The global agricultural machinery market, particularly the segment for compact and utility tractors under 50 horsepower, has witnessed steady expansion, driven by increasing demand for mechanization in small- to medium-scale farming operations. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the tractor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, with Asia-Pacific remaining the largest and fastest-growing region due to rising labor costs and government support for modern farming techniques. Tractors in the 40 hp range have emerged as a preferred choice for versatile field operations, balancing power, efficiency, and affordability. This segment appeals to farmers seeking reliable performance for tilling, planting, and hauling without the operational costs associated with higher-horsepower models. As demand surges, several manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, durability, and localized service networks. Based on production volume, market presence, and technological integration, the following nine companies represent the leading manufacturers of 40 hp tractors globally.
Top 9 40 Hp Tractors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Compact Tractors
Domain Est. 1990
Website: deere.com
Key Highlights: At 75 horsepower, it’s the most powerful compact tractor in the John Deere lineup. Our 4 Series tractors offer all the features and options you need to get it ……
#2 Compact Tractor 40 HP: Farmall A Series
Domain Est. 1995
Website: caseih.com
Key Highlights: The Farmall Compact 40A tractor with 40 HP offers robust power and dependability for modern farming operations….
#3 Massey Ferguson United States
Domain Est. 1996
Website: masseyferguson.com
Key Highlights: Tractors. Massey Ferguson tractors deliver the power, comfort and reliability farmers expect—without the complexity they don’t. From sub-compact to high- ……
#4 WORKMASTER™ Compact 25/35/40 HP Tractors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: agriculture.newholland.com
Key Highlights: WORKMASTER™ Compact 25/35/40 HP Tractors are built to last. They are powerful, yet fuel efficient tractors to help you tackle your toughest tasks….
#5 2000 Platform Compact Tractors (25
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bobcat.com
Key Highlights: Choose from five 2000 platform 25-40 hp compact tractors, all offering the strength you need for a variety of projects, plus a compact 64-inch width and tight ……
#6 Sub
Domain Est. 2014
Website: kubotausa.com
Key Highlights: Learn more about the full line of Kubota tractors – Subcompact (BX Series), Compact Tractors, Specialty & Utility Tractors, the M7 Ag Tractor & our TLB ……
#7 Sub
Domain Est. 2016
Website: badboycountry.com
Key Highlights: Every Bad Boy Tractor features a tough 3-point hitch and front loader quick attach built for a lifetime of work around the field and farm….
#8 TYM tractors
Website: tym.world
Key Highlights: TYM creates tractors that bring together alluring form, advanced function and accessible value. Through our expertise in design, engineering and manufacturing, ……
#9 Solis World
Domain Est. 2012
Website: solisworld.com
Key Highlights: Solis World provides advanced tractors used in over 150+ countries. Built for efficiency, power, and superior farm output….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 40 Hp Tractors

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 40 HP Tractors
The 40 HP tractor segment—a cornerstone of small to mid-sized farming operations globally—is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Driven by technological innovation, shifting agricultural demands, and sustainability imperatives, this market will reflect broader trends reshaping the agricultural machinery industry. Key trends expected to define the 2026 landscape include:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Precision Agriculture Technologies
By 2026, 40 HP tractors will increasingly serve as platforms for precision farming. Expect widespread integration of GPS-guided steering (auto-steer), implement control systems (ISOBUS/ISOMAP), and telematics. These features, once exclusive to high-horsepower models, will become standard or accessible as cost-effective add-ons. Farmers will leverage real-time data for optimized planting, spraying, and harvesting—boosting efficiency and reducing input waste.
2. Electrification and Alternative Powertrains
While full electric 40 HP tractors may still face battery limitations for continuous heavy work, 2026 will see notable progress. Hybrid-electric models and tractors with electric PTO systems will emerge, targeting orchards, vineyards, and organic farms with strict emissions requirements. Manufacturers will experiment with hydrogen fuel cells and bio-diesel compatibility to meet tightening environmental regulations, especially in Europe and North America.
3. Focus on Sustainability and Emissions Compliance
Stricter emissions standards (e.g., EU Stage V and potential Tier 5 regulations) will compel OEMs to refine diesel engines with improved after-treatment systems (DPF, SCR). Simultaneously, demand will rise for tractors with lower carbon footprints. This will drive innovation in fuel efficiency, recyclable materials, and lifecycle sustainability reporting—key differentiators in procurement decisions.
