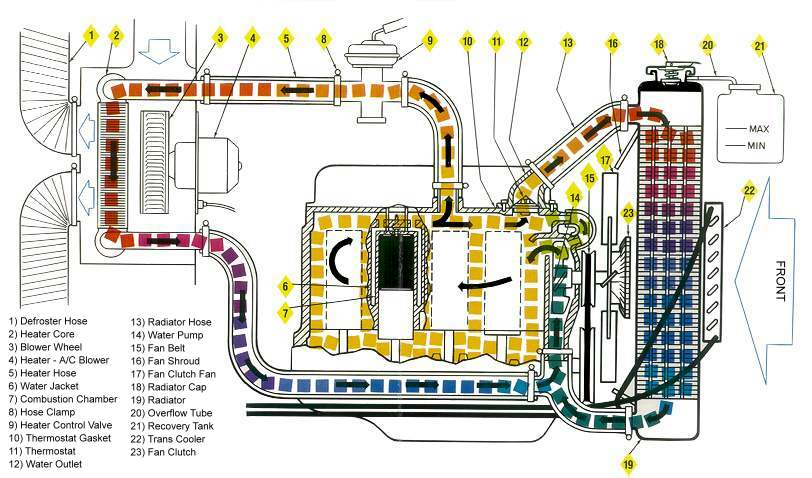
The global automotive cooling systems market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing vehicle production, stricter emission regulations, and the rising adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles that demand advanced thermal management. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 21.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 32.4 billion by the end of the forecast period. This growth is further fueled by technological advancements such as electric water pumps, smart thermostats, and integrated cooling modules that enhance engine efficiency and vehicle reliability.
As automakers prioritize performance, fuel efficiency, and sustainability, the demand for high-performance cooling solutions has intensified—positioning key manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and scale. The following list highlights the top nine auto cooling system manufacturers shaping the industry through technological leadership, global reach, and strategic partnerships. These players are not only responding to current automotive trends but are also engineering the next generation of thermal management systems for internal combustion, hybrid, and fully electric vehicles.
Top 9 Auto Cooling System Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Nissens Automotive
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nissens.com
Key Highlights: As a market-leading manufacturer, Nissens offers a comprehensive thermal & efficiency systems spare parts selection for all vehicle segments….
#2 Engine Cooling Systems
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hortonww.com
Key Highlights: Horton, Inc. is a leading provider of engine cooling systems for a wide range of industries, offering top-quality fan drives, fan clutches, and fans for ……
#3 Titanx Engine Cooling
Domain Est. 2004
Website: titanx.com
Key Highlights: TitanX is a global partner to commercial vehicles manufacturers for heat transfer and engaged in developing thermal management solutions for a cleaner ……
#4 CSF Manufactures Quality and Affordable Vehicle Cooling Products
Domain Est. 2009
Website: csfradiators.com
Key Highlights: CSF manufactures high quality OEM replacement radiators, condensers, intercoolers, transmission oil coolers and more!…
#5 Four Seasons
Domain Est. 1996
Website: 4s.com
Key Highlights: Four Seasons manufactures, remanufactures and distributes a full line of replacement components for mobile climate control and cooling systems. Four Seasons ……
#6 Cooling
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mahle.com
Key Highlights: Cooling for commercial vehicles · Engine cooling components, modules, and systems · Charge air coolers · Cooling modules · Low temperature radiators · Oil heating ……
#7 US Radiator
Domain Est. 1998
Website: usradiator.com
Key Highlights: For over 50 years, U.S. Radiator Corp. has been in the business of providing cooling system confidence. Correct Radiator Fit And Performance….
#8 MotoRad
Domain Est. 2002
Website: motorad.com
Key Highlights: Motorad develops, manufactures and supplies a range of products, including thermostats, caps and sensors, compatible with existing and emerging technologies….
#9 CSF Race
Domain Est. 2010
Website: csfrace.com
Key Highlights: Products. Drop-In Fit Cooling · Intercooler Cores · Universal Oil Coolers · Custom Finishes · Black Series · EV Cooling · Private Label · OE Replacement….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Auto Cooling System

H2: Projected Market Trends for the Auto Cooling System Industry in 2026
By 2026, the global auto cooling system market is expected to undergo significant transformation driven by technological innovation, regulatory mandates, and shifts in the automotive landscape. As vehicle electrification accelerates and emission standards tighten worldwide, cooling system manufacturers are adapting to meet the evolving thermal management demands of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, hybrids, and battery electric vehicles (BEVs). This analysis outlines key trends shaping the auto cooling system market in 2026.
