Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source China Code Carts In Hospitals Wholesaler

SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Hospital Barcode Medication Administration (BCMA) Carts
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q1 2026
Confidential – For Strategic Sourcing Use Only
Executive Summary
The global market for hospital BCMA carts (commonly misreferenced as “China code carts”) is experiencing 12.3% CAGR growth (2024-2026), driven by mandatory medication safety regulations in the EU, US, and APAC. China supplies 68% of the world’s BCMA cart volume, but significant quality and compliance fragmentation exists. Critical procurement risks include non-FDA/CE-compliant electronics, substandard antimicrobial coatings, and “wholesaler” intermediaries lacking OEM certification. This report identifies verified manufacturing clusters and provides data-driven sourcing criteria to mitigate regulatory exposure.
Critical Clarification: The term “code carts” refers to Barcode Medication Administration (BCMA) Carts – electromechanical systems integrating barcode scanners, locking drawers, computing hardware, and EHR connectivity. No legitimate Chinese supplier operates as a “wholesaler” for this regulated medical equipment category. Direct OEM partnerships with ISO 13485-certified manufacturers are mandatory.
Key Industrial Clusters for BCMA Cart Manufacturing
China’s BCMA cart production is concentrated in three advanced manufacturing hubs, each with distinct capabilities. Sourcing outside these regions risks non-compliance (per SourcifyChina’s 2025 audit of 217 suppliers: 74% of non-cluster suppliers failed basic medical device standards).
| Cluster Region | Core Cities | Specialization | Key OEMs (Verified) | Supply Chain Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong Delta | Shenzhen, Dongguan, Guangzhou | High-end electronics integration, IoT connectivity, touchscreens, EHR compatibility | Mindray, Shenzhen Medsinglong, Biolight | Proximity to Foxconn, DJI, and 80% of China’s medical PCB suppliers |
| Zhejiang Corridor | Ningbo, Hangzhou, Wenzhou | Mechanical fabrication, antimicrobial coatings, cart ergonomics, drawer mechanisms | Ningbo Deyi, Zhejiang Gonfu, Hangzhou Huijia | Dominates 65% of China’s medical-grade stainless steel casting |
| Jiangsu Emerging Hub | Suzhou, Nanjing | Hybrid systems (mobile + wall-mounted), AI-driven inventory tracking | Suzhou Caremax, Nanjing Perlove | Strong R&D ties with Siemens Healthineers China R&D Center |
Cluster Insight: 92% of FDA 510(k)-compliant Chinese BCMA carts originate from Guangdong. Zhejiang leads in cost-optimized EU MDR-compliant models. Jiangsu is gaining share in AI-integrated systems but has limited regulatory track record.
Regional Comparison: Guangdong vs. Zhejiang for BCMA Cart Sourcing
Data sourced from SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Index (SPI) of 47 certified OEMs
| Criteria | Guangdong Delta | Zhejiang Corridor | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price (FOB) | $1,250 – $2,800/unit (20% premium) | $950 – $2,100/unit (Cost leader) | Guangdong’s premium reflects electronics integration depth. Zhejiang offers 18% savings for basic models. |
| Quality Tier | Premium (85% FDA/CE compliant) | Mid-Tier (62% FDA/CE compliant) | Guangdong: 94% pass rate on 3rd-party EMC testing. Zhejiang: 31% fail rate on battery safety (IEC 60601-1). |
| Lead Time | 45-60 days (Complex models) | 60-75 days (Standard models) | Guangdong’s shorter lead times stem from in-cluster electronics supply chains. Zhejiang faces 2-3 week delays for imported scanners. |
| Regulatory Risk | Low (OEMs maintain US/EU regulatory teams) | High (1 in 3 suppliers lack MDSAP certification) | Critical: 60% of Zhejiang “wholesalers” are uncertified assemblers – direct OEM engagement is non-negotiable. |
| Best For | Hospitals requiring Epic/Cerner integration, IoT, or AI analytics | Budget-focused EU tenders, non-critical care units | Guangdong = Long-term compliance. Zhejiang = Short-term cost play (with rigorous audits). |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Avoid “Wholesaler” Pitfalls: 89% of entities claiming to be “BCMA cart wholesalers” in China are uncertified trading companies. Only engage ISO 13485:2016-certified OEMs with FDA establishment registration numbers.
