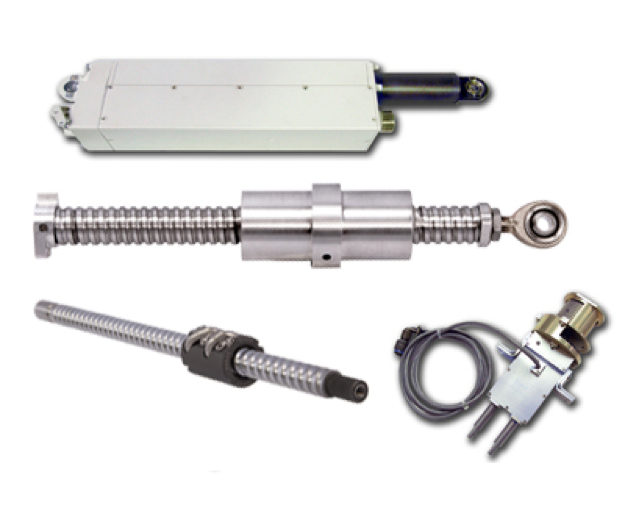
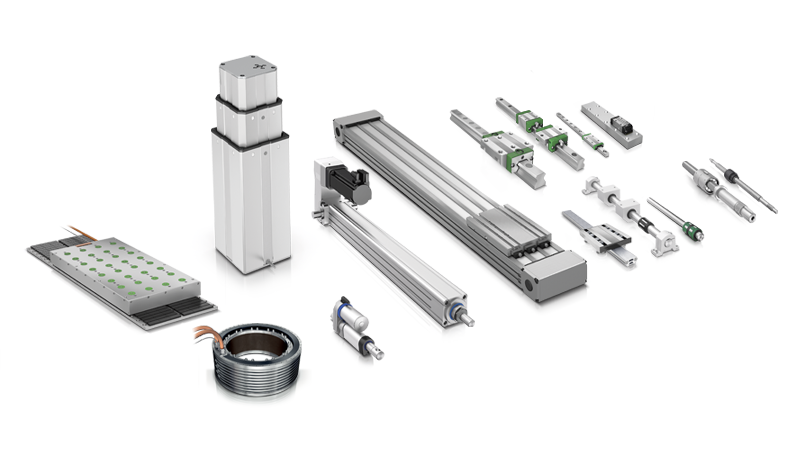
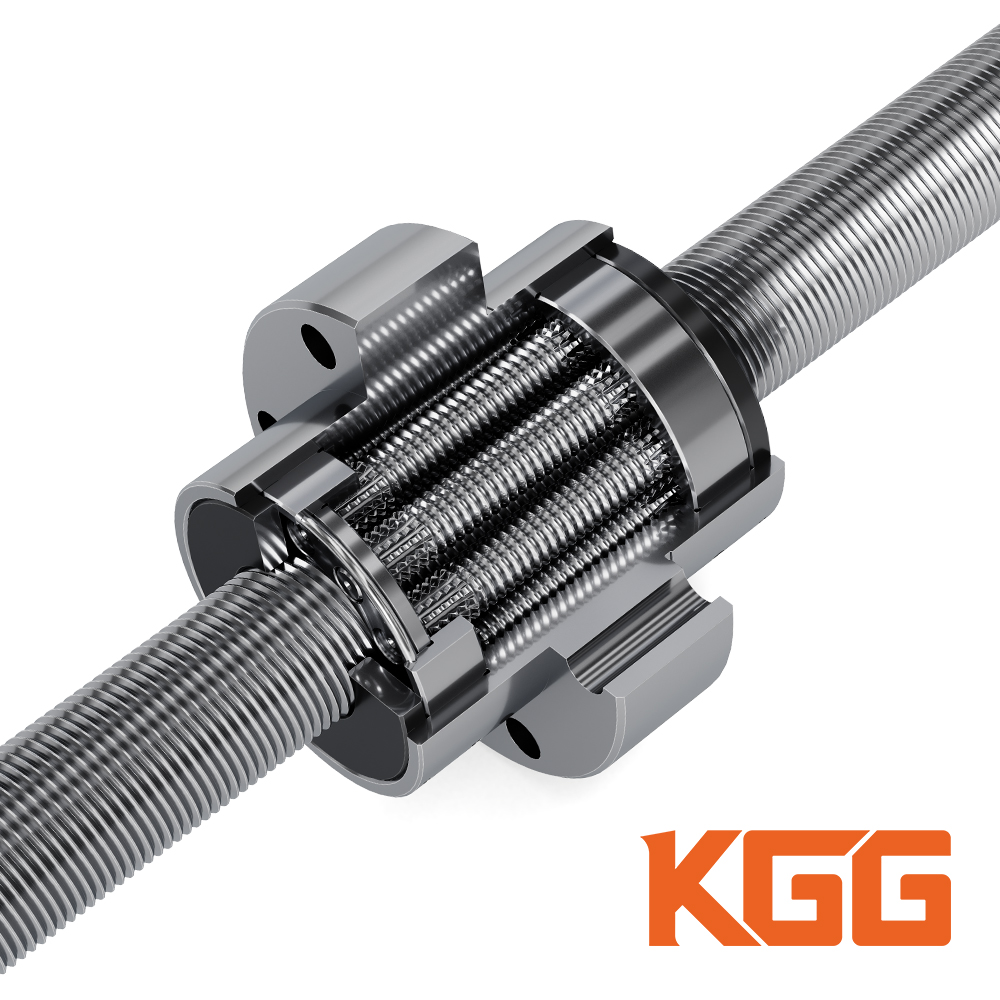
The global ball and screw actuator market has experienced steady expansion, driven by rising automation across industrial manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and semiconductor sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the electric linear actuator market—which includes ball and screw actuators—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by demand for precision motion control and energy-efficient systems. Complementing this, Grand View Research valued the global linear actuators market at USD 8.5 billion in 2022 and forecasts a CAGR of 4.6% through 2030, citing increased adoption in automation and robotics. As industries prioritize accuracy, repeatability, and reliability in motion systems, ball and screw actuators have emerged as critical components due to their high load capacity and mechanical efficiency. With market competition intensifying, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and global reach. Here’s a data-driven look at the top 10 ball and screw actuator manufacturers shaping the future of linear motion technology.
Top 10 Ball And Screw Actuators Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Ball Screw Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ball-screws.net
Key Highlights: Del-Tron Precision, Inc. produces and supplies various automated equipment, such as ball screw actuators. Our engineers have designed our ball screws to offer ……
#2 Ball Screws
Domain Est. 1990
Website: moog.com
Key Highlights: A ball screw is a rolling system consisting of a threaded shaft (screw) and a nut that, internally threaded as well, contains a determined number of balls….