-
Rise of Electric Vehicles and Advanced Thermal Management
The growing adoption of electric vehicles is a primary driver in the auto cooling system market. Unlike ICE vehicles, EVs require sophisticated thermal management systems to regulate battery temperature, maintain optimal performance, and extend battery life. By 2026, liquid cooling systems—particularly cold plate and direct cooling technologies—are expected to dominate the EV segment due to their superior efficiency and reliability. Additionally, integrated thermal systems that manage battery, motor, and power electronics cooling within a single architecture will gain prominence, enabling weight reduction and improved energy efficiency. -
Shift Toward Lightweight and Compact Designs
Automakers are under pressure to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, leading to increased demand for lightweight, compact cooling components. In 2026, aluminum and composite materials will continue to replace traditional copper and steel in radiators and heat exchangers, reducing overall vehicle weight and enhancing performance. Miniaturized and modular cooling systems, designed for space-constrained electric drivetrains, will be critical in urban EVs and autonomous vehicles. -
Integration of Smart Cooling Technologies
The integration of sensors, electronic controls, and predictive algorithms into cooling systems will become standard by 2026. Smart thermostats, variable-speed electric pumps, and adaptive fan controls will enable dynamic thermal regulation based on real-time driving conditions and component loads. These intelligent systems will improve energy efficiency, reduce thermal stress, and support advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) that generate additional heat. -
Growth in Hybrid and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles, which combine ICE and electric powertrains, present complex thermal challenges due to the need to cool multiple heat sources. The hybrid segment is projected to grow steadily through 2026, especially in emerging markets where full electrification is still developing. Cooling systems tailored for dual-powertrain architectures—capable of managing both engine and battery heat—will see increased investment and innovation. -
Stringent Emission Regulations and Environmental Standards
Global emissions regulations, such as Euro 7 in Europe and China 6b, will compel automakers to adopt more efficient cooling solutions that support lower engine temperatures and reduced NOx emissions. Simultaneously, environmental concerns are pushing the industry toward refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP). The transition from R-134a to R-1234yf and natural refrigerants like CO₂ (R-744) in air conditioning systems will influence overall vehicle thermal designs, including condenser and evaporator configurations. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Japan, will remain the largest market for auto cooling systems in 2026 due to high vehicle production and rising demand for electric mobility. Europe will lead in the adoption of advanced and sustainable cooling technologies, driven by strict environmental policies. North America will see growth tied to light-duty truck and SUV electrification, where robust cooling systems are essential due to higher payloads and towing demands. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
The complexity of next-generation cooling systems is prompting increased collaboration between OEMs, Tier-1 suppliers, and tech companies. By 2026, strategic partnerships focused on thermal system integration, software control, and R&D in materials science will be commonplace. Mergers and acquisitions are expected to consolidate the market, with leading players such as Mahle, BorgWarner, Denso, and Valeo expanding their portfolios to offer full thermal management solutions.
In conclusion, the auto cooling system market in 2026 will be defined by innovation in electric vehicle thermal management, the adoption of smart and lightweight technologies, and compliance with global environmental standards. As vehicles become more electrified and connected, cooling systems will evolve from passive components into intelligent, integrated subsystems critical to vehicle performance, safety, and efficiency.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Auto Cooling Systems (Quality & IP)
Sourcing automotive cooling systems involves significant technical and legal complexities. Overlooking key aspects can lead to costly quality failures, production delays, or intellectual property (IP) disputes. Here are critical pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Supplier Qualification
Failing to thoroughly audit a supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, quality management systems (e.g., IATF 16949 certification), and track record in the automotive sector can result in inconsistent product quality. Suppliers without robust statistical process control (SPC) or failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) practices are high-risk.
Insufficient Testing and Validation
Relying solely on supplier-provided test data without independent verification through durability, thermal cycling, burst pressure, and corrosion resistance testing can expose you to premature field failures. Real-world conditions (e.g., extreme temperatures, vibration) must be replicated.
Material and Component Substitution
Unapproved substitutions of materials (e.g., lower-grade aluminum or plastics) or sub-components (e.g., thermostat, water pump impeller) may meet basic specs but fail under long-term stress, affecting reliability and safety.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor batch tracking, missing material certificates (e.g., RoHS, REACH), or inadequate inspection reports make root cause analysis during failures difficult and complicate recall management.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unlicensed or Infringing Designs
Sourcing from suppliers using patented designs (e.g., fin geometry, pump housing) without proper licensing exposes your company to infringement claims, product seizures, and legal liability. This is especially common with OEM-equivalent parts.
Ambiguous IP Ownership in Custom Designs
When co-developing a cooling system, failing to define IP ownership in the contract can lead to disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to improvements or tooling, limiting your ability to switch manufacturers or modify the design.
Reverse-Engineered Components
Using suppliers that replicate OEM parts without innovation risks violating design patents and utility models. These components often lack performance validation and can undermine brand reputation.
Inadequate Protection of Internal Specifications
Sharing detailed technical drawings or performance requirements without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or proper marking of confidential information can result in IP leakage or misuse by the supplier.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct comprehensive due diligence on suppliers, including on-site audits.