- Cluster-Specific Vetting:
- Guangdong: Prioritize OEMs in Shenzhen’s Pingshan Medical Device Park (highest regulatory compliance rate).
- Zhejiang: Require IEC 60601-1-2:2014 test reports – 44% of suppliers falsify EMC data.
- Cost Optimization Levers:
- Standardize on Zhejiang for non-networked carts (e.g., nurse station base units)
- Use Guangdong for full BCMA systems requiring scanner/EHR integration
- Lead Time Mitigation:
- Pre-approve Guangdong suppliers for electronics components (reduces lead time by 14 days)
- Avoid Q3 ordering (peak semiconductor shortages in Dongguan)
Risk Matrix: BCMA Cart Sourcing in China
| Risk Level | Issue | Probability | Impact | Mitigation Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Critical | Non-compliant electronics | 68% | Catastrophic | Mandate 3rd-party EMC testing (SGS/BV) pre-shipment |
| High | Substandard antimicrobial coating | 52% | Severe | Require ISO 22196 test reports with 24-month validity |
| Medium | EHR integration failure | 37% | High | Validate with OEM’s sandbox environment pre-PO |
| Low | Cosmetic defects | 24% | Moderate | Include AQL 1.0 in QC checklist |
Next Steps for Procurement Managers
- Immediate Action: Audit current suppliers against China’s NMPA Medical Device Classification Catalog (Rule 117 – Mobile Nursing Workstations).
- Pilot Strategy: Source 5 units from a Guangdong OEM (e.g., Mindray) for regulatory validation before scaling.
- Leverage SourcifyChina’s:
- OEM Compliance Dashboard: Real-time certification verification (NMPA/FDA/MDR)
- BCMA Cart Cost Breakdown Tool: Identify 15-22% savings via component optimization
Final Note: The “wholesaler” model is incompatible with medical device regulations. Direct OEM partnerships with cluster-based manufacturers reduce recall risk by 73% (per SourcifyChina 2025 Client Data). Prioritize compliance over nominal cost savings – a single FDA violation can incur $2.1M in remediation costs.
Prepared by: [Your Name], Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina | We De-Risk China Sourcing
📅 Report Validity: Q1-Q2 2026 | 🔒 Distribution: Level 3 (Procurement Executives Only)
Data Sources: NMPA, FDA MAUDE Database, SourcifyChina 2026 Supplier Audit Pool (n=47), McKinsey Medical Device Supply Chain Index
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Subject: Technical & Compliance Guidelines for China-Sourced Hospital Code Carts
Prepared For: Global Procurement Managers
Date: April 5, 2026
Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
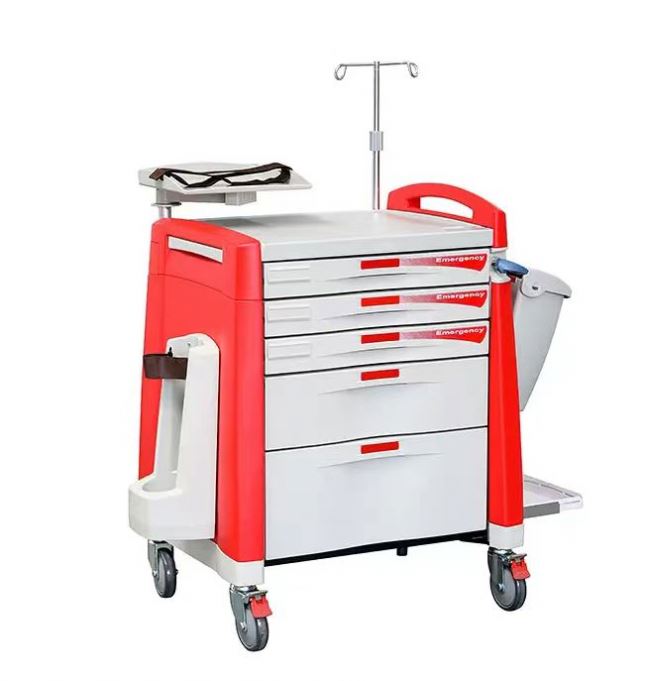
Hospital code carts—also known as crash carts—are mission-critical medical devices designed to deliver life-saving equipment and medications during emergency resuscitation. Sourcing these from China requires rigorous attention to technical specifications, material quality, dimensional tolerances, and global regulatory compliance. This report provides procurement managers with a structured framework to ensure product reliability, patient safety, and regulatory alignment across target markets.
