The global artificial synthetic leather market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising environmental concerns, ethical considerations, and advancements in material technology. According to a report by Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 36.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by increasing demand from the automotive, fashion, and furniture industries, where manufacturers seek sustainable and cost-effective alternatives to genuine leather. Mordor Intelligence also highlights a significant uptick, forecasting a CAGR of over 5.8% during the 2023–2028 period, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a dominant production and consumption hub. As innovation drives performance and aesthetics closer to natural leather, a new generation of synthetic leather manufacturers is leading the charge in quality, scalability, and eco-conscious production. Here are the top 10 artificial synthetic leather manufacturers shaping the future of this dynamic industry.
Top 10 Artificial Synthetic Leather Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Majilite: Faux Leather & Suede
Domain Est. 1997
Website: majilite.com
Key Highlights: Majilite is the leading manufacturer of luxury artificial leather and suede. Experience premium touch, performance, and colors of Majilite….
#2 Manufacturer And Exporter of Artificial Leather, Synthetic Leather …
Domain Est. 2006
Website: mayuruniquoters.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer And Exporter of Artificial Leather, Synthetic Leather, Pvc Vinyl, PU/PVC Leather Cloth….
#3 HR Polycoats Private Limited
Domain Est. 2006
Website: hrcheetal.com
Key Highlights: We started manufacturing artificial leather way back in 1995. We produce our variety of designs for several car manufacturers in India and most footwear ……
#4 Artificial Leather Manufacturer, Synthetic Leather
Domain Est. 2018
Website: artificial-leather.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading manufacturer of Artificial Leather, Faux Leather, Synthetic Leather, Faux Leather for garment, Faux Leather for bag, Faux Leather for footwear….
#5 Synthetic Leather Manufacturer (TPU & PVB)
Domain Est. 2020
Website: epotw.com
Key Highlights: Based in Taiwan, EPO is a professional synthetic leather manufacturer. Our eco-friendly leather is crafted from rPVB or TPU materials, offering customizable ……
#6 Zaibunco
Domain Est. 2021
Website: zaibunco.co.in
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of PU & PVC leather cloth in India, equipped with state-of-the-art machinery and industry-leading quality management systems….
#7 Manufacture of skai® Faux Leather ▷ Composition & Production
Domain Est. 1998
Website: skai.com
Key Highlights: Read here about the composition of our skai artificial leathers and the manufacturing processes that make them so lifelike and comfortable….
#8 Artificial & synthetic leather for public environment, furniture
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nevotex.com
Key Highlights: We have a fastidious selection process and offer a wide range of high-quality phthalate-free PVC and PU artificial leather….
#9 Modern Meadow – Biofabricated Leather Reinvented
Domain Est. 2011
Website: modernmeadow.com
Key Highlights: Discover INNOVERA, Modern Meadow’s next-gen biofabricated leather made from plant proteins and recycled rubber. Animal-free, sustainable, and versatile ……
#10 Winner Nippon
Domain Est. 2015
Website: winnernippon.com
Key Highlights: We produce different varieties of synthetic leather like Napa, Navajo, Embossed leather, Patent, Putina, Microfibre, Nuback, Fibre, Crepe Satin finishes in PU ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Artificial Synthetic Leather

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Artificial Synthetic Leather
The global artificial synthetic leather market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising environmental consciousness, and shifting consumer preferences. As sustainability becomes a central pillar in the fashion, automotive, and furniture industries, synthetic leather—also known as vegan leather or faux leather—is emerging as a key alternative to traditional animal-derived leather. This analysis outlines the primary market trends expected to shape the artificial synthetic leather industry in 2026.
1. Accelerated Demand for Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
By 2026, environmental sustainability will be a dominant driver in material selection across industries. Consumers and brands alike are increasingly prioritizing low-carbon, cruelty-free, and biodegradable materials. This has led to a surge in demand for next-generation synthetic leathers made from plant-based sources such as pineapple (Piñatex), mushroom mycelium (Mylo), apple waste, cactus (Desserto), and other bio-based feedstocks. These materials offer reduced environmental impact compared to petroleum-based polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) leathers, positioning bio-synthetic leather as a high-growth segment.
