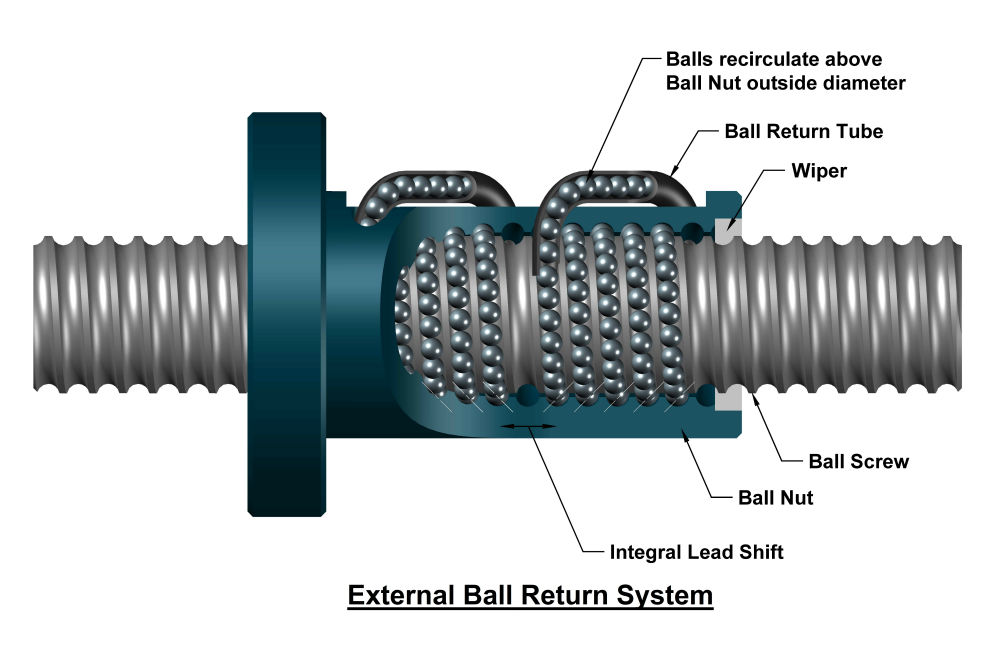
The global ball screws and linear actuators market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision motion control across industries such as automation, aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global ball screw market was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is further fueled by rising adoption of electric linear actuators in factory automation and robotics, with Grand View Research estimating the global linear actuators market to reach USD 15.6 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 5.8% during the forecast period. As industries prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and energy efficiency, the need for high-performance ball screws and actuators continues to rise. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining innovation, precision engineering, and global reach to meet evolving industrial demands. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 ball screws and actuators manufacturers shaping the future of motion control.
Top 10 Ball Screws And Actuators Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ball Screw Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ball-screws.net
Key Highlights: Del-Tron Precision, Inc. produces and supplies various automated equipment, such as ball screw actuators. Our engineers have designed our ball screws to offer ……
#2 Ball Screws
Domain Est. 1990
Website: moog.com
Key Highlights: A ball screw is a rolling system consisting of a threaded shaft (screw) and a nut that, internally threaded as well, contains a determined number of balls….
#3 Nook Industries
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nookindustries.com
Key Highlights: Nook Industries manufacturers linear motion solutions including, precision ball screw, acme screw, screw jack, linear actuator, and electric cylinder ……
#4 PMI PRECISION MOTION INDUSTRIES, INC.
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1990
Website: pmi-amt.com
Key Highlights: PMI GROUP was established in 1990. It’s highly involved in manufacturing of ballscrews, precision ball screw spline, linear guideway, ball spline and actuator….
#5 Ball Screw Actuators
Website: kurodaprecision.com
Key Highlights: This is Ball Screw Actuators information page for KURODA Precision Industries Ltd. KURODA Precision is a precision equipment manufacturer of precision ball ……
#6 Actuator
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: THK develops and manufactures mechanical components including the Linear Motion system, LM Guides, Ball Splines, Ball Screws, and electric actuators for our ……
#7 Ball Screws
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Recognized worldwide for its expertise in ball screw design, engineering, and manufacturing, NSK provides precision-ground units in both standard and custom ……
#8 Schaeffler Linear Motion
Domain Est. 2006
Website: medias.schaeffler.us
Key Highlights: Our Range of Linear Motion Products · Low duty linear actuators · High-performance actuators · Lifting columns · Roller screws · Ball screws · 7th axis for robots….
