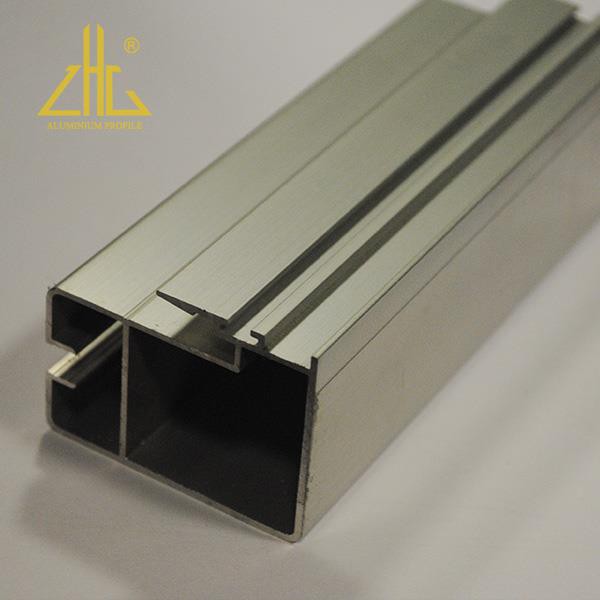
The global anodized aluminum market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand across aerospace, automotive, construction, and consumer electronics industries. According to Mordor Intelligence, the anodized aluminum market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% through 2029, fueled by the material’s superior corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic versatility. This growth is further supported by rising investments in lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce carbon emissions, particularly in transportation sectors. As sustainability and performance take center stage, manufacturers are innovating with advanced anodizing techniques and eco-friendly processes. In this evolving landscape, a select group of industry leaders has emerged, setting benchmarks in quality, scale, and technological advancement. Below is a data-driven look at the top 9 anodized aluminum material manufacturers shaping the future of this high-performance material.
Top 9 Anodized Aluminum Material Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SAF
Domain Est. 1992
Website: saf.com
Key Highlights: As the largest single source for architectural aluminum sheet, extruded shapes, aluminum anodizing, painting, and fabricating services, we look forward to ……
#2 – Lorin
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lorin.com
Key Highlights: Lorin Industries has dedicated itself to the art of aluminum anodizing, achieving unrivaled expertise and delivering exceptional, tailor-made solutions to ……
#3 Anodized Aluminum
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pac-clad.com
Key Highlights: Petersen offers PAC 500 anodized aluminum in a complete range of bronze shades and black. PAC 300 clear anodized aluminum is available in gauges .032-.125….
#4 Innovative anodized aluminum packaging for the world’s top brands
Domain Est. 1997
Website: anomatic.com
Key Highlights: Anomatic is a global supplier of high volume anodized aluminum packaging serving the beauty, personal care, auto, medical, electronics, and spirits ……
#5 Anodized Aluminum
Domain Est. 1997
Website: azahner.com
Key Highlights: Anodization turn porous raw aluminum into a durable surface that is an excellent option for interior and exterior applications….
#6 Aluminum Anodizers Council
Domain Est. 1998
Website: anodizing.org
Key Highlights: Anodizing is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant, anodic oxide finish….
#7 Aluminum Anodizing Companies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: aluminumanodizing.com
Key Highlights: Instantly connect with the leading aluminum anodizing companies who offer top-of-the-line customer support and high quality products for competitive prices….
#8 Anodized Aluminum
Domain Est. 2000
Website: dri-design.com
Key Highlights: Discover the beauty of Anodized Aluminum, a premium metal finish that seamlessly merges science and nature….
