The automotive charcoal canister market is experiencing robust growth, driven by stringent global emissions regulations and increasing demand for fuel-efficient vehicles. According to Grand View Research, the global automotive evaporative emissions control systems market, which includes charcoal canisters, was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by the rising production of passenger and commercial vehicles, especially in emerging economies, as well as the adoption of advanced emission control technologies to comply with standards such as Euro 6 and EPA Tier 3. With automakers prioritizing vapor recovery systems to minimize hydrocarbon emissions, the demand for high-performance charcoal canisters has surged. As a result, a select group of manufacturers have risen to prominence, leveraging innovation, global supply chain integration, and strategic partnerships to capture market share. The following list highlights the top 10 automotive charcoal canister manufacturers shaping this evolving industry landscape.
Top 10 Automotive Charcoal Canister Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Carbtrol
Domain Est. 1998
Website: carbtrol.com
Key Highlights: For more than 35 years, Carbtrol has developed, designed and manufactured industrial activated carbon filter systems and related technologies….
#2 Fuel Vapor Carbon Canister
Domain Est. 1999
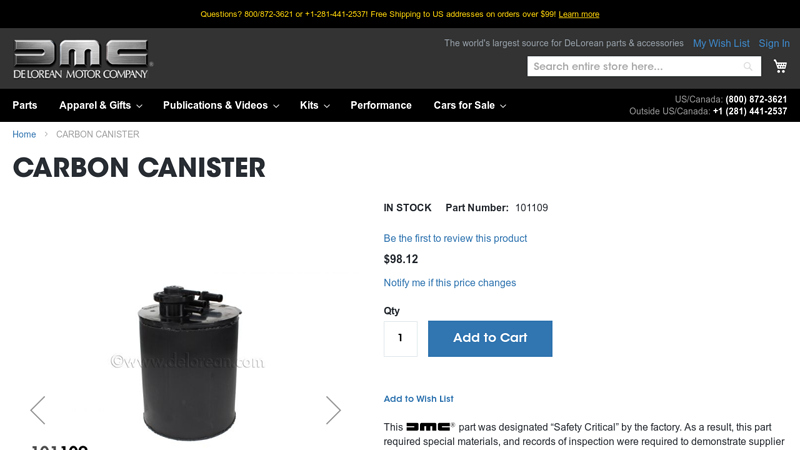
#3 Carbon Canister
Domain Est. 2013
Website: store.classicdmc.com
Key Highlights: Carbon Canister | Official Classic DeLorean Motor Company® | New, Original, and Reproduction Parts.Missing: automotive manufacturer…
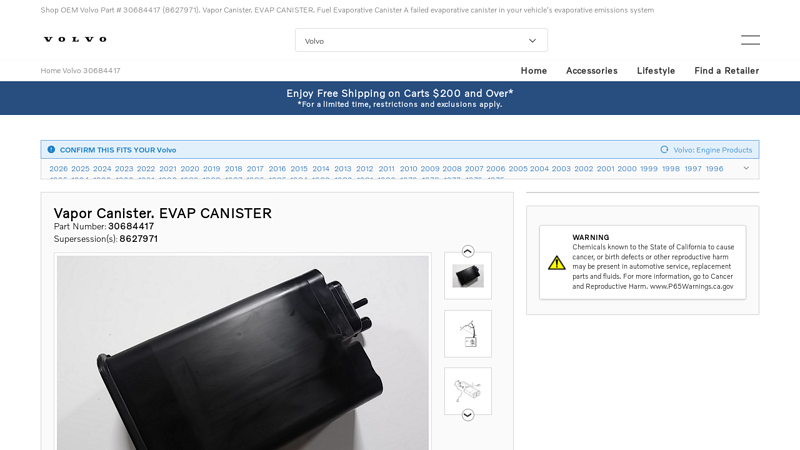
#4 30684417
Domain Est. 1994
Website: usparts.volvocars.com
Key Highlights: A failed evaporative canister in your vehicle’s evaporative emissions system, also known as a charcoal canister, will often have no noticeable symptoms beyond a ……
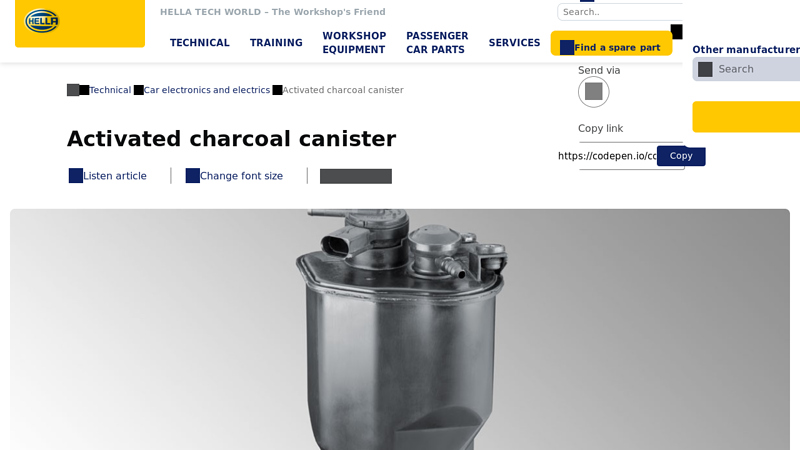
#5 Activated charcoal canister – facts & info
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hella.com