2. Technological Advancements in Material Science
Innovation in material engineering is enhancing the performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal of synthetic leather. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to leverage nanotechnology, 3D printing, and precision fermentation to create materials that closely mimic the texture, breathability, and aging characteristics of real leather. These advancements will not only improve product quality but also expand applications into high-end fashion, luxury automotive interiors, and technical apparel.
3. Regulatory Pressure and Corporate ESG Commitments
Stringent environmental regulations—particularly in the EU and North America—are pushing companies to reduce their reliance on fossil fuel-derived materials and hazardous chemicals. The European Green Deal and similar policies are incentivizing circular economy practices, including the use of recyclable and compostable materials. Simultaneously, brands are setting ambitious Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) targets, with many pledging to eliminate animal leather from their supply chains. These commitments are accelerating the adoption of certified synthetic alternatives.
4. Expansion in Application Sectors
While fashion and footwear remain major markets, the automotive and furniture industries are increasingly adopting synthetic leather due to its design flexibility, cost-efficiency, and ethical appeal. Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers, in particular, are incorporating premium synthetic interiors to align with their eco-conscious branding. In 2026, the transportation sector is expected to become one of the fastest-growing end-users of artificial leather.
5. Price Competitiveness and Scalability Improvements
Historically, bio-based and high-performance synthetic leathers have faced challenges related to high production costs and limited scalability. However, by 2026, advancements in fermentation-based production and agricultural waste utilization are expected to lower costs and enable mass production. Partnerships between biotech firms and large manufacturers (e.g., Adidas, Mercedes-Benz, Hermès) are also facilitating commercial scalability, making premium synthetic leather more accessible.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific will remain the largest producer and consumer of synthetic leather, led by China, India, and South Korea, due to established manufacturing infrastructure and growing domestic demand. However, North America and Europe are expected to lead in innovation and premium bio-based product adoption. Government funding for green materials and strong consumer demand for ethical products will drive growth in these regions.
7. Challenges and Consumer Perception
Despite positive momentum, challenges remain. Issues such as microplastic shedding from PU-based synthetics, limited biodegradability, and greenwashing concerns could hinder market growth. In 2026, transparent labeling, third-party certifications (e.g., Cradle to Cradle, USDA BioPreferred), and lifecycle assessments will be critical for building consumer trust.
Conclusion
By 2026, the artificial synthetic leather market will be defined by a convergence of sustainability, innovation, and mainstream adoption. The shift toward bio-based, high-performance materials—supported by regulatory frameworks, technological breakthroughs, and evolving consumer values—will position synthetic leather not just as a substitute, but as a preferred material across diverse industries. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainable sourcing, and transparent supply chains will be best positioned to lead this transformative market.
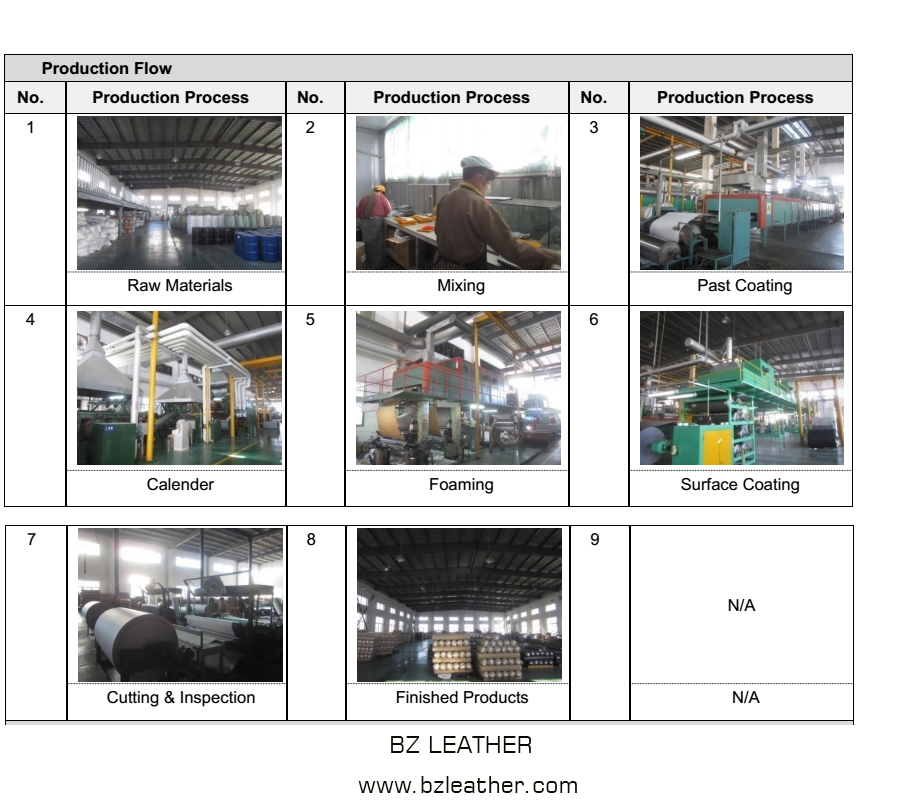
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Artificial Synthetic Leather (Quality, IP)
Quality Inconsistencies and Material Misrepresentation
One of the most frequent challenges in sourcing artificial synthetic leather is encountering inconsistent quality across production batches. Suppliers may provide impressive samples, but the final bulk shipment often differs in texture, colorfastness, durability, or thickness. Additionally, some suppliers mislabel materials—marketing lower-grade PU (polyurethane) leather as premium or eco-friendly alternatives like “vegan leather” without substantiating claims. Buyers must verify technical specifications, conduct third-party lab testing, and implement strict quality control protocols to avoid receiving substandard materials.
