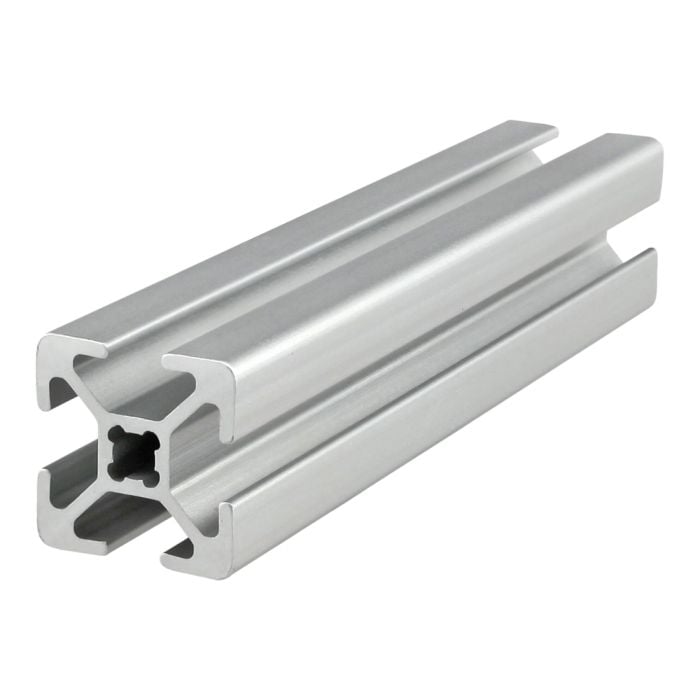
The global aluminum extrusion market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across the construction, automotive, and renewable energy sectors. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 107.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2024 to 2030, fueled by aluminum’s lightweight properties, corrosion resistance, and recyclability. This surge in demand has intensified competition among manufacturers to innovate and scale production of custom aluminum extrusion shapes. As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and sustainable materials, the role of high-precision extruders has become critical. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining advanced tooling capabilities, vertical integration, and global supply chain networks to meet complex engineering requirements. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, innovation metrics, and industry recognition, the following analysis identifies the top 10 aluminum extrusion shapes manufacturers shaping the future of material solutions.
Top 10 Aluminum Extrusion Shapes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 International Extrusions: Aluminum Extrusion
Domain Est. 1998
Website: extrusion.net
Key Highlights: As America’s leading aluminum extrusion manufacturer, we offer a wide range of deliverables in variable billet sizes for industrial or commercial applications….
#2 80/20 Aluminum T-slot Building Systems
Domain Est. 1997
Website: 8020.net
Key Highlights: T-Slots, aluminum extrusions, and parts. Architectural solutions and frames for industrial machine guards, workstations, data center enclosures, and more….
#3 Apex Extrusions
Domain Est. 2010
Website: apexextrusions.ca
Key Highlights: Apex Aluminum is a state-of-the-art aluminum extrusion factory located in Langley, British Columbia, Canada. With a 170000 square foot aluminum extrusion……
#4 SAF
Domain Est. 1992
Website: saf.com
Key Highlights: As the largest single source for architectural aluminum sheet, extruded shapes, aluminum anodizing, painting, and fabricating services, we look forward to ……
#5 Small Custom Aluminum Extrusions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: minalex.com
Key Highlights: Minalex is a trusted, worldwide supplier of Aluminum Window Extrusions. We manufacture extruded aluminum profiles for windows in various shapes, sizes, and ……
#6 Taber Extrusions
Domain Est. 1998
Website: taberextrusions.com
Key Highlights: Taber is proud to be an ISO 9001 certified extruder. With a full range of aluminum alloys, custom aluminum shapes, and diverse machining, we claim the broadest ……
#7 Aluminum Extrusion
Domain Est. 1999
Website: shapecorp.com
Key Highlights: Shape is recognized worldwide as a premier aluminum extruder, fabricator and finisher; capable of producing the most difficult, complex and intricate extrusions ……
#8
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tslots.com
Key Highlights: We offer the best aluminum extrusion TSLOTS in the industry and our in-house experts can work with any idea and any CAD drawing you bring to the table. DOWNLOAD….
