The global aluminum products market continues to expand, driven by increasing demand across aerospace, automotive, construction, and packaging industries. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global aluminum market size was valued at USD 230.9 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by aluminum’s lightweight properties, recyclability, and rising adoption in electric vehicles and sustainable building materials. In parallel, Mordor Intelligence projects a steady rise in aluminum product demand, particularly in emerging economies, where urbanization and industrialization are accelerating infrastructure development. As the industry evolves, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scale, and sustainability in aluminum production. Below, we highlight the top 9 aluminum products manufacturers shaping the future of this dynamic market.
Top 9 Aluminum Products Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Alcoa
Domain Est. 1986
Website: alcoa.com
Key Highlights: Aluminum. Our aluminum segment includes smelting, casting and select energy assets. · Alumina. We are the world’s largest third-party producer of alumina….
#2 Novelis
Domain Est. 2000
Website: novelis.com
Key Highlights: Novelis is the leading producer of flat-rolled aluminum products and the world’s largest recycler of aluminum. About Us · People · Leadership · Investors & ……
#3 AMG Aluminum
Domain Est. 2012
Website: amg-al.com
Key Highlights: AMG Aluminum is a customer-focused, technology-driven organization dedicated to innovation, quality, technical expertise, and rapid response to customer needs….
#4 Century Aluminum Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: centuryaluminum.com
Key Highlights: We are a global metals and mining company, focused on bauxite, alumina and aluminum. We operate globally, with operations in the US, Iceland, Jamaica, and ……
#5 Superior Aluminum Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: superioraluminum.com
Key Highlights: Superior Aluminum Products designs and manufactures aluminum railing, columns, and fence customized for your project….
#6 The Aluminum Association
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aluminum.org
Key Highlights: The U.S. aluminum industry is a key element of the nation’s manufacturing base. Check out our latest study on aluminum’s impact on the American economy….
#7 Kaiser Aluminum
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kaiseraluminum.com
Key Highlights: We deliver highly engineered, semi-fabricated aluminum products that are stronger, lighter, more efficient and sustainable….
#8 We are Constellium
Domain Est. 2006
Website: constellium.com
Key Highlights: Constellium is a global leader in the development, manufacturing, and recycling of aluminum products and solutions. · Discover our products and solutions….
#9 ALUMINUM USA
Domain Est. 2013
Website: aluminum-us.com
Key Highlights: ALUMINUM USA is a premier industry event covering the entire aluminum value chain from upstream (mining, smelting) via midstream (casting, rolling, extrusions) ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Products
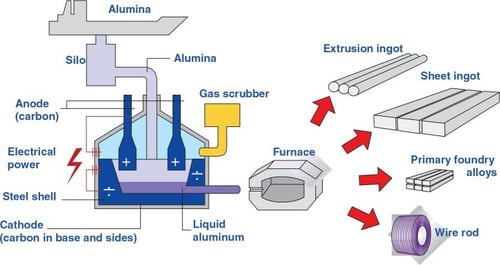
H2 2026 Market Trends for Aluminum Products
The global aluminum products market in H2 2026 is expected to be shaped by a confluence of macroeconomic factors, evolving industrial demand, sustainability imperatives, and technological advancements. Building on trends emerging in the first half of the year, the second half will likely see increased focus on supply chain resilience, green premium adoption, and strategic positioning within key end-use sectors.
1. Demand Dynamics: Resilience in Key Sectors, Cautious Growth Overall
* Automotive (EV Focus): Demand from the automotive sector, particularly electric vehicles (EVs), will remain a primary growth driver. H2 2026 will see continued strong demand for aluminum in EV lightweighting (battery enclosures, chassis, extrusions) to improve range and efficiency. However, overall automotive production growth might be moderate due to lingering consumer caution and high interest rates, tempering total aluminum demand growth compared to pure EV penetration rates. Aluminum content per vehicle is expected to rise steadily.
* Construction & Infrastructure: Government stimulus in key regions (notably North America and parts of Asia) aimed at infrastructure modernization and energy transition projects (e.g., grid upgrades, renewable installations requiring aluminum structures) will provide significant support. Demand for architectural aluminum (windows, facades) may remain more subdued in residential construction but steady in commercial and public projects.