- Require full compliance with automotive standards (e.g., ISO 16750, SAE J2028).
- Perform independent third-party testing and validation.
- Clearly define IP rights, licensing, and confidentiality in sourcing contracts.
- Use only authorized or licensed designs and conduct freedom-to-operate (FTO) analyses.
- Implement strict change control and material approval processes (e.g., PPAP).
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and protection against legal and financial risks in the competitive automotive supply chain.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Auto Cooling Systems
This guide outlines the essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the transportation, storage, and handling of automotive cooling systems, including radiators, water pumps, thermostats, coolant hoses, expansion tanks, and related components.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure adherence to international, national, and regional regulations governing the shipment and handling of automotive parts, especially those containing or transporting fluids.
Environmental Regulations
Auto cooling systems may contain residual coolant or be shipped with coolant, which is often classified as hazardous material. Comply with environmental laws such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations, EU REACH and RoHS directives, and local waste management statutes. Proper disposal of used components and fluids must follow hazardous waste protocols where applicable.
Hazardous Materials Handling
If shipping with coolant (e.g., ethylene glycol or propylene glycol), classify the shipment according to the UN Model Regulations (e.g., UN 3082 for environmentally hazardous substances, liquid). Use proper labeling, packaging, and documentation per IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or 49 CFR (U.S. ground transport) standards.
Import/Export Controls
Verify compliance with customs regulations in both origin and destination countries. Ensure accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes are used—for example, HS 8708.91 for radiators. Obtain necessary permits, especially when exporting to regions with strict automotive part standards (e.g., EU, China, GCC).
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and regulatory compliance during transit.
Packaging Requirements
Use durable, moisture-resistant packaging to prevent corrosion and physical damage. For radiators and fragile components, use corner protectors and interior cushioning. Seal coolant hoses and components in vacuum or sealed plastic to prevent contamination.
Labeling Compliance
All packages must display:
– Product identification (part number, description)
– Handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”)
– Hazard labels if shipping with coolant (e.g., “Environmentally Hazardous”)
– Country of origin
– Compliance marks (e.g., CE, DOT, ISO)
Transportation and Storage
Manage logistics operations to maintain product quality and meet delivery timelines.
Transportation Modes
Choose transport based on urgency, cost, and component sensitivity:
– Air freight: For time-sensitive shipments; ensure compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if coolant is present.
– Ocean freight: Cost-effective for bulk shipments; use sealed containers to prevent moisture exposure.
– Ground transport: Ideal for regional distribution; secure loads to avoid vibration damage.
Storage Conditions
Store components in dry, temperature-controlled environments (15–25°C recommended). Avoid direct sunlight and humidity to prevent rubber degradation and metal corrosion. Stack packages according to weight limits and use pallets for stability. Segregate hazardous shipments from non-hazardous goods.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Maintain traceability and compliance through accurate record-keeping.
Certifications and Inspections
Ensure all components meet industry standards such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO/TS 16949 (automotive), and OEM-specific requirements. Conduct pre-shipment inspections and maintain test reports for materials and pressure testing (e.g., radiator burst pressure tests).
Required Documentation
Prepare and retain:
– Commercial invoice and packing list
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS) for coolant-containing shipments
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Import permits or Letters of Authorization, if required
End-of-Life and Reverse Logistics
Plan for product returns, recalls, and recycling in accordance with environmental laws.
Recycling and Disposal
Partner with certified recyclers for end-of-life cooling systems. Metals (aluminum, copper) and plastics should be processed per local e-waste or automotive recycling regulations. Recover and reprocess used coolant where feasible.
Return Management
Establish a reverse logistics process for defective or excess inventory. Use tracked returns with clear labeling and documentation to ensure accountability and compliance with warranty and repair programs.
By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure safe, compliant, and efficient handling of auto cooling systems across the supply chain.
Conclusion: Sourcing an Auto Cooling System
Sourcing an auto cooling system requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, reliability, and long-term performance. A well-sourced cooling system ensures optimal engine temperature regulation, enhances vehicle efficiency, and contributes to the overall longevity and safety of the automotive application. Key considerations include selecting reputable suppliers with proven industry experience, verifying compliance with international standards (such as ISO/TS 16949), and evaluating the technical compatibility of components like radiators, water pumps, thermostats, hoses, and cooling fans.
Additionally, factors such as supply chain stability, lead times, after-sales support, and total cost of ownership should be thoroughly assessed. The growing trend toward electric and hybrid vehicles also demands forward-thinking sourcing strategies that accommodate advanced cooling technologies, including battery and power electronics thermal management systems.
In conclusion, effective sourcing of auto cooling systems is not merely a procurement decision but a critical component of vehicle design and performance. By partnering with reliable suppliers and staying attuned to technological advancements, automotive manufacturers and aftermarket providers can ensure high-quality, efficient, and sustainable cooling solutions that meet current and future industry demands.