The global babbitt metal market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand from industries such as automotive, marine, and power generation, where durable bearing solutions are critical. According to Grand View Research, the global bearings market was valued at USD 97.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030—highlighting the rising need for high-performance bearing materials like babbitt metal. As industrial applications continue to prioritize reliability and low friction, babbitt metal remains a preferred choice for lining bearings due to its excellent conformability, embeddability, and corrosion resistance. With manufacturing hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific bolstering production capabilities, the competitive landscape features established players and specialized foundries focused on innovation and material precision. In this environment, the following nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining technical expertise, scalable production, and proven performance in mission-critical applications.
Top 9 Babbitt Metal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Babbitt Bearing Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: fusionbabbitting.com
Key Highlights: Fusion Babbitting is a trusted source for new bearing manufacturing in the US. Our facility is equipped to produce the highest-quality bearings for your ……
#2 Quad Industries Inc.: Babbitt Bearings
Domain Est. 2015 | Founded: 1909
Website: quadindustriesinc.com
Key Highlights: Since 1909, Quad Industries Inc. has produced the finest Babbitt bearing products available. We’re committed to using 100% Babbitt metal and American-made ……
#3 American Babbitt Bearing
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americanbabbitt.com
Key Highlights: American Babbitt Bearing has been in business more than 20 years providing our customers with the highest level of quality products that they expect and deserve ……
#4 Manufacturer & Exporter Of Babbitt White Metal Ingots
Domain Est. 2012
Website: rebabbittingbearing.com
Key Highlights: RA Power Solutions with forty-three years of experience is the manufacturer and exporter of Babbitt white metal ingots….
#5 Babbitt Metals
Domain Est. 1997
Website: belmontmetals.com
Key Highlights: Belmont Babbitt Metals featuring tin-base and lead-base babbitts to ASTM, SAE, government, Navy specifications; special and custom alloys….
#6 Babbitt Information
Domain Est. 1998
Website: babbittrepair.com
Key Highlights: Compatibility. Babbitt is extremely compatible with shaft materials. It resists seizing or galling under conditions of metal to metal contact at start-up….
#7 San Jose, California
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1945
Website: bbcmachine.com
Key Highlights: Babbitt Bearing Company was founded in 1945 in San Jose, California. bbc has been providing many industries repair and manufacturing services for over 80 years….
#8 Babbitt
Domain Est. 2001
Website: maycoindustries.com
Key Highlights: Mayco Industries is the leader in lead Babbitt metal for sale. To create a custom Babbitt alloy or for ordering and pricing information, do not hesitate to ……
#9 Babbitt Manufacturing Co
Website: babbittmanufacturingco.com
Key Highlights: We provide a variety of residential and commercial exterior services throughout South Jersey. We offer expert installations, but can also sell materials to you….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Babbitt Metal
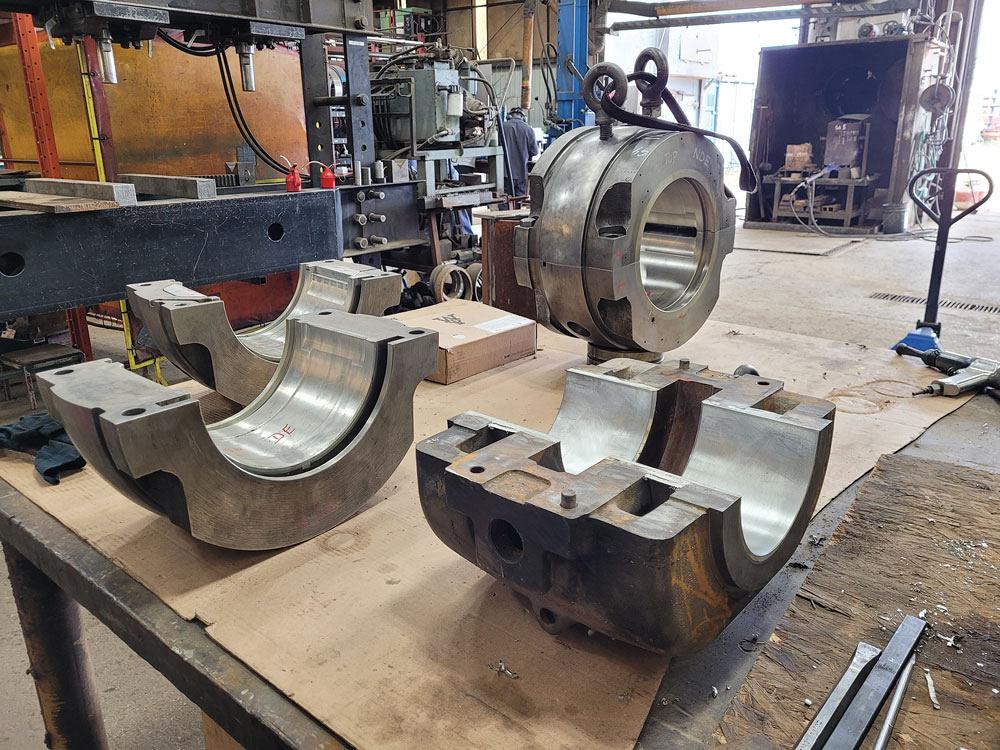

H2: Market Trends for Babbitt Metal in 2026
