The global aluminum laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for lightweight, high-strength joining solutions in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030, with aluminum-specific applications representing a significant share due to the metal’s favorable conductivity, strength-to-weight ratio, and growing use in electric vehicles (EVs). Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of 7.5% for the laser welding market through 2028, underscoring the rising adoption of precision welding technologies in advanced manufacturing. As OEMs prioritize automation, energy efficiency, and structural integrity, aluminum laser welding has emerged as a critical enabling technology. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers leading innovation and market share in aluminum laser welding, based on technological capabilities, industry partnerships, product performance, and market reach.
Top 10 Aluminum Laser Welding Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Company for Industrial Laser Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: laserline.com
Key Highlights: The leading laser company for integrated & customized diode laser manufacturing solutions for various industries & applications….
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Laserax
Domain Est. 2012
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#4 Equipment & Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#5 Civan Lasers
Domain Est. 2021
Website: civanlasers.com
Key Highlights: Dynamic Beam Lasers are a cutting-edge technology that makes welding faster, deeper, and of higher quality, changing the way welding is done today….
#6 Denaliweld
Domain Est. 2023
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#7 Laser welding
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: High-quality laser technology & laser sytems from ALPHA LASER: powerful laser machines for metalworking: mobile, flexible, & precise ✓ technical support ✓….
#8 Laser Welding
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding creates exceptionally high-quality joints with excellent physical and electrical properties, even when joining challenging materials like aluminum ……
#9 Laser Welding Aluminum
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ebindustries.com
Key Highlights: Laser beam welding is one of our most popular services for welding aluminum. The process is ideal for fast, clean welds….
#10 Laser Welding Machine
Domain Est. 2015
Website: varisigns.com
Key Highlights: Our handheld fiber laser welder, with a power of 2000 watts, can weld aluminum letters up to 3mm thick. We can now supply a small weld head for 3D channel ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Laser Welding

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aluminum Laser Welding
The aluminum laser welding market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. Here are the key H2-level trends shaping the landscape:
1. Accelerated Adoption in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Lightweighting:
The primary growth engine for aluminum laser welding will be the global EV boom. As automakers intensify efforts to extend battery range, lightweighting becomes paramount. Aluminum’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal, and high-speed, high-precision laser welding is the preferred joining method for complex EV components like battery trays, motor housings, and structural frames. By 2026, laser welding is expected to dominate aluminum joining in EV production lines, replacing traditional methods like MIG welding due to superior speed, lower heat input (reducing distortion), and better weld quality.
2. Dominance of Fiber Lasers and Advancements in Beam Technology:
Fiber lasers will solidify their position as the technology of choice, favored for their efficiency, reliability, beam quality, and compatibility with robotic automation. Key developments by 2026 will include:
* Higher Power & Brightness: Widespread adoption of multi-kilowatt (6kW-20kW+) fiber lasers enabling faster welding speeds and deeper penetration for thicker sections.
* Wobble Welding & Beam Shaping: Advanced beam oscillation (wobble) and shaping techniques will become standard, significantly improving gap bridging, tolerance to fit-up variation, spatter reduction, and overall weld consistency – crucial for mass production.
* Green and Blue Wavelength Lasers: While still niche, green (515nm) and blue (450nm) lasers will see increased R&D and specialized deployment. Their superior absorption by highly reflective aluminum (especially pure Al and alloys like 1000/5000 series) will address persistent challenges in keyhole stability and spatter, particularly for thin sheets and challenging alloys.
3. Integration of AI, Digital Twins, and Real-Time Process Monitoring:
Intelligence will be embedded into welding systems. By 2026:
* AI-Powered Process Control: Machine learning algorithms will analyze real-time sensor data (vision, spectrometry, acoustic) to automatically optimize parameters, predict defects, and ensure consistent weld quality, reducing scrap and rework.
* Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of welding cells will be used for simulation, optimization, predictive maintenance, and operator training, accelerating setup and improving uptime.
* Advanced In-Process Monitoring: Integrated high-speed cameras, plasma monitoring, and thermography will provide immediate feedback, enabling closed-loop control and traceability for critical applications (e.g., aerospace, EVs).
4. Focus on Automation, Robotics, and Flexible Manufacturing:
Demand for high-volume, consistent production will drive deeper integration of laser welding into automated cells. Expect:
* Increased Robot Adoption: Collaborative robots (cobots) and high-precision articulated arms will handle complex 3D welding paths with greater flexibility.
