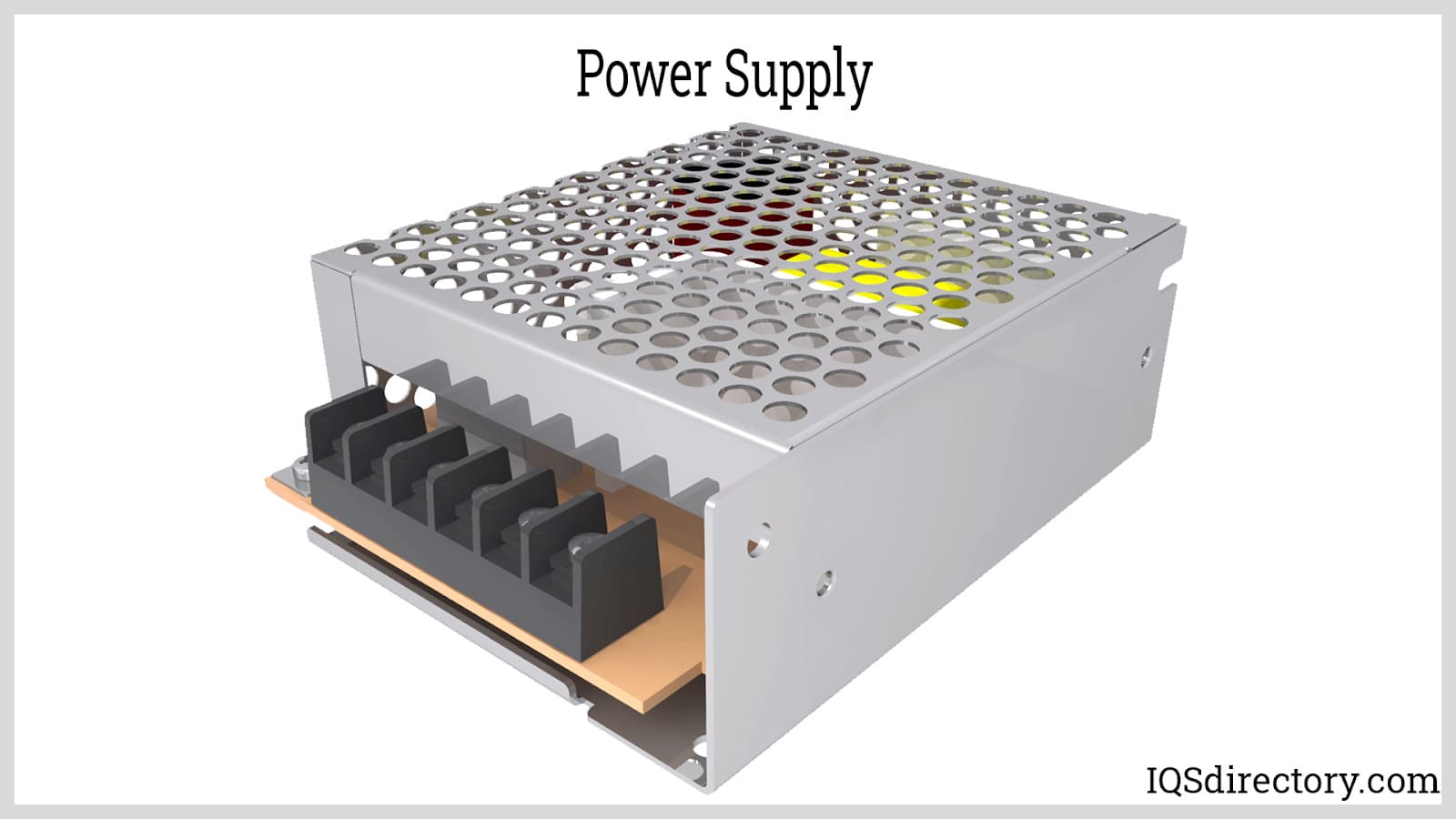
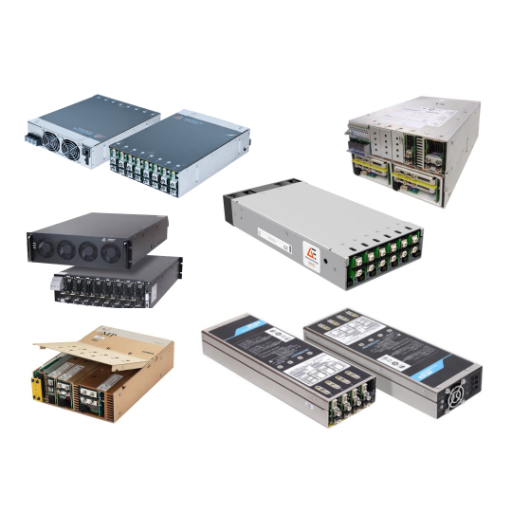
The global market for AC and DC voltage control solutions is witnessing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient power systems, advancements in renewable energy integration, and increasing electrification across industrial and residential sectors. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global power electronics market—encompassing critical AC/DC voltage conversion technologies—was valued at USD 37.3 billion and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further reinforced by Mordor Intelligence, which forecasts the power quality and voltage management equipment market to expand steadily, with increased adoption in data centers, electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, and smart grid deployments. As reliability and precision in voltage regulation become paramount, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to enhance product efficiency, scalability, and compliance with international standards. Against this backdrop, the following list highlights the top 10 AC and DC voltage manufacturers shaping the future of power management through innovation, global reach, and technological leadership.
Top 10 Ac Voltage Dc Voltage Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AC-DC Switching Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1997
Website: technologydynamicsinc.com
Key Highlights: Technology Dynamics Inc. is the leading designer and manufacturer of Switching Power Supplies, DC-DC Converters and DC-UPS Systems for Military, Industrial and …Missing: voltage…
#2 FSP TECHNOLOGY INC. |AC/DC Power Supply Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fsp-group.com
Key Highlights: Explore FSP TECHNOLOGY INC.|AC DC Power Supply Manufacturer. A world-class innovator in AC/DC power supply design and manufacturing. Power Never Ends.Missing: voltage…
#3 Power conversion
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton has over 55 years of program heritage providing AC/DC, DC/DC and DC/AC power-conversion solutions for critical industrial applications….
#4 Cincon
Domain Est. 1998
