The global aluminum and steel manufacturing industry continues to expand, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global aluminum market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by lightweight material adoption in electric vehicles and sustainable infrastructure. Similarly, Grand View Research reports that the global steel market size was valued at USD 1.1 trillion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2030, underpinned by urbanization and industrial development, particularly in Asia-Pacific. As these materials remain foundational to modern manufacturing, a select group of producers have emerged as leaders in innovation, scale, and sustainability. Below are the top 9 aluminum and steel manufacturers shaping the future of the industry.
Top 9 Aluminum Steel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Reliance, Inc.
Domain Est. 1994
Website: reliance.com
Key Highlights: We’re the same company you’ve known and trusted for decades. Our new name reflects how we’ve evolved: Reliance is more than metal. We are industrial strength….
#2 Alcoa
Domain Est. 1986
Website: alcoa.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum. Our aluminum segment includes smelting, casting and select energy assets. · Alumina. We are the world’s largest third-party producer of alumina….
#3 O’Neal Steel: Metal Service Center
Domain Est. 1996
Website: onealsteel.com
Key Highlights: O’Neal Steel supplies aluminum, carbon & alloy steel, stainless, hot rolled, and cold-finished products nationwide. Get a quote now!…
#4 Nucor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nucor.com
Key Highlights: North America’s largest steel manufacturer and recycler. We are a team forged around a vision for leading our industry by providing unparalleled customer care….
#5 Premium Metals & Plastics Distributor
Domain Est. 1996
Website: alro.com
Key Highlights: Your one-stop-shop for premium metals and plastics, offering a vast inventory of in-stock products and processing service options with next day delivery….
#6 Mill Steel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: millsteel.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in a comprehensive range of flat-rolled steel and aluminum. All of our products are evaluated and tested to ensure quality of metal and precision ……
#7 Century Aluminum Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: centuryaluminum.com
Key Highlights: We are a global metals and mining company, focused on bauxite, alumina and aluminum. We operate globally, with operations in the U.S., Iceland, Jamaica, and ……
#8 Novelis
Domain Est. 2000
Website: novelis.com
Key Highlights: Novelis is a subsidiary of Hindalco Industries Limited, an industry leader in aluminum and copper and metals flagship company of the Aditya Birla Group, a ……
#9 Kaiser Aluminum
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kaiseraluminum.com
Key Highlights: We deliver highly engineered, semi-fabricated aluminum products that are stronger, lighter, more efficient and sustainable….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Steel

H2: Projected Market Trends for Aluminum and Steel in 2026
As the global economy continues to recover from post-pandemic disruptions and adapt to evolving geopolitical, environmental, and technological dynamics, the aluminum and steel markets are expected to undergo significant transformations by 2026. Driven by shifts in supply chains, decarbonization mandates, and growing demand from emerging industries, both metals are poised for strategic realignment in production, consumption, and pricing.
1. Demand Growth in Green Energy and Transportation Sectors
By 2026, demand for both aluminum and steel is expected to rise substantially in the renewable energy and electric vehicle (EV) sectors. Aluminum, due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, will remain critical in EV manufacturing, battery enclosures, and solar panel frames. Steel, particularly high-strength and advanced high-strength steel (AHSS), will continue to dominate in EV chassis and infrastructure applications where cost and durability are paramount. The global push toward carbon neutrality is projected to increase aluminum demand by 4–5% annually through 2026, while steel demand in green tech applications is expected to grow at 3–4% per year.
2. Decarbonization Pressures and Green Premiums
Environmental regulations are reshaping production methods. In 2026, aluminum producers investing in renewable-powered smelting (e.g., hydroelectric or solar) will gain competitive advantage, as “green aluminum” gains market share, especially in Europe and North America. Similarly, the steel industry is transitioning toward hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) and electric arc furnace (EAF) technologies to reduce CO₂ emissions. The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) will likely impose costs on high-carbon imports, incentivizing cleaner production. As a result, low-carbon aluminum and steel are expected to command premium pricing—up to 15–20% above conventional grades—by 2026.
3. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical tensions and trade policies will continue to drive regional self-sufficiency. North America and the European Union are expected to expand domestic aluminum and steel production capacity, supported by government incentives such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). In contrast, China’s steel output may stabilize or slightly decline due to government-enforced capacity caps and environmental goals, though it will remain the largest producer. Meanwhile, aluminum refining in Southeast Asia and Africa is projected to grow, supported by bauxite availability and foreign investment.
4. Price Volatility and Input Cost Pressures
Aluminum prices in 2026 will remain sensitive to energy costs, particularly electricity, which accounts for 30–40% of production expenses. Natural gas and coal prices—key inputs for steelmaking—will also influence steel pricing. Recycling rates for both metals are expected to increase (aluminum: ~75% in developed regions; steel: ~85%), helping moderate raw material demand and provide price stability. However, short-term volatility may persist due to energy market fluctuations and policy changes.
5. Innovation and Material Substitution
While aluminum and steel will maintain dominant positions in construction, automotive, and industrial applications, competition from composites and alternative materials (e.g., magnesium alloys, carbon fiber) will grow incrementally. However, cost-effectiveness and scalability will limit substitution in most mass-market applications. Instead, hybrid material solutions—such as aluminum-steel joints in vehicles—will gain traction, supported by advances in joining technologies.
Conclusion
By 2026, the aluminum and steel markets will be characterized by a dual trajectory: increasing demand from sustainable technologies and infrastructure, balanced by supply-side constraints and environmental regulations. Companies that invest in low-carbon production, circular economy models, and regional supply chains will be best positioned to thrive. Policymakers and industry leaders must collaborate to ensure a stable, equitable transition that supports both economic growth and climate objectives.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Aluminum and Steel: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing aluminum and steel, especially for critical applications, involves significant risks beyond simple price comparisons. Two major areas of concern are material quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these can lead to project delays, safety hazards, reputational damage, and costly legal disputes.
Quality Pitfalls in Aluminum and Steel Sourcing
-
Inadequate Specification & Documentation:
- Pitfall: Relying on vague terms like “high-grade aluminum” or “strong steel” without defining exact alloy designations (e.g., 6061-T6, 304L, A572-Grade 50), required mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength, elongation), chemical composition limits, and relevant international standards (ASTM, ISO, EN, JIS).
- Consequence: Receiving material that meets a different standard or grade than required, leading to potential failure in service. Difficulty proving non-conformance without clear specs.
- Mitigation: Develop and enforce detailed, unambiguous technical specifications. Require full Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Mill Certificates (e.g., 3.1, 3.2 per EN 10204) for every batch, traceable to the heat/lot number.
-
Substandard Material & “Bait-and-Switch”:
- Pitfall: Suppliers providing inferior alloys (e.g., scrap-heavy aluminum, lower-grade steel) or substituting cheaper, non-conforming materials, sometimes mislabeling them. This is prevalent with suppliers in regions with less stringent oversight.
- Consequence: Catastrophic failures in structural, aerospace, medical, or high-pressure applications. Increased scrap rates, warranty claims, and safety recalls.
- Mitigation: Rigorous supplier vetting (audits, financial health checks). Implement independent third-party testing (chemical analysis, mechanical testing, NDT) upon receipt, especially for critical components. Maintain traceability throughout the supply chain.
-
Inconsistent Quality & Process Control:
- Pitfall: Suppliers lacking robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) or inconsistent manufacturing processes (casting, rolling, heat treatment), leading to batch-to-batch variability.
- Consequence: Unpredictable performance, difficulties in manufacturing (e.g., inconsistent machinability, formability, weldability), increased rejection rates.
- Mitigation: Prioritize suppliers with certified QMS. Require process capability data (Cp, Cpk). Include clauses for quality audits and process reviews. Implement statistical process control (SPC) requirements.
-
Counterfeit Materials:
- Pitfall: Deliberate falsification of MTRs or use of stolen/re-labeled material from reputable mills to pass off substandard or incorrect material.
- Consequence: Severe safety risks, project failures, significant liability. Extremely difficult to detect without rigorous verification.