4. Smart Connectivity and Farm Management Integration
40 HP tractors will increasingly connect to centralized farm management software (e.g., John Deere Operations Center, CLAAS CEBIS, or third-party platforms). Remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance alerts, and cloud-based data sharing will streamline operations. Smaller farms will benefit from subscription-based digital tools, improving ROI and reducing downtime.
5. Ergonomics, Safety, and Operator Comfort
As labor shortages persist, retaining skilled operators becomes crucial. Tractor cabins will feature enhanced ergonomics, improved HVAC systems, noise reduction, and intuitive digital displays. Advanced safety systems—such as rollover protection (ROPS), collision avoidance sensors, and automated shutdown protocols—will become more common, especially in export markets with rising safety standards.
6. Regional Market Diversification and Localization
Growth in Asia-Pacific (especially India and Southeast Asia) and Africa will drive demand for cost-effective, durable 40 HP models tailored to local crops and terrain. Manufacturers will emphasize modular designs, localized production, and simplified maintenance. In contrast, North American and European markets will prioritize high-tech, premium models with advanced automation.
7. Rise of Compact Utility and Versatile Implement Compatibility
The 40 HP class will see increased demand for compact utility tractors (CUTs) used in landscaping, small-scale agri-tourism, and mixed farming. Quick-attach systems (e.g., 3-point hitch with auto-lock, front-end loaders) and compatibility with a wide range of implements (mowers, sprayers, tillers) will be critical selling points.
8. Competitive Pricing and Financing Innovation
With rising input costs, affordability remains key. OEMs will offer leasing, pay-per-use models, and bundled service packages to lower entry barriers. Competition from Chinese and Indian manufacturers (e.g., Mahindra, Sonalika, Jinma) will pressure pricing, pushing established brands to innovate while maintaining margins.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 40 HP tractor market will be defined by smarter, cleaner, and more connected machines. While core functionality remains vital, success will hinge on digital integration, sustainability, and adaptability to diverse global farming needs. Manufacturers that balance innovation with affordability and reliability will lead this evolving segment.
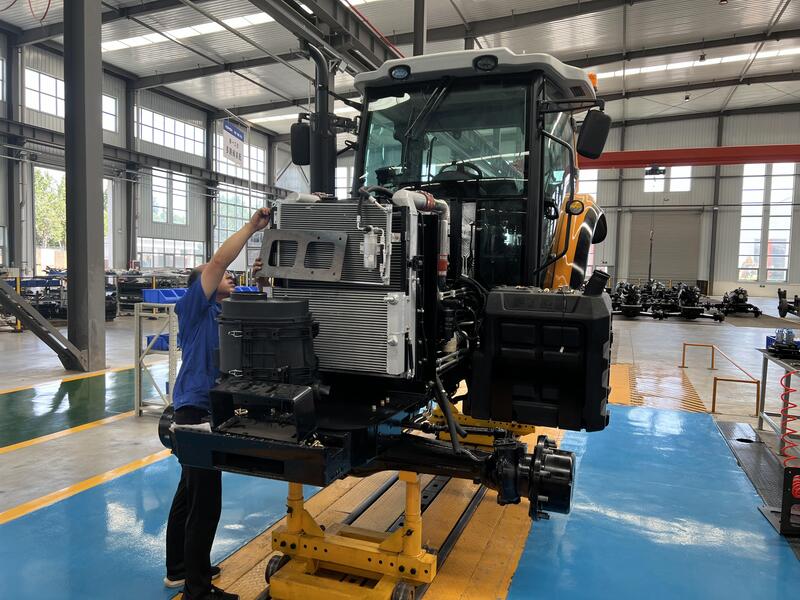

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 40 HP Tractors (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing 40 HP tractors, particularly from emerging manufacturing regions, presents several risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers must carefully navigate. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Substandard Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Many low-cost 40 HP tractors, especially those from less-regulated markets, use inferior materials and components to reduce production costs. This includes thin metal frames, under-spec engines, and low-grade hydraulic systems that wear out quickly under field conditions. Buyers often discover that advertised horsepower or lifting capacity does not match real-world performance due to poor engineering or misrepresentation. Without rigorous factory audits and third-party inspections, these quality issues may remain undetected until after delivery, resulting in frequent breakdowns and high maintenance costs.