#3 Nook Industries
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nookindustries.com
Key Highlights: Nook Industries manufacturers linear motion solutions including, precision ball screw, acme screw, screw jack, linear actuator, and electric cylinder ……
#4 Ball Screw Actuators
Website: kurodaprecision.com
Key Highlights: This is Ball Screw Actuators information page for KURODA Precision Industries Ltd. KURODA Precision is a precision equipment manufacturer of precision ball ……
#5 Actuator
Domain Est. 1995
Website: thk.com
Key Highlights: THK develops and manufactures mechanical components including the Linear Motion system, LM Guides, Ball Splines, Ball Screws, and electric actuators for our ……
#6 Beaver Aerospace
Domain Est. 1997
Website: beaver-online.com
Key Highlights: A global leader in the design and manufacturing of a broad range of custom ball screws and electromechanical actuation systems for the commercial and military ……
#7 Schaeffler Linear Motion
Domain Est. 2006
Website: medias.schaeffler.us
Key Highlights: Our Range of Linear Motion Products · Low duty linear actuators · High-performance actuators · Lifting columns · Roller screws · Ball screws · 7th axis for robots….
#8 Linear Motion Optimized
Domain Est. 2008
Website: thomsonlinear.com
Key Highlights: Linear motion components to help you build better machines and improve lives. What’s new at Thomson? Sign up for emails on products, industry trends, events….
#9 KSS JAPAN
Domain Est. 2010
Website: kssballscrew.com
Key Highlights: KSS is a growing Japanese Ball Screw brand. We have varieties of Ball Screws, and Actuators. Compact and down-sized designing parts are available at KSS….