As the global industrial landscape evolves through 2026, Babbitt metal—a tin-, lead-, or antimony-based alloy used primarily in bearings for heavy machinery—faces a complex shift driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and changing industrial dynamics. While Babbitt metal remains a critical material in high-load, low-speed bearing applications across sectors such as power generation, marine propulsion, and heavy manufacturing, its market trajectory in the second half of 2026 reflects both enduring demand and structural challenges.
1. Stable Demand in Niche Industrial Applications
Despite the rise of advanced polymer and composite bearings, Babbitt metal continues to hold a strong position in applications requiring high embeddability, conformability, and resistance to shock loading. In 2026, industries such as hydropower, mining, and large-scale rail transportation maintain steady demand for Babbitt-lined bearings, particularly in retrofitting and maintenance of legacy equipment. The H2 outlook shows a moderate growth in demand (projected 2–3% year-on-year), primarily from emerging markets in Southeast Asia and Africa where infrastructure development relies on proven, durable bearing solutions.
2. Environmental Regulations and Material Substitution
Environmental and health regulations continue to exert pressure on lead-based Babbitt formulations. The European Union’s ongoing enforcement of REACH and similar legislation in North America are accelerating the shift toward lead-free alternatives, especially tin-antimony-copper variants. In H2 2026, suppliers are increasingly investing in eco-friendly Babbitt alloys, with some manufacturers achieving certification under ISO 14001 standards. This trend is reshaping the supply chain, with a noticeable preference for recyclable and non-toxic formulations in new installations.
3. Impact of Additive Manufacturing and Remanufacturing
The adoption of automated remanufacturing and thermal spray technologies in H2 2026 enables faster, more cost-effective reapplication of Babbitt linings to worn bearing shells. This extends the lifecycle of critical components, particularly in the power and marine sectors. Simultaneously, advancements in additive manufacturing allow for precision deposition of Babbitt alloys, reducing material waste and improving performance consistency—driving efficiency in maintenance operations.
4. Raw Material Volatility and Supply Chain Adjustments
Tin prices remain volatile in 2026 due to geopolitical tensions in key producing regions like Indonesia and Myanmar. This volatility directly impacts Babbitt metal production costs, especially for tin-based grades. In response, producers are diversifying sourcing strategies and entering long-term supply agreements. Additionally, recycling of spent Babbitt bearings is gaining traction, with recovery rates improving through enhanced separation technologies, contributing to supply stability.
5. Competition from Advanced Bearing Technologies
While Babbitt metal retains irreplaceable properties in certain applications, competition from fluid-film, magnetic, and solid polymer bearings is growing—especially in high-speed or maintenance-sensitive environments. However, in H2 2026, market analysis indicates that Babbitt metal is not being displaced but rather complemented, as hybrid bearing systems that combine Babbitt with smart monitoring sensors emerge in predictive maintenance frameworks.
Conclusion
By H2 2026, the Babbitt metal market is characterized by resilience in traditional sectors, innovation in material composition, and adaptation to environmental and economic pressures. While growth is modest, the material’s unique performance attributes ensure its continued relevance. Strategic focus on sustainability, remanufacturing, and supply chain resilience will determine long-term competitiveness in a niche but vital segment of the industrial materials market.
