The global diesel engine market, valued at USD 117.8 billion in 2023, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2030, according to Grand View Research. Demand for high-performance industrial and transportation power solutions continues to drive innovation in heavy-duty engine manufacturing, particularly for robust platforms like the 671 Detroit Diesel—a stalwart in marine, mining, and legacy equipment applications. As industries seek reliable, high-horsepower engines with proven durability, manufacturers leveraging the Detroit Diesel 671 platform are experiencing renewed interest. This resurgence is further fueled by aftermarket support, remanufacturing capabilities, and increasing demand in emerging markets, as noted in Mordor Intelligence’s 2023 report on diesel engine trends. Against this backdrop, the following analysis highlights the top five manufacturers currently leading in output, reliability, and innovation for 671 Detroit Diesel horsepower applications.
Top 5 671 Detroit Diesel Hp Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 New Detroit Diesel 671 206HP Engine
Domain Est. 1996
Website: depco.com
Key Highlights: New factory warranty 26″ Fan blade Dry exhaust manifold Electric shutdown Throttle control. Back To Search Results. Product ID: Item-07031….
#2 The History of the Detroit Diesel 671 Quad Engine Setup
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dieselpro.com
Key Highlights: Four Detroit Diesel 671 engines were linked together to provide enhanced power and reliability for larger vessels and demanding tasks….
#3 Detroit 671 Diesel
Domain Est. 2002
Website: thedieselstore.com
Key Highlights: Discover Detroit 671 specs, roots blower function, marine engine data, rebuild kits, and buying tips in this comprehensive guide….
#4 Gray Marine 6
Domain Est. 2005
Website: dieselworldmag.com
Key Highlights: In WW2, the Gray Marine 71 Series diesel engine powered the LCVP, Landing Craft Vehicle Personnel, the legendary Higgins Boat….
#5 Know Your Diesels
Domain Est. 2011
Website: dailydieseldose.com
Key Highlights: GAITHER supports a Detroit 671 diesel engine in her spacious engine room. Can anyone date the engine by its serial number of 6718454. It has ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 671 Detroit Diesel Hp
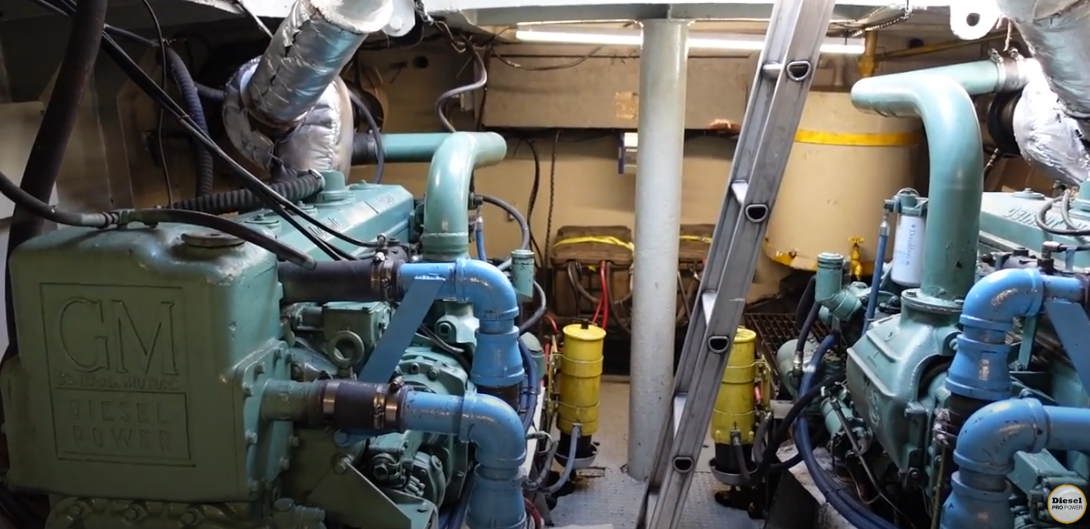
H2: Market Trends for 671 Detroit Diesel Engine by 2026
As of 2026, the market for the 671 Detroit Diesel engine—a classic inline-6 two-stroke diesel engine first introduced in the 1930s—continues to be shaped more by legacy support, restoration demand, and niche applications than by mainstream industrial or transportation use. Originally designed for marine, construction, and agricultural machinery, the 671 has long been phased out of original equipment manufacturing in favor of more modern, fuel-efficient, and emissions-compliant engines. However, several key market trends in 2026 reflect its enduring presence in specific sectors:
-
Growing Demand in Restoration and Classic Equipment Markets