Key Highlights: The activated charcoal canister protects the environment against unburnt fuel vapours. This page explains how the system works, what could cause a fault, ……
#6 Stant
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stant.com
Key Highlights: Stant is a recognized world leader in the design and manufacturing of vapor management systems, fuel delivery systems, thermal management systems and ……
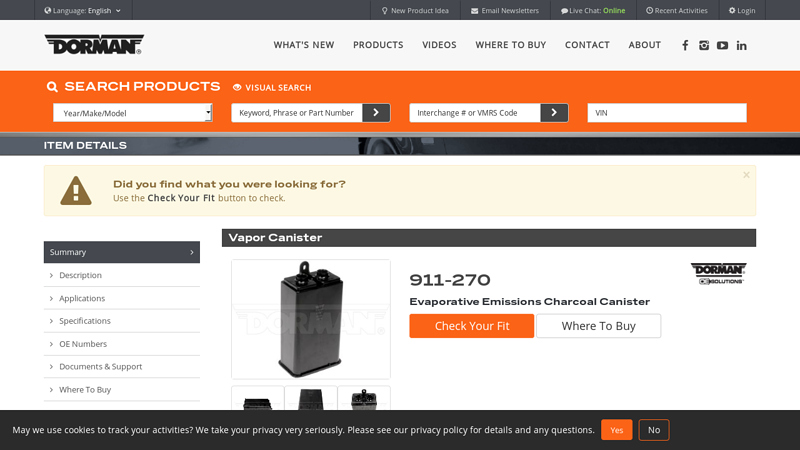
#7 Vapor Canister
Domain Est. 2001
Website: dormanproducts.com
Key Highlights: Direct replacement – this evaporative emissions charcoal canister matches the function and performance of the original canister on specified vehicles · Restores ……
#8 Components
Domain Est. 2009
Website: perkofuelsystems.com
Key Highlights: Carbon canisters have been used in automotive applications for decades. They filter hydrocarbons out of fumes vented during thermal expansion and/or ……
#9 Vapor Canister
Domain Est. 2010
Website: wellsve.com
Key Highlights: Wells Vapor Canisters are engineered and tested to match OE parts in fit, form and function and are compatible with both domestic and imported vehicles….
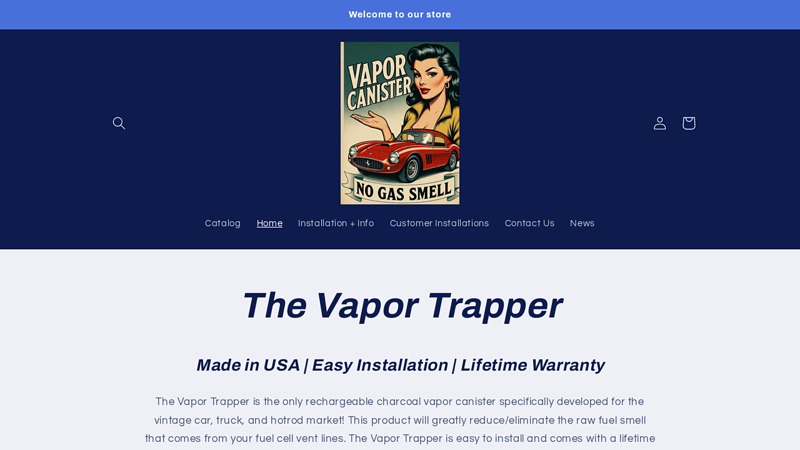
#10 Vapor Canister
Domain Est. 2023
Website: vaporcanister.com
Key Highlights: The Vapor Trapper is the only rechargeable charcoal vapor canister specifically developed for the vintage car, truck, and hotrod market!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automotive Charcoal Canister

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Automotive Charcoal Canisters
The global automotive charcoal canister market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by tightening vehicle emissions regulations, increasing production of internal combustion engine (ICE) and hybrid vehicles, and advancements in evaporative emission control technologies. As governments worldwide continue to enforce stricter environmental standards—such as Euro 7 in Europe, Bharat Stage VI in India, and Tier 3 standards in the United States—the demand for efficient evaporative emission control systems, including charcoal canisters, is expected to rise significantly.
