The global sheet metal fabrication market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 428.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this space is 4×8-foot sheets in 18-gauge thickness—an industry-standard size and gauge widely used for ductwork, enclosures, and structural components due to its balance of strength, formability, and cost-efficiency. As demand for precision-finished, sustainably produced sheet metal rises, manufacturers are investing in advanced rolling, cutting, and coating technologies to improve consistency and throughput. With North America and Asia-Pacific leading in production and consumption, competition among suppliers has intensified, prompting innovations in material quality and supply chain agility. In this data-driven landscape, identifying the top-performing 4×8 18-gauge sheet metal manufacturers requires evaluating capacity, geographic reach, product certifications, and alignment with global sustainability standards.
Top 10 4X8 18 Gauge Sheet Metal Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
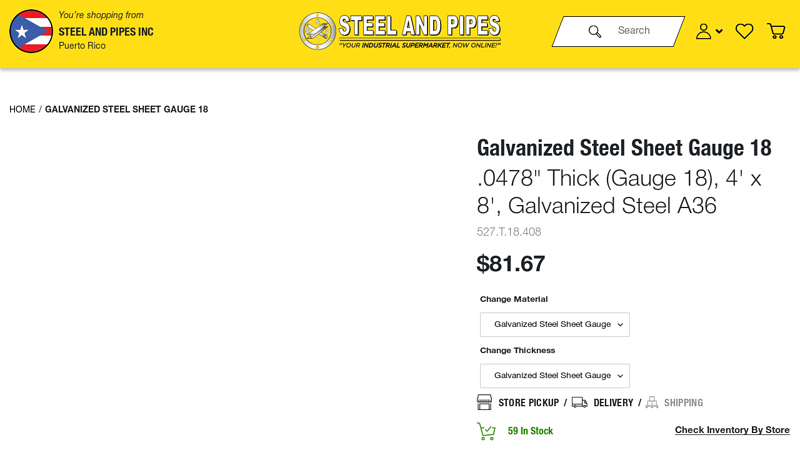
#1 Galvanized Steel Sheet Gauge 18
Domain Est. 1999
Website: store.steelandpipes.com
Key Highlights: In stock 10-day returnsThis is a Gauge 18 Galvanized Steel Sheet 4′ x 8′ Introducing our high-quality Galvanized Steel Sheet, a versatile and durable material that’s perfect for a …
#2 18Ga x 4’W x 8’L ASTM A1008 Type B CS Cold Rolled Steel Sheet
Domain Est. 1995
Website: fastenal.com
Key Highlights: Notes. This low carbon, commercial quality sheet is soft enough to bend flat on itself without cracking. Conforms to ASTM A1008….
#3 Quality Cold Rolled Sheets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bobcometal.com
Key Highlights: Bobco Metals provides businesses and home users with fast, easy and quality Cold Rolled Sheets – 18 Gauge supplies in Los Angeles, CA, USA….
#4 Carbon Steel Sheet
Domain Est. 1996
Website: alro.com
Key Highlights: Alro is your metals supplier superstore stocking carbon steel sheets and more. Our on-hand inventory of carbon steel supply is unmatched in the industry….
#5 18 ga 48″ x 96″ Steel Sheet ASTM
Domain Est. 1999
Website: industrialmetalsupply.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.5 (96) · 30-day returns…
#6 Buy Steel Sheet Online
Domain Est. 1999
Website: metalsdepot.com
Key Highlights: 1–5 day delivery 10-day returnsShop for steel sheet at America’s Metal Superstore. Largest selection of Hot Rolled Steel Sheet, Cold Rolled Steel Sheet, Galvanized Steel Sheet at ….
