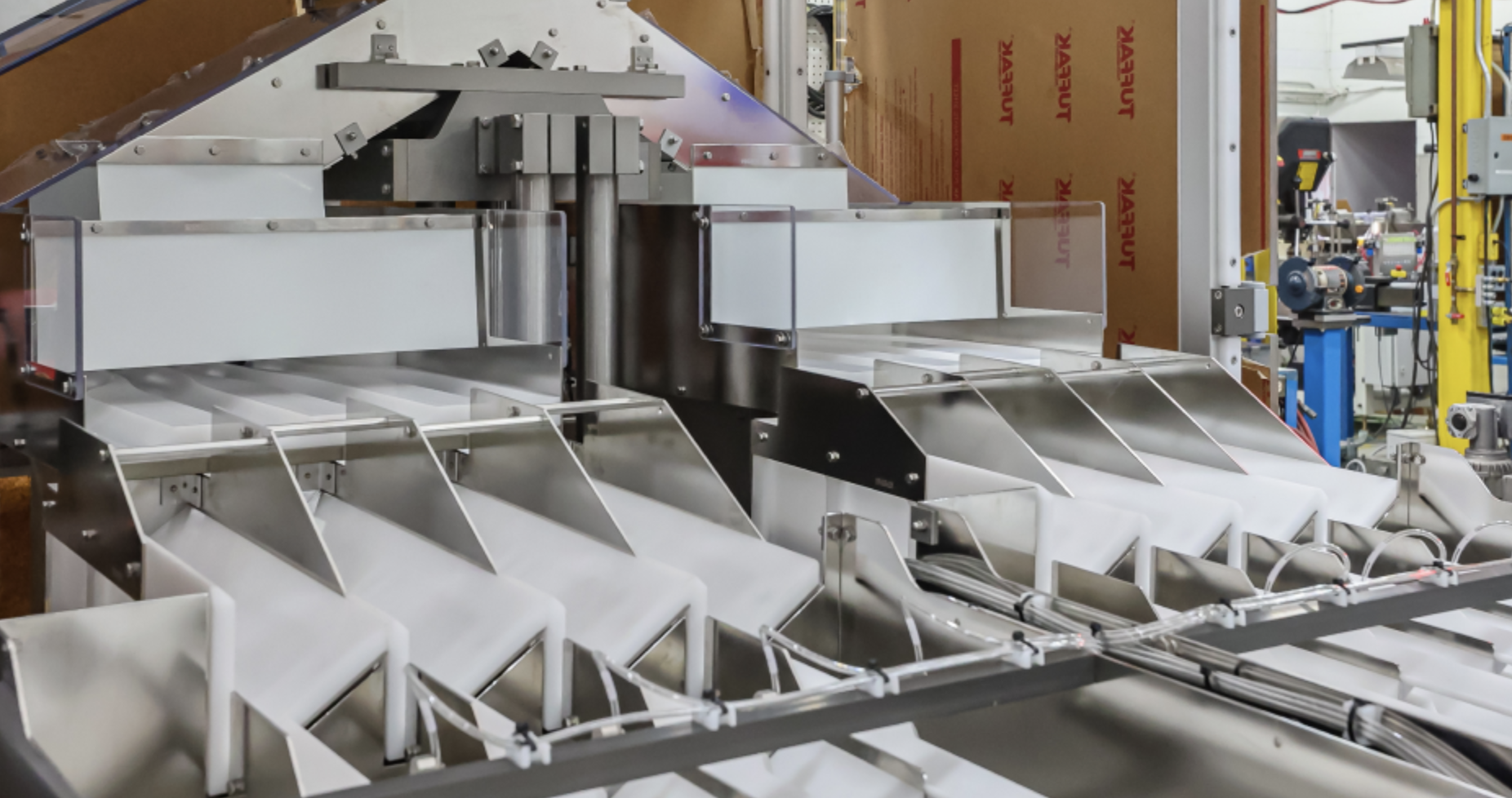
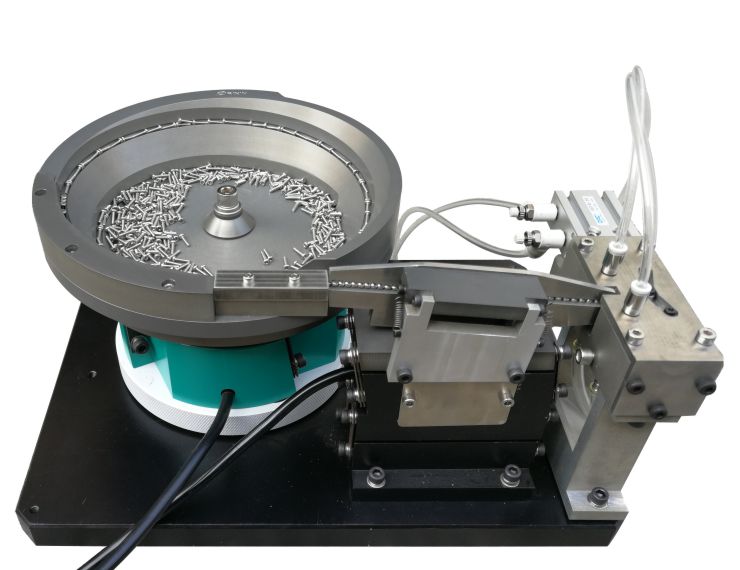
The automated feeding systems market has experienced robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision agriculture, labor cost reduction, and advancements in farm automation technologies. According to Grand View Research, the global smart agriculture market was valued at USD 13.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2% from 2023 to 2030, with automated feeding systems representing a key segment within this expansion. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects the livestock monitoring and automation market—encompassing automated feeders—to register a CAGR of over 9.5% during the forecast period 2023–2028. This growth is fueled by increasing livestock production efficiency targets, integration of IoT and data analytics, and supportive government initiatives promoting smart farming. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining innovation, scalability, and reliability to dominate the global supply landscape. Here are the top 10 automated feeders manufacturers shaping the future of modern animal husbandry.
Top 10 Automated Feeders Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Automatic Feeder Company Inc.
Domain Est. 1996
Website: automaticfeeder.com
Key Highlights: We design, fabricate, install and distribute custom automation equipment and systems. Our products include conveyors, feeders, prefeeders and automatically ……
#2 Industrial Automation Equipment & Flex Feeders
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1946
Website: feedall.com
Key Highlights: Since 1946, Feedall Automation has delivered the best in automation equipment. With the most advanced and comprehensive line of parts feeding systems available….
