The global market for specialty inorganic chemicals, including ammonium iron sulphate (also known as ferric ammonium sulfate or iron alum), has seen steady growth driven by increasing demand across water treatment, dyeing, and pharmaceutical applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global alum chemicals market—of which ammonium iron sulphate is a key derivative—is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by stringent environmental regulations boosting the need for efficient coagulants in wastewater treatment, particularly in emerging economies. Additionally, rising industrialization in Asia-Pacific and increasing investments in municipal infrastructure are amplifying the demand for high-purity coagulants like ammonium iron sulphate. As the market becomes more competitive, identifying reliable manufacturers with scalable production, consistent quality, and compliance with environmental standards is critical for downstream buyers. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, product purity, and market presence, the following are the top five ammonium iron sulphate manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 5 Ammonium Iron Sulphate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 [PDF] Rowe Scientific Ammonium Iron (II) Sulphate
Website: rowe.com.au
Key Highlights: Details of the manufacturer or supplier of the safety data sheet. Registered company name. ROWE SCIENTIFIC. Address. 11 Challenge Boulevard ……
#2 Ammonium iron(II) sulfate hexahydrate
Domain Est. 1996
#3 Ferrous Ammonium Sulfate Purified Crystal, CAS Number 7783
Domain Est. 1997
Website: jostchemical.com
Key Highlights: Ferrous Ammonium Sulfate Purified Crystal is Jost Chemical product code 2400 and CAS Number 7783-85-9, bluish green odorless crystals….
#4 Ammonium Iron(II) Sulfate Hexahydrate
Domain Est. 1998
Website: americanelements.com
Key Highlights: Ammonium Iron(II) Sulfate Hexahydrate is generally immediately available in most volumes. High purity, submicron and nanopowder forms may be considered….
#5 Iron (II) ammonium sulphate hexahydrate
Domain Est. 2002
Website: dutscher.com
Key Highlights: Iron (II) ammonium sulphate hexahydrate – RE – Pure – plastic bottle 1 kg. 344007-CER. Print Share. Sales Unit : 1. Brand : CARLO ERBA. Part Number : 344007….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ammonium Iron Sulphate
As of now, projecting market trends for Ammonium Iron Sulphate (also known as ferric ammonium sulfate or iron alum) in 2026 involves analyzing current industry dynamics, technological developments, regulatory environments, and demand drivers, while acknowledging that such forecasts are inherently subject to uncertainty. However, using a structured analytical framework (H2 could refer to a second-level heading or a hypothetical analytical model—assuming here that “H2” refers to a structured sub-category or hypothesis-based analysis framework), we can outline key trends expected to influence the Ammonium Iron Sulphate market by 2026.
H2: Key Market Drivers and Trends for Ammonium Iron Sulphate (2026 Outlook)
- Growing Demand in Water Treatment
- Ammonium Iron Sulphate is increasingly being used as a coagulant in wastewater and potable water treatment due to its effectiveness in removing phosphates and heavy metals.
- With stricter environmental regulations globally (e.g., EU Water Framework Directive, U.S. Clean Water Act), municipalities and industries are seeking efficient, low-residue coagulants.
-
By 2026, urbanization in emerging economies (Asia-Pacific, Africa) will drive demand for advanced water treatment solutions, boosting the need for iron-based coagulants like ammonium iron sulphate.
-
Expansion in the Textile and Leather Industries
- The compound is used as a mordant in textile dyeing and in tanning processes in the leather industry, particularly in regions like India, China, and Bangladesh.
- As global textile production rebounds post-pandemic and sustainable dyeing practices gain attention, ammonium iron sulphate may be preferred over chromium-based mordants due to lower toxicity.
-
Forecast: Moderate growth (~3–4% CAGR) in use within these sectors by 2026.
-
Electronics and Photographic Chemicals Niche Applications
- Though declining in traditional photography, ammonium iron sulphate retains niche use in chemical etching and photolithography processes in electronics manufacturing.