- Mitigation: Source directly from reputable mills or authorized distributors. Verify MTR authenticity (holograms, watermarks, direct mill confirmation). Conduct independent verification testing. Use blockchain or other traceability technologies where feasible.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls in Aluminum and Steel Sourcing
-
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Alloys or Processes:
- Pitfall: Suppliers using or reverse-engineering your company’s specific, patented alloy formulations (e.g., a unique high-strength aluminum alloy) or manufacturing processes without license or permission. Sourcing from suppliers known to engage in industrial espionage.
- Consequence: Loss of competitive advantage, devaluation of R&D investment, potential patent infringement lawsuits (if you unknowingly use the infringing material), reputational damage.
- Mitigation: Clearly define IP ownership and usage rights in contracts. Conduct thorough due diligence on supplier ethics and history. Use Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) rigorously. Patent your unique formulations/processes.
-
Reverse Engineering and Design Theft:
- Pitfall: Providing detailed specifications, drawings, or prototypes to suppliers (especially in low-cost regions) who then use that information to manufacture and sell identical or similar products to your competitors.
- Consequence: Market share erosion, loss of sales, commoditization of your product. Difficulty proving theft.
- Mitigation: Minimize disclosure of critical design details. Use “black box” specifications where possible. Employ strong, jurisdiction-specific IP clauses in contracts. Choose suppliers with proven track records of IP respect. Consider split-sourcing or using trusted partners for critical components.
-
Weak Contractual IP Protections:
- Pitfall: Contracts lacking clear clauses defining: ownership of background IP, ownership of any new IP developed during the sourcing/manufacturing process, confidentiality obligations, permitted uses of provided information, and consequences of IP infringement.
- Consequence: Ambiguity leading to disputes, loss of control over your IP, inability to enforce rights.
- Mitigation: Engage legal counsel specializing in IP and international trade. Ensure contracts explicitly address all IP aspects, including indemnification clauses for IP infringement by the supplier. Specify governing law and dispute resolution mechanisms.
-
Inadequate Protection in IP-Vulnerable Regions:
- Pitfall: Sourcing from jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement, prevalent counterfeiting, or where “know-how” is not adequately protected, increasing the risk of technology leakage.
- Consequence: High risk of IP theft, difficulty in pursuing legal remedies, potential for your technology to be rapidly copied and sold cheaper.
- Mitigation: Avoid sourcing critical, IP-sensitive components from high-risk regions if possible. If necessary, implement extreme vetting, use trusted local partners with skin in the game, enforce robust contractual protections, and consider alternative supply chain models (e.g., captive manufacturing).
By proactively identifying and addressing these quality and IP pitfalls through rigorous due diligence, clear specifications, strong contracts, independent verification, and strategic supplier selection, companies can significantly reduce the risks associated with sourcing aluminum and steel.
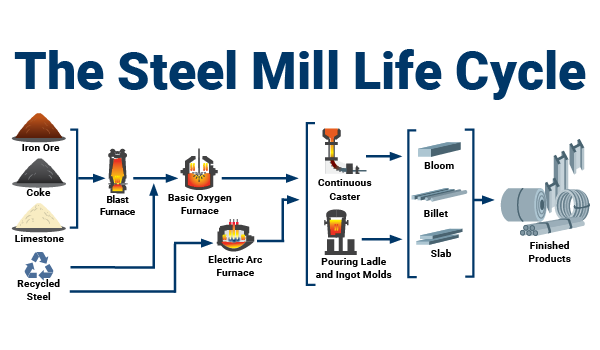
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum and Steel
Overview of Aluminum and Steel in Global Trade
Aluminum and steel are critical industrial metals widely used in construction, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors. Their transportation and regulatory compliance involve specific considerations due to weight, form (e.g., coils, sheets, billets, ingots), international trade policies, and environmental standards. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements for handling these materials across supply chains.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Both aluminum and steel are subject to a range of international, national, and regional regulations. Compliance ensures legal trade, avoids penalties, and supports sustainability goals. Key regulations include:
- Trade Regulations and Tariffs: Monitor country-specific import/export controls, such as U.S. Section 232 tariffs on steel and aluminum, EU anti-dumping measures, and country-of-origin rules under free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, CPTPP).