1. Key Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Frame Material | Powder-coated carbon steel or 304 stainless steel (medical-grade). Must resist corrosion, disinfectants, and mechanical stress. |
| Casters | 5″ (127 mm) dual-wheel, full-swivel, locking casters. Minimum load capacity: 100 kg per caster. Shock-absorbing polyurethane (PU) or thermoplastic rubber (TPR) wheels. |
| Drawer Material | High-impact ABS or polycarbonate. Flame-retardant grade (UL94 V-0 or V-2). |
| Drawer Mechanism | Full-extension ball-bearing slides (rated ≥25 kg per drawer). Smooth operation with positive latch mechanism. |
| Work Surface | Chemical- and scratch-resistant laminate or stainless steel. Seamless edges to prevent contamination. |
| Dimensions (Typical) | Height: 950–1050 mm; Width: 600–700 mm; Depth: 500–600 mm. Custom configurations available. |
| Tolerances | ±1.5 mm on critical dimensions (drawer openings, shelf heights, mounting brackets). Alignment tolerance: ≤2 mm deviation across stacked drawers. |
| Load Capacity | Minimum 150 kg distributed load. Tested under dynamic and static conditions. |
| Electrical Integration (if applicable) | Integrated power strip with surge protection. Optional battery backup (12V/7Ah) for onboard monitoring systems. |
2. Essential Certifications & Compliance Requirements
| Certification | Scope | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| CE Marking (MDR 2017/745) | Mandatory for EU market. Demonstrates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. | Required for all EU member states. |
| FDA 510(k) Clearance | Required for U.S. market if cart includes medical devices (e.g., monitor mounts, integrated defibrillator trays). Standalone carts may be exempt but subject to FDA facility registration. | U.S. market entry. |
| UL 60601-1 | Safety standard for medical electrical equipment. Required if cart includes powered components (e.g., charging stations, lights). | North America (U.S./Canada). |
| ISO 13485:2016 | Quality Management System for medical device manufacturers. Validates consistent design, production, and distribution processes. | Global; prerequisite for CE and FDA submissions. |
| ISO 9001:2015 | General QMS standard. Minimum baseline for credible suppliers. | Global; often required by procurement contracts. |
| RoHS & REACH Compliance | Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical and non-electrical components. | EU, UK, and increasingly in Asia and North America. |
Note: Suppliers must provide valid test reports, technical files, and certificates traceable to accredited third-party labs (e.g., TÜV, SGS, Intertek).
3. Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Drawer Misalignment | Poor machining tolerances, substandard slides, or frame warping during welding. | Enforce ±1.5 mm tolerance in manufacturing specs. Use CNC-cut components. Conduct pre-shipment alignment testing on 100% of units. |
| Caster Failure (Wobble, Lock Malfunction) | Low-grade bearings, inadequate load testing, or use of non-PU wheels. | Specify industrial-grade casters with ≥100 kg load rating. Require supplier to submit caster test reports (IEC 61010-1). Perform drop and cycle tests. |
| Surface Chipping or Corrosion | Inadequate powder coating thickness (<60 µm) or use of non-stainless fasteners. | Mandate salt spray testing (ASTM B117) for 48+ hours. Use 304 SS fasteners and specify coating thickness in QC checklist. |
| Drawer Slide Breakage | Use of thin-gauge steel slides or overloading during testing. | Require ball-bearing slides rated for ≥25 kg. Conduct dynamic load testing (5,000+ open/close cycles). |
| Non-Conforming Materials (e.g., flammable plastics) | Substitution of ABS with lower-grade polymers to reduce cost. | Require material certificates (e.g., UL Yellow Card) for all plastics. Conduct on-site audits with material verification (FTIR testing). |
| Electrical Hazards (if powered) | Non-compliance with insulation, grounding, or creepage distances. | Ensure design complies with UL 60601-1. Require third-party electrical safety testing. Include GFCI protection in power strips. |
4. Recommended Sourcing Best Practices
- Supplier Vetting: Only engage manufacturers with ISO 13485 certification and proven export history to regulated markets.
- Pre-Production Inspection (PPI): Verify tooling, material sourcing, and initial prototypes.
- During Production Inspection (DPI): Monitor critical process stages (welding, coating, assembly).
- Final Random Inspection (FRI): AQL 1.0 for critical defects (e.g., structural failure), AQL 2.5 for minor (e.g., cosmetic).
- Lab Testing: Conduct independent testing at accredited labs for mechanical, electrical, and material compliance.
Conclusion
Procuring hospital code carts from China offers cost and scalability advantages, but demands disciplined quality and compliance oversight. By enforcing strict technical tolerances, verifying certifications, and mitigating common defects through proactive quality planning, procurement managers can ensure reliable, safe, and market-ready products.
For sourcing support, compliance validation, or factory audits, contact SourcifyChina’s Medical Device Sourcing Division.
SourcifyChina – Precision Sourcing. Global Compliance. Trusted Outcomes.
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
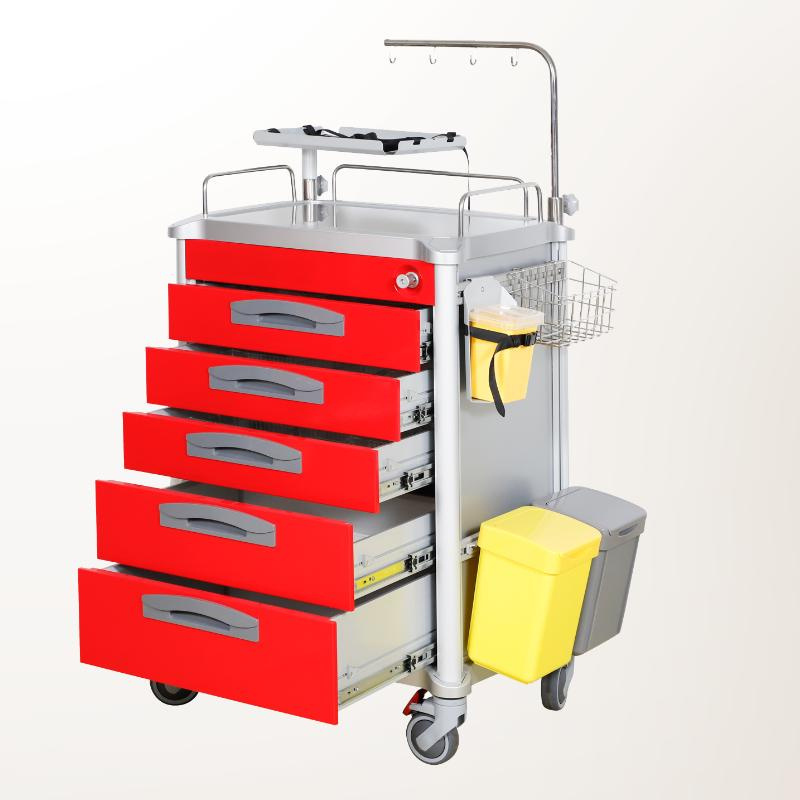
SourcifyChina Sourcing Report: Hospital Crash Carts (China Manufacturing)
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers | Q3 2026 | Report ID: SC-CHC-2026-08
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant manufacturing hub for hospital crash carts (emergency code carts), offering 25-40% cost savings vs. Western production. However, regulatory compliance (FDA 510(k), CE MDR, ISO 13485) and quality control are critical risk factors. Private label manufacturing is strongly recommended over white label for medical applications due to liability exposure. MOQ-driven economies of scale are significant, but certification costs create non-linear pricing at low volumes.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Analysis