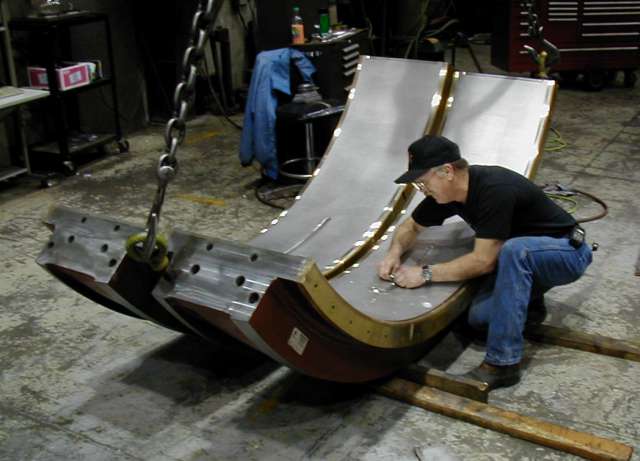

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Babbitt Metal: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing Babbitt metal—a tin- or lead-based alloy used for bearing surfaces—can be fraught with challenges, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inconsistent or Substandard Material Quality
One of the most prevalent issues when sourcing Babbitt metal is receiving alloys that do not meet required specifications. This can stem from poor manufacturing controls, use of recycled or contaminated raw materials, or lack of adherence to industry standards such as ASTM B23 or AMS 4777. Substandard Babbitt may exhibit poor bonding to backing metals, reduced fatigue resistance, or inadequate conformability and embeddability, leading to premature bearing failure in critical machinery.
Misrepresentation of Alloy Composition
Suppliers may misrepresent the chemical composition of Babbitt metal, either unintentionally due to inadequate testing or intentionally to cut costs. For example, reducing the tin content in a tin-based Babbitt (e.g., Grade 11 or 13) significantly lowers cost but also degrades performance under high load or temperature. Without proper certification and third-party verification (e.g., spectrographic analysis), buyers risk receiving off-spec material that compromises equipment reliability.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Reputable applications—especially in aerospace, marine, or power generation—require full traceability of materials. A common pitfall is sourcing Babbitt metal without proper mill test reports (MTRs), heat numbers, or compliance documentation. This absence not only impedes quality assurance but can also violate regulatory or OEM requirements, potentially voiding warranties or certifications.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Some Babbitt metal formulations are proprietary, developed and protected by specific manufacturers or bearing OEMs. Sourcing generic or uncertified equivalents without authorization may infringe on patented alloy compositions or manufacturing processes. This exposes the buyer to legal risks, including liability for IP violations, especially if the end product is sold commercially. Always verify that the supplier has the right to produce and sell the specified alloy.
Use of Counterfeit or Non-Compliant Materials
In global supply chains, counterfeit Babbitt metal—labeled as compliant but failing to meet standards—is a growing concern. These materials may mimic packaging or documentation but perform poorly in service. Relying on unverified suppliers, particularly in regions with weak regulatory oversight, increases the risk of receiving such non-compliant products.
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly vet suppliers is a critical oversight. Some vendors may lack the metallurgical expertise, quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), or production capabilities required for consistent Babbitt metal manufacturing. Conducting on-site audits, reviewing quality processes, and requesting sample testing are essential steps to ensure supplier reliability.
Poor Bonding Performance Due to Processing Issues
Even with the correct alloy, improper casting or centrifugal pouring techniques can result in poor bond integrity between the Babbitt layer and the backing metal (e.g., steel or bronze). Sourcing from suppliers without proven processing controls can lead to delamination under operational stress, causing catastrophic bearing failure.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should prioritize suppliers with verifiable quality certifications, transparent material traceability, and legal rights to produce the specified Babbitt alloy. Requiring independent material testing and maintaining clear contractual specifications can safeguard both performance and intellectual property integrity.
