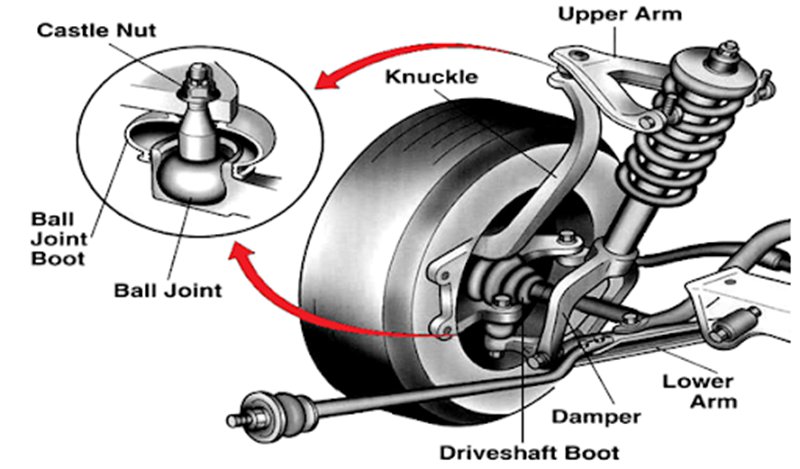
The global automotive suspension parts market is poised for significant expansion, driven by rising vehicle production, increasing demand for enhanced ride comfort, and the growing adoption of advanced suspension technologies. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 35.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. This growth is further fueled by the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs), which require specialized suspension systems to manage added battery weight and improve handling. Additionally, stringent safety and comfort regulations across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are accelerating innovation in suspension components. With increasing focus on lightweight materials and smart suspension systems integrated with vehicle dynamics control, the industry is witnessing a transformation led by key global manufacturers. The following list highlights the top 10 automotive suspension parts manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape.
Top 10 Automotive Suspension Parts Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rare Parts
Domain Est. 1995
Website: rareparts.com
Key Highlights: Looking for the best steering or suspension parts for your classic car or 4×4 truck? We have what you’re looking for. And if we don’t, we’ll build it for you….
#2 SIDEM
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sidem.be
Key Highlights: Sidem is a leading European designer and manufacturer of steering and suspension parts for the car assembly and replacement market….
#3 Advanced Auto Parts Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: shautoparts.com
Key Highlights: SH Auto Parts is an industry-leading auto parts manufacturer, specializing in precision-engineered suspension and steering components like tie rod ends, ……
#4 BILSTEIN Corporate
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bilstein.com
Key Highlights: At BILSTEIN, we manufacture high-quality shock absorbers and suspension systems. As an employer, we are as innovative as our technologies and as passionate ……
#5 Eibach
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eibach.com
Key Highlights: Experience the legacy of Eibach, crafting high-performance suspension systems and automotive components with engineering excellence and precision craftsmanship….
#6 Mevotech
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mevotech.com
Key Highlights: Designed for the Ride. Professional Technicians trust Mevotech’s driveline, steering and suspension parts to perform stronger, and last longer….
#7 Heavy Duty Vehicle Suspension Parts
Domain Est. 2001 | Founded: 1919
Website: triangleusa.com
Key Highlights: Since 1919, the TRIANGLE name has been synonymous with steel leaf springs, Triangle Suspension Parts, FLAGG Suspension Parts and ContiTech Air Springs….
#8 SPL Parts
Domain Est. 2002
Website: splparts.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsSPL Parts designs and builds top shelf suspension components for street and track cars including Nissan, Infiniti, Scion, Subaru, Porsche and more….
#9 Suspension Parts & Components
Domain Est. 2005
Website: moogparts.com
Key Highlights: The smoothest and safest ride combines with legendary MOOG® reliability in our range of suspension parts, trusted by pros, techs and drivers everywhere….
#10 EVO Manufacturing Lift Kits and Accessories
Domain Est. 2008
Website: evomfg.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsExperience superior off-road performance with EVO Manufacturing Lift Kits and Accessories. Specializing in Jeep Wrangler and Gladiator suspension systems, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automotive Suspension Parts

H2: Key Market Trends Shaping the Automotive Suspension Parts Industry in 2026
By 2026, the global automotive suspension parts market is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, shifting vehicle dynamics, and evolving consumer demands. Here are the dominant H2 (highlighted) trends expected to define the landscape:
H2: Electrification Driving Suspension Redesign & Increased Component Demand
The accelerating shift towards Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) is fundamentally altering suspension requirements. The substantial weight of battery packs (often 300-500+ kg) necessitates reinforced suspension components (springs, shock absorbers, control arms, subframes) capable of handling higher loads and stresses. This translates directly into increased material usage, larger component sizes, and higher demand for durable, high-performance parts. Furthermore, the need to optimize range makes weight reduction in other suspension elements (e.g., using aluminum or composites for control arms, knuckles) a critical counter-trend, driving material innovation.