#9 Linear Motion Optimized
Domain Est. 2008
Website: thomsonlinear.com
Key Highlights: Ball Screws, Lead Screws, Glide Screw · Ball Splines · Compact Linear Systems · Lifting Columns · Linear Actuators · Linear Bearings & Guides · Linear Motion ……
#10 KSS JAPAN
Domain Est. 2010
Website: kssballscrew.com
Key Highlights: KSS is a growing Japanese Ball Screw brand. We have varieties of Ball Screws, and Actuators. Compact and down-sized designing parts are available at KSS….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ball Screws And Actuators

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ball Screws and Actuators
The global ball screws and actuators market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, increasing demand for precision motion control, and the expansion of Industry 4.0 across key industrial sectors. Below is an analysis of the major trends expected to shape the market in 2026:
-
Growth in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The continued adoption of automation in manufacturing, logistics, and automotive industries is a primary driver for ball screws and actuators. As manufacturers shift toward smart factories, the need for high-precision linear motion components has intensified. Ball screws, known for their efficiency and accuracy, are increasingly integrated into robotic arms, CNC machines, and automated assembly lines. Electric actuators, in particular, are gaining preference over hydraulic and pneumatic systems due to their energy efficiency, lower maintenance, and compatibility with digital control systems. -
Rise of Electric Actuators in Automotive and Aerospace
The EV (electric vehicle) revolution is accelerating demand for electric linear actuators in automotive applications such as seat adjustment, suspension systems, and throttle control. Similarly, aerospace applications require lightweight, reliable, and high-performance motion solutions. By 2026, ball screws will play a critical role in flight control systems and landing gear mechanisms, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable. -
Miniaturization and Customization
With the growing demand in medical devices, semiconductor manufacturing, and consumer electronics, there is an increasing need for compact, high-precision ball screws and actuators. Manufacturers are investing in miniaturized designs that maintain performance under tight space constraints. Customization capabilities are also becoming a competitive edge, allowing suppliers to meet specific torque, load, speed, and environmental requirements across diverse applications. -
Adoption of Smart Actuators and IoT Integration
The integration of sensors, IoT connectivity, and predictive maintenance features into actuators is transforming the market. Smart actuators equipped with feedback systems enable real-time monitoring of position, load, temperature, and wear. This data enhances system reliability and reduces downtime, aligning with the broader trend of predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0. By 2026, intelligent motion control systems are expected to dominate high-value industrial applications. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing demand for energy-efficient components. Ball screws offer higher mechanical efficiency (up to 90%) compared to traditional lead screws, reducing power consumption. The shift toward electric actuators supports decarbonization efforts, especially in replacing hydraulic systems that use oil and pose environmental risks. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain the largest market due to robust manufacturing activity and investments in automation. North America and Europe are witnessing growth driven by automation in aerospace, medical, and clean energy sectors. Localized production and supply chain resilience will be key strategic focuses for manufacturers to mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks. -
Technological Innovations and Material Advancements
Innovations in materials—such as high-strength alloys, ceramic coatings, and corrosion-resistant finishes—are enhancing the durability and performance of ball screws in harsh environments. Additionally, advancements in lubrication technologies and preloading techniques are extending service life and reducing maintenance needs.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for ball screws and actuators will be defined by digital integration, energy efficiency, and precision engineering. Companies that invest in smart technologies, customization, and sustainable manufacturing practices are likely to gain a competitive advantage in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ball Screws and Actuators: Quality and IP Concerns
Sourcing ball screws and actuators involves critical decisions that can significantly impact the performance, reliability, and legal standing of your machinery. Overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) factors can lead to costly failures, downtime, and legal exposure. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing
One of the most frequent issues is selecting suppliers with inadequate quality assurance processes. Low-cost ball screws or actuators may use substandard materials, inconsistent heat treatment, or imprecise grinding techniques, resulting in premature wear, reduced load capacity, or failure under stress. Without proper certification (e.g., ISO 9001) or traceable batch testing, it’s difficult to verify performance claims.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Performance Data
Some suppliers—especially non-reputable or offshore manufacturers—may exaggerate load ratings, precision class (e.g., claiming C3 when it’s actually C7), or lifespan (L10 life). This misalignment between advertised and actual performance can lead to system underperformance or catastrophic failure in high-precision or high-load applications.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Reputable manufacturers provide full traceability including material certifications, heat treatment records, and inspection reports. Omitting these documents makes it difficult to validate component quality, troubleshoot issues, or comply with industry regulations (e.g., aerospace, medical). Without traceability, identifying root causes during failure analysis becomes nearly impossible.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Components
Purchasing from unauthorized distributors or gray-market channels increases the risk of receiving counterfeit parts that mimic well-known brands (e.g., THK, HIWIN, Bosch Rexroth). These components often violate intellectual property rights and lack the engineering integrity of genuine products. Using them can expose your company to legal liability and warranty voidance.
Infringement of Patented Designs and Technologies
Some actuators or ball screw assemblies incorporate patented technologies (e.g., preload mechanisms, sealing systems, drive integration). Sourcing generic versions that replicate these features without licensing can lead to IP infringement claims, product recalls, or litigation—especially in regulated or export-sensitive industries.
Insufficient IP Due Diligence in Supplier Selection
Failing to verify whether a supplier owns or has rights to the designs they offer is a critical oversight. Contract manufacturers may unknowingly (or knowingly) produce components based on stolen or reverse-engineered designs. Conducting IP audits or requesting proof of design ownership can mitigate legal risks.