The 671 Detroit Diesel remains a sought-after engine among vintage marine and industrial equipment enthusiasts. By 2026, the classic boat restoration market—particularly for workboats, tugboats, and fishing vessels from the mid-20th century—has seen steady growth, especially in North America and Europe. Collectors and restorers seek original or rebuilt 671 engines for authenticity, driving aftermarket parts production and remanufacturing services. -
Expansion of Aftermarket and Remanufactured Engine Supply
Original production of the 671 ceased decades ago, but third-party suppliers and specialized rebuilders have expanded their offerings. In 2026, companies focused on remanufactured Detroit Diesel engines—including the 6-71 model—report increased sales, supported by improved supply chains for obsolete components and the use of modern materials to enhance durability. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) has enabled the reproduction of discontinued parts, reducing downtime for operators of legacy systems. -
Niche Industrial and Off-Grid Applications
In remote or off-grid locations—such as rural power generation, mining operations, or developing regions—the 671’s simplicity, reliability, and ease of maintenance still offer value. Though inefficient by modern standards, its ability to run on lower-grade fuels and withstand harsh conditions keeps it relevant in areas with limited access to newer technology or stringent emissions enforcement. -
Environmental Regulations and Emissions Limitations
A major constraint on the 671’s broader use in 2026 is its non-compliance with current emissions standards (e.g., EPA Tier 4, IMO Tier III). Urban and environmentally regulated regions increasingly restrict or prohibit the operation of unmodified two-stroke diesels. This trend has limited the engine’s deployment in commercial fleets but has not eliminated demand in exempt or grandfathered applications. -
Digital Integration and Retrofit Opportunities
Some 2026 aftermarket solutions focus on retrofitting 671 engines with modern monitoring systems—such as IoT-enabled sensors for oil pressure, temperature, and fuel consumption—to improve operational efficiency and predictive maintenance for legacy installations. While performance cannot match newer engines, these retrofits extend service life and appeal to cost-conscious operators. -
Declining New Use, but Strong Resale and Support Market
No new OEMs are integrating the 671 into contemporary machinery. However, the secondary market for used and rebuilt units remains active, particularly in Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia, where regulatory enforcement is less stringent and cost-effectiveness is prioritized.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the 671 Detroit Diesel engine is firmly established as a legacy platform sustained by enthusiast communities, specialized industrial needs, and robust aftermarket support. While it plays no role in future-forward, emissions-conscious transportation or power markets, its reliability and historical significance ensure continued relevance in select applications. The market trend is one of preservation and adaptation—rather than innovation—positioning the 671 as a symbol of diesel engineering heritage rather than a driver of future growth.