Website: cincon.com
Key Highlights: Cincon Electronics is a leading manufacturer of DC/DC converters and AC/DC power supplies offering the high-quality and reliable power module solutions….
#5 Wall Industries
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wallindustries.com
Key Highlights: Wall Industries manufactures and markets a full line of DC DC converters and AC DC power supplies. Browse our standard and customized power solutions including…
#6 XP Power
Domain Est. 2000
Website: xppower.com
Key Highlights: Looking for the leading manufacturer of AC-DC power supplies, DC-DC converters, high voltage, RF & custom power products? Discover our extensive range….
#7 RECOM: DC/DC & AC/DC Converter
Domain Est. 2006
Website: recom-power.com
Key Highlights: RECOM Power is a leading manufacturer of AC/DC electronic power supplies and DC/DC converters, with over 30,000 compact standard power supplies alongside ……
#8 Power Supplies
Domain Est. 1996
Website: acopian.com
Key Highlights: Millions of Reliable Power Supplies. Acopian can design, build and ship the power supply that meets your needs. · Speak to a Sales Associate or Engineer Now!…
#9 AMETEK Programmable Power
Domain Est. 2007
Website: programmablepower.com
Key Highlights: The AMETEK Programmable Power designs, manufactures, and markets precision, ac & dc programmable power supplies, electronic loads, application-specific ……
#10 AC/DC Power Supplies, Solutions & Equipment Supplier
Domain Est. 2013
Website: preenpower.com
Key Highlights: Preen (AC Power Corp.) provide advanced, reliable and cost effective AC/DC Power Solutions, includes AC Power Source, DC Power Supplies, Power Supplies for ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ac Voltage Dc Voltage

H2: 2026 Market Trends for AC Voltage and DC Voltage
The global power systems landscape is undergoing a transformative shift by 2026, driven by technological advancements, sustainability goals, and evolving energy demands. In this context, both AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) voltage systems are experiencing significant changes in market dynamics, adoption patterns, and application areas.