Lack of Transparency in Raw Materials and Manufacturing Processes
Many suppliers do not fully disclose the composition or origin of raw materials used in synthetic leather production. Hidden use of inferior polymers, harmful plasticizers (e.g., phthalates), or non-compliant solvents can pose compliance risks, particularly in markets with strict environmental and safety regulations (e.g., REACH, RoHS). Without transparent supply chains, brands expose themselves to reputational damage and potential legal liabilities, especially when marketing products as sustainable or non-toxic.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement increases the risk of inadvertently procuring synthetic leather that mimics patented textures, finishes, or technologies (e.g., embossed patterns or proprietary coatings). Using such materials—even unknowingly—can lead to infringement lawsuits, product recalls, or customs seizures. Brands should conduct due diligence on suppliers’ IP compliance, request warranties against infringement, and ensure that designs or finishes are either licensed or original.
Inadequate Performance Testing and Certification
Artificial leathers vary significantly in performance characteristics such as abrasion resistance, UV stability, cold crack resistance, and breathability. Suppliers may omit or falsify test reports, leading to material failure in end-use applications—especially in automotive, furniture, or footwear industries. Relying solely on supplier-provided certifications without independent validation can result in product defects and warranty claims. Always request accredited lab reports aligned with industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM).
Greenwashing and Sustainability Claims Without Verification
Many suppliers promote synthetic leather as “eco-friendly,” “biodegradable,” or “made from recycled content” without third-party certification or traceable proof. This greenwashing can mislead buyers and lead to false marketing claims, inviting regulatory scrutiny and consumer backlash. To mitigate this, require documented evidence such as GRS (Global Recycled Standard) certification, LCA (Life Cycle Assessment) data, or material traceability reports before accepting sustainability claims.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Artificial Synthetic Leather
Overview
Artificial synthetic leather, also known as faux leather, pleather, or vegan leather, is a man-made material designed to mimic the appearance and texture of genuine leather. Commonly composed of polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) on a textile backing, it is widely used in fashion, automotive, furniture, and accessories industries. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for importing, exporting, storing, and distributing artificial synthetic leather globally.
Classification & Tariff Codes
Accurate classification ensures correct duty assessment and compliance with international trade regulations.
– HS Code (Harmonized System): Typically falls under Chapter 59 – Impregnated, coated, covered or laminated textile fabrics.
– 5903.10: Plastic-coated textile fabrics, of a kind used for upholstery, clothing, or similar purposes (common for PU/PVC synthetic leather).
– 3921.13: Plates, sheets, film, foil, and strip, of plastics, non-cellular and not reinforced, laminated with textile fabrics.
– Note: Classification depends on base fabric (e.g., polyester, cotton), coating material (PU vs. PVC), thickness, and end-use. Consult local customs authorities for precise determination.
International Trade Regulations
Compliance with import/export controls is essential across major markets.
– United States (CBP):
– Entry requires a Customs Bond, Entry Summary (Form 7501), and accurate HS code declaration.
– Subject to anti-dumping or countervailing duties if sourced from jurisdictions under investigation (e.g., China for certain coated fabrics).