A key trend shaping the 2026 market landscape is the integration of enhanced canister designs that offer higher hydrocarbon adsorption capacity and improved durability. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting advanced activated carbon materials and modular canister configurations to meet the performance requirements of both conventional and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). With HEVs experiencing frequent fuel tank pressure fluctuations due to intermittent engine operation, next-generation canisters are being engineered for better vapor management and longer service life.
Additionally, regional market dynamics will play a crucial role. Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Japan, is anticipated to dominate the market due to high vehicle production volumes and aggressive adoption of emission norms. Europe and North America will maintain strong demand, supported by regulatory compliance needs and the ongoing presence of ICE and plug-in hybrid vehicles during the transition to full electrification.
Despite the long-term shift toward battery electric vehicles (BEVs), which do not require charcoal canisters, the continued global reliance on ICE and hybrid platforms through 2026 ensures sustained market relevance. Furthermore, aftermarket replacement and servicing of canisters in existing vehicle fleets will contribute to market resilience.
In summary, the 2026 automotive charcoal canister market will be characterized by technological innovation, regulatory influence, and regional growth disparities, with manufacturers focusing on high-efficiency, compact, and cost-effective solutions to remain competitive in an evolving automotive ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Automotive Charcoal Canister (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing automotive charcoal canisters—critical components in evaporative emission control systems—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can result in non-compliance, recalls, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the most common pitfalls:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Quality Compliance
Many sourcing teams focus heavily on reducing unit cost, potentially compromising material quality and manufacturing standards. Low-cost canisters may use substandard activated carbon with reduced adsorption capacity or poor thermal stability, leading to premature failure and emissions non-compliance. Additionally, inferior plastic housings may crack under thermal cycling or fail burst pressure tests, jeopardizing system integrity.
Best Practice: Establish clear technical specifications aligned with OEM or regulatory standards (e.g., EPA, Euro 6), and conduct rigorous supplier audits and sample testing before qualification.
2. Inadequate Verification of Material and Performance Specifications
Suppliers may claim compliance with industry standards without providing verifiable test data. Performance attributes such as hydrocarbon breakthrough time, purge flow characteristics, and carbon loading efficiency are often not independently validated during sourcing.
Best Practice: Require full material disclosure (including carbon source and pelletization method) and third-party test reports for key performance metrics. Conduct in-house or lab-based validation for critical applications.
3. Overlooking Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Charcoal canister designs often incorporate patented technologies—such as unique internal flow baffles, valve mechanisms, or carbon bed configurations. Sourcing from suppliers using reverse-engineered or unlicensed designs exposes the buyer to IP infringement claims, especially in markets like North America and Europe where OEMs aggressively protect IP.
Best Practice: Conduct IP due diligence by reviewing supplier design origins and requesting IP indemnification clauses in contracts. Avoid “copycat” suppliers lacking design ownership or R&D capability.
4. Engaging Suppliers Without OEM Approvals or Qualifications
Some suppliers claim to produce “OEM-equivalent” parts without formal validation from vehicle manufacturers. Using such components in OE or aftermarket supply chains can void warranties and lead to liability if failures occur.
Best Practice: Verify if the supplier is on the OEM’s approved vendor list (AVL) or has documented qualifications (e.g., PPAP submission, IATF 16949 certification). Prioritize suppliers with proven OE experience.