#9 Anodized Aluminum Extrusions & Products
Domain Est. 2001
Website: tri-stateal.com
Key Highlights: Our facilities specialize in creating anodized aluminum extrusions including bars, tubes, rods, and a wide range of die-formed shapes. Contact us today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Anodized Aluminum Material

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Anodized Aluminum Material
The global anodized aluminum market is poised for significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by rising demand across multiple high-growth industries, technological advancements, and increasing emphasis on sustainable materials. Key trends shaping the anodized aluminum landscape in 2026 include:
-
Expansion in Construction and Architecture
The construction sector remains a primary driver of anodized aluminum demand. By 2026, urbanization and the global push for energy-efficient buildings are fueling the adoption of anodized aluminum in façades, window frames, curtain walls, and roofing systems. Its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic versatility make it a preferred material for modern architectural design, especially in green building projects seeking LEED certification. -
Growth in Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics industry continues to adopt anodized aluminum for premium smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearables. By 2026, demand is expected to rise further due to the material’s sleek appearance, thermal conductivity, and electromagnetic shielding properties. Manufacturers are increasingly using colored and textured anodized finishes to differentiate products in a competitive market. -
Automotive and Electric Vehicle (EV) Innovation
The automotive sector—particularly electric vehicles—is a growing application area. Anodized aluminum is favored for lightweighting strategies that improve energy efficiency and extend battery range. In 2026, its use in EV components such as battery enclosures, heat sinks, and interior trims is expected to accelerate, supported by advancements in hard anodizing for enhanced wear and thermal resistance. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing industries toward recyclable and low-impact materials. Anodized aluminum, which is 100% recyclable without degradation and requires less energy to recycle than primary production, aligns with circular economy principles. By 2026, eco-labeling and lifecycle assessments will increasingly influence procurement decisions, favoring anodized over painted or coated alternatives. -
Technological Advancements in Anodizing Processes
Innovations such as pulse anodizing, organic acid anodizing, and smart surface treatments are enhancing performance and reducing environmental impact. These technologies offer improved coating uniformity, reduced energy consumption, and lower effluent generation. By 2026, wider adoption of these processes is expected, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations like the EU and North America. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, will remain the largest market for anodized aluminum due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are witnessing growth driven by high-performance applications in aerospace, defense, and premium construction. Localized production and supply chain resilience will gain importance post-2023 disruptions. -
Price Volatility and Raw Material Supply
While demand grows, the market may face challenges from fluctuating aluminum prices and energy costs affecting anodizing operations. By 2026, companies are expected to adopt long-term supply agreements and invest in energy-efficient anodizing lines to mitigate cost pressures.
In summary, the anodized aluminum market in 2026 will be shaped by cross-sectoral demand, technological innovation, and environmental considerations. Stakeholders who align with sustainability goals and invest in advanced surface engineering are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Anodized Aluminum Material (Quality, IP)
Sourcing anodized aluminum material requires careful attention to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to production delays, product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Inconsistencies and Performance Failures
-
Inconsistent Anodizing Thickness: Suppliers may fail to meet specified coating thickness (e.g., ISO 7599 or MIL-A-8625 standards), resulting in reduced corrosion resistance, wear performance, or electrical insulation properties. Unverified batch testing can allow substandard materials to enter production.
-
Poor Color and Finish Uniformity: Variations in dye lots, sealing processes, or alloy composition can cause visible color mismatches, streaking, or uneven gloss. This is especially critical for consumer-facing products where aesthetics matter.
-
Substandard Base Aluminum Alloy: Using incorrect or off-spec aluminum alloys (e.g., substituting 6061 for 6063) affects machinability, strength, and anodizing response. Some alloys anodize poorly or produce undesirable surface textures.
-
Inadequate Sealing and Corrosion Resistance: Poorly sealed anodized layers absorb moisture and contaminants, leading to premature corrosion or staining. Salt spray test (e.g., ASTM B117) results should be verified.
-
Lack of Process Documentation and Traceability: Without proper documentation of anodizing parameters (voltage, time, temperature, electrolyte), it is difficult to reproduce results or troubleshoot defects. Batch traceability is essential for quality control and recalls.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks and Leakage
-
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Finishes: Custom colors, textures, or performance specifications developed in collaboration with a supplier may be replicated for other clients if IP rights are not contractually protected.
-
Weak or Absent IP Clauses in Contracts: Supplier agreements that lack clear ownership clauses, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), or restrictions on reverse engineering expose companies to IP theft and competitive imitation.
-
Supplier Subcontracting Without Consent: Anodizing may be outsourced by the primary supplier to third-party facilities without approval, increasing the risk of IP exposure and quality deviations.
-
Lack of Control Over Tooling and Fixtures: Custom racking or masking tools used in anodizing may remain with the supplier, enabling them to reproduce unique finishes without authorization.
-
Insufficient Audit Rights: Without contractual rights to audit the supplier’s facility and processes, companies cannot verify compliance with quality or IP protection standards.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require detailed material certifications (e.g., mill test reports, anodizing process sheets).
- Conduct regular on-site supplier audits and sample testing.
- Include explicit IP ownership, confidentiality, and non-compete terms in procurement contracts.
- Limit access to sensitive specifications on a need-to-know basis.
- Use watermarking or traceable identifiers on proprietary finishes where possible.