#9 Aluminum Extruded Shapes
Domain Est. 2002
Website: alum-ext.com
Key Highlights: Provider of custom extruded shapes, taking concepts from design through development and manufacturing. Call 513.563.2205 Email [email protected] ……
#10 Bonnell Aluminum
Domain Est. 2007
Website: bonnellaluminum.com
Key Highlights: Bonnell Aluminum extrudes a variety of shapes used in architectural systems such as storefront, curtain walls and other flushed glazed projects. Learn More….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Aluminum Extrusion Shapes

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Aluminum Extrusion Shapes
The global aluminum extrusion shapes market is projected to experience significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, sustainability imperatives, and technological advancements. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape during this period:
-
Increased Demand from Sustainable Construction and Green Buildings
By 2026, the construction sector will continue to be a primary driver of aluminum extrusion demand. With global emphasis on energy-efficient and sustainable architecture, aluminum’s lightweight, recyclability, and corrosion resistance make it ideal for window frames, curtain walls, and structural components. Green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM are encouraging the use of aluminum, contributing to market expansion. -
Growth in Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Transportation Applications
The automotive industry’s shift toward electric mobility will significantly boost demand for aluminum extrusion shapes. Aluminum extrusions are widely used in EV battery enclosures, chassis components, and structural frames due to their strength-to-weight ratio. As EV production scales globally, extruded aluminum profiles will play a critical role in reducing vehicle weight and improving energy efficiency. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy Infrastructure
Solar panel mounting systems, wind turbine components, and energy storage enclosures increasingly rely on aluminum extrusions. The push for clean energy solutions will accelerate the adoption of aluminum in photovoltaic racking and solar tracking systems, particularly in emerging markets investing heavily in solar infrastructure. -
Regional Market Shifts and Manufacturing Localization
Asia-Pacific, especially China and India, will remain dominant in both production and consumption. However, North America and Europe are expected to see revitalized growth due to nearshoring initiatives, government incentives (e.g., U.S. Inflation Reduction Act), and investments in domestic EV and clean tech manufacturing. This shift may lead to increased regional self-sufficiency in aluminum extrusion supply chains. -
Technological Advancements and Customization
By 2026, advancements in extrusion technology—such as precision tooling, thermal break integration, and multi-cavity dies—will enable more complex, high-performance profiles. Growing demand for customized solutions across industries will push manufacturers toward digitalization, including CAD/CAM integration and AI-driven process optimization. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are pushing aluminum producers to adopt low-carbon production methods. The use of recycled aluminum (post-consumer and post-industrial) in extrusion processes is expected to rise, reducing energy consumption and carbon footprint. Certification of low-carbon aluminum will become a competitive differentiator. -
Rising Raw Material and Energy Costs
Volatility in bauxite supply, alumina refining, and energy prices may pressure margins. However, long-term contracts, vertical integration, and investment in renewable energy for smelting operations will help mitigate these challenges.
In conclusion, the 2026 aluminum extrusion shapes market will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and strong demand from high-growth sectors. Companies that invest in eco-friendly production, diversify applications, and adapt to regional market dynamics will be best positioned for success.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Aluminum Extrusion Shapes (Quality, IP)
Sourcing aluminum extrusion shapes involves more than just finding a low price—overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to costly delays, legal issues, or product failures. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Quality Inconsistencies and Material Non-Conformance
One of the most frequent issues is receiving extrusions that do not meet specified material standards or dimensional tolerances. Suppliers may cut corners by using subpar aluminum alloys (e.g., substituting 6063 for 6061 without approval), failing to adhere to heat treatment requirements (T5 vs. T6 temper), or allowing excessive dimensional variation. This can compromise structural integrity, surface finish, or fit during assembly. Always verify mill certifications (e.g., ASTM B221, EN 755) and conduct incoming quality inspections.
Poor Surface Finish and Defects
Aluminum extrusions are often used in visible applications where aesthetics matter. Common surface defects include die lines, scratches, stains, oxidation, or uneven anodizing. These can result from poorly maintained dies, improper handling, or inadequate post-extrusion processing. Without clear finish specifications and acceptance criteria in procurement agreements, buyers risk receiving parts requiring costly rework or rejection.
Inadequate Tolerance Control
Extrusions that do not meet geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) requirements can lead to assembly issues or functional failures. Some suppliers lack the capability or process control to maintain tight tolerances, especially on complex cross-sections or long lengths. Ensure the supplier has demonstrated experience with your required tolerance class and request first-article inspections (FAI) before full production.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using proprietary or patented extrusion profiles without proper licensing exposes buyers to legal liability. Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” profiles that closely mimic patented designs (e.g., Misumi, item, or Bosch Rexroth profiles), potentially infringing on IP rights. Always confirm that the profile design is either licensed, in the public domain, or custom-developed with clear ownership rights assigned to your company.
Lack of Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Input
Suppliers may accept complex designs that are difficult or inefficient to extrude, leading to high scrap rates, die failures, or extended lead times. Failing to involve the extruder early in the design phase can result in profiles with thin walls, sharp corners, or asymmetrical sections that compromise quality. Engage suppliers during design to optimize for extrusion feasibility and cost.