#10 Electric Actuators, Roller Screws & Drives
Domain Est. 2017
Website: olsenactuators.com
Key Highlights: Olsen Actuators are experts in the design installation and servicing of electromechanical systems across a wide range of applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ball And Screw Actuators

H2: Market Trends for Ball and Screw Actuators in 2026
The global ball and screw actuators market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, growing automation across industries, and the rising demand for precision motion control systems. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Adoption in Automation and Industry 4.0: As manufacturers embrace smart factories and connected production systems, ball and screw actuators are becoming critical components due to their high precision, repeatability, and integration capabilities with IoT-enabled sensors and control systems. This shift is particularly evident in automotive, semiconductor, and electronics manufacturing.
-
Growth in Electric Actuation Demand: With a global push toward energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions, there is a marked transition from hydraulic and pneumatic systems to electric actuators. Ball and screw actuators, known for their energy efficiency and low maintenance, are gaining preference in applications ranging from industrial robotics to medical equipment.
-
Expansion in Emerging Markets: Asia-Pacific—especially China, India, and South Korea—is expected to lead market growth due to rapid industrialization, government initiatives promoting automation, and expanding electronics and automotive sectors. Local manufacturers are increasingly investing in R&D to produce cost-effective, high-performance actuators.
-
Technological Innovations: Advancements such as preloaded ball screws, integrated servo motors, and miniaturized designs are enhancing performance and enabling use in compact and high-precision applications. Developments in materials (e.g., corrosion-resistant coatings) are also extending service life and reliability in harsh environments.
-
Customization and Modular Designs: End users are demanding more application-specific solutions. In response, manufacturers are offering modular ball screw actuators that allow for easy customization in stroke length, mounting options, and feedback systems—reducing lead times and improving scalability.
-
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization: Post-pandemic disruptions have prompted companies to reevaluate supply chains. By 2026, there is a growing trend toward regional manufacturing and inventory localization to mitigate risks, especially in critical sectors like aerospace and defense.
-
Integration with AI and Predictive Maintenance: Ball and screw actuators are being equipped with smart monitoring systems that leverage AI to predict wear, optimize performance, and reduce unplanned downtime. This trend supports the broader move toward predictive maintenance in industrial operations.
In summary, the 2026 landscape for ball and screw actuators is characterized by innovation, digital integration, and expanding applications. Companies that invest in smart, sustainable, and customizable solutions are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving ecosystem.