- Customs Documentation: Accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes are essential:
- Aluminum: Typically HS 76 (e.g., 7606 for aluminum sheets)
- Steel: Typically HS 72 (e.g., 7209 for flat-rolled products)
Ensure proper commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and bills of lading. - Environmental and Safety Standards: Comply with REACH (EU), TSCA (U.S.), and other chemical substance regulations, especially for treated or coated metals.
- Conflict Minerals and Responsible Sourcing: While aluminum is not a conflict mineral, steel production may involve regulated raw materials (e.g., chromium, nickel). Adherence to OECD Due Diligence Guidance is recommended.
- Recycling and End-of-Life Compliance: Follow directives such as the EU End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) and Waste Framework Directive, which impact material traceability and recyclability.
Packaging and Handling Guidelines
Proper packaging and handling prevent damage, ensure safety, and meet carrier requirements:
- Steel Products: Use wooden cradles, steel strapping, and waterproof wrapping for coils and plates. Protect edges to prevent rust and deformation.
- Aluminum Products: Apply anti-corrosion paper or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) film, especially for sheets and extrusions. Avoid contact with dissimilar metals to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Unit Load Optimization: Secure loads on pallets or in containers using dunnage and lashing. Maximize container or flatbed utilization while respecting weight limits.
- Labeling: Clearly mark packages with product type, alloy, dimensions, weight, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”), and safety warnings.
Transportation and Shipment Modes
Choosing the right transport mode depends on volume, distance, cost, and delivery timelines:
- Maritime Shipping: Most common for bulk shipments. Use dry containers for smaller loads or flat-rack/flat-bed containers for oversized coils and beams. Ensure cargo is moisture-protected in humid environments.
- Rail Transport: Cost-effective for long-distance overland movement in regions like North America and Europe. Ideal for large volumes between industrial hubs.
- Road Freight: Best for regional distribution or just-in-time delivery. Use specialized trailers (e.g., lowboys) for heavy or oversized steel beams.
- Air Freight: Rarely used due to high cost and weight; reserved for urgent, high-value components or prototypes.
Storage and Inventory Management
Proper storage minimizes degradation and optimizes supply chain efficiency:
- Indoor Storage: Preferred for both metals to prevent moisture exposure. Use elevated racks to avoid ground contact.
- Environmental Controls: Maintain low humidity and avoid temperature fluctuations. Use desiccants if necessary.
- Segregation: Store aluminum and steel separately to prevent contact-induced corrosion. Clearly label inventory by alloy, grade, and batch number.
- Inventory Tracking: Implement barcode or RFID systems to support traceability, especially for quality control and compliance audits.
Risk Management and Insurance
Mitigate logistical risks through planning and coverage:
- Cargo Insurance: Ensure all shipments are covered for damage, theft, and delays. Specify coverage for high-value or sensitive materials.
- Force Majeure and Supply Chain Disruptions: Monitor geopolitical risks, port congestion, and production outages. Diversify suppliers and logistics partners.
- Quality Assurance: Conduct pre-shipment inspections and retain material test reports (MTRs) for compliance and dispute resolution.
Sustainability and ESG Considerations
Growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors affects metal logistics:
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Use tools like Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) to quantify emissions across the supply chain.
- Recycled Content: Prioritize suppliers using recycled aluminum (up to 95% energy savings) and scrap-based steel production.
- Certifications: Seek materials compliant with standards such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), Responsible Steel, and ASI (Aluminum Stewardship Initiative).
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of aluminum and steel requires attention to regulatory detail, proper handling practices, and sustainable sourcing. By following this guide, businesses can ensure efficient, compliant, and responsible movement of these essential materials across global markets. Regular updates to trade policies and environmental regulations are recommended to maintain ongoing compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing aluminum and steel requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, supply chain reliability, and sustainability. Both materials are essential across various industries due to their strength, durability, and versatility, but they serve different purposes—aluminum for lightweight and corrosion-resistant applications, and steel for high strength and structural integrity. When sourcing these materials, it is crucial to evaluate suppliers based on certifications, production capabilities, environmental practices, and logistical efficiency. Additionally, monitoring market trends, geopolitical factors, and raw material price fluctuations can help mitigate risks and ensure a stable supply. Ultimately, establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers, leveraging global sourcing options, and integrating sustainable procurement practices will enhance operational resilience and support long-term business objectives.