* Modular & Reconfigurable Cells: Systems designed for quick changeover will support mixed-model production, essential for the diverse EV market.
* End-to-End Automation: Integration with material handling, vision systems for part location, and post-weld inspection will create seamless, lights-out manufacturing lines.
5. Addressing Key Challenges: Spatter, Porosity, and Alloy Variability:
Despite progress, challenges persist. By 2026, solutions will focus on:
* Spatter Minimization: Through optimized beam shaping (wobble patterns), tailored pulse waveforms, and improved shielding gas strategies.
* Porosity Control: Enhanced understanding of keyhole dynamics and vaporization, combined with real-time monitoring and parameter adjustment, will reduce hydrogen and shrinkage porosity, especially in high-strength alloys (e.g., 6xxx, 7xxx).
* Handling Diverse Alloys: Development of more robust, adaptive welding strategies and filler materials (e.g., Al-Si, Al-Mg wires for hybrid processes) to reliably weld a wider range of aluminum alloys with varying properties.
6. Sustainability and Cost Pressures Driving Efficiency:
Sustainability goals and economic factors will push for:
* Higher Energy Efficiency: Continued improvement in laser source wall-plug efficiency and overall system optimization.
* Reduced Material Waste: Precision welding minimizes HAZ and distortion, reducing post-processing needs. Better process control lowers scrap rates.
* Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Focus: Suppliers will emphasize not just equipment cost, but reduced consumables, lower energy use, higher throughput, and minimal maintenance to justify investment.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the aluminum laser welding market will be characterized by smarter, faster, more reliable, and increasingly automated systems. Driven overwhelmingly by the EV revolution and enabled by advancements in laser technology, beam control, and digitalization, the market will deliver significant improvements in productivity, quality, and sustainability. Overcoming inherent challenges like spatter and porosity through intelligent process control and emerging wavelengths will be key to unlocking even broader applications across transportation, aerospace, and consumer electronics.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Aluminum Laser Welding (Quality, IP)
Sourcing aluminum laser welding services or components involves several critical challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to production delays, compromised product performance, and legal or competitive risks.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Weld Integrity Due to Material Variability
Aluminum alloys exhibit significant differences in thermal conductivity, reflectivity, and sensitivity to impurities. Sourcing from suppliers without strict alloy verification processes can result in inconsistent weld penetration, porosity, or cracking. It is essential to verify that the supplier controls incoming material specifications and performs pre-weld surface preparation (e.g., cleaning, oxide removal).
Lack of Process Control and Monitoring
High-quality laser welding demands precise control over parameters such as power, speed, focus, and shielding gas. Suppliers without real-time monitoring systems (e.g., weld seam tracking, plasma monitoring) may produce substandard welds that fail in critical applications. Ensure the supplier employs process validation and statistical process control (SPC) to maintain repeatability.
Insufficient Post-Weld Inspection and Testing
Many suppliers perform only visual inspections, missing subsurface defects like micro-cracks or lack of fusion. Sourcing without requiring non-destructive testing (NDT)—such as ultrasonic testing (UT), X-ray, or dye penetrant inspection—increases the risk of field failures. Define clear quality acceptance criteria and inspection protocols in procurement agreements.
Inadequate Operator Skill and Certification
Laser welding aluminum requires specialized training due to its high thermal sensitivity and reflectivity. Suppliers with underqualified technicians may struggle with parameter optimization and troubleshooting. Verify operator certifications (e.g., ISO 14731 or AWS) and assess hands-on experience with aluminum-specific applications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Protection Pitfalls
Unprotected Design and Process Specifications
Sharing detailed CAD models, weld paths, or proprietary joining techniques without proper legal safeguards risks IP theft or reverse engineering. Always execute robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) before disclosing sensitive information and limit data access to need-to-know personnel.
Weak Contractual Clauses on IP Ownership
Ambiguous contracts may not clearly assign IP rights to developed tooling, welding procedures, or process innovations. This can lead to disputes if the supplier claims partial ownership. Explicitly define in sourcing agreements that all IP developed for your project remains your sole property.
Use of Shared or Non-Dedicated Equipment
Some suppliers run multiple clients’ jobs on the same laser systems, increasing the risk of cross-contamination of data or accidental exposure of proprietary parameters. Opt for suppliers with dedicated production cells or strict data segregation protocols to protect sensitive process data.