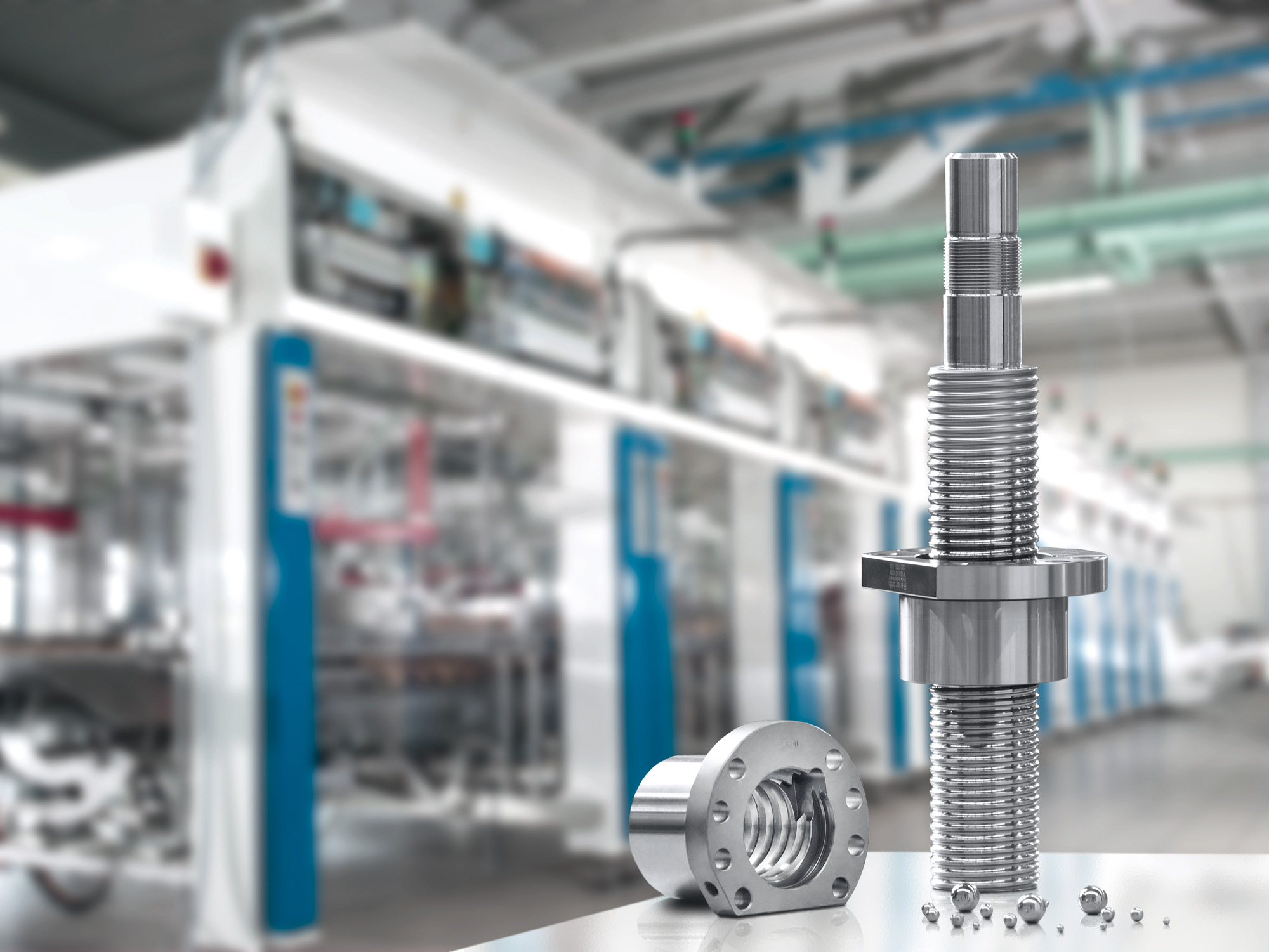
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Ball and Screw Actuators (Quality, IP)
Overlooking Build Quality and Material Specifications
One of the most frequent mistakes when sourcing ball and screw actuators is failing to thoroughly evaluate build quality. Buyers may focus solely on price or basic performance specs without verifying the materials used in the screw, nut, housing, and seals. Low-quality materials can lead to premature wear, reduced load capacity, and shorter service life. Always request detailed technical documentation, including hardness ratings, surface treatments, and tolerance specifications to ensure durability and performance consistency.
Ignoring IP (Ingress Protection) Rating Requirements
A critical oversight is not matching the actuator’s IP rating to the operational environment. Using an actuator with an insufficient IP rating in dusty, wet, or washdown environments can result in contamination, corrosion, and mechanical failure. Conversely, over-specifying an IP rating can lead to unnecessary cost and complexity. Assess the environmental conditions—such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or particulates—and select an actuator with an appropriate IP65, IP67, or higher rating as needed.
Assuming All Ball Screws Are Created Equal
Not all ball screws offer the same precision or efficiency. Sourcing without understanding the difference between rolled and ground screws, or ignoring lead accuracy (e.g., C0 to C10 classes), can compromise system performance. Ground screws provide higher precision but at a higher cost, while rolled screws are economical but less accurate. Selecting the wrong type can affect positioning repeatability and overall system reliability.
Neglecting Anti-Rotation and Guidance Mechanisms
Ball screw actuators often require external guidance or integrated linear bearings to prevent rotation and ensure smooth linear motion. Overlooking this integration can lead to binding, increased wear, or catastrophic failure. Ensure the actuator includes or is compatible with proper anti-rotation features and linear guides suited to the application’s load and alignment requirements.
Underestimating Duty Cycle and Load Conditions
Sourcing actuators based only on nominal load ratings without considering dynamic loads, shock forces, or continuous duty cycles can lead to overheating, mechanical fatigue, or premature failure. Always factor in safety margins and consult manufacturer life expectancy calculations (e.g., L10 life) based on actual operating conditions.
Overlooking IP and Design Infringement Risks
When sourcing from third-party or generic suppliers, there’s a risk of inadvertently purchasing actuators that infringe on patented designs or intellectual property (IP) held by major manufacturers. This can lead to legal liability, supply chain disruptions, or forced redesigns. Source from reputable suppliers and verify that products are IP-compliant, especially in regulated or competitive industries.