5. Insufficient Attention to Long-Term Supply Chain Stability
Charcoal canister performance depends on consistent raw material quality—especially activated carbon, which may be sourced from volatile supply chains. Sudden changes in carbon grade or resin formulation due to supplier substitution can impact emissions performance without immediate detection.
Best Practice: Require supply chain transparency and long-term material sourcing agreements. Implement change notification protocols for any raw material or process changes.
6. Neglecting Regional Regulatory Variations
Emissions regulations vary by region (e.g., LEV III in California, China 6, Bharat Stage VI). A canister meeting one standard may not comply elsewhere due to differences in testing procedures or hydrocarbon retention requirements.
Best Practice: Clearly define target markets during sourcing and ensure canister design and testing align with all applicable regional regulations.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, automotive manufacturers and Tier suppliers can ensure reliable, compliant, and legally secure sourcing of charcoal canisters.
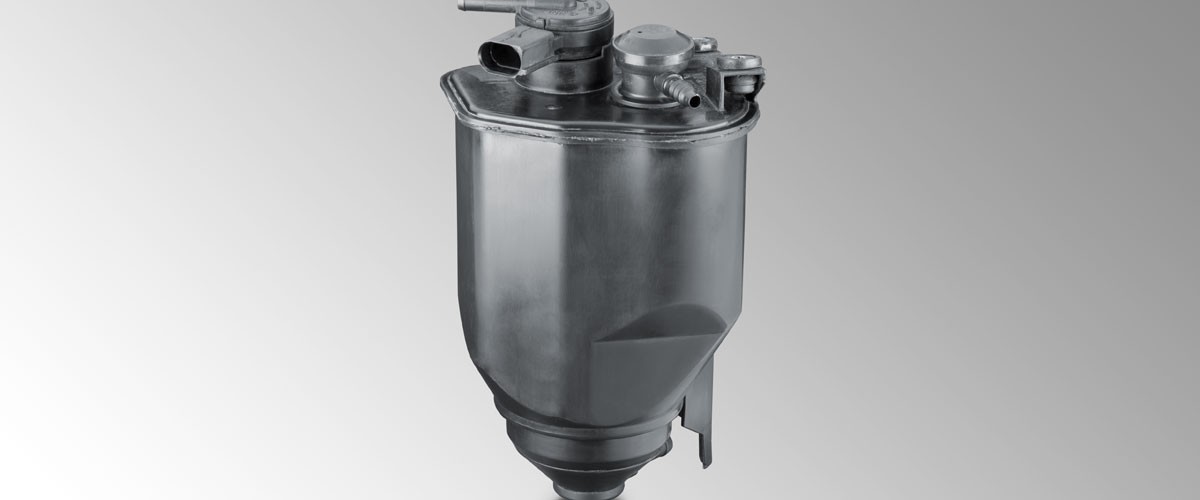

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automotive Charcoal Canister
Overview of Automotive Charcoal Canister
The automotive charcoal canister, also known as an evaporative emissions (EVAP) canister, is a critical component in modern vehicle emission control systems. It captures fuel vapors from the fuel tank and carburetor (if present), preventing their release into the atmosphere. These vapors are stored in activated carbon within the canister and later purged into the engine for combustion during normal operation. Due to its environmental and safety significance, proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance are essential throughout its supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Environmental Regulations
Automotive charcoal canisters are subject to stringent environmental regulations due to their role in controlling hydrocarbon emissions. Key regulatory frameworks include:
- EPA Standards (U.S.): The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) mandates compliance with evaporative emission standards under Title 40 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). Vehicles and their components, including charcoal canisters, must meet specific evaporative emission limits (e.g., LEV III, SULEV).
- Euro Emissions Standards (EU): In Europe, Regulation (EU) 2017/1151 and subsequent amendments under the Euro 6 and upcoming Euro 7 standards govern evaporative emissions. Canisters must demonstrate performance under specified test cycles and durability requirements.
- China GB Standards: In China, GB 18352.6-2016 sets limits on evaporative emissions, requiring certified canister performance as part of the vehicle type approval process.
Manufacturers and distributors must ensure that canisters are tested and certified according to these standards and that documentation is maintained for audit purposes.
Hazardous Materials & Transportation Safety
Although the charcoal canister itself is not classified as hazardous when empty, it may contain residual fuel vapors or activated carbon, which can pose risks under certain conditions.