Inadequate Traceability and Documentation Control
Poor documentation practices can undermine IP protection and quality audits. Ensure the supplier maintains secure, version-controlled records of welding procedures (WPS), parameter logs, and inspection reports, accessible only under controlled conditions.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier audits focusing on quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100), request sample welds for independent testing, and involve legal counsel in contract drafting. Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in aluminum laser welding and transparent IP policies to safeguard both product quality and competitive advantage.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum Laser Welding
Introduction
Aluminum laser welding is a high-precision joining process used across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy. Due to the specialized nature of the process—requiring high-power lasers, inert gas shielding, and strict quality control—effective logistics and compliance management are critical to ensure safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
1. Health and Safety Regulations
- OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
- Ensure proper ventilation to control fumes and particulates; aluminum welding generates hazardous metal fumes (e.g., aluminum oxide).
- Mandate personal protective equipment (PPE): auto-darkening welding helmets, flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and respiratory protection where necessary.
-
Implement laser safety protocols per ANSI Z136.1: use interlocks, beam enclosures, and laser warning signage.
-
NIOSH (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health)
- Monitor airborne aluminum particulates; recommend exposure limits below 10 mg/m³ (total dust) and 5 mg/m³ (respirable fraction).
2. Environmental Regulations
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)
- Manage welding fumes and particulate emissions using local exhaust ventilation (LEV) and filtration systems.
- Classified aluminum welding waste (e.g., dross, filters) may be regulated under RCRA; determine if waste is hazardous based on TCLP testing.
- Ensure proper disposal or recycling of aluminum scrap in compliance with federal and state laws.
3. International Standards
- ISO 3834 (Quality Requirements for Fusion Welding)
- Certification to ISO 3834 ensures welding processes meet quality standards, including documentation, personnel qualification, and process control.
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Management)
- Implement an environmental management system to reduce the ecological footprint of laser welding operations.
- ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety)
- Establish a safety framework to minimize workplace risks associated with high-energy lasers and metal fumes.
4. Industry-Specific Requirements
- AS9100 (Aerospace)
- Traceability of materials, weld parameters, and operator certifications is mandatory.
- Full documentation of welding procedures (WPS) and procedure qualification records (PQR).
- IATF 16949 (Automotive)
- Requires process control, measurement systems analysis (MSA), and advanced product quality planning (APQP) for welding processes.
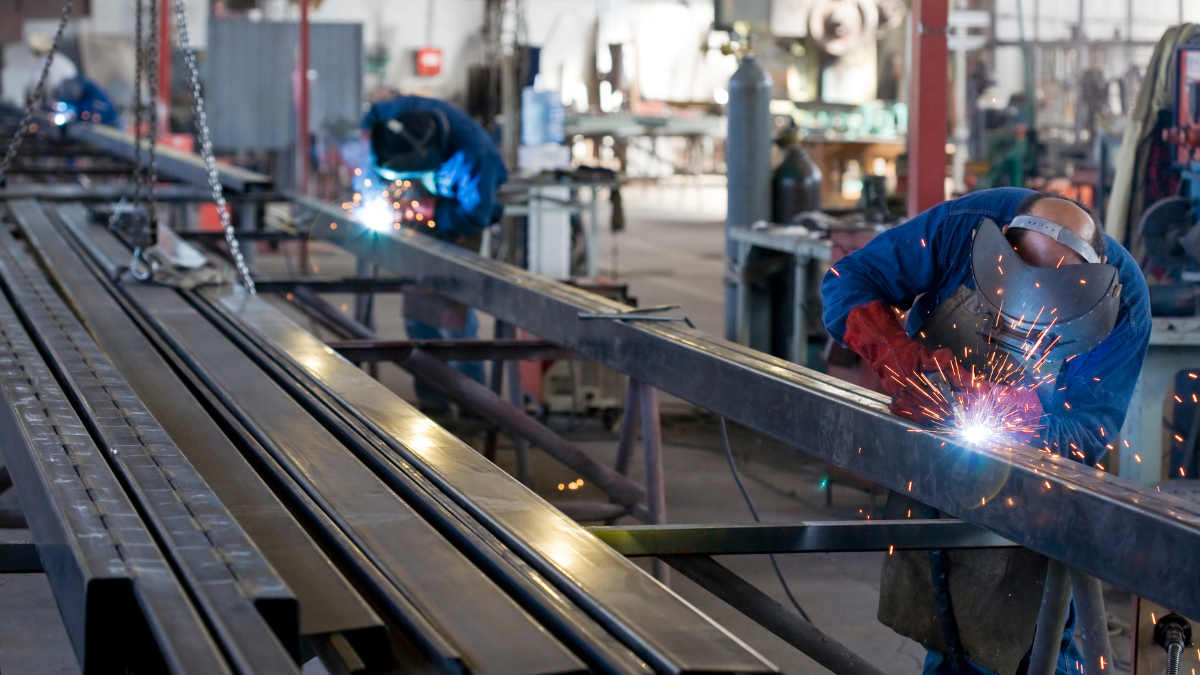
Logistics Management
1. Material Handling and Storage
- Store aluminum stock (sheet, extrusions, castings) in a dry, clean environment to prevent oxidation and contamination.