#7 Steel Cold Rolled Sheet 18 Gauge (Grade CQ)
Domain Est. 1999
#8 18ga (.048″) Cold Rolled, Steel Sheet
Domain Est. 2001
#9 Cold Rolled Steel Sheet Supplier
Domain Est. 2018
#10 4′ X 8′ X 18G STEEL SHEET
Domain Est. 2019
Website: amcolhardwarett.com
Key Highlights: 4′ X 8′ X 18G STEEL SHEET. Home · Products; Product Details. slide 1 of 1. Price. 384.75 TTD. Department: Hardware. » Category: Metal Sheets. Quantity….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 4X8 18 Gauge Sheet Metal

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 4×8 18 Gauge Sheet Metal
The global market for 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal is expected to experience moderate growth by 2026, driven by steady demand across construction, manufacturing, and automotive repair industries. This standardized size and thickness—measuring 4 feet by 8 feet with a thickness of approximately 0.0478 inches (1.21 mm)—remains a staple in light-duty applications due to its balance of strength, formability, and cost-efficiency.
-
Construction Sector Demand
The residential and light commercial construction sectors are anticipated to be primary drivers of 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal demand. Its use in ductwork, roofing underlayment, wall panels, and HVAC systems continues to grow, especially in North America and parts of Asia-Pacific where infrastructure development is accelerating. Green building initiatives may slightly shift preferences toward coated or galvanized variants for enhanced corrosion resistance, supporting long-term durability. -
Manufacturing and Industrial Applications
The manufacturing sector, particularly in equipment enclosures, shelving, and machine guards, will maintain consistent demand. Advances in automation and modular fabrication are streamlining material usage, reducing waste and increasing efficiency in sheet metal processing. Laser cutting and CNC bending technologies are enabling faster turnaround, further integrating 18 gauge sheets into lean production systems. -
Material Substitution and Competition
Despite its widespread use, 18 gauge sheet metal faces competition from alternative materials such as aluminum, composites, and lighter steel gauges. Aluminum variants of the same dimensions are gaining traction in industries seeking weight reduction (e.g., transportation and aerospace support equipment). However, steel remains cost-competitive, especially in price-sensitive markets. -
Raw Material and Pricing Volatility
Steel pricing will remain subject to fluctuations in iron ore, scrap metal, and energy costs. Trade policies, tariffs (especially in the U.S.-China-EU corridors), and supply chain resilience will influence regional availability and pricing. By 2026, increased recycling rates and adoption of electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking may stabilize costs and improve sustainability profiles, benefiting standard products like 4×8 sheets. -
Sustainability and Regulation
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers toward low-carbon steel production and increased use of recycled content. Industry standards such as LEED and BREEAM certifications are encouraging the use of recyclable materials like steel, reinforcing the market position of 18 gauge sheet metal. Galvanized and Galvalume-coated variants are expected to gain preference over bare steel for their longevity and lower lifecycle environmental impact. -
Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: Stable demand driven by infrastructure spending and residential construction.
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest growth region due to urbanization and industrial expansion, particularly in India and Southeast Asia.
- Europe: Moderate growth with a focus on energy-efficient buildings and circular economy practices.
In summary, the 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal market in 2026 will remain resilient, supported by foundational industrial needs and technological integration. While innovation and competition will pressure traditional steel applications, its versatility, recyclability, and cost-effectiveness ensure continued relevance across key end-use sectors.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing 4×8 18 Gauge Sheet Metal (Quality, IP)
Sourcing 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal may seem straightforward, but several quality and intellectual property (IP) pitfalls can compromise project integrity, safety, and compliance. Being aware of these issues helps in selecting reliable suppliers and avoiding costly mistakes.
1. Inconsistent Material Quality and Thickness Tolerance
One of the most frequent issues is inconsistency in the actual thickness of 18 gauge sheet metal. While 18 gauge nominally measures 0.0478 inches (1.21 mm), variations due to poor manufacturing standards or mislabeling can lead to sheets that are thinner or uneven. This compromises structural integrity, especially in load-bearing or precision applications. Buyers should verify mill certifications (e.g., ASTM A1008 for cold-rolled steel) and request material test reports (MTRs) to confirm compliance.