- UN/DOT Classification: Activated carbon may be classified under UN 1362 (Carbon, activated) as a flammable solid (Class 4.2) if shipped separately or in bulk. However, when integrated into a fully assembled canister, it typically does not require hazardous labeling, provided it is dry and free of absorbed flammable liquids.
- IMDG Code (Maritime): For international sea freight, compliance with the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code is required. Assembled canisters not containing fuel residues are generally non-regulated, but packaging must prevent leakage or contamination.
- IATA Regulations (Air): Under IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations, activated carbon is regulated if shipped loose. Completed canisters are typically exempt if properly sealed and declared as non-hazardous.
- ADR/RID (Road/Rail in Europe): For European transport, ADR (road) and RID (rail) regulations apply. Assembled canisters with no residual fuel are generally not classified as dangerous goods.
Best practice includes ensuring canisters are purged and dry before shipment and providing Safety Data Sheets (SDS) when required.
Packaging & Handling Guidelines
Packaging Standards
Proper packaging ensures the integrity of the charcoal canister during transit and protects against contamination:
- Use moisture-resistant packaging to prevent degradation of activated carbon.
- Employ anti-static materials if shipping loose carbon or sensitive electronic purge valves.
- Secure canisters in rigid containers to prevent physical damage (cracking, deformation).
- Label packages with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Keep Dry.”
Storage Conditions
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, high temperatures (>60°C), and sources of ignition.
- Keep away from flammable liquids and strong oxidizers.
- Shelf life of unused canisters is typically 24–36 months; monitor batch dates.
Supply Chain & Logistics Considerations
Inventory Management
- Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation to ensure product freshness.
- Track lot numbers and compliance certifications for traceability.
- Coordinate with OEMs to align with just-in-time (JIT) or lean manufacturing schedules.
Import/Export Documentation
- Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Provide compliance documentation such as:
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
- Test reports (e.g., EVAP system performance)
- Material declarations (REACH, RoHS)
- For exports to the U.S., EPA emission-related parts must comply with 40 CFR Part 85, Subpart P, if sold separately.
Customs Classification
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Typically classified under 8708.29.50 (Parts and accessories of motor vehicles, evaporative emission control systems) in the U.S. Consult local customs authorities for region-specific codes.
- Duty rates and import restrictions vary by country—verify with local customs brokers.
End-of-Life & Recycling Compliance
Waste Management
- Spent charcoal canisters may contain absorbed hydrocarbons and should be treated as hazardous waste in some jurisdictions.
- Follow local regulations for disposal (e.g., EPA hazardous waste rules, EU Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive).
- Consider reclamation programs where activated carbon is regenerated or safely disposed.
REACH & RoHS Compliance (EU)
- Ensure materials used in canister construction (plastics, valves, carbon) comply with:
- REACH (EC 1907/2006): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals.
- RoHS (2011/65/EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances in electrical and electronic components (if applicable to purge valves or sensors).
Conclusion
The logistics and compliance landscape for automotive charcoal canisters involves adherence to environmental, safety, and trade regulations across multiple jurisdictions. By following proper packaging, transportation, documentation, and disposal protocols, stakeholders can ensure regulatory compliance, supply chain efficiency, and environmental responsibility. Regular audits and coordination with regulatory bodies and OEM partners are recommended to stay current with evolving standards.
Conclusion: Sourcing Automotive Charcoal Canisters
In conclusion, sourcing automotive charcoal canisters requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, compliance, and supply chain reliability. As critical components of evaporative emission control systems, charcoal canisters play a vital role in meeting environmental regulations and ensuring vehicle performance. Effective sourcing involves partnering with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards such as ISO/TS 16949 and demonstrate consistent manufacturing quality.
Key considerations include material specifications, custom design capabilities, and the supplier’s ability to scale production in line with OEM demands. Additionally, geographic proximity, lead times, and logistics must be evaluated to mitigate supply chain risks. Sustainability and responsible sourcing of activated carbon—often derived from coconut shells or coal—are also becoming increasingly important in aligning with corporate environmental goals.
Ultimately, a well-structured sourcing strategy for automotive charcoal canisters not only supports regulatory compliance and operational efficiency but also strengthens the overall resilience and competitiveness of the automotive supply chain. Regular supplier audits, ongoing performance monitoring, and fostering collaborative relationships will ensure long-term success in this specialized component procurement process.