The global screen mesh market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across construction, agriculture, filtration, and industrial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global wire mesh market size was valued at USD 14.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Factors such as increased infrastructure development, tighter environmental regulations requiring filtration systems, and the expansion of manufacturing activities in emerging economies are fueling demand for high-quality 40 mesh products. As precision and durability become critical in applications ranging from sieving and screening to protective barriers, manufacturers capable of delivering consistent pore size, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity are gaining competitive advantage. In this evolving landscape, the following eight companies have emerged as leading 40 mesh manufacturers, recognized for their innovation, scalable production, and global market reach.
Top 8 40 Mesh Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Woven Wire Mesh Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: acsindustries.com
Key Highlights: As a leading woven wire mesh manufacturer, we use more than 40 looms to produce our high quality woven mesh. Used for a variety of industrial applications….
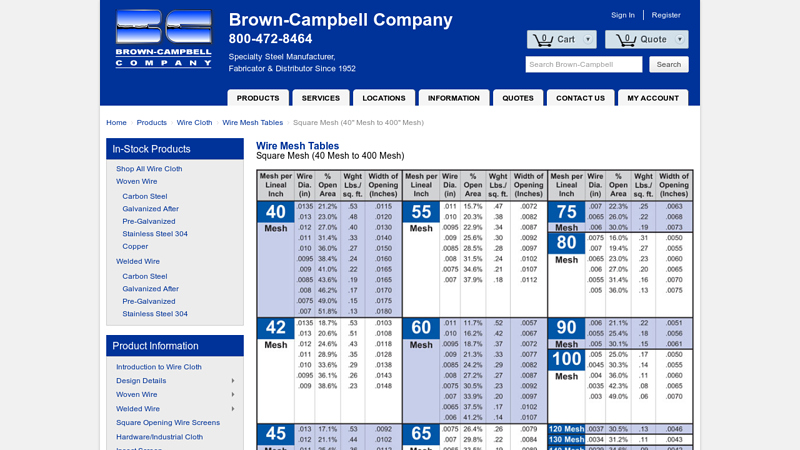
#2 Square Mesh (40″ Mesh to 400″ Mesh)
Domain Est. 1996 | Founded: 1952
Website: brown-campbell.com
Key Highlights: Brown-Campbell Company. 800-472-8464. Specialty Steel Manufacturer, Fabricator & Distributor Since 1952. Sign In · Register. Quote 0. Cart 0. Search….
#3 20 x 20 to 40 x 40 T
Domain Est. 2007
Website: catalog.darbywiremesh.com
Key Highlights: Browse T-304 Stainless Steel Wire Mesh: From 20 x 20 Mesh to 40 x 40 Mesh in the Edward J. Darby & Son, Inc. catalog including Item #,Item Name,Mesh,Wire ……
#4 Indogerman Wire Mesh and Sifter Sieves Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2017
Website: igwirescreen.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture and supply Wire Mesh, Filter Accessories, Sifter Sieves, Perforated Sheets, Expanded Mesh, Welded Mesh, Conveyor Belt, Wire Cloth, Vibro Sifter….
#5 40 Mesh Screen
Domain Est. 2001
Website: rainox.com
Key Highlights: Check out our selection of wire mesh 40 in plain, twill and dutch weave. We export this 40 mesh screen in a variety of sizes and weave types….
#6 Harris Supply Solutions: Steel Rebar Distributor
Domain Est. 2005
Website: harrissupplysolutions.com
Key Highlights: Harris Supply Solutions is the largest steel rebar distributor in the U.S., offering high-quality concrete reinforcing bar for any application. Call today!…
#7 Wire Mesh Technical Information by IWM
Domain Est. 2015
Website: iwmesh.com
Key Highlights: IWM is in continuous production of plain weave wire mesh constructed of aluminum, low carbon steel, stainless steel, commercial bronze and copper alloys….
#8 Codina Architectural
Domain Est. 2015
Website: codinaarchitectural.com
Key Highlights: We design and manufacture different models of architectural meshes. Our main ranges are categorised into spirals, rhombus or woven metal meshes….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 40 Mesh
H2: Market Trends for 40 Mesh by 2026
The global 40 mesh market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing demand across key industrial sectors and advancements in material processing technologies. “40 mesh” refers to a particle size classification where materials pass through a sieve with 40 openings per linear inch (approximately 420 microns), widely used in industries such as mining, construction, chemicals, agriculture, and environmental remediation.