* Packaging: The packaging sector, especially beverage cans and food packaging, will show stable, resilient demand. Growth will be driven by sustainability trends (aluminum’s infinite recyclability) and consumer preference for premium, lightweight, and protective packaging. Regulatory pressure on plastic alternatives will be a tailwind.
* Renewables & Energy: Demand for aluminum in solar panel frames, inverters, and transmission infrastructure will continue its strong upward trajectory, directly tied to global renewable energy deployment targets. The energy transition remains a major structural growth pillar.
* Aerospace & Defense: Recovery and growth in commercial aerospace will support demand for high-value aerospace alloys. Geopolitical tensions may also boost defense spending, translating into demand for specialized aluminum products.
2. Supply Chain & Cost Environment: Stability Emerging, Green Premiums Ascendant
* Energy Costs: Energy remains the dominant cost component. H2 2026 is expected to see relatively stable, though still elevated, global energy prices compared to the volatility of 2022-2023. This provides greater predictability for smelters. However, regional disparities (e.g., high European energy costs) will persist, influencing trade flows.
* Raw Materials (Bauxite & Alumina): Supply of bauxite and alumina is anticipated to be adequate, though logistics and geopolitical factors (e.g., Guinea’s significance) require monitoring. Alumina refining margins may improve slightly as alumina prices stabilize.
* Green Premiums: The “green aluminum” market will mature significantly in H2 2026. A clear price premium (the “green premium”) for aluminum produced with renewable energy or low-carbon processes will become more established and transparent. Major consumers (EV OEMs, tech companies, packaging leaders) will actively procure green aluminum to meet Scope 3 emissions targets, creating a two-tiered market.
* Trade Flows & Protectionism: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and domestic industrial policies (e.g., US Inflation Reduction Act, EU Green Deal Industrial Plan) will continue to influence trade flows. Expect continued scrutiny of Chinese aluminum exports (especially semi-finished goods) and potential for new trade measures or adjustments to existing ones (like CBAM adjustments). Nearshoring and friend-shoring trends will persist, benefiting producers in North America and Europe with access to cleaner energy.
3. Sustainability & ESG: Non-Negotiable Driver
* Decarbonization Imperative: Reducing the carbon footprint of primary aluminum production (currently averaging ~16-17 kg CO2e/kg Al) is the paramount challenge. H2 2026 will see accelerated investment and deployment of:
* Inert Anode Technology: Pilots and early commercialization efforts (e.g., ELYSIS) will be closely watched. While widespread adoption is still years away, progress will be a key market signal.
* Renewable Energy Sourcing: Smelters securing long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) with hydro, wind, and solar will gain a significant competitive advantage and market access.
* Circularity: Recycling rates will continue to rise. The difference between primary and secondary aluminum prices may fluctuate based on scrap availability and demand for high-purity recycled content (e.g., for automotive). Design for recycling will gain importance.
* Transparency & Certification: Demand for verifiable data on product carbon footprint (PCF) will surge. Standards like the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) will become increasingly important for market access. Blockchain for traceability may start gaining traction.
4. Technology & Innovation: Enabling Efficiency and New Applications
* Advanced Alloys: Development and adoption of new high-strength, lightweight, and formable aluminum alloys (e.g., advanced 6xxx and 7xxx series, aluminum-lithium) will accelerate, driven by EV and aerospace demands.
* Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Use of aluminum powders in AM for complex, lightweight components (aerospace, high-performance automotive) will grow, though still a niche volume.
* Process Optimization: Continued focus on improving smelting efficiency (e.g., digital twins, AI for process control) and reducing anode effects to lower emissions and costs.
5. Price Outlook: Moderate Volatility, Green Premium Differentiation
* The LME aluminum price in H2 2026 is likely to trade in a moderately volatile range, influenced by macroeconomic signals (interest rates, growth outlook), energy costs, inventory levels, and LME warehouse dynamics.