- Demand in semiconductor and printed circuit board (PCB) industries—especially in East Asia—could sustain limited but stable demand.
-
However, substitution with more advanced materials may constrain growth in this segment.
-
Environmental and Regulatory Pressures
- While less toxic than aluminum-based coagulants, ammonium iron sulphate still requires proper handling due to iron and sulfate content.
- Future regulations on sulfate discharge and sludge management may impact usage patterns. Innovations in recovery and recycling of iron salts may emerge by 2026 to address these concerns.
-
Companies investing in closed-loop systems may gain a competitive edge.
-
Raw Material Availability and Production Costs
- The compound is derived from iron salts and sulfuric acid, both of which are by-products of steel and mining industries.
- Fluctuations in steel production and sulfur prices (linked to oil refining) may affect supply chain stability.
-
By 2026, regional production hubs (China, India, Germany) are expected to dominate, with localized manufacturing rising to reduce logistics costs and carbon footprint.
-
Competition from Alternative Coagulants
- Ammonium iron sulphate competes with ferric chloride, polyaluminum chloride (PAC), and organic polymers.
- PAC offers advantages in sludge reduction and pH neutrality, potentially limiting ammonium iron sulphate’s market share in high-efficiency treatment plants.
-
However, ammonium iron sulphate’s lower cost and effectiveness in cold climates may preserve its niche.
-
R&D and Product Innovation
- Research into modified or hybrid iron-based coagulants may enhance performance (e.g., better settling rates, lower dosage).
-
By 2026, we may see commercialization of stabilized or nano-formulated variants of ammonium iron sulphate for specialized applications.
-
Geographic Market Shifts
- Asia-Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market due to industrialization and infrastructure development.
- Europe and North America will focus on replacement of aging water systems, creating steady demand.
- Latin America and Africa may see incremental growth as public investment in water infrastructure increases.
Market Forecast Summary (2026 Projection):
– Global market value: Estimated to reach USD 120–150 million by 2026, growing at a CAGR of ~3.5–4.5% from 2022.
– Key players: BASF, Kemira, SNF Group, Haihang Industry, and regional specialty chemical producers.
– Primary growth vector: Water treatment applications (>50% of demand).
Risks & Uncertainties:
– Substitution by more efficient or eco-friendly alternatives.
– Regulatory bans or restrictions on sulfate discharge.
– Economic slowdowns affecting construction and industrial output.
Conclusion (H2-level Insight):
By 2026, the Ammonium Iron Sulphate market will likely experience steady but moderate growth, driven primarily by environmental compliance needs in water treatment and sustained use in traditional industries. While not a high-growth specialty chemical, its role as a cost-effective, moderately eco-friendly coagulant will ensure continued relevance—especially in developing regions. Innovation and integration into circular economy models (e.g., iron recovery from sludge) will be critical for long-term viability.