2. Substandard Alloy Composition and Surface Finish
Not all 18 gauge sheet metal is created equal—material composition (e.g., carbon content in steel, alloy type in aluminum) significantly affects performance. Some suppliers may offer lower-grade materials that lack corrosion resistance, formability, or weldability. Additionally, poor surface finishes (e.g., excessive mill scale, scratches, or oil residue) can interfere with painting, coating, or welding. Always confirm the alloy grade (e.g., 304 vs. 201 stainless steel) and surface treatment (e.g., galvanized, pre-painted) with specifications.
3. Misrepresentation of Origin and Certification (IP and Compliance Risks)
Suppliers may misrepresent the country of origin or falsify compliance documents to appear reputable. This poses intellectual property and regulatory risks, especially when projects require adherence to U.S. Buy American provisions or international standards. Using uncertified or counterfeit materials could lead to liability issues, failed inspections, or project delays. Ensure suppliers provide traceable documentation and avoid those unwilling to disclose mill sources.
4. Counterfeit or Unlicensed Pre-Finished Materials
When sourcing pre-painted, coated, or textured sheet metal, IP violations are a real concern. Some overseas suppliers use patented coating technologies (e.g., specific polymer finishes or embossing patterns) without licensing, exposing buyers to legal risk. Using such materials in commercial products could result in infringement claims. Always verify that proprietary finishes (e.g., branded coatings like HYLAR or PVDF) are authorized and supplied with proper documentation.
5. Lack of Traceability and Mill Test Reports
Reputable projects—especially in aerospace, medical, or construction—require full traceability. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide mill test reports (MTRs) or heat numbers limits accountability and may violate quality assurance protocols. Without traceability, addressing defects or recalls becomes nearly impossible, increasing liability.
6. Inadequate Packaging and Handling Leading to Damage
Poor packaging can result in warped, scratched, or corroded sheets upon delivery. Some suppliers cut corners by using minimal strapping or inadequate moisture barriers, especially with international shipments. This not only affects appearance but can also compromise material performance. Specify protective packaging requirements in procurement contracts to avoid receiving damaged goods.
7. Unverified Supplier Claims and Fake Certifications
Some suppliers advertise ISO certification, ASTM compliance, or mill-direct sourcing without verification. Fake or expired certifications are common in online marketplaces. Always independently verify certifications through official databases or third-party audits. Requesting samples and conducting third-party lab testing can help confirm material authenticity.
By addressing these common pitfalls—focusing on material consistency, compliance, IP integrity, and supplier transparency—buyers can ensure they source high-quality, legally compliant 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal that meets project specifications and regulatory standards.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 4×8 18 Gauge Sheet Metal
This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence related to 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal.
Material Specifications and Identification
- Dimensions: 4 feet wide by 8 feet long (48 inches x 96 inches).
- Gauge: 18 gauge, approximately 0.0478 inches (1.214 mm) thick. Confirm exact thickness based on material type (e.g., steel, aluminum) and standard (e.g., USG, BWG).
- Material Type: Clearly identify the base metal (e.g., Cold Rolled Steel (CRS), Hot Rolled Steel (HRS), Galvanized Steel (G60, G90), Aluminum 3003, 5052, Stainless Steel 304, etc.), as this impacts weight, handling, and compliance.
- Weight: Approximately 30-35 lbs per sheet for mild steel (varies significantly by alloy and coating). Accurate weight is critical for logistics planning.
- Surface Condition: Note protective coatings (oil, mill scale, galvanization, paint), treatments, or finishes impacting handling and environmental regulations.
Handling and Safety Protocols
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandatory use of cut-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots. Consider long sleeves and hearing protection during cutting operations.
- Manual Handling: Use proper lifting techniques (bend knees, keep back straight). 4×8 sheets are large and awkward; utilize two or more personnel for manual movement. Avoid carrying vertically over long distances.
