The global automotive sensor market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), electric vehicles (EVs), and vehicle electrification. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 23.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 41.82 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 11.9% during the forecast period. This growth is further amplified by rising safety regulations, the push for autonomous driving technologies, and the integration of IoT in modern vehicles. As sensors become critical components in powertrain, safety, and environmental monitoring systems, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, shaping innovation and setting performance benchmarks. The following list highlights the top nine auto sensor manufacturers leading this transformation, based on market presence, technological advancement, and product scalability.
Top 9 Auto Sensor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SensoPart
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sensopart.com
Key Highlights: Sensor technology for businesses: ✓ Innovative sensors for your industry sector ✓ Leading sensor manufacturer for more than 30 years ➧ Get expert advice!…
#2 CTS Corporation
Domain Est. 1993
Website: ctscorp.com
Key Highlights: CTS aims to be at the forefront of technology, delivering innovative sensing, connectivity and motion solutions to enable an intelligent and seamless world. Our ……
#3 Sensors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata manufactures a wide variety of high-quality, high-precision sensors thanks to knowledge accumulated over many years, starting with our advanced circuit ……
#4 OMNIVISION
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ovt.com
Key Highlights: OMNIVISION is a leading Semiconductor Manufacturer of Sensing, Analog and Touch & Display Solutions. We offer imaging solutions for the Automotive, ……
#5 Sensata Technologies
Domain Est. 2001
Website: sensata.com
Key Highlights: Our broad range of sensor and control solutions enables smarter and more sustainable industrial designs….
#6 SSI Technologies, LLC
Domain Est. 2011
Website: ssi-sensors.com
Key Highlights: SSI Technologies, LLC, a leading OEM supplier of automotive sensors, has delivered more than 100 million units to its customers where cost, size, and ……
#7 FAE
Founded: 1952
Website: fae.es
Key Highlights: FAE – Francisco Albero S.A.U. is a European automotive manufacturer that has been designing and manufacturing electrical and electronic products since 1952….
#8
Domain Est. 1996
Website: invensense.tdk.com
Key Highlights: TDK InvenSense provides world-leading MEMS sensors and magnetic sensor solutions for consumer and automotive applications that require precision and low power….
#9 Piher Sensing Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: piher.net
Key Highlights: We are experts in contactless and contacting sensor technologies for position, tilt, speed and current measurement. With over 70 years’ experience….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Auto Sensor
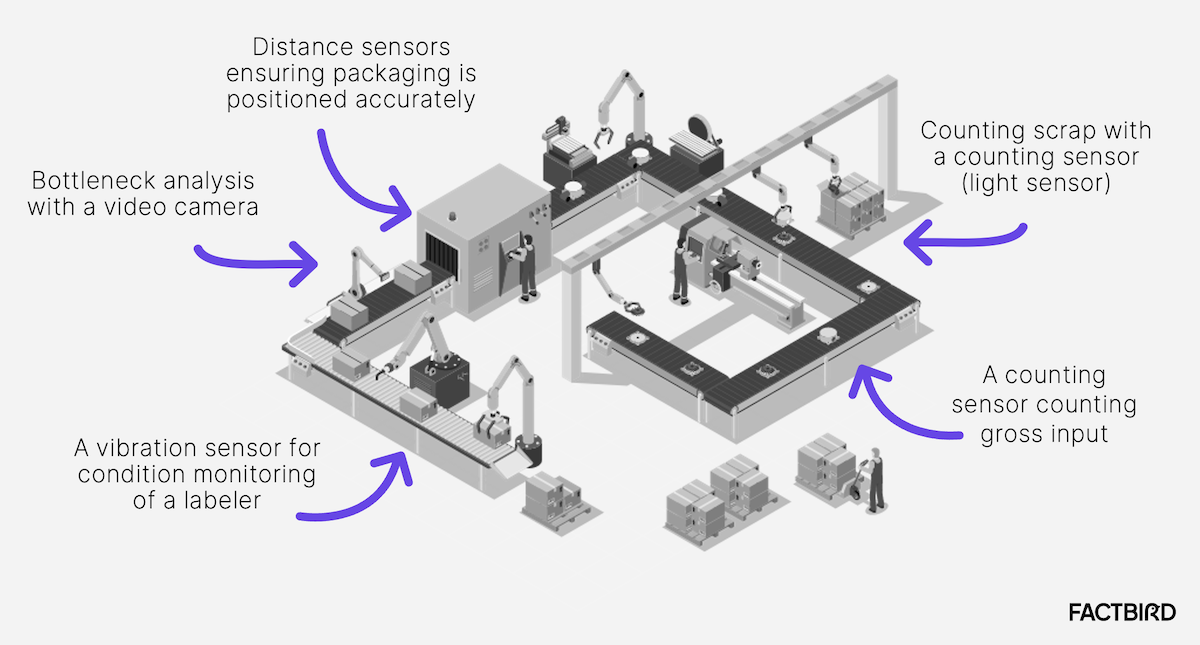
H2 2026 Market Trends for Auto Sensors
The automotive sensor market in H2 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by the accelerating convergence of electrification, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and vehicle connectivity. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
-
Accelerated ADAS Penetration & Sensor Fusion Dominance:
- Regulatory Push: Stricter global safety regulations (e.g., Euro NCAP 2026, NHTSA mandates) are compelling OEMs to deploy Level 2+ ADAS features (automatic emergency braking, lane keeping, adaptive cruise) as standard equipment, significantly boosting demand for radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors.
