The global ball bearing market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand from the automotive and industrial sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 27.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2030. A significant portion of this demand originates from the cycling industry, where performance, durability, and precision are paramount. As bicycles evolve—from high-end mountain bikes to electric and urban commuter models—the need for reliable, high-efficiency ball bearings has surged. These components are critical in minimizing friction in hubs, pedals, headsets, and bottom brackets, directly influencing ride quality and longevity. With the global bicycle market also expanding—fueled by sustainability trends and urban mobility shifts—manufacturers specializing in ball bearings for bikes are positioned at the intersection of innovation and industrial growth. The following list highlights the top 9 ball bearing manufacturers leading this niche through technological advancement, quality engineering, and strategic market reach.
Top 9 Ball Bearing In Bike Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Enduro Bearings
Domain Est. 2004
Website: endurobearings.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer and supplier of premium bearings and related products for industry and cycling. Enduro Industrial products click here to enter indistrial ……
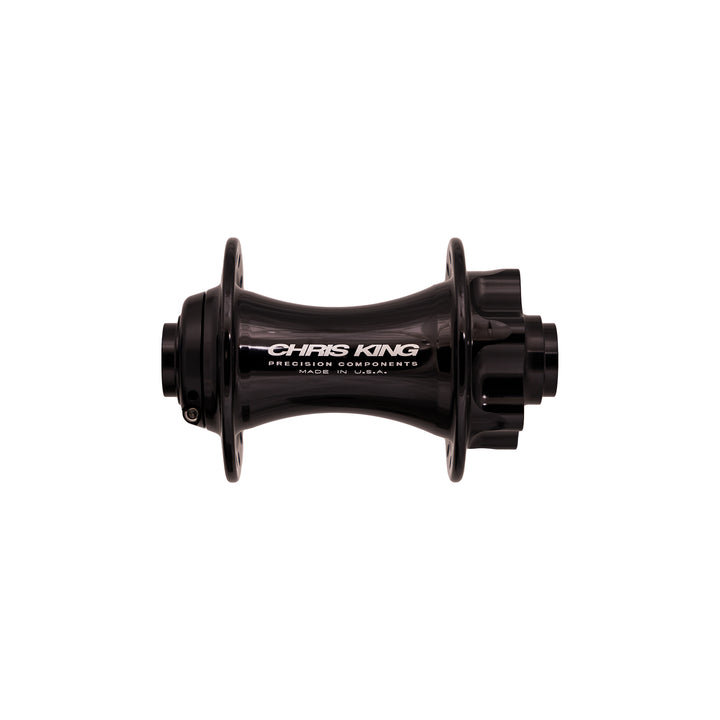
#2 Chris King Hubs, with legendary made
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1976
Website: chrisking.com
Key Highlights: 4-day deliveryChris King Precision Components has been domestically producing bicycle components of the highest quality since 1976. We are the manufacturer, not just a ……
#3 TPI BEARINGS
Founded: 1966
Website: tpibearings.co
Key Highlights: Founded in 1966, TPI is a leading MIT (Made-in-Taiwan) manufacturer of deep groove ball and needle roller bearings….
#4 Ball Bearings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Ball bearings are the most-well known type of bearing. They typically offer lower load capacity but can support high speeds and have been proven in countless ……
#5 Ceramic Bicycle Bearings
Domain Est. 1998
Website: acerracing.com
Key Highlights: With our high-quality materials, precision engineering, and variety of sizes and styles, ACER Racing ball bearings are the perfect choice for cyclists of all ……
#6 Wheel Bearings
Domain Est. 2000
#7 CeramicSpeed
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 2004
Website: ceramicspeed.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $199 Free 14-day returnsCrafting the fastest bearing products for cycling and industry since 2004. Hand built in Denmark. Never Compromise….
#8 Enduro Bearings Cycling Products
Domain Est. 2004
Website: cycling.endurobearings.com
Key Highlights: An Enduro exclusive, XD15 Ceramic-Hybrid bearings utilize an advanced, nitrogen-infused stainless alloy that will never rust or corrode….
#9 Koyo Bearings /JTEKT CORPORATION
Website: koyo.jtekt.co.jp
Key Highlights: List of product types: Deep Groove Ball Bearings, Angular Contact Ball Bearings, Special Environment Ball Bearings (EXSEV series), Thrust Ball Bearings….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ball Bearing In Bike

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Ball Bearings in Bicycles
The global market for ball bearings in bicycles is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological innovations, and the broader shift toward sustainable transportation. As cycling gains momentum as a preferred mode of urban mobility and recreational activity, the demand for high-performance, durable, and lightweight components—particularly ball bearings—is expected to rise substantially.