– European Union (EU):
– Requires EORI number, Import Control System (ICS2) declaration, and compliance with REACH and RoHS.
– Goods may be subject to TARIC additional codes and anti-dumping measures.
– China:
– Export license may be required depending on volume and destination.
– Comply with China Compulsory Certification (CCC) if used in regulated end-products (e.g., automotive interiors).
Chemical & Environmental Compliance
Synthetic leather may contain regulated substances requiring documentation.
– REACH (EU Regulation):
– Restricts Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs) such as phthalates (DEHP, DBP, BBP) and heavy metals (lead, cadmium).
– Suppliers must provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and SVHC declarations if concentration exceeds 0.1%.
– RoHS (EU & China):
– Limits hazardous substances (e.g., lead, mercury, cadmium) in electrical/electronic components; applicable if used in such products.
– California Proposition 65:
– Requires warning labels if products contain listed carcinogens or reproductive toxins (e.g., certain phthalates).
– Oeko-Tex Standard 100:
– Voluntary certification ensuring textiles are free from harmful levels of toxic substances; often requested by brands.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling facilitate smooth logistics and regulatory acceptance.
– Packaging:
– Rolls must be wrapped in protective plastic and secured on pallets to prevent moisture, dust, and physical damage.
– Use moisture barriers in humid climates to avoid mildew.
– Labeling:
– Include product name, composition (e.g., “100% PU-coated polyester”), weight, width, batch/lot number, and country of origin.
– In the U.S. and EU, country of origin labeling is mandatory for imported goods.
– Add care instructions and compliance marks (e.g., CE, Oeko-Tex) if applicable.
Transportation & Handling
Optimize logistics for durability and cost-efficiency.
– Mode of Transport:
– Ocean freight is cost-effective for bulk shipments; air freight for urgent or high-value orders.
– Use dry, ventilated containers to prevent condensation.
– Storage Conditions:
– Store in cool, dry areas (15–25°C) away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent plasticizer migration or cracking.
– Keep rolls vertically or on racks to avoid deformation.
– Handling:
– Use appropriate lifting equipment; avoid dragging or dropping rolls.
– Protect edges from abrasion during loading/unloading.
Sustainability & ESG Considerations
Growing demand for eco-friendly materials affects compliance and market access.
– Recyclability:
– PU leather is more recyclable than PVC; disclose end-of-life options.
– Environmental Claims:
– Avoid misleading terms like “eco-leather” without certification (e.g., ISO 14021 for environmental labels).
– PFAS and Microplastics:
– Monitor regulatory developments (e.g., EU restriction on PFAS) and microplastic shedding in washing.
Documentation Checklist
Ensure all documents are accurate and complete:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading / Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
– REACH/RoHS Compliance Declaration
– Test Reports (e.g., Oeko-Tex, Prop 65)
– Import/Export Licenses (if required)
Conclusion
Successfully managing artificial synthetic leather logistics requires attention to classification, chemical compliance, packaging, and evolving environmental standards. Partnering with certified suppliers and staying updated on regional regulations will minimize delays, avoid penalties, and support sustainable business practices. Regular audits and due diligence are recommended to maintain compliance across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Artificial Synthetic Leather:
Sourcing artificial synthetic leather presents a viable, sustainable, and ethical alternative to genuine leather, especially in light of growing environmental concerns and animal welfare considerations. Advances in material science have led to high-quality synthetic options—such as polyurethane (PU) and innovative bio-based leathers—that closely mimic the look, feel, and durability of real leather, while offering additional benefits like water resistance, easier maintenance, and lower production costs.
When sourcing synthetic leather, it is crucial to evaluate suppliers based on material quality, environmental impact, consistency, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., REACH, RoHS). Partnering with transparent, responsible suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly manufacturing processes—including reduced carbon emissions and recyclable or biodegradable materials—can enhance brand reputation and support sustainability goals.
Furthermore, as consumer demand for ethical and sustainable products continues to rise, investing in innovative and responsibly sourced synthetic leather not only aligns with market trends but also positions businesses at the forefront of the evolving materials landscape. In conclusion, strategic sourcing of artificial synthetic leather enables cost-effective, scalable, and conscientious production—making it a smart choice for fashion, automotive, furniture, and other industries seeking performance and purpose.