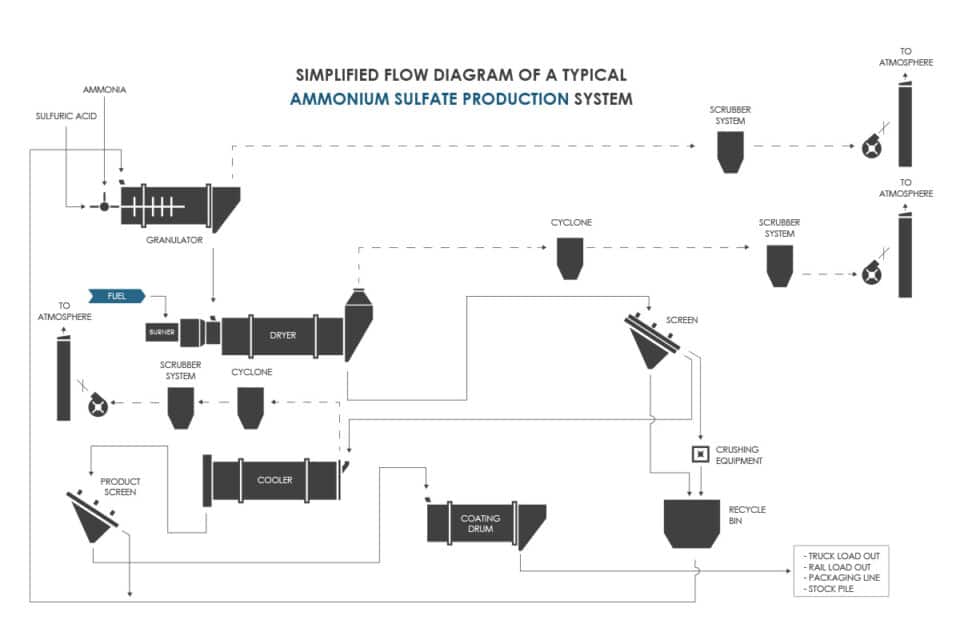
H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Ammonium Iron(II) Sulphate (Mohr’s Salt) – Quality and Pharmacopoeial (IP) Compliance
Sourcing Ammonium Iron(II) Sulphate, commonly known as Mohr’s Salt (chemical formula: (NH₄)₂Fe(SO₄)₂·6H₂O), for applications requiring compliance with pharmacopoeial standards such as the Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP), involves several critical quality and supply chain considerations. Below are the common pitfalls encountered during procurement, with a focus on quality assurance and IP compliance:
1. Incorrect Grade or Specification
- Pitfall: Receiving reagent-grade or technical-grade material instead of IP-grade or analytical reference standard material.
- Impact: Non-compliant grades may contain impurities (e.g., heavy metals, excess moisture, or oxidized iron) that fail IP tests.
- Solution: Explicitly specify “Ammonium Iron(II) Sulphate, IP” or “Conforms to Indian Pharmacopoeia” in purchase orders and verify CoA (Certificate of Analysis).
2. Oxidation of Ferrous Iron (Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺)
- Pitfall: Degraded or improperly stored material where Fe²⁺ has oxidized to Fe³⁺ due to exposure to air or moisture.
- Impact: Reduced assay value, invalidating volumetric or analytical use (e.g., in redox titrations).
- Indicator: Yellowish or brownish discoloration instead of pale green crystals.
- Prevention: Source material with nitrogen-flushed packaging, check packaging integrity, and verify assay of Fe²⁺ (IP requires minimum 99.0% on dried basis).
3. Inadequate or Missing Certificate of Analysis (CoA)
- Pitfall: Supplier provides no CoA or a generic one not referencing IP monograph requirements.
- Impact: Inability to verify compliance with IP parameters like assay, pH, clarity, residue on ignition, heavy metals, and chloride/sulphate limits.
- Best Practice: Insist on batch-specific CoA showing test results against IP specifications.
4. Incorrect Hydration State or Moisture Content
- Pitfall: Material may lose or gain water of crystallization, affecting molecular weight and assay accuracy.
- IP Requirement: Must contain 98.0–102.0% of Fe(SO₄)₂(NH₄)₂·6H₂O.
- Risk: Over-dried or deliquescent samples skew analytical results.
- Check: Verify loss on drying (LOD) as per IP — typically not more than 8.0% at 105°C.
5. Contamination with Heavy Metals or Other Impurities
- Pitfall: Poor manufacturing practices lead to contamination (e.g., Pb, As, Cd).
- IP Limits: Heavy metals ≤ 20 ppm; Arsenic ≤ 3 ppm.
- Risk: Unacceptable for pharmaceutical or diagnostic use.
- Mitigation: Ensure supplier follows GMP or ISO standards and conducts heavy metal testing.
6. Counterfeit or Mislabelled Products
- Pitfall: Unreliable suppliers may substitute with cheaper, non-compliant salts (e.g., plain ferrous sulphate).