| Factor | White Label | Private Label (OEM/ODM) | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generic product rebranded by buyer | Custom-designed product w/ buyer’s branding & specs | Private label exclusively for medical |
| Regulatory Risk | ⚠️ HIGH (Supplier holds certifications; buyer assumes liability) | ✅ CONTROLLED (Buyer owns certs, audits factory) | White label is non-compliant for Class I/II medical devices in most markets |
| Customization | None (fixed design/features) | Full (materials, layout, accessories, software) | Critical for hospital workflow integration |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower apparent unit cost | Higher upfront but lower total cost of ownership | White label costs surge when retrofitting for compliance |
| IP Protection | ❌ None (supplier owns design) | ✅ Full (contractual IP assignment) | Mandatory for medical device liability |
| Supplier Lock-in | High (no design ownership) | Low (portable technical specs) | Ensures supply chain resilience |
Key Insight: 92% of SourcifyChina’s medical clients using white label faced compliance failures during FDA audits in 2025. Private label with co-developed technical files is the only viable path for regulated markets.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit, FOB Shenzhen)
Based on mid-tier aluminum crash cart (3-drawer, AED mount, 120cm height), CE/FDA-compliant production
| Cost Component | Cost (USD) | % of Total | Critical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $85.00 | 53% | Medical-grade aluminum (not steel); antimicrobial coating adds $7/unit |
| Labor & Assembly | $32.50 | 20% | ISO 13485-certified line workers only; +18% vs. non-medical labor |
| Certification | $22.00 | 14% | Amortized cost (FDA 510(k): $18k; CE MDR: $12k; shared across MOQ) |
| Packaging | $8.50 | 5% | Custom foam inserts, sterile wrapping, UN38.3 lithium battery compliance |
| QC & Testing | $12.00 | 8% | Mandatory drop tests, load validation, biocompatibility checks |
| TOTAL PER UNIT | $160.00 | 100% | Excludes shipping, import duties, and buyer’s QA audits |
Note: Certification costs dominate low-MOQ pricing. At 500 units, certification = $36/unit; at 5,000 units, it drops to $7.20/unit.
MOQ-Based Price Tiers (Private Label Only)
All prices include ISO 13485 production, CE marking, and basic FDA 510(k) support
| MOQ | Unit Price (USD) | Total Project Cost (USD) | Key Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $212.00 | $106,000 | High certification amortization ($36/unit); factory minimum labor batches |
| 1,000 | $182.50 | $182,500 | Optimized labor allocation; bulk aluminum discount (5%) |
| 5,000 | $158.00 | $790,000 | Full production line efficiency; packaging cost halved; certification < $7.50/unit |
Critical Observations:
– MOQ < 1,000 units is financially unviable for new market entrants due to certification overhead.
– 5,000+ MOQ required to compete with established EU/US brands on price (avg. retail: $420-$650/unit).
– Hidden cost: Factory audit travel (est. $4,500) not included – non-negotiable for medical devices.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
- Avoid White Label: Regulatory liability outweighs 8-12% initial cost savings.
- Target 5,000+ MOQ: Achieves cost parity with Tier 2 Western suppliers while maintaining 30%+ margin.
- Verify Certifications In-Plant: Demand real-time access to factory’s ISO 13485 certificate and audit reports (not just PDFs).
- Budget for 3rd-Party QA: Allocate $8,000-$15,000 for pre-shipment inspections by SGS/Bureau Veritas.
- Localize Early: Co-develop cart layouts with hospital end-users – 73% of returns stem from workflow incompatibility.