#3 Automation Devices
Domain Est. 1996
Website: autodev.com
Key Highlights: ADI is a vibratory feeding systems manufacturer with a vast product line of parts feeding and automation equipment serving a variety of industries….
#4 Performance Feeders
Domain Est. 1999
Website: performancefeeders.com
Key Highlights: Performance Feeders is a leading builder of vibratory feeders, centrifugal feeders, custom conveyor systems and part handling systems….
#5 Fortville Feeders
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1979
Website: fortvillefeeders.com
Key Highlights: Since 1979, Fortville Feeders has designed and built automated parts feeder systems to meet your unique manufacturing needs….
#6 Deer Feeders, Bird Feeders, Fish Feeders for Outdoors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sweeneyfeeders.com
Key Highlights: Automatic timers: Programmable digital timers deliver precise, consistent feeding schedules to support wildlife feeding. Pond and Lake Fish Feeders. Sweeney ……
#7 Friction Feeder Machines and Automated Packaging Systems
Domain Est. 2004
Website: pineberryinc.com
Key Highlights: We design, manufacture and integrate our Friction Feeders, Print on Demand, and Sortation systems to automate end to end Order Fulfilment and Packaging Lines….
#8 Asyril
Domain Est. 2007
Website: asyril.com
Key Highlights: Asyril specializes in the design of innovative systems that integrate perfectly into any automation machine to optimize its flexibility, ……
#9 About
Domain Est. 2012
Website: hoosierfeeder.com
Key Highlights: Hoosier Feeder started in 2007 with two brothers and a focus on building solid vibratory feeder bowls and backing it up with reliable service….