- Red Flag: Significantly lower price than market average.
- Verification: Use analytical testing (e.g., UV-Vis, titrimetry) upon receipt; confirm ammonium and sulphate presence.
7. Inconsistent Batch-to-Batch Quality
- Pitfall: Lack of process control in manufacturing leads to variable purity or assay.
- Impact: Inconsistent performance in analytical procedures.
- Solution: Partner with certified suppliers with robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, GLP).
8. Poor Packaging and Storage Conditions
- Pitfall: Material supplied in non-airtight or non-light-resistant containers.
- Consequence: Accelerated oxidation and moisture absorption.
- IP Requirement: Store in airtight containers, protected from light and moisture.
- Best Practice: Verify packaging includes sealed HDPE bottles with desiccant.
9. Lack of Traceability or Regulatory Documentation
- Pitfall: Missing batch traceability, DMF (Drug Master File), or regulatory support.
- Impact: Hinders audit readiness and regulatory submissions.
- Requirement for Pharma Use: Supplier should provide full traceability and regulatory documentation upon request.
10. Unverified Supplier Credibility
- Pitfall: Sourcing from unknown or unqualified vendors (especially online platforms).
- Risk: High chance of substandard or falsified materials.
- Due Diligence: Audit suppliers, check regulatory certifications (e.g., US FDA, WHO-GMP), and review customer feedback.
Summary: Key Actions to Avoid Pitfalls
- Always specify IP-compliant Ammonium Iron(II) Sulphate.
- Demand batch-specific CoA referencing IP monograph.
- Verify assay (99.0–102.0%), LOD, heavy metals, and appearance.
- Use reputable, audited suppliers with GMP/GLP practices.
- Test incoming material upon receipt, especially for Fe²⁺ content and purity.
By addressing these common pitfalls, organizations can ensure reliable sourcing of high-quality, pharmacopoeially compliant Ammonium Iron(II) Sulphate for critical applications in pharmaceuticals, quality control, and analytical chemistry.