-
Growth of DC Voltage Systems
By 2026, DC voltage technologies are gaining strong momentum, particularly in renewable energy integration, data centers, electric vehicles (EVs), and low-voltage power distribution. The rise of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, which inherently produce DC power, is accelerating the deployment of DC microgrids and DC-based energy storage solutions. High-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission is also expanding to efficiently transport renewable energy over long distances with reduced losses compared to traditional AC lines. -
Resilience of AC Voltage Infrastructure
Despite the rise of DC, AC voltage remains the backbone of global power distribution due to its well-established infrastructure, ease of voltage transformation, and compatibility with most industrial and residential equipment. By 2026, modernization of AC grids—through smart grid technologies, advanced metering, and automation—is enhancing reliability and enabling bidirectional power flow to support distributed energy resources. -
Hybrid AC/DC Systems
A defining trend in 2026 is the emergence of hybrid AC/DC systems, especially in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and urban power networks. These hybrid architectures leverage the strengths of both voltage types: AC for legacy compatibility and long-distance transmission, and DC for efficient integration of renewables, batteries, and digital loads (e.g., LEDs, computers, and EV chargers). Power electronic converters play a critical role in enabling seamless interconnection. -
Technological Innovation and Efficiency
Advancements in semiconductor materials—such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN)—are reducing conversion losses between AC and DC, making dual-voltage systems more efficient and cost-effective. This is particularly relevant in EV fast-charging stations and telecom power supplies, where DC power delivery is preferred. -
Regional Adoption Patterns
In North America and Europe, regulatory support for energy efficiency and grid modernization is fostering investment in both AC grid upgrades and DC microgrids. In contrast, Asian markets—led by China and India—are rapidly deploying HVDC links to connect remote renewable resources to urban load centers, reinforcing DC’s strategic importance. -
Market Drivers and Challenges
Key drivers for DC adoption include the global push for decarbonization, digitalization of infrastructure, and the proliferation of DC-powered devices. However, challenges remain, such as standardization gaps, interoperability issues, and the high initial cost of DC infrastructure.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for AC and DC voltage reflects a dynamic coexistence, with DC gaining ground in niche and high-efficiency applications while AC continues to dominate in legacy and large-scale transmission. The future lies in intelligent, flexible energy systems that leverage the complementary benefits of both AC and DC technologies.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing AC and DC Voltage Supplies (Quality and IP Considerations)
When sourcing power supplies that deliver both AC and DC voltage, especially for industrial, commercial, or embedded applications, overlooking key quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to system failure, safety hazards, or reduced lifespan. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
One of the most prevalent pitfalls is selecting power supplies with substandard components or inadequate manufacturing quality. Low-cost units may use inferior capacitors, transformers, or rectifiers that degrade quickly under load or temperature stress. This results in unstable output voltage, increased ripple, and premature failure. Always verify compliance with recognized standards (e.g., UL, CE, IEC) and consider the operating temperature range and expected lifespan.
Inadequate Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
Choosing a power supply with an insufficient IP rating for the intended environment is a critical error. For example, using an IP20-rated unit in outdoor or high-dust industrial settings can lead to contamination, short circuits, or corrosion. Always match the IP rating to the environment—IP65 or higher is typically required for outdoor, washdown, or dusty conditions to ensure protection against dust and water ingress.
Mismatched Voltage Regulation and Load Stability
Some AC/DC power supplies fail to maintain stable output under variable loads, leading to voltage droop or spikes. This is particularly problematic in sensitive electronic systems. Avoid units without proper regulation specifications or load regulation data. Ensure the supply can handle the full range of expected loads without compromising voltage quality.
Lack of Isolation and Safety Features
Inadequate galvanic isolation between input (AC) and output (DC) can pose serious safety risks and introduce electrical noise. Ensure the unit provides sufficient isolation voltage (e.g., 3 kV or higher) and includes essential safety features such as over-voltage, over-current, and short-circuit protection.