1. Growth in E-Bike Adoption Fuels Demand
One of the most influential trends shaping the 2026 market is the rapid expansion of the electric bicycle (e-bike) sector. E-bikes place greater mechanical stress on components due to increased speed and weight, necessitating higher-grade ball bearings with enhanced load capacity and durability. Manufacturers are responding by developing sealed, corrosion-resistant bearings optimized for e-bike drivetrains, hubs, and bottom brackets. This trend is especially prominent in Europe and North America, where government incentives and urban infrastructure support e-bike usage.
2. Emphasis on Lightweight and High-Efficiency Bearings
Cyclists and manufacturers alike are prioritizing efficiency and performance. In 2026, expect increased adoption of hybrid ceramic ball bearings (using silicon nitride balls with steel races), which offer reduced friction, lower weight, and longer service life. These bearings are becoming standard in mid-to-high-end road, mountain, and gravel bikes, driven by competitive cycling and enthusiast demand for marginal gains.
3. Integration of Smart Maintenance Technologies
As connectivity and IoT expand into cycling, smart bearings with embedded sensors are emerging. While still in early stages, by 2026, some premium bicycle models may feature ball bearings with wear-monitoring capabilities, providing riders with real-time data on bearing health and maintenance needs via smartphone apps. This trend supports predictive maintenance and enhances user experience.
4. Sustainability and Circular Economy Practices
Environmental concerns are influencing material choices and manufacturing processes. Leading bearing manufacturers are investing in recyclable materials, energy-efficient production, and longer-lasting designs to reduce waste. Additionally, remanufactured or re-greased bearing services are gaining traction in the aftermarket, aligning with circular economy principles.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific remains the largest producer and consumer of bicycle ball bearings, led by China and India, where urbanization and government-backed cycling initiatives are accelerating demand. Meanwhile, Europe maintains a strong position in high-value, precision-engineered bearings due to its advanced manufacturing base and stringent quality standards. North America is seeing growth in the premium and e-bike segments, driving demand for specialized bearing solutions.
6. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted manufacturers to diversify sourcing and increase regional production. By 2026, more companies are expected to adopt nearshoring strategies, particularly in Europe and North America, to ensure reliable supply of critical components like ball bearings.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for ball bearings in bicycles will be defined by innovation, performance optimization, and sustainability. As the cycling industry evolves, ball bearing manufacturers must adapt to emerging technologies and shifting consumer expectations to maintain competitiveness in a dynamic global landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ball Bearings for Bikes: Quality and Intellectual Property Issues
Sourcing ball bearings for bicycles may seem straightforward, but several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can compromise performance, safety, and legal compliance. Being aware of these issues is essential for manufacturers, distributors, and component assemblers.
Poor Material Quality and Manufacturing Tolerances
One of the most frequent pitfalls is selecting ball bearings made from substandard materials or with inconsistent manufacturing tolerances. Low-cost suppliers may use inferior-grade steel or improper heat treatment processes, resulting in premature wear, increased friction, and bearing failure. Poorly machined races or imprecise ball sizing can lead to vibration, noise, and reduced efficiency—especially under load or in wet conditions.
Inadequate Sealing and Corrosion Resistance
Many budget bearings lack effective sealing (e.g., single lip seals instead of double-lip or labyrinth seals), leaving them vulnerable to water, dirt, and grit. This compromises longevity, particularly in off-road or all-weather cycling environments. Additionally, insufficient corrosion-resistant coatings or materials can lead to rust and degradation, especially in coastal or winter riding conditions.
Misrepresentation of Bearing Specifications
Suppliers—especially in unregulated or opaque markets—may falsely advertise bearing specifications such as ABEC ratings, load capacity, or rotational speed. For instance, a bearing may be labeled ABEC-5 but not meet actual tolerances. This misrepresentation can lead to compatibility issues, safety risks, and failure under expected operating conditions.
Counterfeit or Branded Imitation Bearings
A significant IP-related pitfall is the proliferation of counterfeit bearings bearing fake logos or names resembling well-known brands (e.g., “Shimano,” “Chris King,” or “Enduro”). These knockoffs infringe on trademarks and patents, and often perform far below genuine products. Sourcing such components exposes buyers to legal liability, brand reputation damage, and potential recalls.
Lack of Traceability and Certifications
Reputable bearing manufacturers provide material certifications, quality control documentation, and traceability codes. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide these documents increases the risk of receiving non-compliant or untested products. This is particularly problematic for OEMs needing to meet safety or regulatory standards.