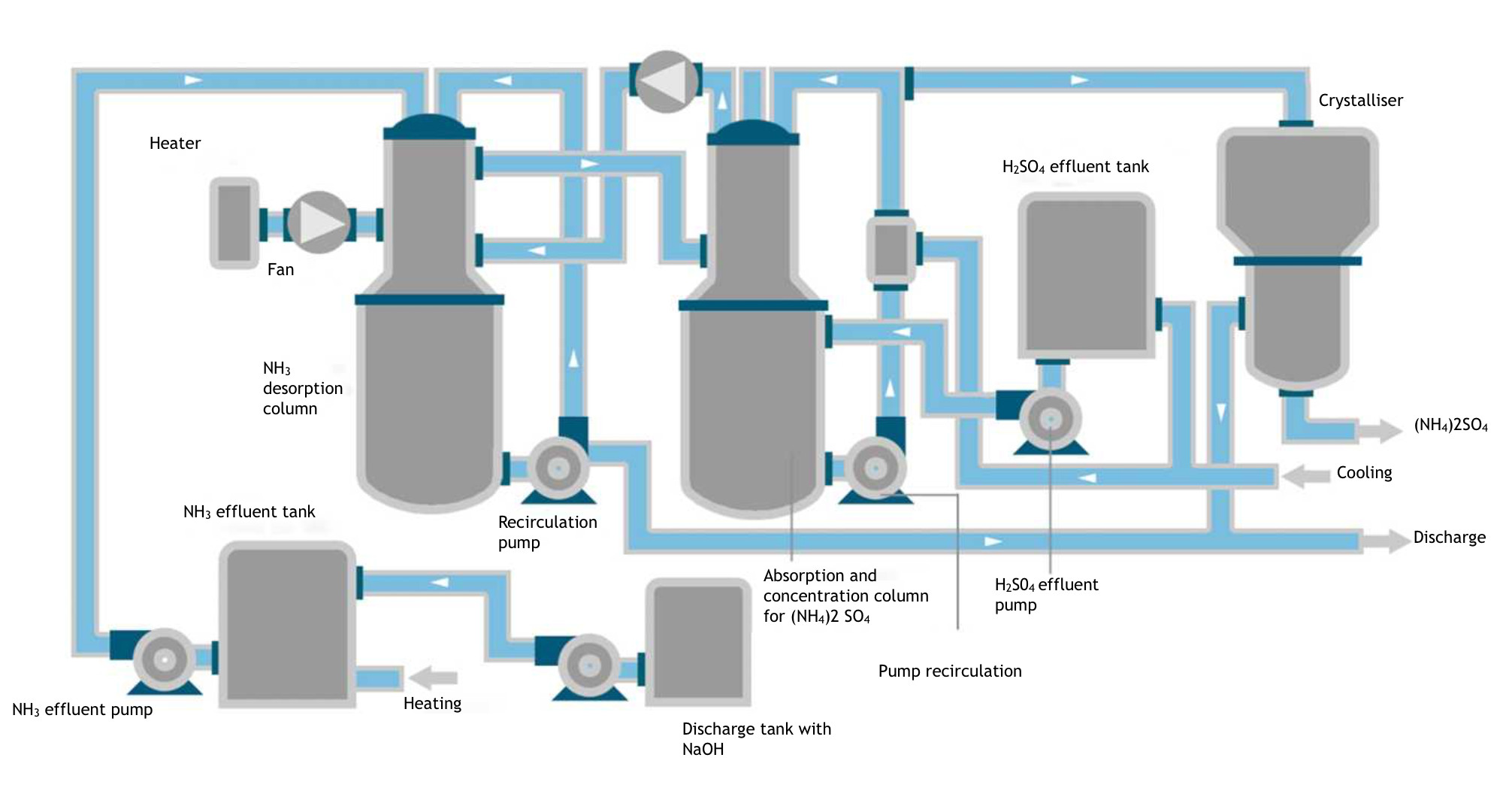
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ammonium Iron Sulphate (Ammonium Ferric Sulphate)
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ammonium Iron Sulphate
Ammonium Iron Sulphate (also known as Ammonium Ferric Sulphate or Iron(III) Ammonium Sulphate), with the chemical formula NH₄Fe(SO₄)₂·12H₂O, is commonly used in water treatment, dyeing, tanning, analytical chemistry, and as a catalyst. Proper logistics and compliance practices are essential due to its chemical properties and regulatory status.
1. Chemical Identification
- Chemical Name: Ammonium Iron(III) Sulphate Dodecahydrate
- CAS Number: 7783-83-7
- UN Number: Not regulated as hazardous for transport under UN TDG/ADR/IMDG when in solid form and meeting criteria (may vary by concentration and form)
- EC Number: 232-027-9
- Formula: NH₄Fe(SO₄)₂·12H₂O
2. Hazard Classification (GHS)
Based on available data and supplier SDS (Safety Data Sheet), typical classifications include:
- Skin Irritation: Category 2 (H315: Causes skin irritation)
- Eye Irritation: Category 2 (H319: Causes serious eye irritation)
- Hazardous to Aquatic Life: Category Chronic 2 (H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects)
Note: Not classified as flammable, explosive, or acutely toxic under normal handling conditions.
3. Storage Requirements
- Environment: Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
- Containers: Keep in tightly sealed, corrosion-resistant containers (e.g., HDPE or glass).
- Segregation:
- Keep away from strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, and moisture-sensitive chemicals.
- Do not store with food, animal feed, or pharmaceuticals.
- Shelf Life: Typically 24–36 months if stored properly. Check for caking or discoloration.
4. Handling Precautions
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE): gloves (nitrile or neoprene), safety goggles, lab coat.
- Avoid inhalation of dust; use local exhaust ventilation if powder handling in large quantities.