H2: Active and Semi-Active Suspension Systems Transitioning from Premium to Mainstream
Once exclusive to luxury and high-performance vehicles, active (e.g., hydraulic, pneumatic) and semi-active (e.g., magnetorheological fluid dampers like MagneRide) suspension systems are rapidly moving downmarket. Fueled by consumer demand for superior ride comfort, handling stability (especially crucial for heavier EVs), and enhanced safety (e.g., pre-crash leveling), these systems are becoming key differentiators. By 2026, expect significant adoption growth in mid-tier EVs and increasingly in ICE vehicles, driving demand for sophisticated sensors (accelerometers, position sensors), electronic control units (ECUs), and complex hydraulic/pneumatic actuators, moving beyond traditional passive coil springs and shock absorbers.
H2: ADAS and Autonomous Driving Requiring Integrated, Predictive Suspension
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and the progression towards higher levels of autonomy (L3+) demand suspension systems that are no longer passive but are active partners in vehicle dynamics. Suspension components must integrate seamlessly with ADAS sensors (cameras, radar, LiDAR) and vehicle networks. The key trend is predictive suspension – systems that use real-time road data (from cameras/sensors) and GPS terrain mapping to proactively adjust damping, ride height, and even individual wheel response before encountering bumps, potholes, or curves. This requires highly responsive components, advanced software algorithms, and robust connectivity, creating a complex ecosystem beyond simple mechanical parts.
H2: Lightweighting Imperative Intensifying Material Innovation
The relentless pressure to improve fuel efficiency (ICE) and extend EV range, combined with stringent emissions regulations, makes lightweighting a paramount priority. This drives significant R&D and adoption of advanced materials in suspension components:
* High-Strength Steels (HSS) & Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS): For critical load-bearing parts requiring strength and cost-effectiveness.
* Aluminum Alloys: Widely adopted for control arms, knuckles, and subframes to reduce unsprung and overall weight.
* Composite Materials (e.g., CFRP – Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer): Emerging for specific high-performance or ultra-lightweight applications, though cost remains a barrier for mass adoption.
* Magnesium Alloys: Potential for even greater weight savings, facing challenges in corrosion resistance and cost.
H2: Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization Gaining Strategic Importance
Geopolitical uncertainties, past disruptions (e.g., pandemic, chip shortages), and the need for faster response times are pushing OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers towards more resilient and regionalized supply chains. This trend impacts suspension parts manufacturers through:
* Nearshoring/Friendshoring: Increased investment in manufacturing capacity in North America and Europe to serve local EV production hubs.
* Vertical Integration: Some OEMs may bring more component design and manufacturing in-house, especially for critical EV-specific parts.
* Dual Sourcing & Inventory Management: Greater emphasis on securing multiple suppliers and strategic stockpiling of critical components (e.g., specific sensors, ECUs).
* Focus on Local Content: Regulatory pressures (e.g., US IRA) incentivizing local sourcing, benefiting regional suppliers.
These interconnected H2 trends highlight a market moving beyond simple replacement parts towards sophisticated, integrated systems central to the performance, efficiency, safety, and intelligence of next-generation vehicles, with significant implications for manufacturers, suppliers, and aftermarket players by 2026.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Automotive Suspension Parts (Quality, IP)
Sourcing automotive suspension parts requires careful attention to detail, as poor choices can lead to safety risks, legal issues, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers should be aware of.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material and Manufacturing Standards
Many suppliers, especially in emerging markets, may use substandard materials or fail to adhere to automotive-grade manufacturing processes. Suspension components like control arms, struts, and bushings must meet strict tolerances and durability requirements. Inconsistent heat treatment, poor welding, or non-compliant alloys can lead to premature failure under stress.
Lack of Certifications and Traceability
Reputable suspension parts should come with certifications such as IATF 16949 (quality management for automotive production) and material test reports. A common pitfall is sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide full traceability or documentation, making it difficult to verify compliance with OEM or safety standards.
Poor Fit and Performance Compared to OEM
Aftermarket parts vary widely in dimensional accuracy and performance. Some low-cost alternatives may not match original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications, leading to improper fitment, increased wear on other components, or compromised vehicle handling and safety.
Inadequate Testing and Validation
Reliable suspension parts undergo rigorous testing for fatigue, corrosion resistance, and load-bearing capacity. Suppliers that skip or minimize testing protocols may deliver parts that fail prematurely in real-world conditions, exposing buyers to warranty claims and liability.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of OEM Designs and Logos
Some suppliers produce “copy” parts that replicate patented or trademarked OEM designs without authorization. Using such components exposes the buyer to legal risk, including infringement claims, customs seizures, or brand damage—especially if the parts are marketed as compatible or “OEM-style.”
Grey Market and Counterfeit Components
The suspension market is vulnerable to counterfeit or grey market goods falsely labeled as genuine OEM or premium aftermarket brands. These parts may lack proper IP licensing and often come with falsified documentation, increasing the risk of legal exposure and quality issues.
Misrepresentation of Brand Affiliation
Suppliers may imply or falsely claim partnerships with recognized brands or OEMs to gain credibility. This misrepresentation not only violates trademark laws but can also mislead procurement teams into believing they are purchasing authorized, high-quality components.