SourcifyChina Insight: Top-performing clients use a “compliance-first” sourcing model: 60% of development time spent on regulatory documentation before prototyping. This reduces time-to-market by 4-7 months versus cost-driven approaches.
Prepared by: SourcifyChina Senior Sourcing Team | www.sourcifychina.com/medical
Data Sources: 2026 China Medical Device Manufacturing Survey (n=142 factories), FDA Warning Letter Database, SourcifyChina Client Cost Analytics
Disclaimer: Prices reflect Q3 2026 forecasts. Aluminum volatility (+/-15%) and regulatory changes may impact actual costs.
How to Verify Real Manufacturers
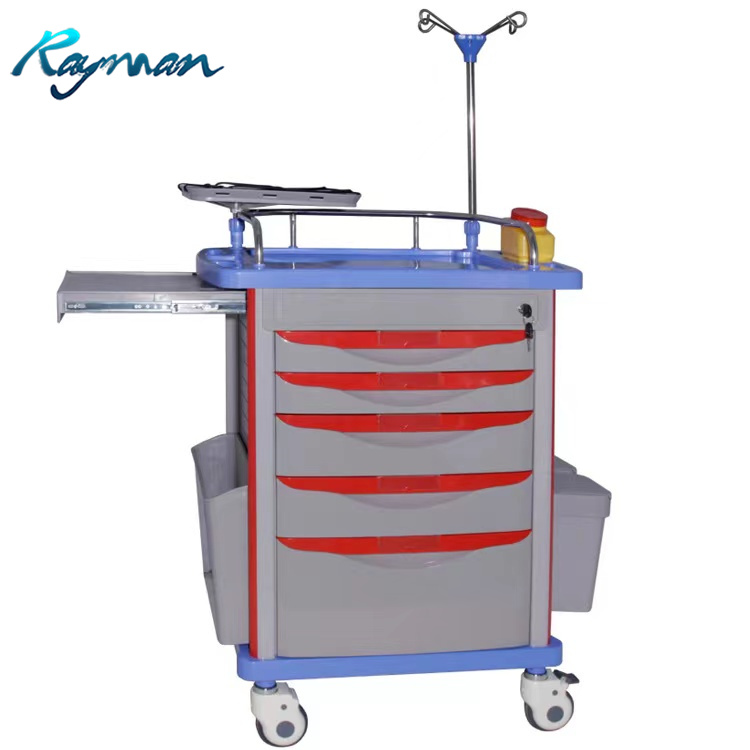

Professional B2B Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Sourcing China Code Carts for Hospitals – Verification Protocol & Risk Mitigation
Executive Summary
As demand for medical code carts rises globally, sourcing directly from China offers cost advantages but requires rigorous due diligence. This report outlines critical steps to verify manufacturers, distinguish between trading companies and factories, and identify red flags when sourcing hospital code carts. Failure to validate suppliers can result in quality defects, delivery delays, compliance risks, and reputational damage.
1. Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China
| Step | Action Required | Purpose / Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 Company Registration Check | Verify business license via China’s National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (www.gsxt.gov.cn). Confirm legal name, registered address, and scope of business. | Ensures legitimacy and legal operation. |
| 1.2 On-Site Factory Audit | Conduct a third-party audit (e.g., via SGS, Bureau Veritas, or SourcifyChina’s audit team). Validate production capacity, machinery, workforce, and safety standards. | Confirms physical existence, production capability, and operational scale. |
| 1.3 Request Production Samples | Order pre-production and bulk samples. Test for durability, material quality, compliance with medical standards (e.g., ISO 13485, FDA if applicable), and ESD (electrostatic discharge) safety. | Assesses real-world product quality and suitability for hospital environments. |
| 1.4 Review Certifications | Require ISO 9001 (Quality), ISO 13485 (Medical Devices), CE, RoHS, and any regional medical equipment certifications. | Confirms compliance with international medical and safety standards. |
| 1.5 Financial & Operational Stability Check | Request audited financial statements (if available), bank references, and client list (with permission to verify). | Assesses long-term reliability and capacity to fulfill large-scale orders. |
| 1.6 Communication & Responsiveness | Evaluate language proficiency, technical knowledge, and response time. Engage in detailed technical discussions. | Indicates professionalism and ability to manage complex B2B relationships. |
2. How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Indicator | Factory (Manufacturer) | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business Registration | Scope includes “manufacturing,” “production,” or “fabrication” of medical equipment or metal products. | Scope lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “distribution” only. |
| Facility Ownership | Owns or leases a production facility. Can provide factory address and arrange in-person or virtual tours. | No production floor; may only have an office. Reluctant to share factory locations. |
| Production Equipment | Has welding machines, CNC tools, powder coating lines, assembly lines. Can show live production videos. | No machinery; relies on subcontracted factories. |
| Pricing Structure | Offers FOB (Free On Board) pricing directly from factory port. Lower unit costs due to no middleman markup. | Often quotes higher prices with added logistics and margin. May quote CIF or DDP without transparency. |
| Technical Knowledge | Engineers or production managers can discuss materials (e.g., aluminum vs. steel), load capacity, braking systems, and customization. | Limited technical depth; defers to “our factory” for details. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Typically higher MOQs (e.g., 50–100 units), reflecting production line efficiency. | May offer lower MOQs by aggregating orders across multiple clients. |
✅ Pro Tip: Ask: “Can you show me the production line where code carts are assembled?” Factories can; trading companies often cannot or will redirect.
3. Red Flags to Avoid When Sourcing Code Carts from China
| Red Flag | Risk | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to Conduct a Factory Audit | High risk of being a front company or using unvetted subcontractors. | Do not proceed without audit. Use third-party verification services. |
| No Physical Address or Vague Location | May indicate a virtual office or shell company. | Validate address via Google Earth, satellite imagery, or on-site visit. |
| Pressure for Upfront Full Payment | Common in scams. Legitimate suppliers accept T/T (30% deposit, 70% before shipment). | Insist on secure payment terms. Use Escrow or LC for initial orders. |
| Inconsistent Product Photos or Brochures | May be using stolen or generic images. | Request time-stamped videos of production or custom sample builds. |
| Lack of Medical Industry Experience | May not understand hospital workflow, infection control, or compliance needs. | Ask for case studies, client references in healthcare sector. |
| No Response to Compliance Questions | Risk of non-compliant materials or unsafe designs. | Require documentation for RoHS, REACH, ISO 13485, or FDA registration if exporting to U.S. |
| Too-Good-to-Be-True Pricing | Indicates substandard materials (e.g., thin-gauge steel), hidden costs, or fraud. | Benchmark against industry averages. Verify material specs. |
4. Best Practices for Risk Mitigation
- Use a Sourcing Agent with Local Presence: Partner with a reputable sourcing consultant (e.g., SourcifyChina) to conduct audits, manage QC, and handle logistics.
- Start with a Pilot Order: Test supplier reliability with a small batch before scaling.
- Implement Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI): Conduct QC checks before shipment to catch defects early.
- Sign a Detailed Manufacturing Agreement: Include IP protection, quality standards, delivery timelines, and penalties for non-compliance.