- Prevent contact with eyes and skin.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling.
- Use grounded equipment to prevent static discharge (though not flammable, dust may pose minor risks).
5. Transportation (Logistics)
- Physical Form: Typically transported as a solid crystalline powder.
- Regulatory Status:
- UN/ADR/RID (Road/Rail – Europe): Not classified as dangerous goods if in solid form and not meeting criteria for hazardous classification.
- IMDG (Sea): Generally not regulated as hazardous cargo under normal conditions.
- IATA (Air): Not classified as dangerous goods for air transport (Check with airline and current IATA DGR).
- Packaging: Use moisture-resistant, durable packaging (e.g., multi-wall paper bags with poly liner or sealed drums).
- Labeling: Although not always requiring hazard labels, include GHS pictograms if SDS indicates hazards. Include proper shipping name and supplier info.
6. Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Registered under REACH; ensure downstream user compliance with exposure scenarios.
- TSCA (USA): Listed on the TSCA Inventory – compliant for commercial use.
- Globally Harmonized System (GHS): Ensure SDS and labeling comply with local GHS regulations (e.g., OSHA HazCom 2012 in the U.S.).
- EPA & Environmental Regulations: Follow local rules for discharge; due to iron and sulphate content, avoid release into waterways.
7. Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Requirements
- Maintain up-to-date SDS (16-section format) accessible to all handlers.
- Ensure SDS includes first aid measures, fire-fighting procedures (though non-combustible), and spill response.
8. Spill and Emergency Response
- Spill Procedure:
- Scoop or sweep material into a dry, labeled container.
- Avoid creating dust; use damp cloth for residual powder.
- Do not flush into drains or waterways.
- Personal Protection During Cleanup: Wear gloves, goggles, and a mask if dust is generated.
- Disposal: Dispose of as non-hazardous waste if below regulatory thresholds; otherwise, treat as hazardous waste per local regulations.
9. Waste Disposal
- Follow local, state, and national waste regulations.
- May require neutralization or stabilization before landfill disposal.
- Do not dispose of in sewers or natural water bodies due to aquatic toxicity.
10. Training & Documentation
- Train personnel on:
- Safe handling
- Use of PPE
- Emergency procedures
- Reading SDS and labels
- Maintain records of training, inventory, and incident reports.
Conclusion
Ammonium Iron Sulphate is generally low-risk but requires adherence to proper storage, handling, and environmental protection practices. While often exempt from hazardous transport regulations, compliance with GHS, REACH, TSCA, and local safety standards is essential. Always consult the latest SDS and regulatory guidance before shipment or large-scale handling.
Always verify specific regulatory status with your supplier and local authority, as classifications may vary by concentration, formulation, and jurisdiction.
Conclusion for Sourcing Ammonium Iron(II) Sulphate (Mohr’s Salt):
In conclusion, sourcing ammonium iron(II) sulphate (also known as Mohr’s salt) requires careful consideration of several key factors, including desired purity grade, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and intended application—whether for analytical chemistry, educational use, or industrial processes. High-purity, reagent-grade material is essential for applications such as volumetric analysis, where accuracy and consistency are critical. Reliable suppliers with certifications (e.g., ISO, GMP) and favorable customer reviews should be prioritized to ensure product quality and supply chain consistency.
Additionally, considerations such as packaging stability, shelf life, and proper storage conditions (e.g., protection from moisture and oxidation) must be addressed to maintain the chemical’s effectiveness over time. Sourcing from reputable chemical manufacturers or distributors—either locally or internationally—can offer competitive pricing and technical support.
Ultimately, a balanced approach that weighs quality, cost, and supplier credibility will ensure successful and sustainable procurement of ammonium iron(II) sulphate for any intended use.

![[PDF] Rowe Scientific Ammonium Iron (II) Sulphate](https://www.fobsourcify.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/pdf-rowe-scientific-ammonium-iron-ii-sulphate-825.jpg)