Skipping Prototyping and Supplier Qualification
Rushing into mass procurement without prototype testing or proper supplier vetting increases the risk of compatibility and quality issues. Evaluate suppliers based on certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), quality control processes, and customer references. Test sample units under real-world conditions to validate performance before full-scale deployment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ball and Screw Actuators
Overview and Purpose
This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the handling, transportation, import/export, and installation of ball and screw actuators. It is designed for manufacturers, distributors, engineers, and procurement teams to ensure safe and compliant operations across the supply chain.
Product Classification and Specifications
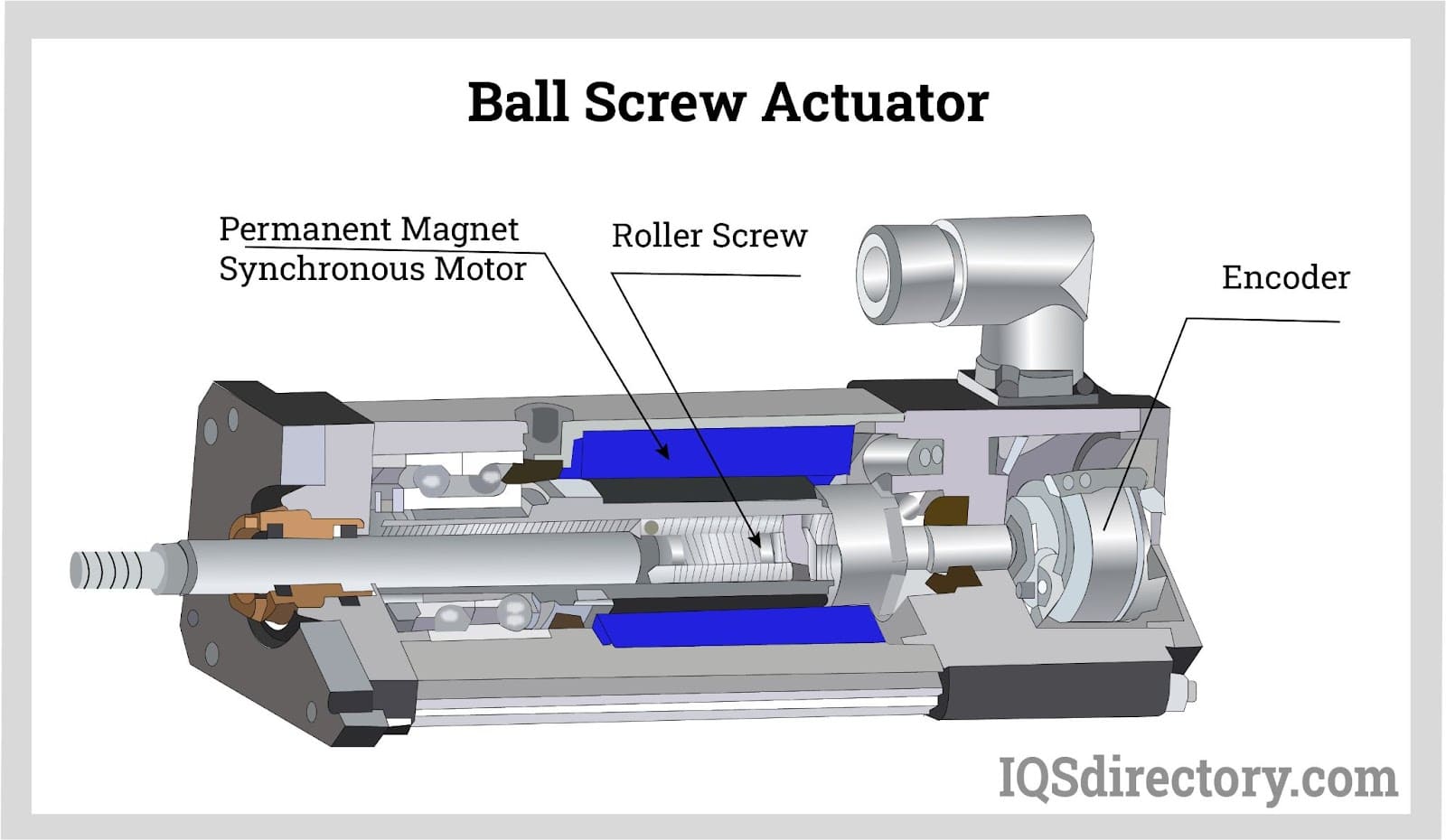
Ball and screw actuators are electromechanical or electro-hydraulic linear motion devices that convert rotary motion into precise linear force and movement. Key classifications include:
– Type: Ball screw vs. roller screw actuators
– Drive mechanism: Electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic
– Load capacity, stroke length, speed, and accuracy ratings
Understanding these specifications is critical for proper packaging, handling, and regulatory classification.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents damage during transit and ensures product integrity:
– Use anti-static and moisture-resistant materials for electric variants
– Secure actuators with foam inserts or custom cradles to prevent shaft rotation or internal component shifting
– Label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Protect from Moisture” indicators
– Avoid stacking heavy items on actuator packages
Transportation and Shipping Guidelines
- Domestic Shipping (e.g., within the U.S. or EU):
- Follow carrier-specific regulations (e.g., FedEx, UPS, DHL) for dimensional weight and hazardous material exemptions
- Confirm non-hazardous classification; most electric actuators do not contain restricted components
- International Shipping:
- Comply with IATA/IMDG regulations if batteries or motor components are included
- Provide detailed commercial invoices, packing lists, and Harmonized System (HS) codes (typically 8483.10 or 8537.10)
- Ensure voltage and motor specifications match destination country standards (e.g., 110V vs. 230V)
Import and Export Compliance
- Export Controls:
- Verify if actuators fall under export control regimes such as EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations)
- Most industrial-grade actuators are EAR99 (low concern), but high-precision or aerospace-grade models may require licenses
- Customs Documentation:
- Accurate HS codes, country of origin, and end-use declarations are mandatory
- Include certificates of conformity (e.g., CE, UKCA) where applicable
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Ensure actuator models meet relevant compliance certifications:
– CE Marking (EU): Compliance with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), EMC Directive (2014/30/EU), and RoHS (2011/65/EU)
– UL/CSA (North America): For electrical safety in industrial environments (e.g., UL 508)
– REACH (EU): Declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in materials used
– IP Ratings: Confirm ingress protection (e.g., IP65) for environmental resistance
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives for end-of-life disposal in the EU
- Recycle packaging materials and encourage return programs for obsolete units
- Provide product lifecycle data to support sustainability reporting
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain complete records for compliance audits and quality assurance:
– Bill of materials (BOM) with RoHS/REACH compliance data
– Test reports (e.g., load, endurance, EMI)
– Serial number tracking for traceability across supply chain
– User manuals with safety warnings and installation instructions in local languages
Installation and End-User Compliance
- Provide clear installation guidelines to prevent misuse
- Include torque specifications, alignment procedures, and maintenance schedules
- Advise end-users to comply with local OSHA, WHMIS, or equivalent workplace safety regulations
Summary and Best Practices
To ensure seamless logistics and compliance:
– Verify regulatory requirements by destination country
– Use certified suppliers and logistics partners experienced in industrial automation components
– Conduct regular audits of packaging, labeling, and documentation processes
– Train procurement and logistics teams on export controls and hazardous material handling
Adhering to this guide minimizes delays, avoids penalties, and supports the reliable deployment of ball and screw actuators worldwide.
Conclusion: Sourcing Ball and Screw Actuators
Sourcing ball and screw actuators requires a careful evaluation of application requirements, performance specifications, and supplier capabilities. These precision components are critical in applications demanding accurate linear motion, high efficiency, and long service life—common in automation, aerospace, medical equipment, and industrial machinery.
Key considerations when sourcing include load capacity, lead accuracy, backlash, speed, environmental resistance, and duty cycle. Ball screws offer superior efficiency and precision for high-performance applications, while lead screws may be preferable for lighter loads or cost-sensitive projects where noise and efficiency are less critical.
Selecting a reliable supplier with proven quality standards, customization options, technical support, and consistent lead times is essential. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—factoring in maintenance, lifespan, and integration effort—can lead to more informed decisions than focusing solely on initial cost.
In summary, successful sourcing of ball and screw actuators hinges on aligning technical requirements with supplier expertise, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and value across the application lifecycle.