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Parts and Technology
A significant IP risk involves the unauthorized use of branded components—such as engines, transmissions, or electronics—originally designed by established manufacturers (e.g., Perkins, Bosch, or John Deere). Some suppliers source counterfeit or reverse-engineered parts without licensing agreements, which not only violates international IP laws but also compromises reliability and safety. Additionally, tractor designs themselves may infringe on patented technologies or registered外观 designs, exposing importers to legal action in their home markets, particularly in regions with strict IP enforcement like the EU or North America.
Lack of Certification and Compliance Documentation
Many budget 40 HP tractors fail to meet international safety, emissions, or performance standards (e.g., CE, EPA, or ISO). Suppliers may provide forged or incomplete certification documents, misleading buyers about compliance. The absence of genuine IP-related documentation—such as licensing agreements for technology or trademarks—further increases legal exposure. Without proper due diligence, buyers risk customs seizures, fines, or being barred from selling the equipment in regulated markets.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Traceability
Poor-quality tractors often come with limited or nonexistent after-sales networks, making it difficult to obtain genuine spare parts. This forces operators to rely on locally produced knock-off components, perpetuating a cycle of breakdowns and downtime. Moreover, the lack of traceability in spare parts supply chains increases the likelihood of inadvertently using IP-infringing components, further entangling the buyer in intellectual property risks.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough supplier vetting, including on-site factory audits, verification of IP rights and certifications, and independent performance testing. Engaging legal counsel to review contracts for IP indemnification clauses and using escrow services until compliance is confirmed can significantly reduce exposure. Partnering with reputable distributors or original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) with established IP practices is often safer than sourcing from unknown third-party exporters.
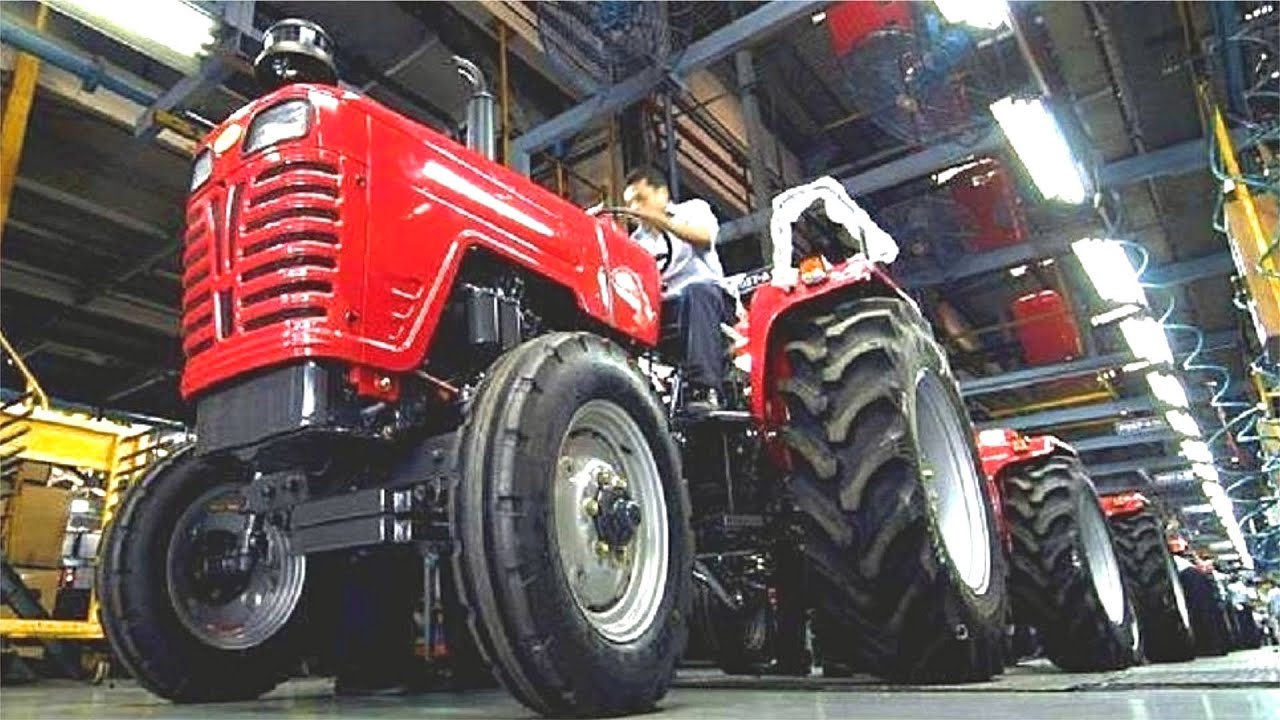

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 40 HP Tractors
Transporting and operating 40 horsepower tractors involves careful planning to ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and efficiency. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for domestic and international movement of 40 HP tractors.