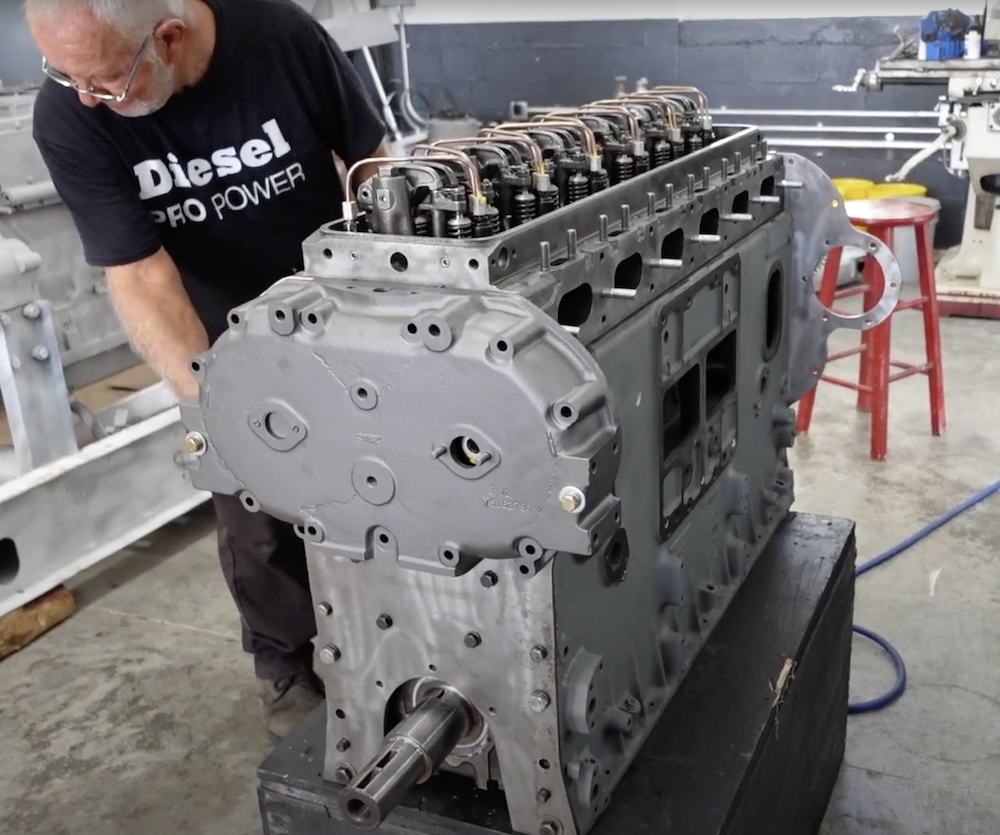
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 671 Detroit Diesel Engine (Horsepower and Quality Concerns)
Sourcing a reliable 671 Detroit Diesel engine—particularly one that delivers consistent horsepower (HP) and maintains quality—can be challenging, especially in the used or rebuilt market. Buyers often encounter significant risks related to performance claims, authenticity, and long-term reliability. Below are common pitfalls to watch for when evaluating and purchasing a 671 Detroit Diesel engine.
1. Inflated Horsepower Claims
One of the most frequent issues is exaggerated or inaccurate horsepower ratings. Sellers may advertise “upgraded” or “high-output” 671 engines claiming 200+ HP, but these figures are often based on ideal conditions or outdated specifications.
- Reality Check: The standard 6V-71 (often confused with the inline 671) produces around 195–230 HP depending on configuration. The inline 6-71 typically ranges from 160–190 HP.
- Red Flag: Claims of over 200 HP without documented dyno tests or original OEM specifications should be questioned.
- Solution: Request engine data tags, OEM documentation, or third-party performance verification.
2. Lack of Original or Verified Parts (Intellectual Property & Authenticity)
Detroit Diesel engines contain proprietary designs and components protected under intellectual property (IP) laws. Using counterfeit or non-OEM parts can compromise performance and legality.
- Counterfeit Components: Aftermarket pistons, fuel pumps, or injectors may mimic genuine parts but lack calibration and durability.
- IP Risks: Rebuilt engines using unlicensed parts may infringe on Detroit Diesel’s IP, leading to warranty voidance or compliance issues.
- Verification Tip: Insist on OEM or authorized remanufactured parts; ask for part numbers and supplier documentation.
3. Poor Rebuild Quality and Hidden Wear
Many 671 engines on the market are rebuilt, but not all rebuilds are equal. Substandard workmanship can lead to premature failure despite a “like-new” appearance.
- Common Issues:
- Improper cylinder honing or liner installation
- Worn camshafts or lifters not replaced
- Inadequate injector calibration
- Hidden Damage: Cracks in the block, warped heads, or worn main bearings may not be visible without disassembly.