Limited Liability and Warranty Enforcement
IP-infringing parts often come with weak or unenforceable warranties. If a legal dispute arises due to IP violations, the supplier may disappear or refuse responsibility, leaving the buyer liable for damages, recalls, or regulatory penalties.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers thoroughly, demanding certifications, conducting product audits, and ensuring compliance with IP laws and industry standards.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automotive Suspension Parts
Overview
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the global supply chain of automotive suspension parts, including components such as shock absorbers, struts, control arms, springs, and bushings. Ensuring regulatory adherence and efficient logistics operations is critical for safety, quality, and market access.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
International Standards and Certifications
Suspension parts must comply with international standards such as:
– ISO 9001 (Quality Management)
– IATF 16949 (Automotive Quality Management Systems)
– ECE Regulations (e.g., ECE R90 for replacement suspension components in Europe)
– FMVSS No. 126 (U.S. stability control requirements, relevant for suspension integration)
Manufacturers and suppliers must maintain valid certification and provide documentation upon request.
Regional Market Regulations
- European Union (EU): Parts must carry the E-mark certification per ECE R90. CE marking may also apply depending on integration.
- United States: No federal certification for individual suspension components, but products must comply with DOT safety standards when installed. Aftermarket parts may be subject to state-level regulations (e.g., California’s CARB for coatings).
- China: Requires CCC (China Compulsory Certification) for certain automotive parts. Check CNCA lists for inclusion.
- Other Markets: Countries such as Russia (EAC), South Korea (KC), and Australia (ADR) have their own conformity assessment schemes.
Environmental and Chemical Compliance
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals. Suspension parts containing SVHCs (Substances of Very High Concern) above thresholds must be reported.
- RoHS (EU & China): Restriction of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in electrical/electronic components (relevant for integrated sensors).
- Conflict Minerals (U.S. Dodd-Frank Act): Suppliers must disclose use of tantalum, tin, gold, and tungsten sourced from conflict-affected regions.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Packaging Requirements
- Use durable, shock-resistant packaging to prevent damage during transit.
- Include corrosion protection (e.g., VCI paper) for metal components.
- Clearly mark “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” where applicable.
- Ensure compliance with ISTA or ASTM packaging testing standards for transport simulation.
Labeling and Traceability
- Labels must include:
- Part number and name
- Manufacturer name and address
- Batch/lot number or serial number
- Compliance marks (e.g., E-mark, IATF 16949)
- Country of origin
- Implement barcode or QR code systems for full traceability across the supply chain.
Shipping and Transportation Logistics
Mode of Transport Selection
- Air Freight: For urgent deliveries or high-value components; requires proper hazardous material classification if shock absorbers contain pressurized gas.
- Ocean Freight: Standard for large-volume shipments; use containerized transport with moisture protection.
- Ground Transport: Preferred for regional distribution; ensure proper load securing to prevent shifting.
Hazardous Material Considerations
- Some shock absorbers contain pressurized nitrogen and may be classified under UN1066, Compressed Gas.
- Proper documentation (e.g., SDS, dangerous goods declaration) and packaging per IMDG Code (sea) or IATA DGR (air) are required.
- Non-hazardous components must be clearly differentiated in shipping manifests.
Customs and Import Clearance
- Provide accurate HS (Harmonized System) codes, typically under 8708.80 (parts and accessories for suspension systems).
- Submit required documents: commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and compliance certificates.
- Leverage FTA (Free Trade Agreements) where applicable (e.g., USMCA, RCEP) to reduce tariffs.
Quality Control and Documentation
Incoming and Outgoing Inspections
- Conduct dimensional, material, and functional testing per OEM specifications.
- Use calibrated equipment and documented inspection reports.
- Retain records for minimum 10 years (as per IATF 16949).
Required Documentation
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
- Material Test Reports (MTRs)
- PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) documentation for OEM suppliers
- Customs declarations and import permits
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Defective or Non-Conforming Parts
- Establish clear return material authorization (RMA) process.
- Inspect returned parts and document root cause (e.g., manufacturing defect, shipping damage).
- Comply with local waste disposal regulations; recycle metal components where possible.
Warranty and Recall Management
- Track part serial numbers to enable rapid recall response.
- Coordinate with distributors and OEMs during safety-related recalls.
- Report incidents to relevant authorities (e.g., NHTSA in the U.S., RAPEX in EU) when required.
Best Practices Summary
- Partner with certified logistics providers experienced in automotive parts.
- Conduct regular compliance audits across suppliers and transportation partners.
- Invest in digital supply chain tools for real-time tracking and compliance monitoring.
- Train staff on changing regulations and hazardous materials handling.
By adhering to this guide, stakeholders can ensure the safe, compliant, and efficient movement of automotive suspension parts globally.
In conclusion, sourcing automotive suspension parts requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Selecting reputable suppliers, whether OEM, aftermarket, or remanufactured, is critical to ensuring vehicle safety, performance, and longevity. Factors such as material quality, manufacturing certifications, lead times, and after-sales support must be carefully evaluated to make informed procurement decisions. Additionally, leveraging global supply chain networks while maintaining stringent quality control helps optimize costs without compromising performance. Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy for suspension components supports efficient vehicle operation, enhances customer satisfaction, and contributes to long-term success in the automotive industry.