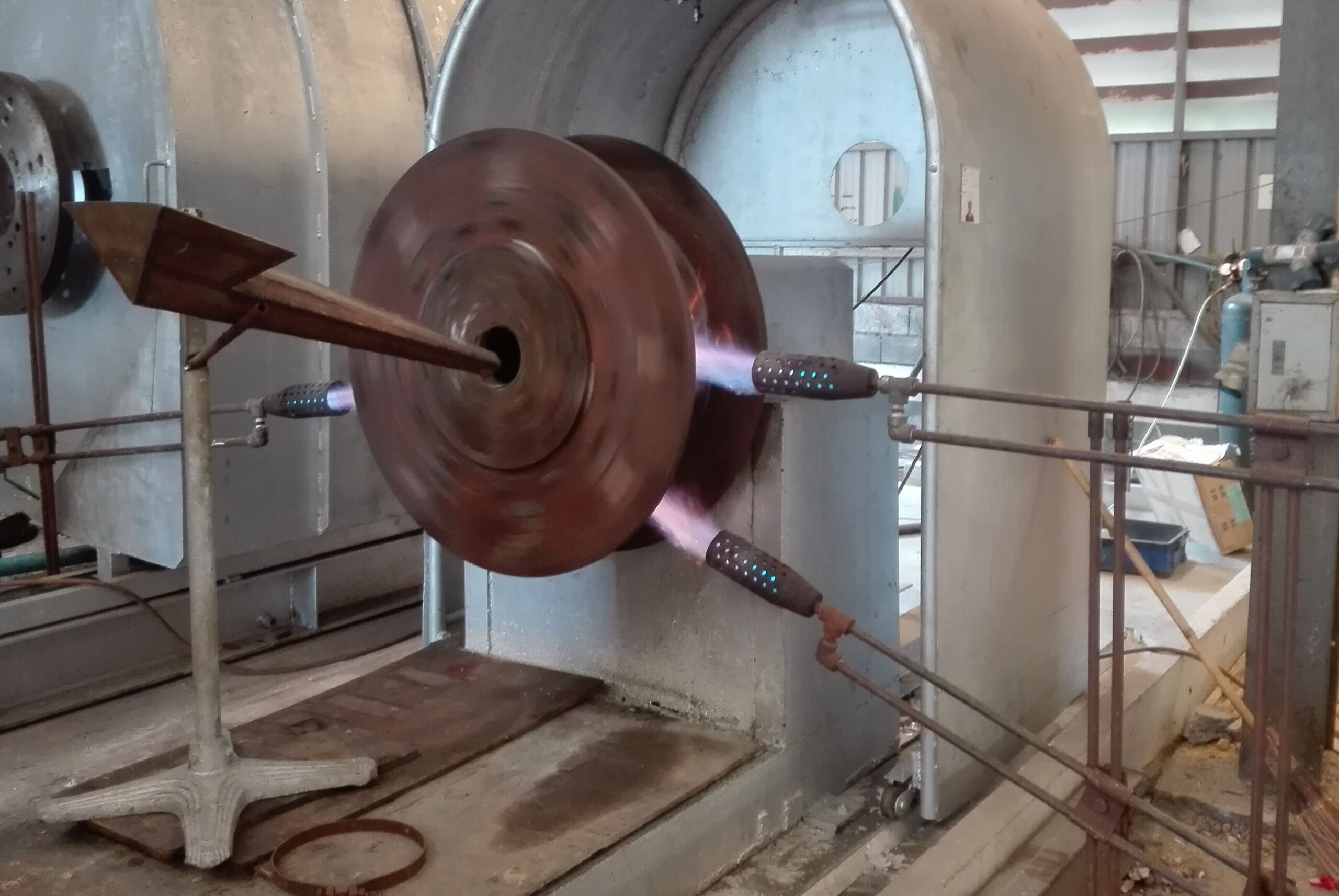

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Babbitt Metal
Babbitt metal, also known as white metal, is a soft, corrosion-resistant alloy primarily composed of tin, lead, copper, and antimony, commonly used in bearings and other friction-reducing applications. Due to its composition and industrial use, transporting, storing, and handling Babbitt metal requires adherence to specific logistical and regulatory compliance standards. This guide outlines best practices and legal requirements to ensure safe and compliant operations.
Regulatory Classification and Hazard Identification
Babbitt metal is generally considered a non-hazardous material for transport when in solid form and not classified as a dangerous good under major transport regulations (e.g., DOT 49 CFR, ADR, IMDG, IATA). However, if the alloy contains more than 50% lead, it may be subject to lead-specific regulations due to toxicity concerns. Always verify the exact composition with the manufacturer’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS), particularly Section 14 (Transport Information), to determine regulatory status.