#10 Feeding systems: vibrating bowl feeder, conveyor, hopper
Domain Est. 2016
Website: icm-automation.com
Key Highlights: ICM designs its own medium or high-speed feeding systems in order to fully control the feeding of the automatic machines….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Automated Feeders
2026 Market Trends for Automated Feeders
The automated feeders market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and growing demand across various sectors. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Smart Integration and IoT Dominance
By 2026, IoT-enabled automated feeders will dominate the market. Devices will feature advanced connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G) allowing real-time monitoring, remote feeding control via mobile apps, and integration with smart home ecosystems like Google Home and Amazon Alexa. Predictive analytics will enable feeders to learn pet or livestock eating habits and adjust portions automatically, reducing waste and improving health outcomes.
2. AI and Machine Learning Optimization
Artificial intelligence will play a crucial role in personalizing feeding routines. AI algorithms will analyze consumption patterns, activity levels, and health data (via integrated sensors or companion wearables) to recommend optimal feed types and schedules. In agriculture, AI-driven feeders will enhance livestock productivity by tailoring nutrition to individual animal needs, supporting precision farming.
3. Expansion in Livestock and Aquaculture
Beyond pets, automated feeders will see accelerated adoption in commercial agriculture. In livestock farming, robotic systems will improve feed efficiency, reduce labor costs, and support sustainable practices. Similarly, in aquaculture, automated underwater feeders with environmental sensors will optimize feeding in response to water conditions, promoting healthier fish growth and minimizing ecological impact.
4. Focus on Sustainability and Eco-Design
Environmental concerns will drive innovation in materials and energy efficiency. Manufacturers will prioritize recyclable components, solar-powered units, and reduced plastic usage. Smart scheduling will help minimize overfeeding and food waste, aligning with global sustainability goals and appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
5. Growth in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe lead in adoption, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will experience rapid market growth. Rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and increased awareness of animal health will fuel demand for automated feeding solutions in both pet care and agriculture.
6. Enhanced Security and Customization
Biometric authentication (e.g., facial or RFID recognition for pets) will prevent unauthorized access. Customizable feeding zones, portion control, and multi-pet recognition will become standard features, especially in multi-animal households and large-scale farming operations.
In conclusion, the 2026 automated feeders market will be defined by intelligence, connectivity, and sustainability, serving diverse needs from companion animals to global food production systems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Automated Feeders: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing automated feeders—especially for specialized applications like industrial automation, agriculture, or pharmaceuticals—can present significant challenges. Two major areas where companies often encounter problems are product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can result in costly delays, operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Build and Performance Standards
Automated feeders sourced from low-cost or unverified suppliers may lack consistent manufacturing quality. Components such as motors, sensors, and control systems can vary significantly between batches, leading to unreliable performance, frequent breakdowns, and increased maintenance costs.
2. Lack of Rigorous Testing and Validation
Some suppliers skip comprehensive testing under real-world operating conditions. This can result in feeders that perform adequately in demonstrations but fail when integrated into high-throughput or continuous production environments.
3. Poor Material Selection and Durability
Inferior materials (e.g., substandard plastics, non-food-grade metals, or inadequate corrosion resistance) can compromise the longevity and safety of the feeder, especially in harsh or regulated environments (e.g., food processing or cleanrooms).
4. Inadequate Documentation and Support
Low-quality suppliers may provide incomplete technical documentation, unclear maintenance guidelines, or limited after-sales support. This complicates troubleshooting, integration, and compliance with industry standards.
5. Misaligned Specifications and Customization Gaps
Suppliers may overpromise on customization but deliver feeders that don’t fully meet technical requirements—such as feed rate accuracy, compatibility with existing systems, or integration with control software—leading to costly redesigns or retrofits.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Risk of IP Infringement
Sourcing from suppliers who use copied or reverse-engineered designs can expose your company to third-party patent, trademark, or copyright claims. This is particularly common with feeders manufactured in regions with weak IP enforcement.
2. Lack of IP Ownership Clarity
When custom feeders are developed, contracts may not clearly assign IP rights to the buyer. This can result in disputes over ownership of design improvements, software algorithms, or mechanical innovations, limiting your ability to modify, reproduce, or protect the technology.
3. Exposure of Proprietary Processes
Sharing detailed operational requirements with suppliers may inadvertently disclose trade secrets or unique production methods. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and secure development practices, this information could be used or shared without authorization.