- Sensor Fusion Imperative: Achieving higher automation levels (Level 3/4) requires robust sensor fusion. H2 2026 will see a surge in demand for high-performance radar (4D imaging radar) and high-resolution cameras (8MP+) as core components, alongside LiDAR gaining traction in premium segments. Suppliers offering integrated fusion software stacks will gain a competitive edge.
- Radar Evolution: 4D imaging radar becomes more mainstream, offering superior object classification, elevation detection, and performance in adverse weather compared to traditional radar, creating opportunities for semiconductor and module suppliers.
-
Electric Vehicle (EV) Ecosystem Expansion:
- Battery & Powertrain Sensing: The proliferation of EVs drives massive demand for high-accuracy battery management system (BMS) sensors (voltage, current, temperature) and motor position/speed sensors (resolvers, encoders). Demand for current sensors (especially closed-loop Hall effect and fluxgate) remains exceptionally high.
- Thermal Management: Complex EV thermal systems require more temperature sensors (PTC/NTC) and pressure sensors across batteries, motors, and power electronics.
- Efficiency Focus: Sensors enabling predictive maintenance and optimizing powertrain efficiency (e.g., advanced pressure sensors in HVAC, motor control) are critical for maximizing EV range.
-
Connected & Smart Mobility Integration:
- V2X Enablement: As V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) deployment grows (driven by infrastructure investment), demand increases for positioning sensors (high-precision GNSS, IMUs) and environmental sensors that feed data into V2X communication modules. These enable cooperative ADAS and traffic efficiency applications.
- In-Cabin Sensing: Focus on driver monitoring systems (DMS) and occupant monitoring systems (OMS) intensifies due to regulations (e.g., Euro NCAP) and safety concerns. This drives demand for in-cabin cameras, IR sensors, and microphones. Occupant presence detection sensors (radar, ultrasonic) become standard for airbag deployment and child presence alerts.
- Data as a Service: Sensor data (anonymized and aggregated) becomes valuable for traffic management, urban planning, and insurance (UBI), creating new revenue models for OEMs and sensor/data platform providers.
-
Supply Chain Resilience & Localization:
- Geopolitical Diversification: Ongoing supply chain lessons and geopolitical tensions will push OEMs and Tier 1s to further localize sensor production (especially in North America and Europe via CHIPS Act/Inflation Reduction Act incentives) and diversify suppliers, benefiting regional manufacturers.
- Vertical Integration: Key players (e.g., Tesla, some Tier 1s) may increase in-house sensor development and production for strategic control and cost optimization, particularly for critical ADAS components.
-
Technology & Cost Pressures:
- Miniaturization & Integration: Demand grows for smaller, more integrated sensor modules (e.g., combined radar/camera units) to save space, reduce weight, and lower costs.
- Cost Reduction Imperative: As ADAS and EV features become standard, intense price pressure on sensors continues. This drives innovation in semiconductor processes (e.g., SiC, advanced nodes), packaging, and manufacturing efficiency.
- Sustainability Focus: Increased scrutiny on material sourcing, recyclability, and energy efficiency in sensor manufacturing and operation.
Conclusion: H2 2026 presents a dynamic and growth-oriented market for auto sensors, fundamentally driven by safety regulations, electrification, and connectivity. Success will favor suppliers offering technologically advanced, cost-effective, and reliable sensors (particularly in radar, camera, LiDAR, and EV-specific types), with strong capabilities in sensor fusion software, robust supply chains, and regional manufacturing presence. The integration of sensors into broader vehicle intelligence and data ecosystems will be a defining characteristic.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Auto Sensors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing automotive sensors requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to significant risks, including product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Assurance and Inadequate Testing
One of the most frequent issues is selecting suppliers that lack rigorous quality control processes. Automotive environments demand high reliability due to extreme temperatures, vibration, and safety-critical functions. Sensors that haven’t undergone proper AEC-Q100 or ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949) qualification may fail prematurely, leading to costly recalls or safety hazards.