Ignoring Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Poorly designed power supplies can emit excessive electromagnetic interference (EMI) or be susceptible to it, disrupting nearby electronics. Always check for EMC compliance (e.g., FCC Part 15, EN 55032) and consider the need for filtering or shielding, especially in sensitive environments.
Overlooking Thermal Management and Derating
Many failures stem from overheating due to poor thermal design or operation beyond specified temperature limits. Ensure the power supply includes adequate heat dissipation mechanisms and review derating curves—output capacity often decreases at higher ambient temperatures. Avoid enclosing high-wattage supplies in poorly ventilated spaces without considering thermal buildup.
Assuming Universal Input Compatibility
While many supplies support wide AC input ranges (e.g., 90–264 VAC), not all handle frequency variations (50/60 Hz) or voltage sags effectively. Confirm input specifications match your regional power grid characteristics to avoid malfunctions during brownouts or frequency fluctuations.
By carefully evaluating quality metrics and IP requirements during sourcing, you can avoid these common pitfalls and ensure reliable, safe, and long-lasting performance of your AC/DC power systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for AC Voltage and DC Voltage Equipment
Overview of AC and DC Voltage Systems
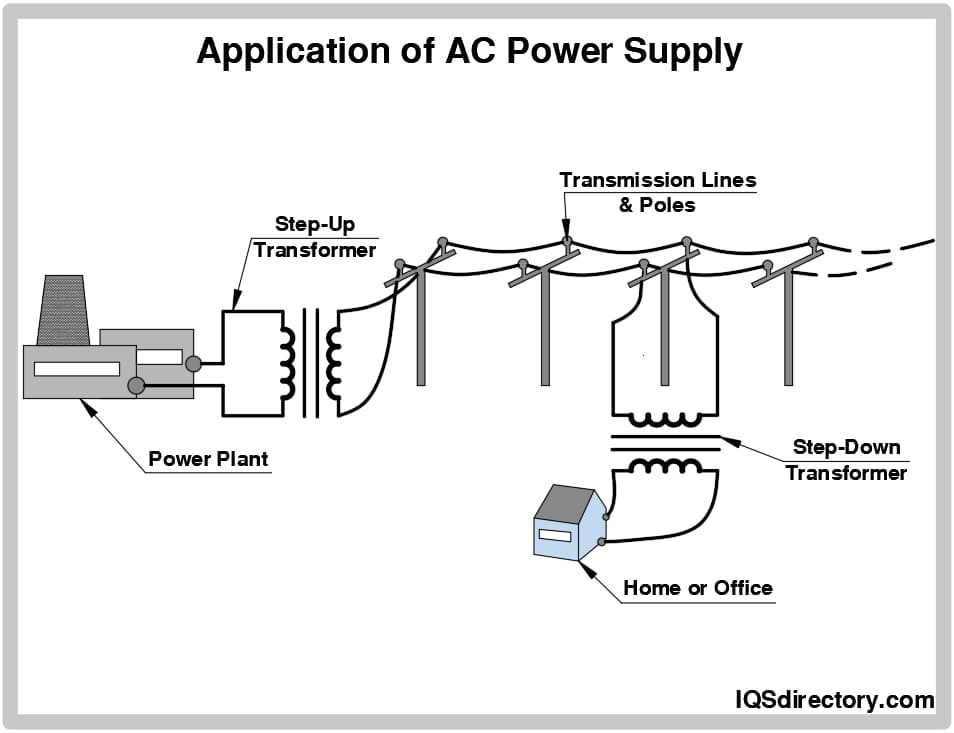
Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) voltage systems serve distinct purposes in power distribution and electronic applications. AC voltage, commonly used in mains power grids and industrial applications, periodically reverses direction. DC voltage, which flows in a single direction, is essential for batteries, solar panels, and most electronic devices. Understanding the differences is crucial for safe handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Electrical equipment operating on AC or DC voltage must comply with international and regional safety standards. Key certifications include:
- IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use (covers both AC and DC).
- UL 61010-1: North American equivalent of IEC 61010-1.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- FCC Part 15 (USA): Regulates electromagnetic interference (EMI) for digital devices powered by AC/DC sources.