* Key differentiator: The most significant trend will be the widening gap between the price of conventional aluminum and certified low-carbon (“green”) aluminum. The “green premium” will solidify as a core market feature, potentially becoming a larger factor in producer profitability than the base LME price swing for those with the right assets.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The aluminum products market in the second half of 2026 will be characterized by differentiation. While overall demand growth is steady but not explosive, the market is fundamentally splitting:
1. Commodity Aluminum: Facing moderate demand, cost pressures, and competition, particularly from regions with lower energy costs or carbon costs.
2. Green/Value-Added Aluminum: Experiencing strong, structurally driven demand from ESG-conscious industries (EVs, tech, renewables), commanding premium prices, and benefiting from supportive government policies.
Success will hinge on a producer’s ability to secure low-carbon energy, achieve operational efficiency, provide verifiable sustainability credentials, and innovate for high-growth, high-value applications. Supply chains will continue to adapt towards resilience and sustainability, with transparency and decarbonization being the dominant themes shaping strategy and investment.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Aluminum Products (Quality, IP)
Sourcing aluminum products—whether raw materials, extrusions, castings, or finished components—can present several challenges, particularly concerning quality control and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate risks and ensures reliable supply chains.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Specifications
One of the most common issues is receiving aluminum that does not meet specified grades (e.g., 6061-T6, 7075, etc.). Suppliers may substitute lower-grade alloys to cut costs, leading to performance failures in end applications. Without proper material certification (e.g., mill test reports), verifying compliance becomes difficult.
2. Poor Surface Finish and Dimensional Tolerances
Aluminum products such as extrusions or machined parts often require tight tolerances and high surface quality. Inadequate tooling, outdated equipment, or lack of quality control processes at the supplier level can result in warped profiles, surface defects (scratches, pits, or oxidation), or dimensional inaccuracies.
3. Inadequate or Falsified Certifications
Some suppliers provide forged or incomplete documentation, such as Material Test Reports (MTRs) or RoHS/REACH compliance certificates. This lack of traceability increases the risk of non-compliance with industry standards or regulatory requirements.
4. Inconsistent Heat Treatment
Improper or inconsistent heat treatment can significantly affect mechanical properties like strength and ductility. For example, failing to properly age-harden aluminum (T4, T6 temper) may lead to premature failure in structural applications.
5. Contamination and Recycling Mixing
Recycled aluminum is cost-effective but can introduce impurities if not properly sorted. Mixing different alloy scraps can result in off-spec chemical compositions, affecting performance and weldability.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Design Theft and Reverse Engineering
When sourcing custom aluminum parts (e.g., proprietary extrusion dies or machined components), there’s a risk that suppliers may copy designs or use them to serve competing customers. This is especially prevalent in regions with weak IP enforcement.
2. Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts
Many procurement agreements fail to clearly define ownership of tooling, molds, or custom designs. Without explicit IP clauses, suppliers may claim partial rights or reuse tooling for third parties, undermining competitive advantage.
3. Unauthorized Production or Overproduction
Suppliers might produce excess units beyond the agreed order and sell them independently. This not only dilutes market exclusivity but can also result in counterfeit or gray-market products.
4. Weak Enforcement in Offshore Sourcing
Sourcing from countries with limited IP protection frameworks increases the risk of replication and unauthorized distribution. Legal recourse is often slow, costly, or ineffective in such jurisdictions.
5. Shared Tooling and Multi-Client Dies
Some aluminum extruders use shared or multi-client dies to reduce costs. Unless explicitly prohibited, your custom profile could be replicated for competitors, violating design confidentiality.
Mitigation Strategies
- Require certified material test reports (MTRs) and conduct third-party inspections.
- Audit suppliers regularly for quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001) and production capabilities.
- Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clearly define IP ownership in contracts.
- Retain ownership of custom tooling and include audit rights.
- Work with reputable suppliers and consider local or nearshore sourcing for critical components.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, businesses can ensure both the quality integrity and IP security of their aluminum product sourcing.