Misrepresentation of IP Ownership
Suppliers may claim ownership of sensor designs or embedded firmware when, in reality, the IP is licensed, shared, or even infringes on third-party patents. Failing to conduct thorough IP due diligence can result in legal liability, production halts, or forced redesigns. Always verify patent portfolios, design rights, and licensing agreements.
Use of Counterfeit or Substandard Components
Low-cost suppliers may use counterfeit or out-of-spec components to cut costs. These components often fail under real-world conditions and can compromise the entire vehicle system. Implement strict supply chain traceability and perform independent component testing to mitigate this risk.
Lack of Long-Term Supply Commitment
Automotive product lifecycles span years, sometimes decades. Suppliers without a clear long-term supply strategy may discontinue sensors unexpectedly, disrupting production. Ensure contracts include obsolescence management plans and last-time buy (LTB) notifications.
Inadequate Documentation and Compliance
Missing or incomplete documentation—such as material composition (RoHS, REACH), test reports, or failure mode analyses—can delay certifications and audits. Ensure suppliers provide full compliance documentation aligned with automotive standards.
Overlooking Software and Firmware IP
Many modern sensors include proprietary firmware or calibration algorithms. If not properly licensed or transferred, this can restrict your ability to service, update, or integrate the sensor. Clarify software licensing terms and source code availability upfront.
Insufficient Supplier Audits
Relying solely on certifications without on-site audits can be misleading. Conduct regular audits to verify manufacturing practices, quality systems, and IP handling procedures at the supplier’s facility.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a structured sourcing strategy that emphasizes technical validation, legal diligence, and long-term partnership development with trusted suppliers.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Auto Sensor
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance requirements for the distribution, import, export, and handling of Auto Sensor products. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, operational efficiency, and product integrity across the supply chain.
Product Classification & Documentation
Auto Sensors are typically classified under HS Code 8542.39 (Integrated Circuits) or 8537.10 (Control Panels/Boards) depending on design. Confirm exact classification with local customs authorities. Required documentation includes a Commercial Invoice, Packing List, Bill of Lading/Air Waybill, Certificate of Origin, and Product Compliance Certificates (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS).
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all Auto Sensor models meet regional regulatory standards:
– EU: CE marking, RoHS 2 (2011/65/EU), REACH, and WEEE compliance.
– USA: FCC Part 15 certification for electromagnetic compatibility.
– China: CCC certification if applicable; adherence to China RoHS.
– Global: IATF 16949 quality management standards for automotive components.
Maintain up-to-date technical files and Declaration of Conformity for audit readiness.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Use ESD-safe packaging with anti-static shielding for all Auto Sensors. Label each unit with:
– Product name and model number
– Serial/lot number
– CE/FCC mark (as applicable)
– RoHS compliance symbol
– Manufacturer information
– Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”)
Outer shipping boxes must include barcodes, shipping marks, and hazard labels if batteries are included.
Shipping & Transportation
Ship via certified logistics partners experienced in handling electronic components. Use temperature-controlled environments when necessary (operating range: -40°C to +105°C; storage: -40°C to +85°C). Avoid exposure to moisture, vibration, and extreme pressure. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if sensors contain restricted materials.
Import/Export Controls
Verify export licensing requirements under EAR (U.S.) or similar regimes. Some sensor technologies may be subject to dual-use controls. Screen end-users against denied party lists (e.g., BIS, EU, UN). Maintain records of export transactions for a minimum of five years.
Inventory & Warehousing
Store Auto Sensors in a clean, dry, climate-controlled warehouse (15–30°C, 30–60% RH). Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory rotation. Use ESD-protected storage areas and grounded shelving. Conduct quarterly audits to ensure stock integrity and traceability.
Returns & End-of-Life Management
Establish a returns authorization (RMA) process for defective units. For end-of-life products, comply with WEEE directives by partnering with certified e-waste recyclers. Maintain documentation of proper disposal or recycling to meet environmental obligations.
Audit & Recordkeeping
Conduct annual internal compliance audits covering logistics, safety, and regulatory adherence. Retain all shipping, compliance, and transaction records for a minimum of seven years. Prepare for third-party or regulatory inspections with accessible digital archives.
Adhering to this guide ensures seamless logistics operations and full compliance with international standards for Auto Sensor distribution.
Conclusion for Sourcing Auto Sensors:
In conclusion, sourcing auto sensors requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. As automotive systems become increasingly reliant on sensor technology for safety, performance, and connectivity, selecting the right suppliers is critical. Key considerations include technical specifications, supplier reputation, production scalability, certifications (such as ISO/TS 16949), and after-sales support. A diversified sourcing strategy—leveraging both established manufacturers and innovative technology partners—can enhance supply chain resilience and support continuous innovation. Ultimately, effective sourcing of auto sensors not only ensures optimal vehicle functionality but also contributes to long-term competitiveness in the rapidly evolving automotive market.