- Mechanical Handling: Employ material handling equipment such as:
- Sheet Lifters/Vacuum Lifters: Essential for safe and efficient crane or forklift lifting of individual or stacked sheets.
- Forklifts: Use wide, long forks. Secure loads properly. Exercise extreme caution due to the load’s height and potential instability.
- Sheet Carts/Rollers: Use specialized carts designed for sheet metal transport within facilities.
- Edge and Corner Hazards: Treat all edges and corners as sharp. Handle carefully to prevent cuts and punctures. Use edge protectors during transport if necessary.
- Slip and Trip Hazards: Keep work areas clear of debris, oil, or water. Secure sheets properly when stacked to prevent shifting.
Packaging and Unit Load Formation
- Protection: Sheets are typically bundled with protective interleaf paper, plastic sheeting, or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper to prevent scratching and corrosion. Ensure packaging remains intact.
- Banding: Secure bundles with steel or plastic strapping. Banding must be tight and placed appropriately (usually near edges) to prevent shifting and splaying. Use edge protectors under bands to prevent damage.
- Palletization: Load sheets onto sturdy, undamaged wooden or metal pallets (e.g., 48″ x 40″ standard).
- Stacking: Distribute weight evenly. Limit stack height based on pallet strength, forklift capacity, and stability (typically 3-5 feet high, check carrier rules). Use dunnage or separator boards between layers if stacking multiple bundles.
- Securing: Secure bundles to the pallet using strapping, shrink wrap, or stretch film. Stretch wrap is common for securing the overall unit load after banding. Ensure wrap tension is sufficient to prevent shifting but not so tight as to damage packaging or sheets.
- Labeling: Clearly label each bundle and pallet with:
- Material Type & Grade (e.g., CRS 1008, Aluminum 5052-H32)
- Dimensions (4′ x 8′ x 18 Ga)
- Quantity (Number of Sheets)
- Weight (Gross and Net)
- Lot/Batch Number (Traceability)
- Handling Symbols (e.g., “This Side Up,” “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”)
- Supplier Information
Transportation Requirements
- Vehicle Selection: Use flatbed trailers, step-deck trailers, or enclosed vans appropriate for the shipment size and weight. Ensure the vehicle deck is clean, dry, and free of protrusions.
- Loading:
- Load sheets flat whenever possible. If vertical loading is necessary (e.g., on a gooseneck trailer), use specialized racks or cradles designed for sheet metal.
- Position the load centrally on the trailer for balance.
- Ensure pallets are placed on dunnage (wood blocks) to allow forklift access and prevent moisture wicking.
- Securement (Critical for Flatbeds):
- Compliance: Adhere strictly to FMCSA (Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration) cargo securement rules (49 CFR Part 393, Subpart I) or equivalent local regulations.
- Method: Use a combination of tiedowns (straps, chains, binders) and blocking/chaining.
- Tiedowns: Use enough tiedowns to meet the Minimum Working Load Limit (WLL) requirements (typically 50% of cargo weight for transverse securement). Place tiedowns over the load and anchor to trailer anchor points. Use tiedown protection (edge protectors, chafe guards) where straps contact sharp edges.
- Front-to-Rear: Use headboards, bulkheads, or front-end structures to prevent forward movement. If insufficient, use tiedowns at a steep angle (max 45 degrees from horizontal).
- Side-to-Side: Use tiedowns at angles no greater than 45 degrees from horizontal, anchored to the sides of the trailer. Use side rails or stakes if available.
- Inspection: Perform a thorough securement check before departure and after the first 25-50 miles, and after any significant stop.
- Weather Protection: On flatbeds, use high-quality, properly secured tarps to protect sheets from rain, snow, and road debris. Ensure tarps are waterproof and cover the entire load adequately. For sensitive materials (e.g., uncoated steel), VCI paper under the tarp adds corrosion protection.
