets and shrapnel, is subject to strict logistics and compliance requirements due to its specialized application in defense, law enforcement, and security sectors. Proper handling, transportation, export control, and documentation are critical to ensure legal compliance and operational safety.
Classification & Regulatory Framework
Ballistic steel is often classified under international and national export control regimes due to its military or dual-use nature. Key regulatory frameworks include:
– International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) – In the U.S., ballistic steel used in defense articles may be listed on the U.S. Munitions List (USML), requiring ITAR authorization for export.
– Export Administration Regulations (EAR) – If not ITAR-controlled, ballistic steel may fall under the Commerce Control List (CCL) with ECCN (e.g., 1A002 or 9A991), requiring a license depending on destination and end use.
– Wassenaar Arrangement – Guides multilateral export controls; ballistic protection materials are often subject to reporting and licensing.
– National Regulations – Countries such as the UK, Canada, Australia, and EU members have their own arms export controls that align with international standards.
Export Licensing Requirements
Prior to shipment, confirm the appropriate export classification:
– Determine if the product is ITAR-controlled (USML Category X – Gun Ammunition, or Category XII – Fire Control, Laser, Imaging, and Guidance Equipment, as applicable).
– If EAR-controlled, verify ECCN and license exception eligibility (e.g., LVS, STA).
– Submit a license application to the relevant authority (e.g., U.S. Department of State’s DDTC for ITAR; BIS for EAR).
– Maintain records of classification, licenses, and end-user documentation for at least 5 years.
End-User & End-Use Compliance
- Obtain a signed End-User Statement (EUS) or End-Use Certificate (EUC) to verify the legitimacy of the buyer and intended use.
- Conduct due diligence to avoid restricted destinations or parties listed on denied persons lists (e.g., U.S. SDN, EU Consolidated List).
- Implement internal compliance programs (ICPs) to screen transactions and manage red flags.
Packaging & Handling
- Ballistic steel plates must be packaged to prevent physical damage, corrosion, and exposure during transit.
- Use moisture-resistant wrapping, edge protectors, and robust wooden or steel crates.
- Label packages clearly with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack”).
- Ensure weight distribution complies with transport safety standards.
Transportation & Logistics
- Coordinate with freight forwarders experienced in handling defense or controlled goods.
- Air, sea, and ground shipments must comply with IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations as applicable.
- For ITAR-controlled items, use ITAR-compliant carriers and avoid transshipment through unauthorized countries.
- Provide accurate shipping manifests, commercial invoices, packing lists, and export documentation.
Customs Clearance
- Declare accurate HS codes and export control classifications at origin and destination.
- Include export license numbers (if required) on all customs documentation.
- Be prepared for inspections; ballistic steel may attract heightened scrutiny at borders.
- Maintain proof of delivery and import compliance in the destination country.
Recordkeeping & Audits
- Retain all export documentation, including licenses, communications, and shipping records, for the required retention period (typically 5 years).
- Conduct regular internal audits to verify compliance with export control policies.
- Prepare for government audits by maintaining an organized compliance file.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Violations of export controls can result in severe consequences, including:
– Fines up to $1 million per ITAR violation.
– Criminal penalties, including imprisonment.
– Loss of export privileges.
– Reputational damage and contract termination.
Best Practices
- Train employees on export compliance annually.
- Use commodity classification tools or consult legal experts for uncertain items.
- Establish a compliance officer or team to oversee ballistic steel shipments.
- Monitor regulatory changes and updates from DDTC, BIS, and other authorities.
By adhering to this guide, organizations can ensure the secure, legal, and efficient global movement of ballistic steel while minimizing regulatory risk.
Conclusion for Sourcing Ballistic Steel
Sourcing ballistic steel requires a strategic approach that balances performance, compliance, cost, and supply chain reliability. High-quality ballistic steel must meet rigorous international standards—such as NIJ, CEN, or STANAG—to ensure reliable protection in demanding applications. Key considerations include material certification, hardness (typically between 500–600 Brinell), impact resistance, and consistent thickness.
Establishing relationships with reputable, certified suppliers—preferably with a proven track record in defense, law enforcement, or security sectors—is critical. Due diligence should involve auditing manufacturing processes, testing protocols, and traceability of materials. Additionally, logistical factors such as lead times, minimum order quantities, and import/export regulations must be factored into sourcing decisions, especially for global procurement.
In sum, successful sourcing of ballistic steel hinges on technical precision, regulatory compliance, and strong supplier partnerships. Investing time in vetting suppliers and ensuring material integrity ultimately enhances safety, reduces risk, and supports mission-critical operations across military, law enforcement, and private security applications.