Transportation and Handling
40 HP tractors must be securely transported to prevent damage and ensure road safety. Key logistics practices include:
- Load Securing: Use heavy-duty tie-down straps (minimum 4–6 straps), wheel chocks, and load binders to immobilize the tractor on trailers. Ensure straps are rated for the tractor’s weight (typically 2,500–4,000 lbs).
- Trailer Selection: Use a lowboy, flatbed, or specialized farm equipment trailer with adequate weight capacity and non-slip surfaces.
- Route Planning: Avoid low bridges, narrow roads, and weight-restricted bridges. Check local regulations for oversized load permits if dimensions exceed limits.
- Pre-Transport Inspection: Verify fuel levels (keep low to reduce fire risk), disconnect batteries, and ensure all moving parts are secured.
Domestic Regulatory Compliance (U.S. Example)
Compliance with national and state regulations is essential for legal operation and transport:
- EPA Emission Standards: 40 HP tractors must comply with Tier 4 Final (or equivalent) emissions regulations. Verify compliance via EPA certification label on the tractor.
- DOT Requirements: When transported on public roads, adhere to Department of Transportation (DOT) rules:
- Display proper lighting and reflective markings.
- Use slow-moving vehicle (SMV) emblem if operating under 25 mph.
- Obtain permits for oversized or overweight loads, as required by state law.
- State Registration: Tractors used on public roads typically require registration, insurance, and titling through the state’s Department of Motor Vehicles or equivalent agency.
International Shipping and Import Compliance
Exporting or importing 40 HP tractors involves additional regulatory steps:
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Classify tractors using the correct HS code (e.g., 8701.30 for tractors with diesel engines over 37 kW) for customs declaration.
- Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, bill of lading, packing list, certificate of origin, and export declaration.
- Import Duties and Taxes: Research destination country tariffs, VAT, and import restrictions. Some countries impose agricultural equipment-specific duties or require local certification.
- Certification Requirements: Ensure tractors meet target market standards (e.g., CE marking for EU, INMETRO for Brazil, CCC for China). This may include safety, emissions, and noise certifications.
Safety and Operational Compliance
Operators and handlers must follow safety protocols and regulatory standards:
- Operator Training: Ensure operators are trained and comply with OSHA standards (in the U.S.) or equivalent local regulations.
- Roll-Over Protection (ROPS): Verify that tractors are equipped with ROPS and seat belts where required by law (e.g., OSHA 29 CFR 1928.51).
- Noise and Exhaust Compliance: Confirm adherence to sound level limits and exhaust emission standards in the jurisdiction of use.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Maintain compliance through proper documentation and upkeep:
- Service Records: Keep logs of maintenance, repairs, and emissions system checks to demonstrate regulatory compliance.
- Emission System Integrity: Do not tamper with emission control devices (e.g., diesel particulate filters, SCR systems), as this violates EPA and similar international regulations.
- Transport Logs: For commercial haulers, maintain driver logs per FMCSA rules if applicable.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient movement and use of 40 HP tractors across regions and markets. Always consult local authorities and regulatory bodies for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing 40 HP Tractors
Sourcing 40 HP tractors presents a strategic opportunity for agricultural operations, small to mid-sized farms, and agri-entrepreneurs seeking a balance between power, versatility, and cost-efficiency. This horsepower range offers sufficient strength for essential farming tasks such as plowing, tilling, seeding, and hauling, while remaining manageable in terms of fuel consumption, maintenance, and operator skill requirements.
After evaluating available options—both domestic and international—key considerations include reliability, after-sales service, spare parts availability, and total cost of ownership. Well-established brands often provide better long-term value through robust build quality and support networks, though competitive pricing from emerging manufacturers may suit budget-conscious buyers.
Additionally, features such as transmission type, loader compatibility, PTO options, and fuel efficiency should align with specific operational needs. It is also advisable to factor in financing options, warranty coverage, and dealer proximity when finalizing procurement decisions.
In conclusion, sourcing 40 HP tractors should be guided by a clear understanding of farm requirements, long-term sustainability goals, and regional service infrastructure. With careful evaluation and supplier due diligence, acquiring a 40 HP tractor can significantly enhance productivity and operational efficiency in diverse agricultural environments.