Proactively addressing these pitfalls ensures reliable supply, consistent product performance, and protection of valuable design and technical innovations.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Anodized Aluminum Material
Overview of Anodized Aluminum
Anodized aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal widely used in aerospace, automotive, construction, and consumer electronics. The anodizing process enhances aluminum’s natural oxide layer, improving durability, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Proper logistics and compliance protocols are essential to maintain material integrity and meet regulatory standards.
International Shipping & Packaging Requirements
Anodized aluminum is generally classified as non-hazardous and safe for international transport. However, specific packaging guidelines must be followed to prevent surface damage during transit:
– Use protective wrapping (e.g., plastic film or kraft paper) to prevent scratching.
– Secure materials on pallets with edge protectors and strapping.
– Avoid direct contact with moisture; use moisture-barrier packaging if shipping in humid climates.
– Label packages clearly with “Fragile” and “Protect from Moisture” warnings.
Compliance with IATA, IMDG, and ADR regulations is required when shipping via air, sea, or road, respectively—even for non-hazardous goods.
Import/Export Regulations and Documentation
When moving anodized aluminum across borders, ensure compliance with the following:
– HS Code Classification: Typically falls under HS Code 7616.99 (Other articles of aluminum). Confirm with local customs authorities for precise categorization.
– Certificates of Origin: Required by many countries to determine tariff eligibility; especially important under trade agreements like USMCA, EU-UK TCA, or RCEP.
– Customs Declarations: Accurately declare value, weight, and quantity. Misdeclaration may lead to delays or penalties.
– Export Licensing: Generally not required for anodized aluminum, but verify restrictions in embargoed countries or sensitive end-use sectors (e.g., defense).
Environmental & Safety Compliance
While anodized aluminum is not classified as hazardous, the anodizing process may involve regulated chemicals (e.g., sulfuric acid, chromic acid). Compliance obligations include:
– REACH (EU): Ensure substances used in anodizing (e.g., dyes, sealants) are registered and do not contain SVHCs above threshold levels.
– RoHS (EU): Confirm compliance if the material is used in electrical/electronic equipment; anodized layers are typically compliant.
– TSCA (USA): Verify that processing chemicals are listed and comply with EPA regulations.
– Waste Management: Spent electrolytes and sludge from anodizing are often regulated as hazardous waste; proper disposal documentation is required.
Industry-Specific Standards and Certifications
Different sectors impose additional compliance requirements:
– Aerospace (AMS, AS Standards): Materials may need certification to AMS 2469, AMS 2470, or AS9100 for quality management.
– Architectural (AAMA Standards): Anodized finishes for building components must meet AAMA 611 or AAMA 2604 for performance.
– Food Contact (FDA, EU 10/2011): If used in food equipment, confirm that the anodized surface is non-leaching and complies with food-grade regulations.
Storage and Handling Best Practices
To maintain quality and ensure compliance throughout the supply chain:
– Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent moisture-induced staining.
– Keep materials off the ground using pallets and avoid stacking heavy items on top.
– Use clean, non-abrasive handling tools to prevent surface marring.
– Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory practices to minimize long-term storage risks.
Traceability and Recordkeeping
Maintain detailed records for compliance audits and quality assurance:
– Batch numbers, anodizing date, and coating thickness specifications.
– Certificates of Compliance (CoC) or Mill Test Reports (MTRs) from suppliers.
– Shipping logs, customs documentation, and storage conditions.
Digital traceability systems are recommended for high-regulation industries.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for anodized aluminum ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and smooth international trade. By following packaging, documentation, and industry-specific standards, businesses can mitigate risks and maintain supply chain efficiency. Always consult with regulatory experts and stay updated on evolving compliance requirements in target markets.
Conclusion:
Sourcing anodized aluminum material offers a reliable solution for applications requiring durability, corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and lightweight performance. The anodizing process enhances the natural properties of aluminum, providing a protective oxide layer that improves wear resistance and longevity. When sourcing anodized aluminum, it is essential to consider factors such as alloy type, thickness of the anodized layer, color consistency, supplier credibility, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., MIL-A-8625 or ISO 7599). Working with reputable suppliers who maintain strict quality control and offer customization options ensures consistent material performance and finish. Additionally, evaluating cost, lead times, and environmental impact supports sustainable and efficient sourcing decisions. Overall, anodized aluminum is a versatile and high-performance material well-suited for industries ranging from aerospace and automotive to architecture and consumer electronics, making it a strategic choice for long-term project success.