Insufficient Documentation and Traceability
A lack of proper documentation—such as material test reports (MTRs), die records, or process certifications—can hinder traceability and quality assurance. In regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, medical), this can lead to non-compliance. Ensure contracts require full documentation and lot traceability for every production batch.
Overlooking Secondary Operations
Many extrusions require secondary operations like cutting, drilling, bending, or surface treatment. If these are outsourced or inconsistently managed, quality can vary significantly. Confirm that the supplier controls or coordinates all downstream processes to maintain consistent quality and avoid misalignment or dimensional drift.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls through clear specifications, supplier vetting, and legal diligence, companies can ensure reliable supply, maintain product quality, and protect their intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Aluminum Extrusion Shapes
Overview of Aluminum Extrusion Logistics
Aluminum extrusion shapes are widely used across industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods due to their strength, light weight, and versatility. Efficient logistics and strict compliance are critical to ensure timely delivery, product integrity, and adherence to international and local regulations throughout the supply chain.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging safeguards aluminum extrusions from damage during transit. Extrusions should be bundled securely using non-abrasive materials such as plastic or rubber spacers to prevent scratching. Protective end caps, shrink wrap, or stretch film protect cut ends and surfaces. Bundles must be labeled clearly with product details, batch numbers, and handling instructions. Wooden or metal skids are recommended for palletizing to support handling with forklifts or cranes.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
Aluminum extrusions can be shipped via truck, rail, sea, or air, depending on volume, destination, and urgency. Over-the-road trucking is common for regional distribution due to flexibility and direct delivery. For international shipments, containerized sea freight is cost-effective for large volumes. Rail is suitable for long-distance land transport. Climate control is generally not required, but protection from moisture and extreme weather is essential to prevent oxidation or water staining.
Storage Conditions and Inventory Management
Store aluminum extrusions indoors in a dry, well-ventilated environment to prevent corrosion. Keep materials off the ground using pallets or racks and avoid contact with dissimilar metals to prevent galvanic corrosion. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize aging and maintain material quality. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of surface degradation or packaging damage.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Aluminum extrusions must comply with international and regional standards such as ISO 20285 (extrusion tolerances), EN 755 (European standard), and ASTM B221 (U.S. standard). Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (environmental management) are often required. Material test reports (MTRs) and mill certificates must accompany shipments to verify chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Export and Import Regulations
For international trade, exporters must comply with export control regulations, including proper Harmonized System (HS) code classification—typically 7604.10 or 7604.21 for aluminum alloy and non-alloy extrusions. Accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin are required. Some countries impose anti-dumping or countervailing duties on aluminum products; staying informed on trade policies between exporting and importing nations is essential.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Aluminum extrusion production and handling must adhere to environmental regulations governing emissions, waste disposal, and energy use. OSHA (U.S.) or equivalent local safety standards apply to workplace handling, including proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and safe lifting practices. Hazard communication standards require clear labeling of any chemical treatments (e.g., anodizing agents or coatings) used in post-extrusion processes.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain comprehensive documentation throughout the logistics chain, including order confirmations, shipping manifests, customs declarations, and compliance certificates. Full traceability—from raw material sourcing to final delivery—supports quality assurance and regulatory audits. Digital tracking systems (e.g., ERP or SCM software) enhance visibility and enable rapid response to compliance inquiries or recalls.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Identify potential risks such as supply chain disruptions, port delays, or regulatory changes. Diversify shipping routes and carriers where possible. Maintain safety stock for critical components and develop contingency plans for natural disasters or geopolitical events. Regular training for logistics and compliance teams ensures preparedness and adherence to evolving standards.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for aluminum extrusion shapes ensures product quality, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction. By following standardized packaging, transport, storage, and documentation practices—and staying current with international trade regulations—businesses can optimize supply chain performance and minimize legal and operational risks.
In conclusion, sourcing aluminum extrusion shapes requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, lead times, and supplier reliability. Aluminum extrusions offer significant advantages in terms of strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, design flexibility, and recyclability, making them ideal for a wide range of applications across industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
When sourcing, it is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who demonstrate technical expertise, consistent quality control, and the ability to meet customization needs. Consideration should also be given to tooling costs, minimum order quantities, and geographic proximity to reduce shipping times and expenses. Utilizing standard profiles where possible can help minimize costs, while custom designs should be optimized for manufacturability to avoid unnecessary complications.
Furthermore, staying informed about material certifications, industry standards, and sustainability practices ensures compliance and supports long-term project success. In a competitive and evolving market, a well-structured sourcing strategy for aluminum extrusions not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to innovation and product differentiation. Ultimately, effective sourcing is a critical component in delivering high-quality, cost-efficient, and sustainable solutions.