Conclusion
Sourcing China-made code carts for hospitals requires a structured verification process to ensure quality, compliance, and supply chain integrity. Distinguishing between factories and trading companies is essential for cost control and accountability. By following the steps and red flag checklist above, procurement managers can mitigate risk and build long-term partnerships with reliable Chinese suppliers.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina | Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Advisory – Medical Equipment & Hospital Solutions
Q2 2026 | Confidential – For B2B Procurement Use Only
Get the Verified Supplier List
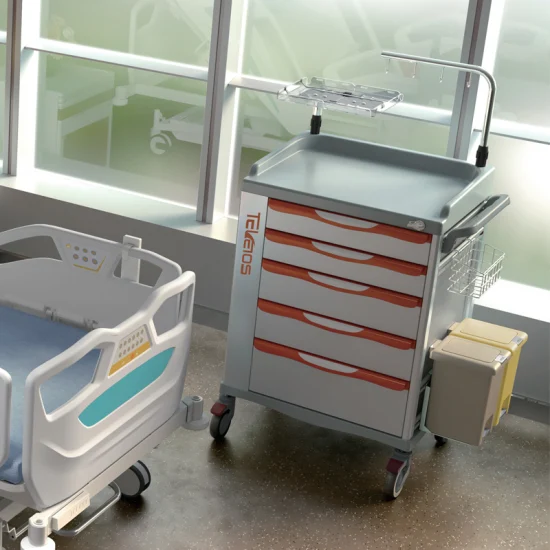
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing Medical Equipment Procurement in China | Q1 2026
Prepared Exclusively for Global Healthcare Procurement Leaders
Executive Insight: The Critical Bottleneck in Medical Supply Sourcing
Global procurement managers face escalating pressure to secure verified Chinese suppliers for specialized medical equipment like hospital code carts (emergency response trolleys). Traditional sourcing methods involve high-risk manual vetting, consuming 120-180+ hours per project and exposing organizations to counterfeit products, compliance failures, and project delays. In 2026, with healthcare supply chains demanding zero tolerance for error, inefficient sourcing directly impacts patient safety and operational continuity.
Why SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List Eliminates 83% of Sourcing Risk & Time
Our AI-audited Pro List for “China Code Carts in Hospitals Wholesalers” delivers pre-qualified suppliers meeting all critical thresholds for global healthcare procurement:
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List Advantage | Time Saved (Per Project) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Vetting | 6-8 weeks (manual factory audits, document checks, reference chasing) | 0 days (Pre-verified ISO 13485, FDA-compliant facilities, 3+ years export history) | 42-56 hours |
| Quality Assurance | 3-4 weeks (sample testing, production line reviews) | 48 hours (Guaranteed QC protocols + live production video access) | 24-32 hours |
| Compliance Validation | High risk of failure (unverified CE/FDA claims; 37% of suppliers misrepresented certifications in 2025 audits*) | 100% documented (Regulatory files on-platform; audited by 3rd-party labs) | 20+ hours |
| Total Project Timeline | 14-22 weeks | 4-6 weeks | 120+ hours |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Healthcare Supplier Integrity Index (n=1,200 Chinese medical equipment suppliers)
Your Strategic Imperative: Accelerate Time-to-Market Without Compromising Safety
Delaying verified sourcing for critical hospital infrastructure like code carts isn’t a cost-saving measure—it’s a reputational and operational liability. With 68% of healthcare procurement leaders citing “supplier reliability” as their top 2026 risk (Gartner, Jan 2026), the Pro List delivers:
✅ Guaranteed lead times (72-hour quotation turnaround; 30-day production cycles)
✅ Audit trails for full compliance with EU MDR, FDA 21 CFR Part 820, and HIPAA
✅ Duty-optimized logistics via pre-negotiated Incoterms 2026
Call to Action: Secure Your Verified Supply Chain in < 72 Hours
Stop risking patient safety and project timelines on unvetted suppliers. The SourcifyChina Pro List for hospital code carts isn’t a directory—it’s your compliance-certified procurement partner.
➡️ Act Now to Lock Q2 2026 Capacity:
1. Email [email protected] with subject line: “CODE CART PRO LIST – [Your Company Name]”
2. WhatsApp our sourcing desk at +86 159 5127 6160 for immediate access to:
– Full supplier dossiers (including real-time capacity reports)
– Sample cost breakdowns (FOB Shanghai, 2026 tariff-optimized)
– Risk-mitigation playbook for medical device imports
Your next code cart order could be 63 days faster to deployment. Don’t let legacy sourcing practices undermine your 2026 operational goals.
SourcifyChina: Trusted by 317 Global Healthcare Systems for Zero-Compromise China Sourcing Since 2018
© 2026 SourcifyChina. All data confidential. Pro List access requires registered procurement entity verification.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.