- RoHS and REACH (EU): Restrict hazardous substances in electrical equipment.
Ensure all products meet applicable standards before shipment to avoid customs delays or penalties.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging and labeling are essential to prevent damage and ensure regulatory compliance during transit.
- Voltage Labeling: Clearly mark equipment with rated input/output voltages (e.g., “AC 120V” or “DC 24V”) using durable labels.
- Polarity Indication: For DC-powered devices, clearly indicate positive (+) and negative (–) terminals.
- Warning Labels: Include safety warnings such as “Danger: High Voltage,” especially for equipment operating above 50V AC or 120V DC.
- Environmental Protection: Use anti-static, shock-resistant packaging for sensitive electronics. For battery-powered DC devices, comply with UN 38.3 for lithium batteries.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Shipping AC/DC voltage equipment requires adherence to transportation safety regulations:
- Lithium Batteries (DC Systems): Governed by IATA DGR (air), IMDG Code (sea), and ADR (road). Packages must be marked with Class 9 hazard labels and include proper documentation.
- High-Voltage Equipment (AC/DC): Devices exceeding safety extra-low voltage (SELV) limits may require special handling and shielding.
- Insulation and Isolation: Ensure conductive parts are insulated to prevent short circuits during transit.
- Temperature Control: Avoid exposing sensitive components to extreme temperatures, which can affect performance and safety.
Storage and Handling Protocols
Safe storage minimizes risks of electrical hazards and product degradation.
- Dry, Ventilated Environment: Store equipment in areas with controlled humidity to prevent corrosion and insulation breakdown.
- Separation of AC/DC Components: Keep high-voltage AC units separate from low-voltage DC systems to avoid interference or accidental contact.
- Discharge Procedures: For capacitive DC systems, implement safe discharge protocols before handling or servicing.
- Inventory Management: Track shelf life of components like electrolytic capacitors, which degrade over time, especially in high-temperature storage.
Import and Export Compliance
Cross-border movement of electrical equipment requires adherence to customs and trade regulations.
- HS Codes: Use appropriate Harmonized System codes (e.g., 8504 for transformers, 8507 for batteries) to classify AC/DC components.
- Country-Specific Voltage Standards: Ensure equipment is compatible with local grid voltages (e.g., 120V AC/60Hz in the USA, 230V AC/50Hz in EU).
- Conformity Assessment: Some countries require local testing or certification (e.g., CCC in China, KC in South Korea, PSE in Japan).
- Documentation: Provide technical specifications, test reports, and certificates of conformity with shipments.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
Prioritize personnel and product safety throughout the logistics chain.
- Training: Ensure staff are trained in handling high-voltage equipment and emergency response.
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Implement procedures when servicing AC/DC systems.
- Grounding and Shielding: Use proper grounding techniques during storage and transit to prevent static discharge.
- Regular Audits: Conduct compliance and safety audits for logistics partners and warehousing facilities.
Conclusion
Managing logistics and compliance for AC and DC voltage equipment demands attention to technical specifications, safety standards, and regulatory requirements. By following this guide, businesses can ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling of electrical products across global supply chains. Always consult local regulations and update procedures as standards evolve.
Conclusion on Sourcing AC Voltage and DC Voltage:
In summary, sourcing AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) voltage involves selecting the appropriate method or device based on the specific application requirements. AC voltage is commonly sourced from power grids, generators, or inverters and is ideal for long-distance power transmission and powering household and industrial equipment. It periodically changes direction and magnitude, making it suitable for transformers and motors.
On the other hand, DC voltage is typically sourced from batteries, solar panels, rectifiers, or DC power supplies. It provides a constant voltage level, which is essential for electronic devices, digital circuits, and applications requiring stable and ripple-free power.
Choosing between AC and DC voltage sources depends on factors such as efficiency, application type, transmission distance, and device compatibility. With the increasing use of renewable energy and electronic devices, both AC and DC power systems play crucial roles, often integrated through converters and inverters to ensure optimal performance. Understanding how to properly source and convert between AC and DC voltage is fundamental in modern electrical and electronic engineering.