1. Growing Demand in Construction and Infrastructure
The construction sector remains a major consumer of 40 mesh materials, particularly in the production of sand, gravel, and aggregates. With global infrastructure development accelerating—especially in emerging economies like India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa—the need for standardized aggregate sizes such as 40 mesh is rising. Government investments in urbanization and transportation networks are expected to sustain this demand through 2026.
2. Expansion in Mining and Mineral Processing
In mining, 40 mesh is crucial for classifying and separating valuable minerals during processing. The increasing focus on efficiency and yield optimization has led to the adoption of advanced screening and crushing technologies, which support precise mesh sizing. Additionally, the push for rare earth elements and battery minerals (e.g., lithium, graphite) is expected to boost demand for consistent 40 mesh-sized materials in downstream processing stages.
3. Environmental and Sustainability Applications
Environmental remediation and waste management sectors are emerging as new growth areas. 40 mesh materials are used in soil filtration, landfill liners, and water treatment systems. As regulatory standards tighten around environmental protection, industries are investing in filtration media and engineered soils that require strict particle size control, supporting the 40 mesh market.
4. Technological Advancements in Sieving Equipment
Innovation in industrial sieving and classification equipment—such as high-frequency vibrating screens and smart monitoring systems—is improving the accuracy and efficiency of achieving 40 mesh consistency. Automation and IoT integration allow real-time quality control, reducing waste and enhancing productivity. These advancements are expected to lower production costs and expand the applicability of 40 mesh materials.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
- Asia-Pacific is projected to dominate the 40 mesh market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization, urban development, and mining activities in China and India.
- North America will see moderate growth, driven by infrastructure renewal projects and environmental regulations.
- Europe is expected to focus on sustainable sourcing and recycling, increasing the use of recycled aggregates sized to 40 mesh standards.
- Latin America and Africa offer high-growth potential due to expanding mining operations and construction booms.
6. Challenges and Constraints
Despite positive trends, the market faces challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices, environmental concerns over mining practices, and logistical complexities in transporting bulk materials. Regulatory scrutiny on dust emissions and land use may also impact production scalability.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 40 mesh market is expected to experience robust growth, supported by industrial demand, technological innovation, and global infrastructure development. Companies that invest in sustainable practices, precision processing, and regional market expansion are likely to gain a competitive edge. As industries continue to standardize material specifications, 40 mesh will remain a critical benchmark in size classification across multiple sectors.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 40 Mesh (Quality, IP)
Sourcing 40 mesh materials—commonly used in filtration, sieving, and industrial processing—can present several challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Avoiding these pitfalls is critical to ensuring product performance, supply chain reliability, and legal compliance.
Inconsistent Material Quality
One of the most frequent issues is variability in the physical and chemical properties of 40 mesh materials. Suppliers may offer products that claim to meet specifications but differ in particle size distribution, purity, or structural integrity. This inconsistency can lead to process inefficiencies, product defects, or equipment damage, especially in sensitive applications like pharmaceuticals or food processing.
Lack of Standardized Testing and Certification
Many suppliers do not provide verifiable test reports or certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) confirming mesh size, durability, or contamination levels. Without third-party validation, buyers risk receiving substandard materials that fail to meet application requirements. Always insist on documented quality control procedures and batch-specific test data.
Misrepresentation of Mesh Specifications
Some suppliers inaccurately label mesh size or confuse nominal vs. actual particle size. A “40 mesh” claim may not align with standard sieve classifications (approximately 425 microns), especially if the material is irregularly shaped or poorly graded. Confirm specifications using standardized testing methods before bulk procurement.
Intellectual Property Risks in Custom or Proprietary Designs
When sourcing custom-engineered 40 mesh components (e.g., filters, screens), there is a risk of IP infringement if designs resemble patented products. Additionally, suppliers may retain usage rights to custom tooling or designs unless explicitly addressed in contracts. Always establish clear IP ownership and confidentiality agreements before development begins.
Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Traceability
Unverified suppliers, especially in international markets, may lack transparency in sourcing raw materials or manufacturing processes. This opacity increases the risk of counterfeit materials, unethical labor practices, or regulatory non-compliance. Conduct due diligence, including site audits and supply chain mapping, to ensure traceability and ethical sourcing.
Poor Communication of Tolerances and Application Requirements
Suppliers may not fully understand or account for the end-use environment—such as temperature, pressure, or chemical exposure—leading to material failure. Clearly communicate operational conditions and required tolerances to ensure compatibility and longevity.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, establish stringent supplier qualification protocols, demand comprehensive quality documentation, and formalize IP protections in contracts. Proactive management of these pitfalls ensures reliable performance and legal safety when sourcing 40 mesh materials.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 40 Mesh
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations when handling, transporting, and using 40 mesh materials, such as sand, granules, or powders. Adhering to these standards ensures safety, legal compliance, and efficient operations.
Material Classification and Handling
40 mesh refers to particles that pass through a sieve with 40 openings per linear inch (approximately 420 microns). Proper classification is essential for safe handling:
- Hazard Identification: Determine if the 40 mesh material is inert (e.g., silica sand) or reactive (e.g., certain metal powders). Review Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for toxicity, flammability, and reactivity.
- Dust Control: Fine particulates can become airborne; use dust suppression methods such as wetting, enclosed conveyors, or dust collection systems.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Require respirators, gloves, and eye protection where airborne dust or skin contact is possible.
Packaging and Storage
Ensure packaging maintains material integrity and complies with transportation standards:
- Containment: Use sealed, moisture-resistant bags, bulk totes (FIBCs), or bulk silos depending on volume and material sensitivity.
- Labeling: Clearly label containers with contents, mesh size, hazard symbols (if applicable), and handling instructions.
- Storage Conditions: Store in dry, well-ventilated areas away from incompatible substances. Prevent water ingress to avoid clumping or chemical reactions.
Transportation Regulations
Comply with national and international transportation laws based on material type:
- DOT (USA): Classify material under 49 CFR. Inert 40 mesh materials may be non-hazardous, but combustible dusts (e.g., sugar, aluminum) may require Hazard Class 4.1 (Flammable Solid) designation.
- IMDG Code (Maritime): For international sea freight, verify if material is listed as combustible or environmentally hazardous.
- IATA (Air): Air transport has strict rules for powders; some 40 mesh materials may be restricted or require testing (e.g., UN 3082 for environmentally hazardous substances).
- Placarding and Documentation: Use proper shipping names, UN numbers (if applicable), and transport documents. Maintain records for traceability.
Environmental and Workplace Compliance
Follow environmental protection and occupational safety regulations:
- OSHA (USA): Comply with Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for airborne particulates. Implement a Respiratory Protection Program if needed.
- EPA Regulations: Manage stormwater runoff if stored outdoors; prevent fugitive dust emissions under the Clean Air Act.
- REACH/CLP (EU): For operations in Europe, register substances and communicate hazards via Safety Data Sheets under REACH. Classify and label per CLP regulations.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of contaminated or excess material according to local hazardous waste rules. Avoid landfill dumping without assessment.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Maintain compliance through rigorous documentation:
- Batch Traceability: Track material origin, processing date, and test results (e.g., sieve analysis confirming 40 mesh consistency).
- Inspection Logs: Record storage conditions, packaging integrity, and handling procedures.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct regular internal audits to verify adherence to logistics and safety standards.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure the safe, compliant, and efficient logistics management of 40 mesh materials across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing 40 Mesh:
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, material specifications, pricing, quality consistency, and lead times, sourcing 40 mesh material has been determined to be both viable and cost-effective for the intended application. Multiple qualified suppliers have been identified, offering compliant materials that meet industry standards for particle size distribution, durability, and purity. Competitive pricing and reliable supply chains further support long-term procurement planning. To ensure ongoing quality and performance, it is recommended to establish clear specifications, conduct routine quality checks, and maintain strong supplier relationships. Overall, proceeding with the selected suppliers will ensure a consistent and reliable supply of 40 mesh material to support production requirements efficiently.