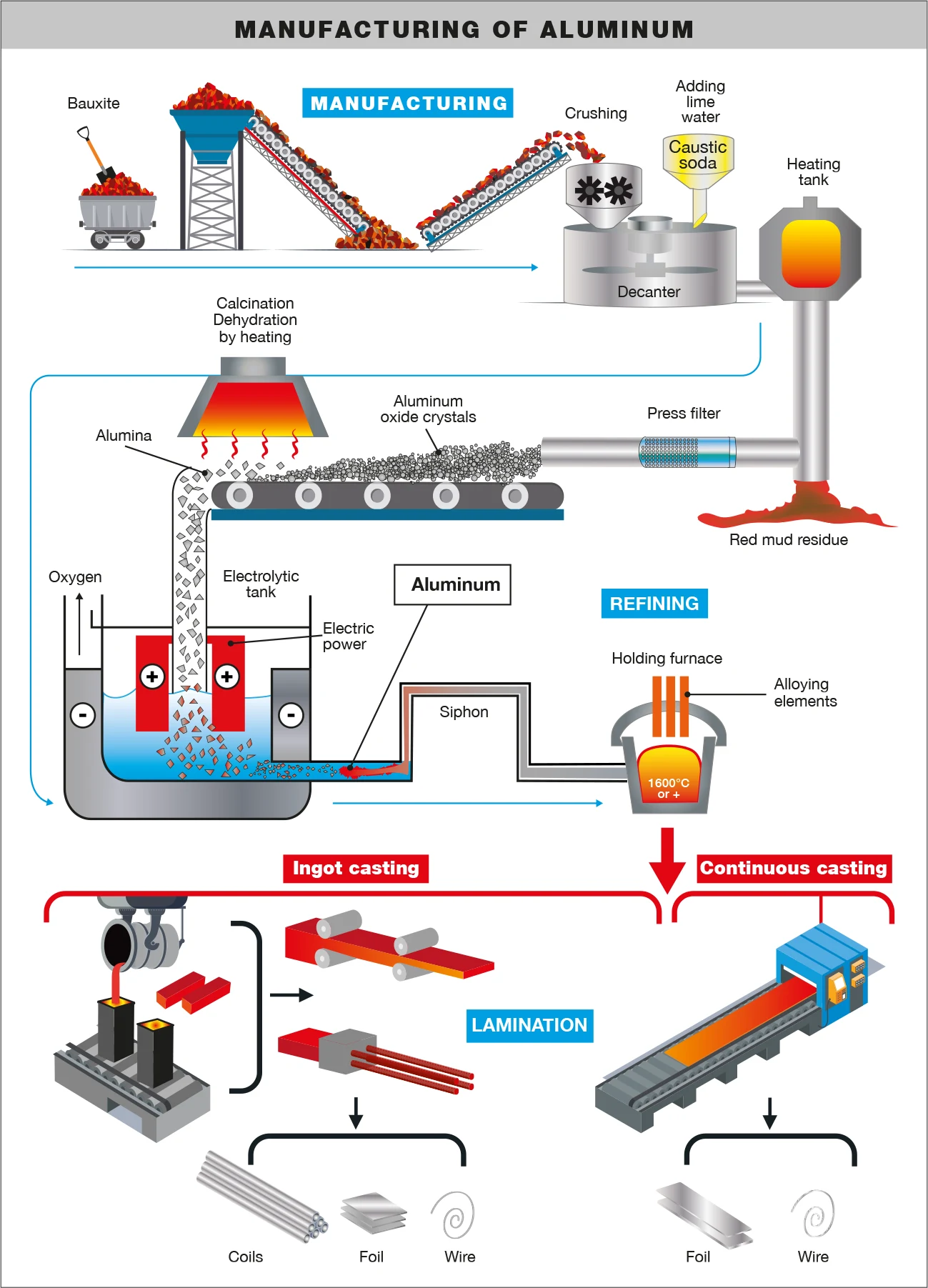
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum Products
Overview of Aluminum Product Characteristics
Aluminum products vary widely in form, including ingots, sheets, coils, extrusions, foils, and finished components. Their lightweight nature, high strength-to-weight ratio, and corrosion resistance make them ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and packaging. However, these products require careful handling and specific storage conditions to prevent surface damage, oxidation, and contamination during transit and storage.