- UN Number: Typically not assigned for solid Babbitt metal unless classified as hazardous.
- Proper Shipping Name: “Metal Alloy, Not Otherwise Specified” or similar, if applicable.
- Hazard Class: Usually Class 9 (Miscellaneous) if regulated; otherwise, non-regulated.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
When shipping Babbitt metal:
- Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., steel drums, wooden crates, or heavy-duty poly-lined containers) to prevent physical damage and environmental exposure.
- Securely seal packages to prevent spillage of scrap or granular forms.
- Label packages with:
- Full product name: “Babbitt Metal” or “Tin-Based Bearing Alloy”
- Manufacturer/supplier name and contact information
- Batch or lot number
- Weight and dimensions
- If lead content exceeds regulatory thresholds (e.g., OSHA or EPA limits), include appropriate hazard communication labels (e.g., “Caution: Contains Lead”).
Transportation and Handling
- Mode of Transport: Babbitt metal in solid form can generally be shipped via road, rail, sea, or air without restrictions as a non-hazardous good—provided it meets classification criteria.
- Load Securing: Ensure loads are stabilized using straps, dunnage, or bracing to prevent shifting during transit.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Babbitt metal has a relatively low melting point (typically 200–250°C depending on formulation). Avoid exposure to high temperatures during transport or storage.
- Handling Precautions: Use mechanical aids (e.g., forklifts, pallet jacks) for heavy ingots or blocks. Minimize manual handling to reduce injury risk.
Storage Guidelines
- Store in a dry, well-ventilated area protected from moisture to prevent oxidation or corrosion.
- Keep away from incompatible materials such as strong acids or oxidizing agents.
- Use pallets to elevate material off the floor and prevent contamination.
- If lead-containing, implement lead-safe storage practices:
- Prohibit eating, drinking, or smoking in storage areas.
- Provide handwashing facilities nearby.
- Clearly label containers with “Contains Lead – Handle with Care.”
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) Compliance
- OSHA Compliance (U.S.): If Babbitt metal contains lead above 0.1%, it may fall under OSHA’s Lead Standard (29 CFR 1910.1025). Employers must:
- Conduct air monitoring if dust or fumes are generated (e.g., during melting or machining).
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, respirators, and protective clothing.
- Implement engineering controls (ventilation) and hygiene practices.
- EPA Regulations: Regulate lead-containing waste under RCRA. Spent Babbitt metal or machining swarf may be classified as hazardous waste—conduct waste characterization testing.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Monitor compliance with substance restrictions, particularly lead and antimony, in products placed on the European market.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain the following records to ensure compliance:
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for the specific Babbitt metal alloy
– Shipping manifests and bills of lading
– Waste disposal documentation (if applicable)
– Employee training records for handling lead-containing materials
– Air monitoring and medical surveillance records (under OSHA lead standard)
Import and Export Considerations
- Verify customs classification (HS Code) for Babbitt metal—typically under 8112.21 (Tin Alloys) or 7806.00 (Lead Alloys), depending on composition.
- Check for import restrictions or tariffs in destination countries, especially concerning lead content.
- Comply with export control regulations if technology or alloys are subject to ITAR or EAR.
Emergency Response
- In case of fire: Use dry chemical, CO₂, or sand to extinguish. Do not use water on molten metal.
- If molten Babbitt metal is spilled, allow to cool before cleanup. Do not touch with bare hands.
- In case of exposure to dust or fumes (e.g., during melting), evacuate area and use appropriate respiratory protection. Refer to SDS Section 6 for first aid measures.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant logistics for Babbitt metal depend on accurate material classification, proper packaging, and adherence to environmental and occupational health regulations. Always consult the SDS and engage regulatory experts when handling lead-containing alloys or planning international shipments. Proactive compliance reduces risk, ensures supply chain continuity, and protects worker and environmental health.
In conclusion, sourcing Babbitt metal requires careful consideration of several key factors including the specific application requirements, material composition (whether tin-based or lead-based), supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with industry standards and environmental regulations. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who can provide consistent quality, proper certification, and technical support. Additionally, evaluating factors such as lead time, minimum order quantities, and logistical capabilities ensures a smooth supply chain. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy for Babbitt metal contributes to improved performance, longevity, and reliability of bearing systems in industrial and mechanical applications.