Ignoring Patent-Protected Designs
Some high-performance bicycle bearings incorporate patented designs—such as angular contact configurations, specific cage geometries, or proprietary sealing systems. Sourcing generic copies of these patented designs, even unintentionally, can result in intellectual property infringement claims, leading to legal disputes, shipment seizures, or financial penalties.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should work with trusted suppliers, demand full documentation and testing reports, verify IP compliance, and consider third-party quality inspections. Investing in genuine, high-quality bearings not only ensures better performance and rider safety but also protects against legal and reputational risks associated with IP violations and substandard components.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ball Bearings in Bicycles
Overview and Product Classification
Ball bearings used in bicycles are critical components that ensure smooth rotation in hubs, bottom brackets, headsets, and pedals. From a logistics and compliance perspective, these components are typically classified as industrial mechanical parts. They are often categorized under HS (Harmonized System) code 8482.10 – “Ball bearings.” Proper classification is essential for international shipping, customs clearance, and assessing applicable duties and taxes.
Regulatory Compliance
Manufacturers and distributors must ensure ball bearings comply with relevant regional and international standards. Key regulations include:
– ISO 15:2017 – Standard for boundary dimensions of radial bearings.
– ISO 492:2014 – Specifies tolerances for radial ball bearings.
– REACH & RoHS (EU) – Compliance with chemical restrictions and hazardous substance limitations is mandatory for entry into European markets.
– Proposition 65 (California, USA) – Requires warnings if products contain chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm.
Ensure all bearings are tested and certified where required, and maintain documentation for audits.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit. Guidelines include:
– Use anti-corrosion packaging (e.g., VCI paper or sealed plastic) to protect against moisture.
– Clearly label packages with product specifications: bearing type, dimensions (ID × OD × width), ABEC rating (if applicable), and batch/lot number.
– Include multilingual labels when shipping internationally, showing HS code, country of origin, and net weight.
– Mark fragile or “this way up” indicators as needed.
Import/Export Documentation
Accurate documentation ensures smooth customs clearance. Required documents typically include:
– Commercial Invoice (detailing value, quantity, and description)
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin (to claim tariff preferences under trade agreements)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Test Reports or Compliance Certificates (e.g., ISO, RoHS)
Ensure all descriptions match the HS code 8482.10 and avoid vague terms like “machine parts.”
Transportation and Handling
Ball bearings are small but sensitive to shock, vibration, and contamination. Best practices:
– Use rigid, stackable containers or pallets for bulk shipments.
– Avoid exposure to dust, water, and extreme temperatures during storage and transit.
– Segregate from hazardous materials in accordance with IATA/IMDG regulations if shipped by air or sea.
– Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory management to prevent long-term storage issues.
Tariffs and Trade Considerations
Tariff rates vary by destination country. For example:
– USA: Generally duty-free for ball bearings under HTSUS 8482.10.
– EU: Usually 0% import duty, but VAT applies.
– India: May attract customs duty (currently around 7.5%) and GST.
Monitor trade policies and potential anti-dumping measures, particularly on bearings from certain manufacturing regions.
Recordkeeping and Traceability
Maintain detailed records for at least 5–7 years, including:
– Supplier compliance certificates
– Batch testing results
– Shipping and customs documents
– Customer certifications (if applicable)
Traceability helps address recalls, warranty claims, and compliance audits efficiently.
Sustainability and End-of-Life
While ball bearings are long-lasting, consider sustainability practices:
– Encourage recycling of steel components through proper disposal channels.
– Choose suppliers with ISO 14001-certified environmental management systems.
– Minimize packaging waste using recyclable materials.
By following this guide, businesses can ensure efficient logistics and full compliance when shipping ball bearings for bicycles globally.
Conclusion for Sourcing Ball Bearings for Bikes:
Sourcing high-quality ball bearings for bicycles is crucial for ensuring smooth performance, durability, and rider safety. After evaluating various suppliers, materials, and manufacturing standards, it is evident that selecting bearings made from chrome steel or ceramic materials—with proper ABEC ratings, effective sealing, and corrosion resistance—significantly impacts the bike’s overall efficiency and longevity. It is recommended to source from reputable manufacturers who adhere to international quality standards (such as ISO or ABEC) and offer consistent product reliability. Additionally, considering cost, availability, and after-sales support will ensure a sustainable supply chain. Ultimately, investing in premium ball bearings not only enhances cycling performance but also reduces long-term maintenance costs, making it a strategic decision for both manufacturers and consumers.