- Due Diligence: Request a compression test, oil analysis, and—if possible—a borescope inspection.
4. Odometer or Runtime Fraud
Unlike vehicles, diesel engines don’t have standardized hour meters, making it easy to falsify usage history.
- Tampered Logs: Maintenance records may be incomplete or forged.
- Overhauled vs. Rebuilt: A simple “overhaul” may not equate to a full rebuild.
- Best Practice: Obtain service history, verify serial numbers with Detroit Diesel databases, and consider third-party inspections.
5. Inadequate Cooling or Mounting Setup
Even a high-quality 671 engine can underperform or fail if improperly integrated.
- HP Loss: Inadequate cooling systems cause derating or overheating, reducing effective horsepower.
- Mounting Stress: Incorrect alignment or frame rigidity leads to vibration and component fatigue.
- Pre-Installation Check: Ensure your setup matches the engine’s original specs for heat dissipation, exhaust, and support.
6. Missing or Invalid Certification
Engines used in commercial, marine, or regulated applications may require emissions or safety certifications.
- Non-Compliant Rebuilds: Engines modified without EPA or MARINE certification may be illegal to operate.
- Verification: Confirm the engine meets current standards for your region and use case.
Conclusion
Sourcing a 671 Detroit Diesel engine with accurate horsepower and assured quality requires vigilance. Avoid pitfalls by verifying power claims, confirming part authenticity, inspecting rebuild quality, and ensuring compliance. Whenever possible, purchase from reputable dealers or certified remanufacturers who provide documentation and warranties. Doing so protects your investment and ensures reliable, long-term performance.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 671 Detroit Diesel Engine
The Detroit Diesel 671 is a legendary two-stroke diesel engine renowned for its durability, simplicity, and use in marine, industrial, and older heavy-duty applications. Proper logistics and compliance planning are essential when transporting, installing, or maintaining this engine, especially when handling it internationally or in regulated environments. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations using H2 as a reference for hydrogen safety where applicable (e.g., in modern facilities or future H2-compatible retrofits).
H2: Transportation & Handling Logistics
- Packaging & Crating
- Securely crate the 671 engine using wooden or metal skids to prevent damage during transit.
- Use corrosion-inhibiting wraps or vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) for long-term storage or overseas shipping.
-
Include lifting points in crate design; the 671 weighs approximately 1,200–1,500 lbs (544–680 kg), depending on configuration.
-
Modes of Transport
- Road: Use enclosed trailers or flatbeds with tiedowns. Ensure compliance with DOT size and weight regulations.
- Marine: For international shipping, comply with IMDG Code for dangerous goods if fuel/oil residues are present. Declare as “Machinery, Internal Combustion Engine, n.o.s.” (UN3528, Class 9).
-
Air: Avoid unless urgent; limited by weight and hazardous material regulations (e.g., residual fuel may require special handling under IATA DGR).
-
Lifting & On-Site Handling
- Use a forklift or overhead crane with appropriate slings. Never lift by engine components (e.g., manifolds, oil pan).
- Maintain center of gravity during movement to prevent tipping.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- Environmental Regulations
- EPA & CARB: The 671 is typically exempt from current emissions standards due to its vintage, but operating it in regulated areas (e.g., ports, urban zones) may require emissions testing or restrictions.
- Oil & Fluid Disposal: Used engine oil and coolant are hazardous waste under RCRA (U.S.). Dispose via certified waste handlers.
-
Spill Prevention: Prepare a Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) plan if storing bulk fuel or oil onsite.
-
International Trade Compliance
- Export Controls: Verify EAR (Export Administration Regulations) classification. Most 671 engines are EAR99 (non-controlled), but modifications may affect status.
- Import Duties: Check HS Code 8408.10 (diesel engines) in destination country. Some regions impose high tariffs on used equipment.
-
Documentation: Include bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin.