Overlooking Compliance with International Standards
Ball screws and actuators used in global markets must often comply with regional standards (e.g., CE, UL, RoHS). Sourcing components without proper certification can delay product launches, result in import denials, or expose end-users to safety risks.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, verification of technical documentation, and attention to both quality systems and intellectual property rights. Partnering with reputable, authorized suppliers ensures long-term reliability and legal compliance.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ball Screws and Actuators
Overview
Ball screws and actuators are precision mechanical components widely used in automation, aerospace, industrial machinery, and medical equipment. Due to their high accuracy and performance requirements, proper logistics handling and compliance with international and regional regulations are essential to ensure product integrity, safety, and legal conformity.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent damage during transit and storage.
- Protective Packaging: Use anti-corrosion materials (e.g., VCI paper), rigid outer containers, and internal supports to prevent axial or radial loading.
- Moisture Control: Include desiccants and humidity indicators, especially for long-term storage or ocean freight.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and component specifications (e.g., lead accuracy, preload class).
- Handling Procedures: Use appropriate lifting equipment; avoid dropping or impact. Never rotate the shaft when unsupported.
Storage Conditions
Improper storage can cause corrosion, deformation, or lubricant degradation.
- Environment: Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled area (15–25°C, 40–60% RH).
- Orientation: Store ball screws horizontally on flat supports to prevent sagging.
- Duration: Limit storage time; inspect lubrication and corrosion protection every 6 months.
- Isolation: Keep away from dust, chemicals, and vibration sources.
Transportation Guidelines
Ensure safe and compliant shipping across domestic and international channels.
- Domestic (e.g., USA, EU):
- Use shock-absorbing pallets and secure strapping.
- Follow carrier-specific rules (e.g., FedEx, DHL) for heavy or long items.
- International:
- Comply with ISPM 15 for wooden packaging materials (heat-treated and stamped).
- Use export-grade crates for sea or long-distance air freight.
- Include detailed packing lists and commercial invoices.
Export Compliance
Ball screws and actuators may be subject to export control regulations due to dual-use potential.
- Classification:
- Check ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL).
- Typical ECCNs: 2B201 (for high-precision ball screws), 2A292 (linear actuators with specific performance).
- Licensing Requirements:
- Verify if shipment requires a license based on destination, end-use, and end-user.
- Screen parties against denied persons lists (e.g., BIS, EU Consolidated List).
- Documentation:
- Prepare export declaration (e.g., EEI via AES in the U.S.).
- Include end-user statements if required.
Import Regulations
Compliance with import laws ensures smooth customs clearance and avoids delays.
- Tariff Classification:
- Use HS codes such as 8483.40 (ball screws) or 8412.29 (actuators) depending on design and application.
- Confirm local customs rulings (e.g., EU TARIC, U.S. HTS).
- Duties and Taxes:
- Calculate applicable import duties, VAT, or GST based on declared value and origin.
- Leverage trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) where possible.
- Certifications:
- Provide conformity documents (e.g., CE, UKCA) if required by destination country.
- Include RoHS and REACH compliance declarations for EU shipments.
Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to environmental, safety, and quality standards is mandatory.
- RoHS (EU): Ensure materials are free of restricted substances (Pb, Cd, Hg, etc.).
- REACH (EU): Declare Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) if present above thresholds.
- CE Marking: Required for actuators sold in the EU under Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC or EMC Directive.
- UKCA Marking: Required for UK market post-Brexit.
- UL/CSA (North America): Apply for certification if integrated into safety-critical systems.
Quality and Traceability
Maintain documentation for audit readiness and customer assurance.
- Serial Number Tracking: Assign unique IDs for traceability of manufacturing batch, calibration, and test data.
- Certificates of Conformance (CoC): Provide with each shipment, including dimensional and functional test results.
- Calibration Records: Retain for precision components, especially in aerospace or medical applications.
End-of-Life and Recycling
Follow environmental directives for disposal and recycling.
- WEEE (EU): Register with national WEEE authorities if selling complete equipment containing actuators.
- Recycling Instructions: Provide guidelines for disassembly and material recovery (steel, aluminum, lubricants).
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance management for ball screws and actuators involves careful handling, proper documentation, adherence to international trade laws, and conformity with environmental and safety standards. Proactive planning reduces risk, ensures product reliability, and supports global market access.
Conclusion: Sourcing Ball Screws and Actuators
Sourcing high-quality ball screws and actuators is critical to ensuring the performance, precision, and reliability of motion control systems across various industrial applications. When selecting suppliers and components, several factors must be carefully evaluated, including precision grade, load capacity, stiffness, environmental resistance, lead time, and total cost of ownership.
Off-the-shelf solutions from reputable manufacturers can offer fast delivery and proven reliability, while custom designs may be necessary for specialized applications requiring unique dimensions, performance characteristics, or integration needs. Partnering with experienced suppliers who provide technical support, certification, and traceability enhances system integrity and reduces long-term maintenance risks.
Additionally, considering global sourcing options can offer cost advantages, but it must be balanced with concerns over quality control, logistics, and after-sales service. Prioritizing suppliers with strong engineering expertise, quality management systems (e.g., ISO certifications), and a track record in your industry will help mitigate risks.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach—balancing technical requirements, cost efficiency, supply chain reliability, and long-term service support—ensures optimal performance of ball screws and actuators in your application. Investing time in due diligence during the procurement phase leads to improved machine uptime, accuracy, and overall operational success.