4. Embedded Third-Party Software Risks
Automated feeders often include control software or firmware that may incorporate unlicensed or open-source code. This can introduce licensing compliance issues or vulnerabilities that impact your own product’s legality and security.
5. Supplier Lock-In and Dependency
If the supplier retains exclusive rights to critical components or software, you may become dependent on them for upgrades, repairs, or replacements—limiting your flexibility and increasing long-term costs.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including audits of manufacturing processes and quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
– Require detailed technical specifications, performance testing reports, and sample validation.
– Establish clear contractual terms around IP ownership, confidentiality, and compliance.
– Use NDAs and secure communication channels during the design and development phase.
– Engage legal counsel to review contracts and ensure IP protections are enforceable.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns during the sourcing process, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and secure automated feeding solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Automated Feeders
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the deployment and operation of automated feeders across various industries, including agriculture, manufacturing, and food service.
Supply Chain and Distribution Logistics
Ensuring timely delivery and installation of automated feeders requires coordination with suppliers, transporters, and on-site teams. Components such as motors, sensors, control units, and feed storage bins must be sourced reliably and shipped to intended locations. Use of standardized packaging and modular designs simplifies transportation and reduces damage risk. Maintain an inventory buffer for critical spare parts to minimize downtime.
Installation and Site Preparation
Prior to installation, assess site-specific logistics including power availability, network connectivity, and physical space requirements. Ensure ground stability and protection from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures. Coordinate with facility managers to schedule installation during low-activity periods to minimize operational disruption. Confirm alignment with building codes and safety regulations during setup.
Regulatory Compliance
Automated feeders must comply with relevant local, national, and international standards. In agricultural settings, adherence to animal welfare regulations (e.g., EU Directive 98/58/EC) is essential to ensure proper feeding schedules and portion control. In food processing environments, equipment must meet FDA or equivalent food safety standards (e.g., 21 CFR Part 117) for sanitation and material safety. All electrical components should be certified (e.g., CE, UL) for safe operation.
Data Management and Cybersecurity
Many automated feeders incorporate IoT capabilities for remote monitoring and data collection. Ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR or CCPA when storing or transmitting operational data. Implement secure communication protocols (e.g., TLS encryption) and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly update firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
Maintenance and Servicing Logistics
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule to inspect mechanical components, clean feed pathways, and verify sensor accuracy. Train on-site personnel or contract service providers to perform routine checks. Maintain a log of maintenance activities for audit and compliance purposes. Service vehicles should carry essential tools and replacement parts to reduce turnaround time.
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
Evaluate the environmental impact of automated feeders, including energy consumption and material waste. Optimize feeder programming to reduce overfeeding and food waste, supporting sustainability goals. Recycle end-of-life units in accordance with local e-waste regulations (e.g., WEEE Directive in the EU). Use energy-efficient components to meet environmental standards and reduce operational costs.
Training and Operational Documentation
Provide comprehensive training for operators and maintenance staff on safe and efficient use of automated feeders. Maintain up-to-date user manuals, safety warnings, and emergency shutdown procedures. Documentation should be readily accessible on-site and available in required languages to meet workplace safety standards (e.g., OSHA regulations).
Monitoring and Audit Readiness
Implement logging features to record feeding times, quantities dispensed, and system alerts. This data supports traceability and is critical during regulatory audits. Regularly review system performance against compliance benchmarks and adjust protocols as needed to maintain adherence to evolving standards.
Conclusion: Sourcing Automated Feeders
After thorough evaluation of market options, technical requirements, and operational needs, sourcing automated feeders presents a strategic opportunity to enhance efficiency, consistency, and scalability in feeding operations. These systems reduce labor dependency, minimize waste, and ensure precise portion control, contributing to improved animal health and overall productivity.
Key considerations in the sourcing process—such as reliability, ease of maintenance, compatibility with existing infrastructure, and supplier support—underscore the importance of selecting vendors with proven track records and responsive service networks. Additionally, investing in scalable and adaptable technology allows for future expansion and integration with other smart farming systems.
In conclusion, sourcing automated feeders is a worthwhile investment for modern agricultural and livestock operations aiming to optimize resource use, improve animal welfare, and increase long-term profitability. With careful vendor selection and proper implementation, automated feeding systems can deliver significant operational advantages and a strong return on investment.