- Segregate aluminum from ferrous materials to avoid cross-contamination, which can compromise weld integrity.
- Use non-metallic or stainless-steel handling tools to prevent iron inclusions.
2. Equipment and Consumables
- Laser Systems: Schedule preventive maintenance and calibration per manufacturer guidelines (e.g., fiber laser output, beam alignment).
- Shielding Gas: High-purity argon or argon-helium mixtures must be stored safely; ensure gas cylinders are secured and labeled.
- Optics and Nozzles: Maintain spares inventory; clean or replace protective lenses regularly to maintain beam quality.
3. Transportation and Shipping
- For outsourced welding services, ensure transport of parts is in protective packaging to prevent surface damage.
- Use humidity-controlled containers for sensitive components to avoid moisture-related defects.
- Comply with DOT (Department of Transportation) regulations when shipping compressed gases (e.g., argon cylinders).
4. Process Documentation and Traceability
- Maintain digital logs of:
- Laser parameters (power, speed, pulse frequency)
- Shielding gas flow rates and purity
- Operator certifications and shift logs
- In-process inspection results (e.g., NDT reports)
- Implement barcode or RFID tracking for critical weld joints in regulated industries.
Quality Assurance and Inspection
1. Pre-Welding Checks
- Verify material certification (e.g., ASTM B209 for aluminum plate).
- Clean surfaces using stainless steel brushes or solvents to remove oxides and hydrocarbons.
- Confirm joint fit-up and alignment per engineering drawings.
2. In-Process Monitoring
- Use real-time monitoring systems (e.g., coaxial cameras, spectrometers) to detect defects like porosity or lack of fusion.
- Record welding parameters for every joint; integrate with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES).
3. Post-Welding Inspection
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
- Visual inspection (VT) per AWS D1.2 (Structural Welding Code – Aluminum)
- Radiographic testing (RT) or ultrasonic testing (UT) for critical joints
- Dye penetrant testing (PT) for surface cracks
- Destructive Testing:
- Tensile, bend, and microsection testing for procedure qualification.
Training and Personnel Certification
- Ensure welders and operators are certified per AWS D1.2 or equivalent standards.
- Provide laser safety training (e.g., LSO – Laser Safety Officer designation).
- Conduct regular refresher courses on compliance updates, equipment operation, and emergency procedures.
Conclusion
Successful aluminum laser welding operations depend on rigorous adherence to compliance standards and efficient logistics planning. By integrating regulatory requirements into daily operations, maintaining material and process traceability, and investing in personnel training, organizations can achieve high-quality, repeatable welds while minimizing risk and ensuring legal compliance. Regular audits and continuous improvement (e.g., Lean, Six Sigma) are recommended to sustain performance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Aluminum Laser Welding
Sourcing aluminum laser welding services requires a strategic approach that balances technological capability, material expertise, and supplier reliability. Aluminum presents unique challenges due to its high thermal conductivity, reflectivity, and sensitivity to atmospheric contamination, making laser welding a precise but demanding process. Therefore, selecting qualified suppliers with proven experience in aluminum laser welding—equipped with advanced fiber lasers, appropriate shielding gas systems, and robust process controls—is critical.
Key considerations include evaluating the supplier’s technical competencies, quality certifications (such as ISO 3834 or AS9100), post-weld inspection methods, and track record in similar applications, particularly in industries like aerospace, automotive, or electronics where performance and integrity are paramount. Additionally, proximity, scalability, and cost-efficiency should align with project timelines and volume requirements.
In conclusion, successful sourcing hinges on partnering with specialized, reliable vendors who combine technical excellence with consistent quality management. Investing time in due diligence and supplier qualification ensures robust, repeatable welds that meet performance standards, ultimately supporting product reliability and long-term cost savings.