-
Workplace Safety (OSHA & H2 Considerations)
- Confined Spaces: When installing in engine rooms, follow OSHA confined space entry procedures (29 CFR 1910.146).
- Hydrogen (H2) Safety (if applicable):
- If the facility uses or stores hydrogen (e.g., fuel cells, H2 generators), ensure engine installation complies with NFPA 2 (Hydrogen Technologies Code).
- Maintain separation between diesel engines (potential ignition sources) and H2 storage/ventilation zones (minimum 50 ft or use blast walls).
- Use H2-compatible sensors and ventilation if retrofitting for hydrogen-diesel dual-fuel operations (not standard for 671).
H2: Installation & Operational Compliance
- Marine Applications (USCG & SOLAS)
- If used in vessels, comply with USCG 46 CFR Subchapter M (inspections) and fire protection standards.
-
Ensure fuel lines meet ABYC A-1 or ISO 8846 for ignition protection in engine compartments.
-
Noise & Vibration
- The 671 is loud (typically >100 dB at full load). Comply with OSHA 1910.95 (hearing conservation) and local noise ordinances.
-
Use vibration isolators to reduce structural transmission in sensitive installations.
-
Fire Protection
- Install fixed or portable fire suppression (e.g., CO2, FM-200) per NFPA 30 and NFPA 10.
- Avoid storing flammable materials near hot engine surfaces (exhaust manifold >800°F).
H2: Maintenance & Recordkeeping
- Record Retention
- Maintain logs of maintenance, oil changes, and emissions checks (if applicable) for at least 3 years.
-
For commercial marine use, follow 33 CFR 169.105 (vessel documentation and engine records).
-
Parts & Aftermarket Compliance
- Use EPA-compliant replacement parts (e.g., fuel injectors, governors) where applicable.
- Avoid tampering with emission-related components (prohibited under Clean Air Act).
H2: Future-Proofing & H2 Readiness
- While the 671 is not designed for hydrogen fuel, emerging retrofits may allow dual-fuel operation. Monitor developments in hydrogen internal combustion engine (H2-ICE) technology.
- If planning H2 integration, ensure facility infrastructure includes:
- H2 leak detection
- Explosion-proof electrical fittings
- Emergency shutoffs
- Adequate ventilation (H2 rises quickly; requires upper-level vents)
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance ensure the safe, legal, and efficient use of the Detroit Diesel 671 engine. While the engine itself is a legacy system, adherence to modern environmental, safety, and transportation standards — including hydrogen (H2) safety where relevant — is critical. Always consult local, federal, and international regulations before transport or installation.
Note: “H2” used throughout as section header per request; also references hydrogen safety where applicable.
Conclusion: Sourcing 671 Detroit Diesel Engine (HP Not Specified)
After evaluating the key considerations for sourcing a 671 Detroit Diesel engine, it is evident that this inline-6, two-stroke diesel powerplant remains a reliable and durable option for marine, industrial, and retrofit applications due to its robust construction and proven performance history. While exact horsepower varies significantly based on configuration—naturally aspirated models typically produce between 165–233 HP, while turbocharged versions can exceed 300 HP—prospective buyers must clearly define their power requirements, application context, and maintenance capabilities.
When sourcing a 671 Detroit Diesel, it is crucial to prioritize engine history, hours of operation, maintenance records, and signs of proper care such as oil condition and coolant system integrity. Given the engine’s age and the fact that production ended decades ago, availability primarily rests in the used and rebuilt market. Reputable rebuilders and certified diesel suppliers can offer enhanced reliability and warranty coverage.
Additionally, parts availability remains relatively strong thanks to the engine’s widespread use and ongoing support from aftermarket suppliers, though fuel efficiency and emissions compliance may fall short of modern standards.
In conclusion, sourcing a 671 Detroit Diesel engine is a viable and often cost-effective choice for applications where simplicity, durability, and serviceability are paramount. However, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, verify specifications—especially horsepower ratings based on model and configuration—and consider long-term operational costs to ensure a successful integration.