Storage Conditions
- Environment: Store indoors in a clean, dry, well-ventilated area, protected from direct weather exposure, excessive humidity, and corrosive atmospheres (e.g., salt spray, chemical fumes).
- Racking: Store sheets flat on level, sturdy racks or elevated pallets. Avoid direct contact with concrete floors (use dunnage).
- Stacking: Limit stack height based on material strength and stability. Do not stack non-uniform bundles. Keep stacks away from high-traffic areas.
- Moisture Control: Maintain low humidity. Use desiccants if necessary in enclosed storage. Ensure protective packaging remains intact.
- Separation: Store different metals (especially dissimilar metals like steel and aluminum) separately to prevent galvanic corrosion. Isolate coated materials from abrasives.
Regulatory Compliance
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS): Maintain up-to-date Safety Data Sheets for the specific sheet metal type and any coatings (e.g., galvanizing, oil). SDS must be readily available to personnel. Key hazards include skin/eye irritation from metal dust or oils, potential fumes during cutting/welding.
- Hazard Communication (HazCom): Comply with OSHA HazCom Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200). Ensure all containers (bundles, pallets) are properly labeled with hazard information as per the SDS.
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG): While solid sheet metal typically isn’t classified as hazardous for transport under DOT/IMDG/ADR, exceptions exist:
- Oiled Sheets: Sheets coated with flammable or combustible oils may require classification (e.g., UN1263, Paint, flammable, n.o.s., Class 3) and associated documentation, placarding, and packaging if the flash point is low enough. Consult SDS and regulations.
- Magnesium Alloys: Certain magnesium alloys can be classified as hazardous.
- Contaminated Scrap: Returnable scrap potentially contaminated with cutting fluids or other hazardous substances may have different regulations.
- Environmental Regulations:
- Spill Prevention: Implement measures to contain leaks from oiled sheets. Have spill kits available.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of scrap metal, used packaging (especially oily rags/VCI paper), and cutting swarf according to local, state, and federal regulations (e.g., RCRA). Oily rags may be regulated hazardous waste.
- Stormwater: Prevent metal fines, oils, or cleaning agents from entering storm drains during handling or outdoor storage.
- Customs and International Trade: For cross-border shipments, ensure accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes (e.g., 7209.17.xx for flat-rolled iron/steel, 7210.70.xx for galvanized, 7606.12.xx for aluminum) and comply with import/export documentation, tariffs, and rules of origin (e.g., USMCA).
- Industry Standards: Adhere to relevant standards for material (e.g., ASTM A109 for CRS, ASTM A653 for Galvanized, AMS for aerospace alloys) and handling (e.g., ANSI MH29.1 for pallets).
Traceability and Documentation
- Maintain records linking material shipments to purchase orders, supplier certifications (mill test reports), and internal lot numbers.
- Retain shipping documents (bills of lading, packing lists) and SDS for the required period.
- Implement a system to track material usage, especially for quality-critical applications.
Adhering to this guide ensures the safe, efficient, and legally compliant movement and storage of 4×8 18 gauge sheet metal throughout the supply chain. Always consult specific supplier recommendations, internal safety policies, and up-to-date regulatory sources.
In conclusion, sourcing 4×8 sheets of 18-gauge sheet metal requires careful consideration of material type (such as mild steel, stainless steel, or aluminum), supplier reliability, cost, lead times, and shipping logistics. Multiple reputable suppliers—including local metal service centers, national distributors like Ryerson or Alro, and online vendors such as Online Metals or Metals Depot—offer this common size and thickness, making it widely accessible. It is advisable to compare pricing, material certifications, cut-to-size options, and delivery capabilities to ensure the product meets project specifications and timelines. By leveraging quotes from multiple sources and considering total landed costs, businesses and individuals can make a cost-effective and efficient procurement decision for 4×8 18-gauge sheet metal.