Regulatory and International Compliance
Aluminum products are subject to various international trade regulations, including export controls, import tariffs, and environmental standards. Exporters must comply with regulations from agencies such as the U.S. Department of Commerce (Bureau of Industry and Security), the European Union’s REACH and RoHS directives, and local customs authorities. Proper classification under the Harmonized System (HS Code) — typically 7601–7616 — is essential for accurate duty assessment and compliance. Additionally, conflict minerals reporting may apply if aluminum is sourced from regions under scrutiny.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to protect aluminum products from mechanical damage, moisture, and contamination. Sheets and coils should be wrapped in protective film, placed on wooden pallets, and secured with strapping. Extrusions and long bars require cradles or bundling to prevent bending. Use of desiccants and vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) is recommended for sea shipments to mitigate moisture-related corrosion. Handling must avoid direct contact with steel or other dissimilar metals to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Aluminum products can be transported via road, rail, sea, or air, depending on volume, destination, and urgency. For ocean freight, containers must be well-ventilated and moisture-controlled, especially for long voyages. Aluminum’s recyclability and sustainability profile often qualify shipments for green logistics incentives. Ensure proper load distribution and secure lashing to prevent shifting during transit. Temperature fluctuations should be minimized, particularly for coated or anodized aluminum, which may be sensitive to extreme conditions.
Documentation and Traceability
Accurate documentation is vital for smooth customs clearance and compliance. Required documents typically include commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and material test reports (MTRs) confirming alloy composition and mechanical properties. For regulated industries (e.g., aerospace), full traceability via mill test certificates (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2) is mandatory. Digital tracking systems and blockchain solutions are increasingly used to enhance supply chain transparency.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Aluminum production and transport are governed by environmental standards such as ISO 14001 and safety regulations like OSHA (in the U.S.) or ADR (for European road transport). Dust from aluminum machining residues can be flammable; therefore, proper storage and transport of scrap or swarf must follow hazardous materials guidelines (e.g., UN 3170 for aluminum waste). Recycling documentation should be maintained to support compliance with circular economy policies and carbon footprint reporting.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Customs clearance for aluminum products may involve anti-dumping or countervailing duties, especially when imported from countries under trade investigations (e.g., China, Russia, or certain Middle Eastern nations). Importers should verify current duty rates and country-specific trade agreements. Use of Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) status can expedite clearance. Accurate valuation, including details on processing, alloy type, and fabrication, helps avoid disputes with customs authorities.
Storage and Inventory Management
Aluminum should be stored indoors in dry, well-ventilated areas, off the ground on pallets or racks. Avoid exposure to saltwater, acids, alkalis, and high humidity. Coated or painted aluminum must be protected from UV radiation and temperature extremes. Implement first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory practices to minimize aging-related quality issues. Regular inspections help detect early signs of corrosion or packaging degradation.
End-of-Life and Recycling Compliance
Aluminum is highly recyclable, and many regions enforce recycling mandates. Producers and distributors must comply with Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) regulations where applicable. Documentation of recycling streams, recycled content percentages, and proper waste handling (especially for mixed-metal scrap) supports compliance and sustainability reporting. Certifications such as the Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) can enhance market access and customer trust.
Conclusion and Best Practices
Successful logistics and compliance for aluminum products require a proactive approach integrating regulatory knowledge, proper handling, and documentation rigor. Partnering with certified suppliers, using digital tracking tools, and staying updated on trade policy changes are essential best practices. Regular training for logistics and compliance teams ensures ongoing adherence to evolving standards and maintains supply chain integrity.
In conclusion, sourcing aluminum products requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. Aluminum’s lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and recyclable properties make it a preferred material across industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. When selecting suppliers, businesses should prioritize those with strong quality certifications, transparent production practices, and adherence to environmental and ethical standards. Evaluating factors such as alloy specifications, fabrication capabilities, lead times, and logistical support is essential to ensure the sourced products meet technical and operational requirements. Additionally, considering long-term partnerships and regional sourcing options can enhance supply chain resilience and reduce costs. With increasing focus on sustainability, sourcing aluminum from suppliers that utilize recycled content and energy-efficient production methods supports both environmental goals and regulatory compliance. Ultimately, a well-informed and holistic sourcing strategy enables organizations to leverage the full benefits of aluminum while maintaining competitiveness and responsibility in the global market.